-
0 items in quote
No products in the Quote Basket.
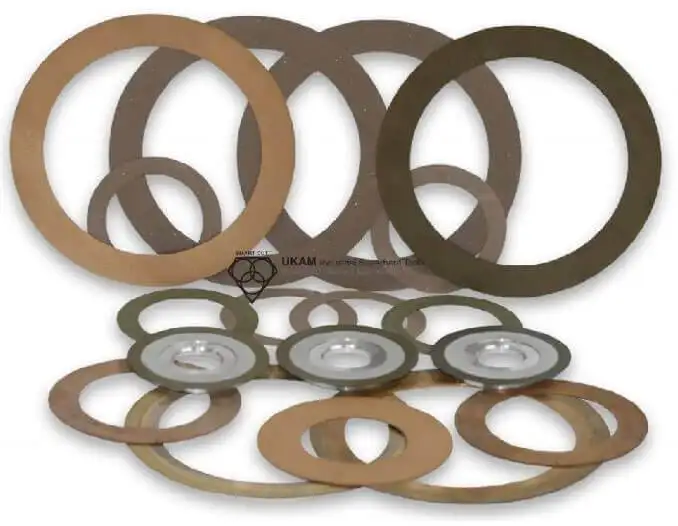
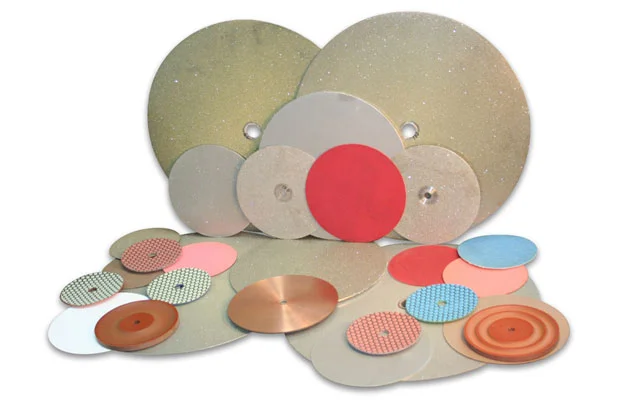
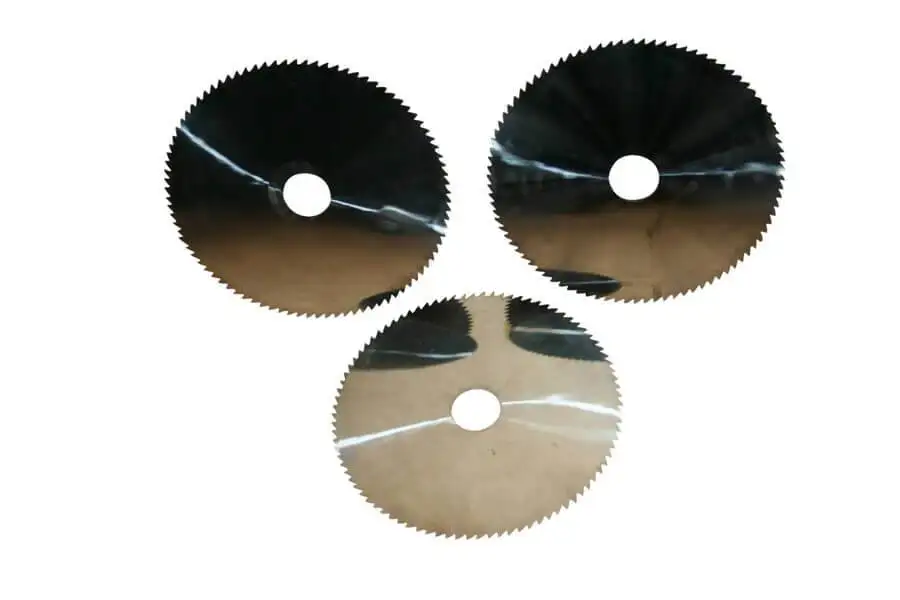
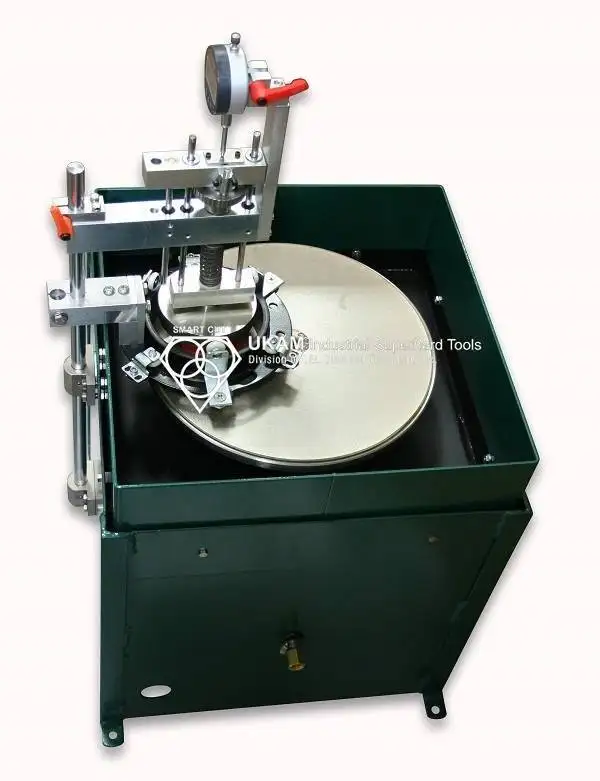
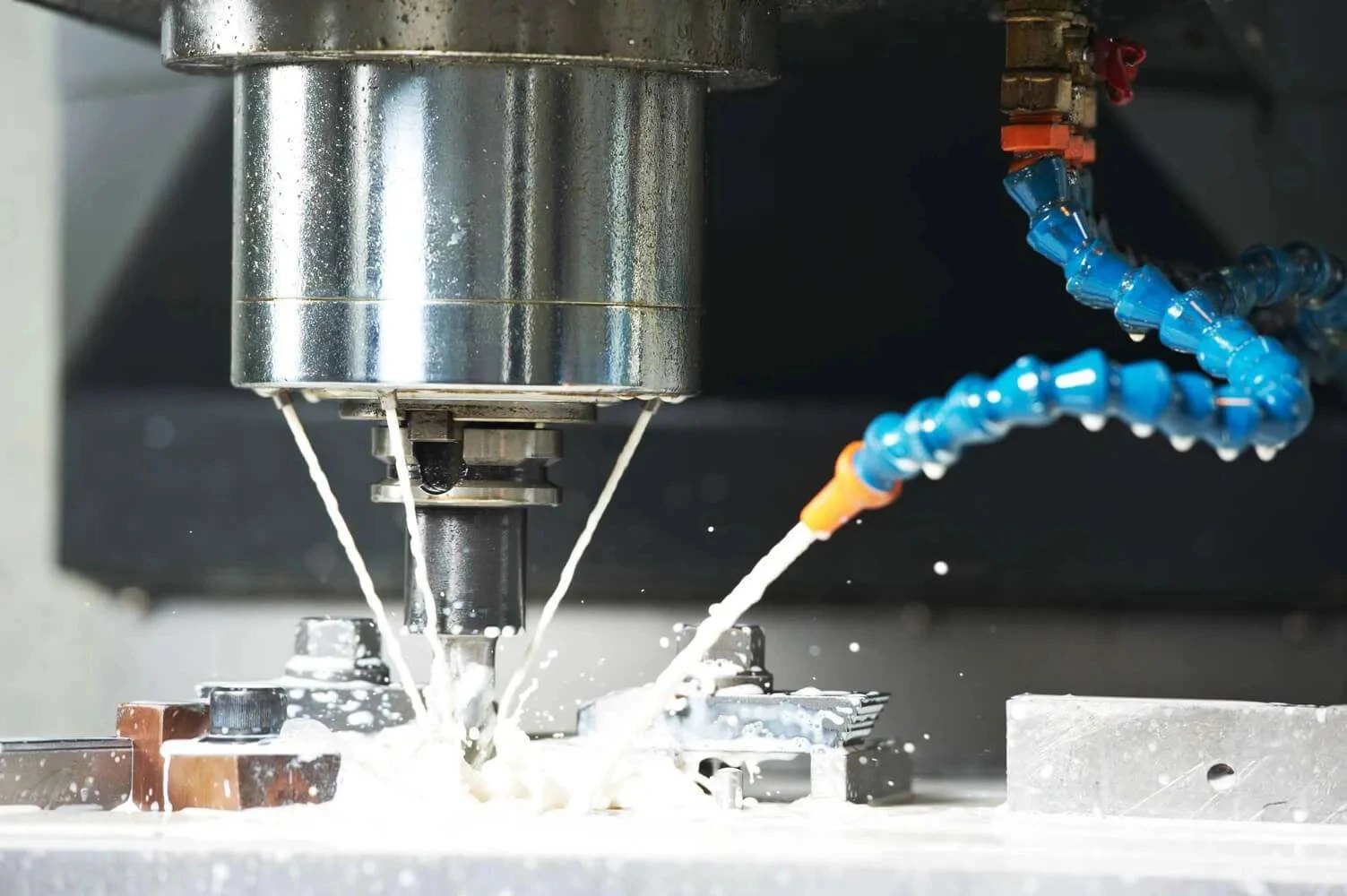
SMART CUT® Ultra Thin Abrasive Cut off Blades
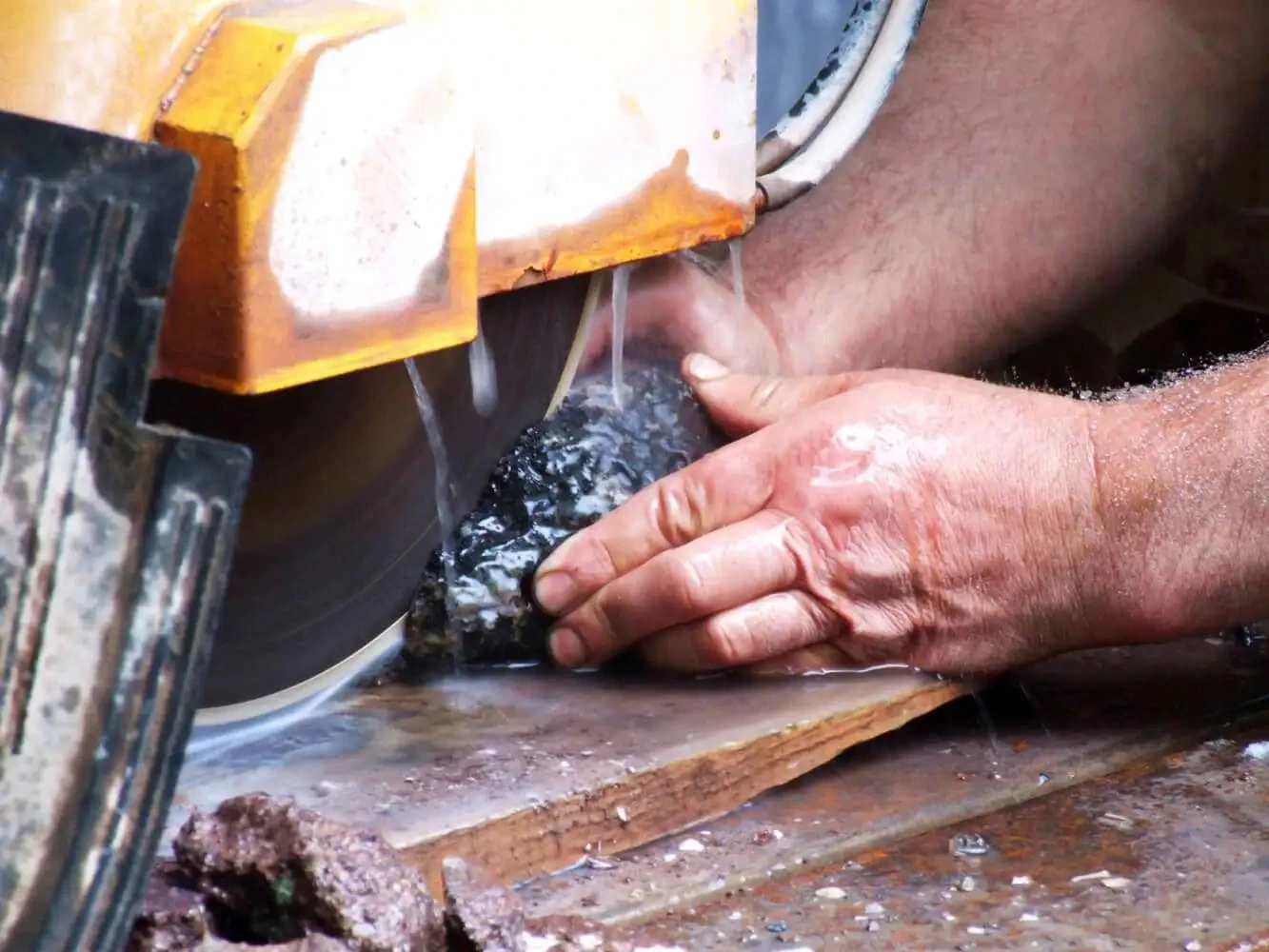
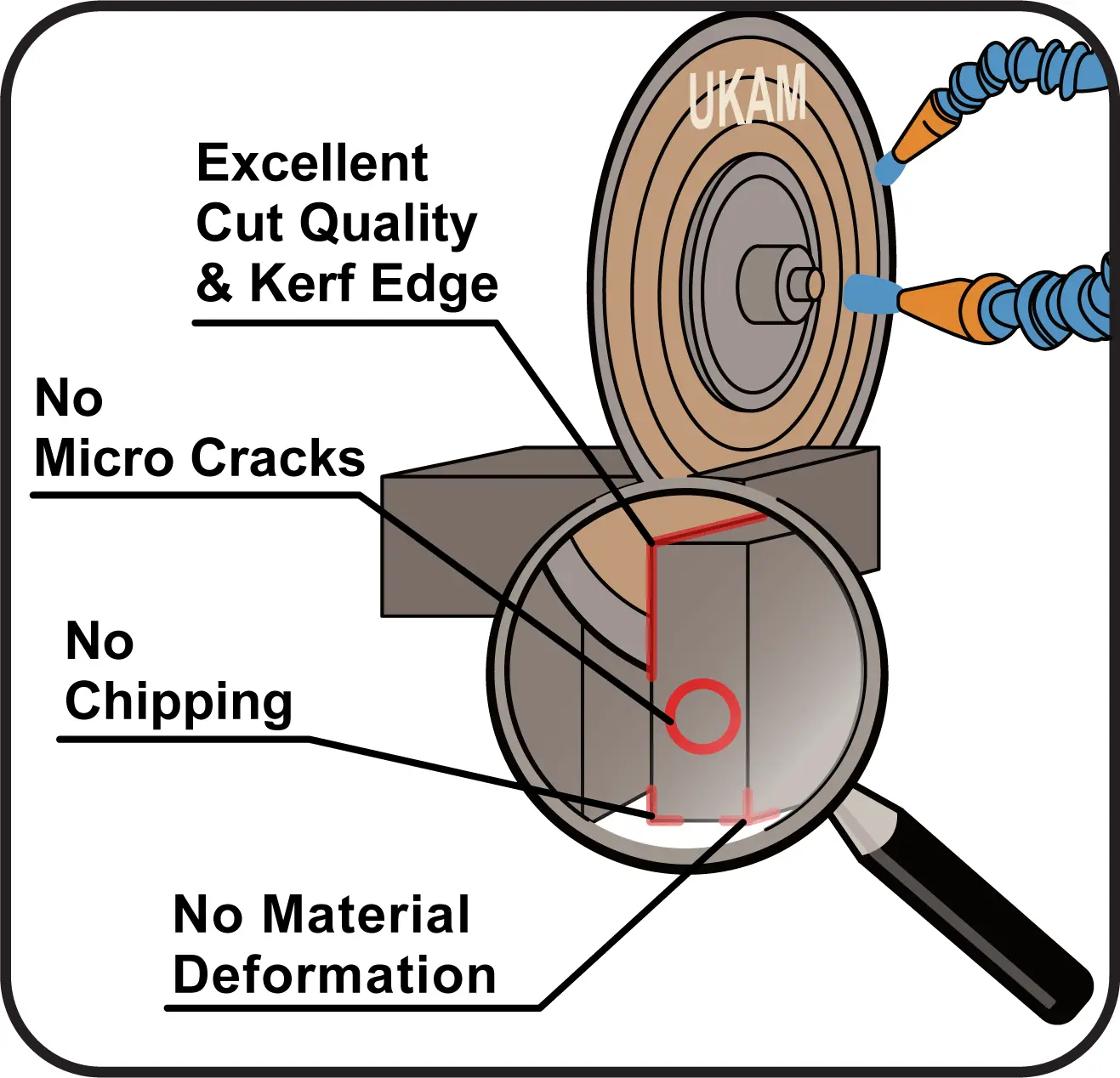
SMART CUT® Series Ultra Thin Abrasive Blades are designed to provide high quality sectioning results with no burning and minimal surface deformation. This can reduce the amount of grinding & polishing required later in the preparation process. Our blades are Formulated for fast sectioning with minimum kerf loss. They Provide for cool cutting action & Minimize the structural damage to the sample/material.
The thin kerf is designed to save money by reducing kerf loss. This is especially important when cutting very expensive materials, or when kerf loss represents a significant portion of the original material cost.
Used On: All Low & High Speed Wafering Saws, Sectioning Saws, Such as Buehler, Struers, Leco, & many others.
Custom manufacturing
Custom manufacturing
DESCRIPTION
SPECIFICATIONS
INDUSTRIES USED IN
FAQ
ACCESSORIES
USAGE RECOMMENDATION
DESCRIPTION
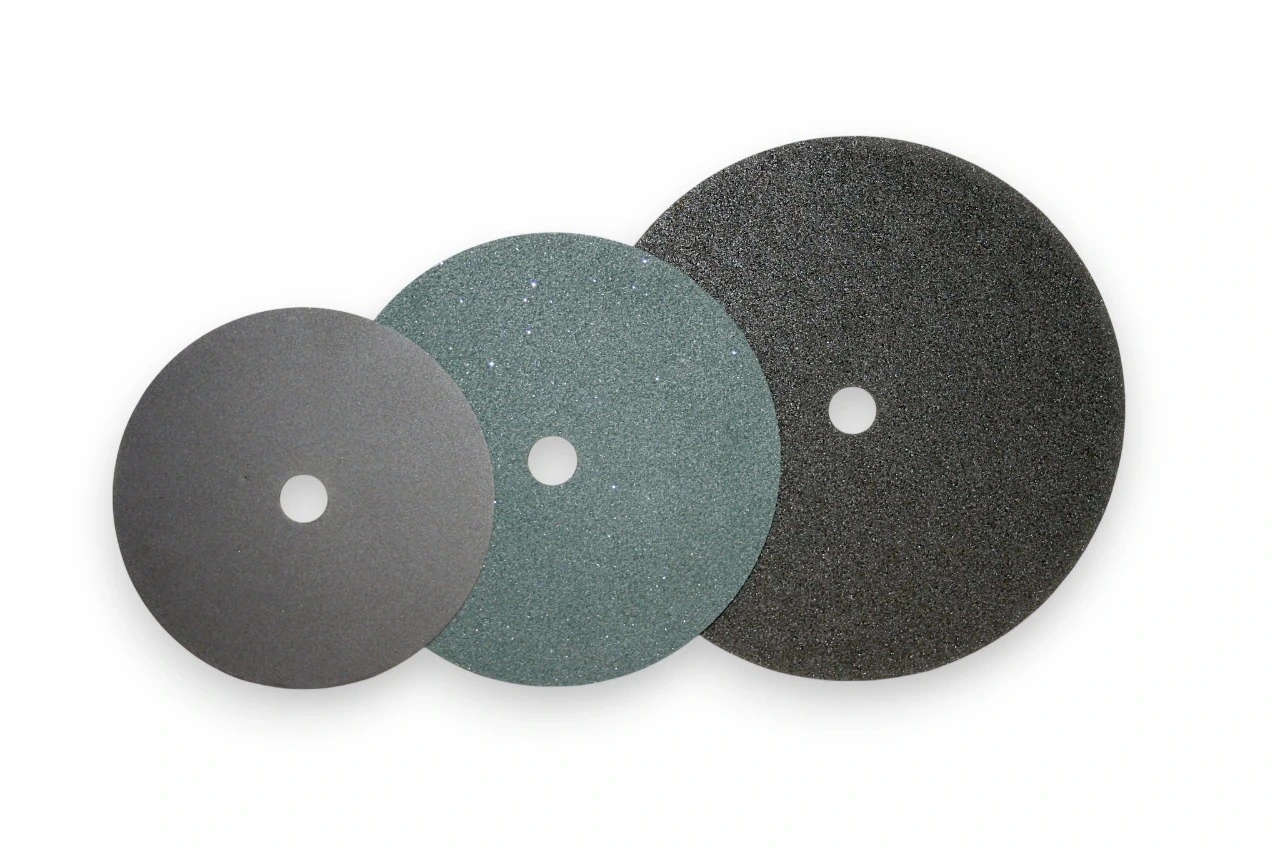
SMART CUT® Ultra Thin Abrasive Blades provide precision cutting with minimal material loss because the ultra thin profile allows accurate sectioning while preserving valuable material. This is especially important when you work with high value or limited samples where conservation directly affects cost and yield. The blade design ensures reduced surface deformation, helping maintain the integrity of the material structure during sectioning and supporting reliable evaluation and downstream processing. During operation, the blades deliver a cool cutting action that limits heat generation and reduces the risk of thermal damage or microstructural changes, making them suitable for heat sensitive materials.
SMART CUT® Ultra Thin Abrasive Blades offer universal application capability through the use of two abrasive options. Silicon carbide is used for non ferrous and non metallic materials, while aluminum oxide (alumina) is used for ferrous materials. This allows you to process a wide range of materials within the same blade family. The design improves cost efficiency by minimizing kerf loss, preserving more of the sample, and lowering the cost per cut, which is critical when working with expensive or difficult to replace materials. Clean cutting performance results in reduced post processing requirements, as less grinding and polishing are needed, saving time and lowering overall sample preparation costs.
SMART CUT® Ultra Thin Abrasive Blades provide wide equipment compatibility, as they are designed to fit standard low speed and high speed saws from many manufacturers such as BUEHLER, STRUERLS, LECO, & many others. A medium grit size delivers balanced cutting speed and surface finish, allowing you to maintain productivity while achieving consistent cut quality across many applications. The use of high quality abrasive materials ensures a long service life and consistent performance, reducing blade change frequency and helping you maintain stable and repeatable cutting results over time
Cross Reference: BUEHLER, STRUERS, LECO, & Other Item Numbers
SPECIFICATIONS
Product Type: Ultra Thin Abrasive Cut off Blades
Usage Compatibility: Suitable for all low and high-speed wafering saws and sectioning saws, including those from Buehler, Struers, and Leco.
Design Features
- Ultra Thin for minimal material loss
- Engineered for no burning and minimal surface deformation
- Formulated for cool cutting action to minimize structural damage
- Minimum kerf loss to save material and cost, particularly with expensive samples
Material Specificity
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) blades for non-ferrous/non-metallic materials (e.g., copper, aluminum, nickel alloys)
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)blades for ferrous materials (e.g., carbon steel, cast iron, spring steel)
Dimensions
- Thickness range0.012” (0.3 mm) to 0.035” (0.8mm)
- Diameter range4” (100mm) to 8” (200mm)
- Standard arbor size½” (12.7mm)
Available Sizes and Grit
- Sizes from 4” to 8” diameter
- Medium grit specification
Packaging
- Sold in packages of 10 pieces
Equipment: Compatible with a variety of sectioning saws from brands like Buehler, Struers, Leco, etc.
Materials: Effective on non-ferrous metals, ferrous metals, and assorted non-metallic substrates.
INDUSTRIES USED IN

INDUSTRIES USED IN:
- Advanced Ceramics
- Composites
- Glass
- Geology
- Quartz
- Materials Research
- Medical Devices
- Metallography
- Photonics / Optics
- Semiconductor

Ferrous & Non-Ferrous Metals:
- Plain Carbon Steels
- Electronic Packages
- Stainless Steels Plastics
- Tool Steels Fasteners
- Aluminum Refractories
- Copper Base Alloys Integrated Circuits
- Magnesium Thermal Spray Coatings
- Titanium Metal Matrix Composites
- Biomedical Wafers
- Petrographic
- PCB.s Ceramics
FAQ
Ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades are specialized cutting instruments designed for precision sectioning of materials. They are made from a composite of alumina oxide and silicon carbide, which are abrasives known for their hardness and durability. These blades are primarily used in sample preparation for materials research and metallography. They are ideal for cutting delicate and composite materials where minimal material deformation and maximum cut quality are desired. Alumina oxide and silicon carbide are chosen for their abrasive qualities, which allow for precise cutting with minimal damage to the sample. Alumina oxide provides a hard, durable surface, while silicon carbide offers a sharp, brittle cutting edge that maintains its form even at high temperatures. While ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades are versatile, they are best used on materials such as metals, ceramics, composites, and mineral samples. Users should select the appropriate blade type and specification for their specific material and application. Choosing the right blade involves considering the material to be cut, the desired surface finish, the level of precision required, and the cutting equipment available. You should also consider the thickness and diameter of the blade to ensure it is compatible with your cutting machine. The thickness of ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades can vary, but they generally range from about 0.010 inches to 0.050 inches. The specific thickness will depend on the required precision and the material being cut. These blades are designed for precision sectioning of various materials using low and high-speed wafering saws and sectioning saws. They are ideal for preparing material samples with minimal kerf loss and surface deformation. Yes, SMART CUT blades are compatible with a range of equipment from various manufacturers, including Buehler, Struers, and Leco, among others. There are two main types of blades: Silicon Carbide (SiC) blades for non-ferrous metals and non-metallic materials, and Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) blades for ferrous metals. They can handle materials like copper, aluminum, nickel, carbon steel, cast iron, and spring steel. The blades are available in diameters ranging from 4 inches (100mm) to 8 inches (200mm), with thickness options from 0.012” (0.3mm) to 0.035” (0.8mm). The standard arbor hole size is ½ inch (12.7mm). The blades are sold in packages of 10 pieces. ‘Medium grit’ refers to the coarseness level of the abrasive material on the blade, which is designed to offer a balance between cutting speed and the quality of the finish on the material being cut. Yes, the high-quality cuts made by these blades typically require less grinding and polishing, reducing subsequent sample preparation steps. Ultra-thin blades reduce material loss during cutting, which is essential when working with expensive or limited materials. They also ensure a narrower cut, which can be critical in precision applications. When used correctly with the appropriate safety equipment and procedures, ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades are safe. However, due to their sharpness and the potential for creating airborne particles, users must wear protective gear and follow proper safety protocols. To extend the life of your blade, use it at the recommended speeds and feed rates, avoid excessive force, and use adequate coolant if required. Proper mounting and periodic inspection for wear or damage are also important. Yes, ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades can be used with both manual and automated cutting systems. Ensure the equipment is calibrated to the blade specifications for optimal performance. If a blade becomes dull, it may not perform cuts as efficiently or precisely, and attempting to use a damaged blade can be unsafe. Replace the blade with a new one if you notice signs of dulling or damage. Yes, there are different grades, with variations in grain size, bond type, and concentration of the abrasive. The grade you choose should match your cutting requirements. Dispose of used blades according to your facility’s safety and waste disposal procedures. These may be considered sharp waste or hazardous depending on local regulations, so handle and discard them responsibly. Typically, ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades are not designed to be sharpened and should be replaced once they become dull. Attempting to sharpen them can be unsafe and may compromise the integrity of the blade. SMART CUT blades are described as having a medium grit, which is suitable for a wide range of cutting applications, offering a good balance between cutting speed and finish quality. While these blades are designed for use with both low and high-speed saws, it’s crucial to refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for optimal blade speeds, which can vary based on the material being cut and the specific blade used. Store the blades in their original packaging or a protective case, in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture to prevent warping and corrosion. Keep them away from vibration and shock to avoid damage. The life expectancy of an ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blade depends on the frequency of use, the type of materials being cut, and the user’s adherence to the recommended cutting parameters. With proper use and maintenance, blades can last for several hours of continuous cutting. However, very brittle or hard materials may shorten blade life due to increased wear. Blade loading can be addressed by using a lower feed rate, adjusting the cutting speed, or using a different blade with a more open structure to allow for better material clearing. Additionally, ensuring adequate coolant flow can help clear swarf and prevent loading. Ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades are typically used with a coolant to reduce heat generation, improve cut quality, and extend blade life. Dry cutting is possible in some applications but usually not recommended as it can result in reduced blade life and potentially affect the sample due to heat generation. Water-based coolants are commonly used with ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades. However, specific coolant requirements may vary depending on the material being cut and the blade specifications. Always check the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate coolant. To ensure compatibility, check the blade’s diameter, thickness, arbor size (center hole diameter), and the maximum operating speed. These should match the specifications of your cutting machine. Also, ensure that your machine can accommodate the coolant flow if necessary. It’s not recommended to use the same blade for different types of materials, as this can affect blade life and cutting quality. Silicon Carbide blades are specialized for certain materials, just as Aluminum Oxide blades are for others. Always use the appropriate blade for the material to achieve the best results. You should consider replacing the blade when you notice a decrease in cutting performance, visible wear, or if the blade becomes damaged or chipped. SMART CUT blades are designed for a wide range of materials, but they may not be suitable for certain hardened steels or specialty materials. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or contact customer service for advice on cutting specific materials. Proper use and maintenance are key. Always use the correct blade speed, do not force the blade through the material, and allow the blade to cool down after heavy use. Clean the blade after use to prevent material build-up, which can affect performance. Always wear appropriate safety gear, including safety glasses and gloves. Make sure the blade is properly installed and that the saw is in good working condition. Never operate the saw without the necessary safety guards in place. Abrasive cut-off blades typically cannot be resharpened due to the nature of the abrasive surfaces. Once the abrasive material wears down, the blade should be replaced. The feed rate will depend on the material being cut and the specific saw being used. Refer to the saw and blade manufacturer’s recommendations for optimal feed rates. Generally, a slower feed rate will extend blade life and potentially improve cut quality. Blades come ready to use Performance can be measured by the quality of the cut (such as the smoothness of the edge and the absence of sample deformation), the speed of cutting, and the number of cuts made before the blade becomes dull. Regular monitoring and recording of these factors can help in assessing performance. Yes, the bonding material that holds the abrasive grains together can vary. Common bond types include resin, rubber, and vitrified bonds. Each type has different properties affecting blade life, cut quality, and the materials they are best suited for. While some blades are marketed as general-purpose, it’s often best to use material-specific blades to ensure optimal cutting performance and to avoid potential contamination between different materials. Yes, these blades are typically used with a cutting fluid to both cool the blade and to wash away the debris, which can prolong blade life and improve the cut quality. Blade life varies significantly depending on the material being cut, the frequency of use, and the cutting conditions. Users should monitor performance and wear during use for a better assessment of blade life. Thinner blades remove less material, which can help minimize sample deformation and material loss. However, they may also be more prone to breakage if used improperly. Thicker blades may be more durable but can result in greater material loss and potential sample damage. If there is any debris or coolant residue on the blade after use, it should be gently cleaned with a soft brush and appropriate cleaning solution, then dried carefully to prevent rust or corrosion. Always wear safety glasses, gloves, and appropriate protective clothing. Ensure the cutting area is clear of obstructions and that you have a proper grip and body stance to avoid injury. Never exceed the recommended speed for the blade, and ensure that the blade guard and other safety features of your cutting equipment are in place and functional. Different materials require different blade speeds. Harder materials typically require a slower blade speed to reduce the risk of overheating, whereas softer materials can be cut at higher speeds. Always refer to the material-specific guidelines provided with the blade or equipment. Optimal RPM settings depend on the blade size and material being cut. Users should refer to the documentation provided with their cutting equipment and the blade for the best RPM settings. Signs that a blade needs to be replaced include a noticeable decrease in cutting performance, visible wear or damage to the blade edge, increased cutting forces or vibration, or the inability to produce a clean cut. Additionally, if the blade develops any cracks, it should be replaced immediately for safety reasons. Heat-induced changes are a concern in precision cutting. Ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades can generate heat, which may affect the microstructure of certain materials. Proper use of coolants and correct cutting parameters can help to minimize this risk. Yes, extreme temperatures and humidity can affect the performance and lifespan of the blade. Blades should be used and stored in a controlled environment to prevent premature aging or damage. Cutting at an angle requires a blade that can maintain its structural integrity without flexing. Ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades are generally designed for straight cuts, and using them for angled cuts could result in blade deflection or breakage. Maintenance includes cleaning the blade after use, inspecting for wear or damage, and ensuring proper storage. Additionally, the cutting equipment should be maintained according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent undue stress on the blade. The maximum cut depth will depend on the diameter of the blade. Users should ensure that the blade diameter is larger than the material thickness and consult with the blade specifications for maximum cutting capacities. Select a blade thickness based on the precision required and the material you are cutting. Thinner blades are for more precise, delicate cuts, while thicker blades may offer more durability for tougher materials. Maintenance typically involves regular cleaning, inspection for wear or damage, and proper storage to prevent corrosion or other damage. Extremely hard or abrasive materials can wear down the cutting edge faster. It’s important to match the blade to the material’s hardness and abrasiveness, as specified by UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools. Larger blades can cut through thicker materials and may last longer due to the greater cutting surface area, but they require saws that can accommodate their size and might result in higher material loss due to wider cuts. This will depend on the capabilities of the saw used with the SMART CUT blades. Some saws may allow for angled cuts, but it’s important to ensure that the blade is suitable for this type of operation to avoid damage or safety hazards. The cutting fluid helps to keep the blade cool and reduces friction, which can significantly affect the quality of the cut and the lifespan of the blade. It’s important to use the appropriate fluid as recommended by the blade and saw manufacturers. Blades should be stored in racks or containers that prevent them from moving or banging against each other, which could cause chipping or breakage. Many manufacturers supply or recommend specific storage solutions for their blades. To ensure a perpendicular cut, the sample must be securely clamped and the blade should be properly aligned with the cutting machine. Regular calibration of the cutting equipment is essential for maintaining cutting accuracy. Thicker samples may require blades with a more robust construction or different abrasive grit sizes to maintain an efficient cutting process. Adjustments to the feed rate and cutting speed may also be necessary to accommodate the increased material volume. These blades are designed specifically for low and high-speed wafering saws, sectioning saws, and similar equipment. Using them on machines they are not designed for could result in poor performance or damage to both the blade and the material. High humidity can affect the blade’s lifespan by causing rust on its metal components, while extreme temperatures might affect the bonding materials within the blade. Proper environmental control is crucial for maintaining blade integrity. There is a risk of cross-contamination, particularly when cutting materials that may leave a residue on the blade. It is best to clean the blade between cuts or use separate blades for materials where contamination could be a concern. Ultra-thin abrasive cut-off blades are primarily designed for cutting, but some may be suitable for precision slotting or grooving if they have the necessary thickness and rigidity. It is important to verify this with the manufacturer before attempting such applications. If a blade becomes jammed, immediately turn off the cutting machine and carefully remove the blade from the sample, taking care to avoid personal injury or further damaging the blade. Determine the cause of the jamming before resuming operation. As a blade wears, its cutting edges can become rounded, leading to a less precise cut, with potential burr formation or sample distortion. Regular monitoring of blade condition and timely replacement can ensure consistent cut quality. Using an incorrect blade speed can have several consequences: Too slow: Can result in inefficient cutting, increased physical effort from the machine or operator, and potentially poor cut quality. The optimal feed rate depends on the material hardness, abrasiveness, and the desired cut quality. It’s often determined by starting at a lower rate as recommended by the blade manufacturer and then adjusting based on the results and the cutting machine’s performance. Yes, they can be suitable for this application due to their precision and minimal kerf width, which allows for cutting without significant removal or damage to adjacent layers. However, specific blade selection and cutting parameters must be carefully managed. Blade wear can be measured by examining the diameter reduction, changes in blade thickness, or by using a microscope to inspect the abrasiveness of the cutting edge. Many industries use standardized tests and measurement tools for monitoring blade wear. A training session should include: Blade recycling and repurposing depend on local regulations and facilities capable of handling this type of waste. Some components may be recyclable, but it’s important to follow proper disposal guidelines due to the abrasive materials involved. Documentation should include the blade’s specification sheet, safety data sheet (SDS), operating instructions, maintenance logs, and a record of training for operators. Consider the blade’s initial cost, lifespan, cutting speed, frequency of replacement, quality of cuts, and any costs associated with downtime or sample waste. It’s also important to consider the potential cost of safety incidents if lower-quality blades are used. Check the cutting speed and ensure it’s appropriate for the material. You may need to reduce the feed rate or use a blade with a different abrasive. Also, confirm the cutting fluid is applied correctly and that the blade is not worn out. Discoloration can occur due to overheating. Ensure adequate cooling with the correct cutting fluid, adjust the feed rate, and check that you’re using the correct blade type for the material. This could be due to a number of factors, including blade dullness, incorrect blade selection for the material, insufficient cooling, or an issue with the saw’s calibration. Inspect the blade and setup, and adjust as necessary. Abrasive blades are not typically re-sharpened due to the way abrasive particles are bonded to the blade. Once worn, the blade is usually replaced. However, check with UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools for any reconditioning services they may offer. Clean the blades with a soft brush and appropriate cleaning fluid to remove debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals that may damage the blade’s bond or abrasive materials. Blades should be inspected before each use for signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Regular inspection can prevent blade failure and ensure consistent cutting performance. Continuous use of the blades without adequate cooling can lead to overheating and potential damage. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for usage cycles to maintain blade integrity and performance. Optimal speed can vary based on material hardness, density, and the blade’s properties. Start with the manufacturer’s recommended speeds for different materials and adjust based on the results and blade performance. Dressing is a process used for precision grinding wheels rather than for abrasive cut-off blades. For these ultra-thin abrasive blades, dressing is not typically required or recommended. Ensure proper use of cutting fluid, correct blade selection for the material being cut, appropriate feed rates, and avoid pushing the blade beyond its designed capacity. Regular cleaning and correct storage will also help extend blade life. ‘Kerf’ refers to the width of the cut or the amount of material removed by the blade, while ‘cut quality’ refers to the smoothness and precision of the cut edges. SMART CUT blades are designed to minimize kerf and maximize cut quality, saving material and reducing subsequent processing steps.
ACCESSORIES
Showing 1 – -1 of 16 results Showing all 16 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Name A – Z
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
Image | Item No. | Description | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Color: 5/8″-11″ thread. Fits into drill press chuck. Shank adapter threads into 5/8″-11″ female thread of diamond drill. Can be used with any other tool with 5/8″-11″ thread. | $26.72 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
Color: 5/8″-11″ thread. Fits into drill press chuck. Shank adapter threads into 5/8″-11″ female thread of diamond drill. Can be used with any other tool with 5/8″-11″ thread. | $22.46 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1 Gallon Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $99.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1 Quart Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $34.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
5 Gallons Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $317.41 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
55 Gallons Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $1,745.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1/2″ x 1/2″ x 6.0″ White Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $8.65 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ White Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1/2″ x 1/2″ x 6.0″ White For use on diamond tools 150 to 220 Grit Size. | $8.65 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh size) or finer. | $15.39 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0″ x 2.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh size) or finer. | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0″ x 2.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
$154.87 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||
$154.87 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||
$235.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
USAGE RECOMMENDATION
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Articles
02
Jun
The diamond blade itself is only a small factor in your cutting operation. Successful diamond sawing is both an art & science. Requiring proper use and understanding of the right: RPM’s, Coolants, Equipment, Dressing Devices, Accessories…
02
Jun
Precision & Ultra Thin Diamond Blade Guide
Diamond and CBN blades are available in an extensive array of varieties, each differing in bond types, manufacturing methods, and design specifics. Ultra Thin & High Precision Diamond Blades are particularly versatile, applicable…
02
Jun
Troubleshooting Diamond Sawing Problems
Having issues with your diamond cutting operation? This Illustrated Guide can help. Learn the most common problems most people have in using diamond cutting blades. How to resolve them and avoid them in…
02
Jun
How to Improve & Optimize Your Diamond Sawing Operation
There are numerous variables that affect the performance of diamond and CBN cutting blades. Understanding these variables will help end users select the right diamond blade specifications for their applications and optimize their cutting operations…
02
Jun
Evaluating & Comparing Diamond Blades
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Proper testing procedures and methodologies must be set up and used to obtain accurate as well as repeatable testing results. This article will discuss several simple procedures which…
02
Jun
Selecting Right Wafering Blade for your application
Cross Sectioning is the first and most important step in the sample preparation process. Getting the best results involves obtaining a smooth surface finish, minimum chipping, material deformation, without sacrificing cutting speed. Today, most laboratories, work with dozens…
02
Jun
Wafering Blade Usage Recommendations
The wafering/sectioning blade itself is only a small factor in your sectioning operation. Successful wafering/sectioning operation is both an art & science. Requiring proper use and understanding of selecting the right diamond wafering/sectioning…
02
Jun
Wafering Blade Case Studies
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Case Studies
This study evaluates the cutting performance of SMART CUT® Diamond & CBN Wafering Blades compared to Conventional Wafering Blades under identical test conditions. The objective was to measure differences…
22
Apr
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Performance Metrics
When evaluating Diamond & CBN wafering blades, especially for metallography and sample preparation, it is critical to consider a set of key evaluation criteria and performance metrics. These factors help determine the effectiveness of a…
24
Apr
Understanding & Comparing Diamond & CBN Wafering Blades
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Diamond wafering blades are designed for sectioning a large variety of materials and sample types. In order to identify the best diamond wafering blade for your specific material/application,…
25
Apr
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Guide
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
All you need to know about wafering blades (understanding variables & specifications)
This guide is designed to help you navigate the various variables and possibilities associated with diamond wafering…
31
Jul
Top 5 Diamond & CBN Cutting Blade Performance Metrics
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
When evaluating diamond and cubic boron nitride (CBN) cutting blades, it’s crucial to consider key performance metrics and criteria. Different applications have varying goals, making it…
01
Aug
Diamond & CBN Cutting Blade Performance Metrics that you Should Know
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
When evaluating diamond and cubic boron nitride (CBN) cutting blades, it’s crucial to consider key performance metrics and criteria. Different applications have varying goals, making it important to…
02
Aug
Total Cost of Ownership & Why its Important
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Diamond and CBN cutting blades are available in a myriad of specifications, with virtually limitless options. The industry is saturated with numerous manufacturers, each professing to offer the…
19
Aug
Understanding & Calculating Return on Investment for Diamond & CBN Blades
The term “ROI” (Return On Investment) is frequently mentioned across various industries, often with different interpretations depending on the context. However, few take the time to thoroughly understand what ROI truly represents and its specific…
09
Sep
Understanding Tradeoffs – Searching for Perfect Diamond Drill & Tool
Choosing the right diamond drill or tool can significantly impact efficiency, cost, and quality. However, this is not a simple and clear-cut process. Selecting the optimal drill or tool involves navigating a complex landscape of…
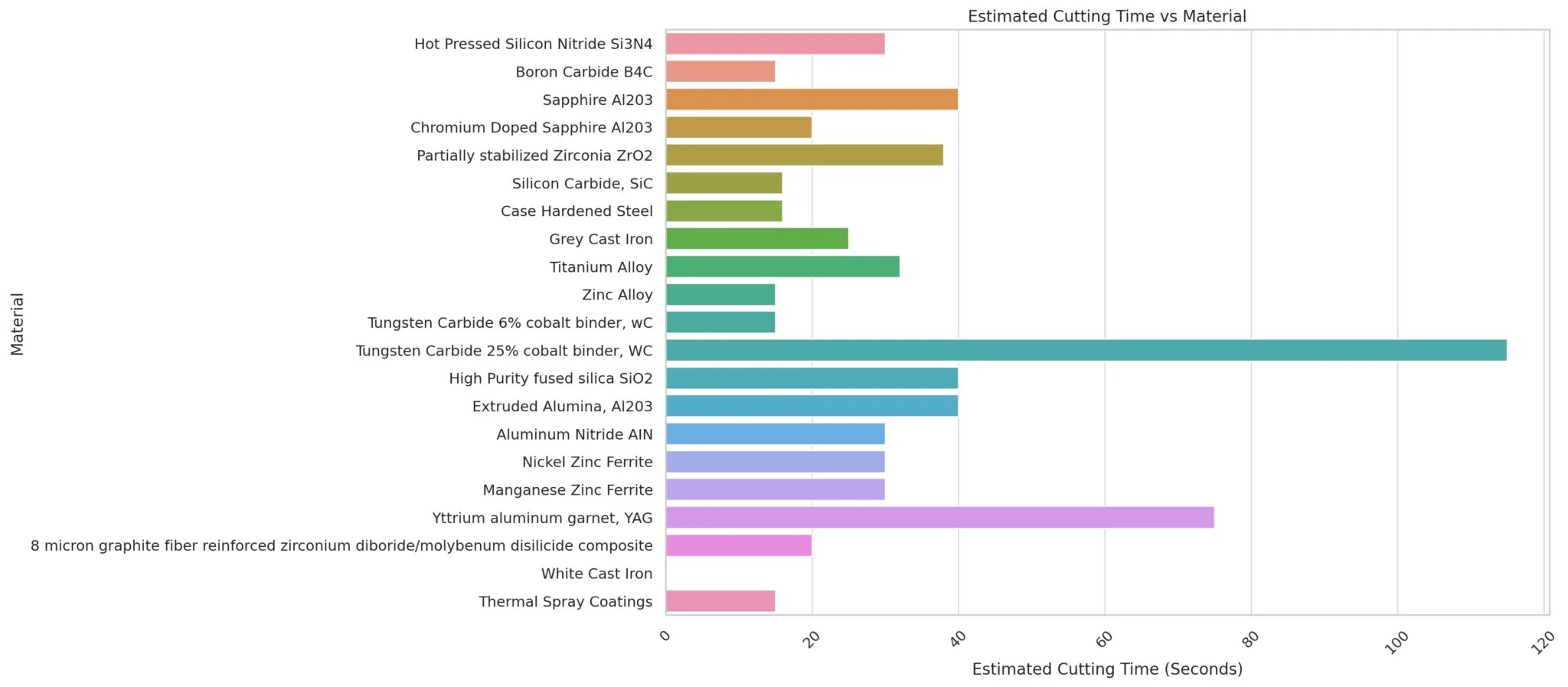
Examples of cutting times for Sectioning of Specific Materials 0.25″ (6.4mm) diameter rod. Using various cutting speeds.
|
Material |
Blade Type |
Diamond Concentration |
Speed (RPM’s) |
Load (grams) |
Estimated Cutting Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Hot Pressed Silicon Nitride Si3N4 |
Series 20LCU |
Low |
4,000 |
800 |
0:30 |
|
Boron Carbide B4C |
Series 20LCU |
Low |
3,500 |
700 |
0:15 |
|
Sapphire Al203 |
Series 15LCU |
Low |
1,500 |
300 |
0:40 |
|
Chromium Doped Sapphire Al203 |
Series 15LCU |
Low |
500 |
500 |
0:20 |
|
Partially stabilized Zirconia ZrO2 |
Series 15LCu |
Low |
2,500 |
500 |
0:38 |
|
Silicon Carbide, SiC |
Series 15LCU |
Low |
2,500 |
500 |
0:16 |
|
Case Hardened Steel |
Series 15HCU |
High |
2,500 |
500 |
0:16 |
|
Grey Cast Iron |
Series 15HCU |
High |
2,500 |
500 |
0:25 |
|
Titanium Alloy |
Series 15HCU |
High |
2,500 |
500 |
0:32 |
|
Zinc Alloy |
Series 15HCU |
High |
2,500 |
800 |
0:15 |
|
Tungsten Carbide 6% cobalt binder, wC |
Series 15HCU |
High |
4,500 |
900 |
0:15 |
|
Tungsten Carbide 25% cobalt binder, WC |
Series 15HCU |
High |
1,500 |
300 |
1:55 |
|
High Purity fused silica SiO2 |
Series 15HCU |
High |
2,500 |
500 |
0:40 |
|
Extruded Alumina, Al203 |
Series 15HCU |
High |
3,000 |
600 |
0:40 |
|
Aluminum Nitride AIN |
Series 15HCU |
High |
1,500 |
300 |
0:30 |
|
Nickel Zinc Ferrite |
Series 15HCU |
High |
1,500 |
300 |
0:30 |
|
Manganese Zinc Ferrite |
Series 15HCU |
High |
Content |
5,000 |
0:30 |
|
Yttrium aluminum garnet, YAG |
Series 15HCU |
High |
3,000 |
Content |
1:15 |
|
8 micron graphite fiber reinforced zirconium diboride/molybenum disilicide composite |
Series 15HCU |
Low |
2,500 |
300 |
0:20 |
|
White Cast Iron |
Series Metacut CBN |
High |
2,500 |
700 |
|
|
Thermal Spray Coatings |
Series 15HCU |
High |
3,000 |
700 |
Choosing the right Abrasive for Your Application
Silicon Carbide (Resin Bond)
Ultra Thin Abrasive Cutting Blades
The silicon carbide wheels are formulated for non-ferrous and non-metallic materials. SMART CUT® series SiC blade provides excellent cutting rates and lower cost sectioning of large variety of samples such as , non-ferrous metal samples material, such as Copper, Aluminum, and Nickel and their alloys
Aluminum Oxide (Resin Bond)
Ultra Thin Abrasie Cutting Blades
The aluminum oxide wheels are designed for ferrous materials. SMART CUT® series alumina oxide cutting blade provides better cutting rate to cut metallic material at much lower cost, especially for cutting ferrous metal samples, such as carbon steel, cast iron, and spring steel etc
ADVANTAGES:
-
 Precision Cutting
Precision Cutting
-
 Minimal Material Loss
Minimal Material Loss
-
 Reduced surface deformation
Reduced surface deformation
-
 Cool Cutting Action
Cool Cutting Action
-
 Universal Material Capability
Universal Material Capability
-
 Improved Cost Efficiency
Improved Cost Efficiency
-
 Reduced Post Processing
Reduced Post Processing
-
 Post Processing
Post Processing
-
 Compatible with most sectioning/wafering saws
Compatible with most sectioning/wafering saws
-
 Balanced cutting speed and surface finish
Balanced cutting speed and surface finish
-
 Longer Life
Longer Life
-
 Consistent Performance
Consistent Performance
SMART CUT® Aluminum Oxide
Ultra Thin Abrasive Cutting Blades
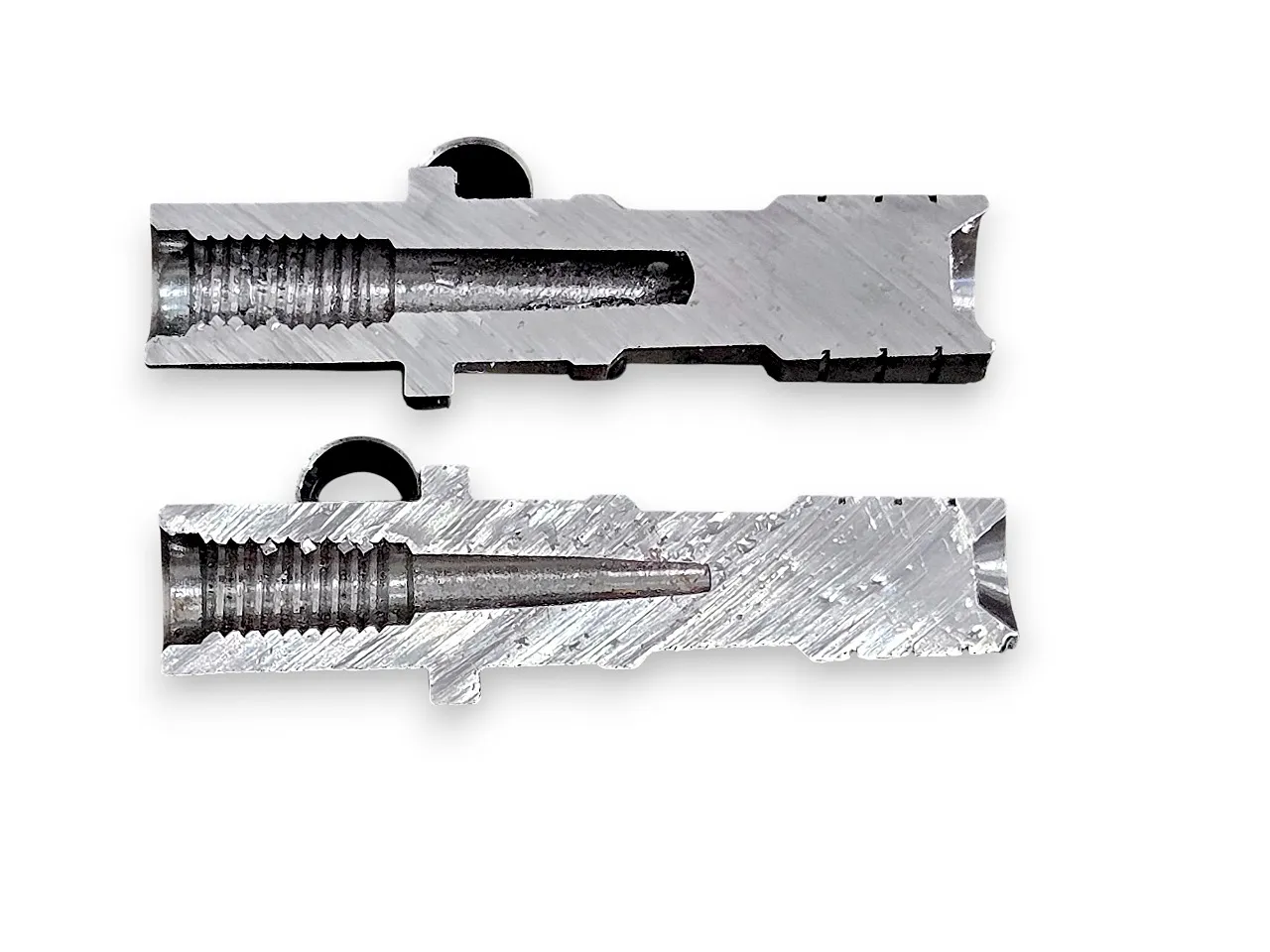



SMART CUT® Aluminum Oxide Ultra Thin Abrasive Cutting Blades are designed for cutting ferrous metals where toughness and control are required. The aluminum oxide abrasive resists rapid wear, allowing the blade to maintain a stable cutting edge when cutting steel and iron based alloys.
They perform consistently on carbon steel, cast iron, spring steel, and alloy steels. The abrasive wears predictably, providing longer blade life and reliable cutting rates on ferrous materials. For ferrous applications, aluminum oxide blades offer a lower cost per cut and dependable performance when used with proper RPM and feed rates.
Showing 1 – -1 of 5 results Showing all 5 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Price low to high
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
item number | Image | Description | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 4” x 0.015” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $109.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 5” x 0.020” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $119.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 6” x 0.020” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $129.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 7” x 0.025” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $159.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 8” x 0.035” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $175.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
SMART CUT® Silicon Carbide
Ultra Thin Abrasive Cutting Blades

SMART CUT® Silicon Carbide Ultra Thin Abrasive Cutting Blades are designed for non ferrous metals and non metallic materials that require sharp, fast cutting action. Silicon carbide is a very hard and sharp abrasive, which cuts efficiently with low cutting force.
SMART CUT® silicon carbide blades perform well on copper, aluminum, nickel, and their alloys. The abrasive fractures easily to expose new sharp edges, resulting in fast cutting rates and reduced blade loading on softer metals. For non ferrous and non metallic applications, silicon carbide blades provide an economical and effective cutting solution.
Showing 1 – -1 of 5 results Showing all 5 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Price low to high
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
Image | Description | Unit | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SMART CUT® SiC Abrasive Blade 4” x 0.015” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | Package of 10 pcs | $109.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
SMART CUT® SiC Abrasive Blade 5” x 0.020” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | Package of 10 pcs | $119.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
SMART CUT® SiC Abrasive Blade 6” x 0.020” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | Package of 10 pcs | $129.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
SMART CUT® SiC Abrasive Blade 7” x 0.025” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | Package of 10 pcs | $159.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
SMART CUT® SiC Abrasive Blade 8” x 0.035” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | Package of 10 pcs | $175.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
SMART CUT Silicon Carbide
Ultra Thin Abrasive Cutting Blades



Showing 1 – -1 of 5 results Showing all 5 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Price low to high
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
item number | Image | Description | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 4” x 0.015” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $109.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 5” x 0.020” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $119.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 6” x 0.020” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $129.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 7” x 0.025” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $159.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® Al2O3 Abrasive Blade 8” x 0.035” x 1/2" hole, medium grit | $175.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
Metallographic Ultra Thin
Abrasive Cut Off Blade - Selection Guide
|
Attribute |
Resin Bond (Aluminum Oxide) |
Resin Bond (Silicon Carbide) |
Rubber Bond (Aluminum Oxide) |
Rubber Bond (Silicon Carbide) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Abrasive Type |
Aluminum Oxide |
Silicon Carbide |
Aluminum Oxide |
Silicon Carbide |
|
Primary Metallographic Use |
Ferrous metals such as carbon steel, alloy steel, and cast iron |
Brittle and non-ferrous materials such as ceramics, glass, carbides, and non-ferrous metals |
Delicate ferrous or mixed materials sensitive to heat and stress |
Delicate brittle and non-ferrous materials sensitive to chipping and cracking |
|
Typical Metallographic Application |
General-purpose metallographic sectioning |
Sectioning of brittle or hard non-ferrous samples |
Sectioning of brittle or hard non-ferrous samples |
Precision sectioning of fragile brittle samples |
|
Cutting Method |
Wet cutting with coolant required |
Wet cutting with coolant required |
Wet cutting with coolant required |
Wet cutting with coolant required |
|
Recommended Operating Speed |
Low to Medium |
Low to Medium |
Low |
Low |
|
Feed / Force Sensitivity |
Moderate |
Moderate |
High |
High |
|
Coolant Compatibility |
Water-based, water-soluble synthetics, emulsions |
Water-based, water-soluble synthetics, emulsions |
Water-based, water-soluble synthetics, emulsions |
Water-based, water-soluble synthetics, emulsions |
|
Cut Quality |
Good to very good when properly selected |
Good to very good on brittle materials |
Excellent with minimal deformation |
Excellent with minimal chipping |
|
Risk of Thermal Damage |
Moderate if parameters are incorrect |
Moderate if parameters are incorrect |
Low when used correctly |
Low when used correctly |
|
Wear Behavior |
Moderate wear with long usable life |
Moderate wear dependent on material hardness |
Faster controlled wear to maintain sharp cutting |
Faster controlled wear to maintain sharp cutting |
|
Precision Capability |
High, dependent on blade thickness, runout, and setup |
High, dependent on blade thickness, runout, and setup |
Very high, ideal for delicate samples |
Very high, ideal for delicate samples |
|
Dressing Frequency |
Occasional |
Occasional |
More frequent |
More frequent |
|
Suitability for Delicate Samples |
Limited |
Limited |
Excellent |
Excellent |
|
Relative Cost |
Low to moderate |
Low to moderate |
Moderate to high |
Moderate to high |
*Recommended operating speed and feed classifications are provided as general metallographic guidance.
Actual RPM and feed or force depend on blade diameter, material hardness and cross section, blade thickness, machine rigidity, coolant flow, and sample mounting.
Always start at the lowest practical settings and adjust based on cutting stability and sample condition.
Resin Bond Cut-Off Blades - Aluminum Oxide
Specification & Item Number Cross Reference Table
This table provides a direct specification and part number cross-reference between SMART CUT® aluminum oxide resin bond cut-off blades and equivalent items from major metallography suppliers.
|
SMART CUT® SPECIFICATION |
SMART CUT® ITEM |
Struers ITEM |
LECO ITEM |
Allied High Tech ITEM |
NOTES / DIFFERENCES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
4" x 0.015" x 1/2" Al₂O₃ Resin |
4063001 |
N/A |
811-146 |
N/A |
LECO is rubber bond and thinner at 0.25 mm |
|
5" x 0.020" x 1/2" Al₂O₃ Resin |
4063002 |
40000045 (30A13) |
812-515 |
N/A |
LECO thicker at 0.61 mm |
|
5" x 0.020" x 1/2" Al₂O₃ Resin |
4063002 |
40000044 (50A13) |
812-515 |
N/A |
Struers 50A13 for harder ferrous > HV 500 |
|
6" x 0.020" x 1/2" Al₂O₃ Resin |
4063003 |
40000102 (30A15) |
809-314 |
80-11300 |
LECO arbor is 25.4 mm. Allied arbor is 32 mm |
|
6" x 0.020" x 1/2" Al₂O₃ Resin |
4063003 |
40000101 (40A15) |
809-314 |
80-11300 |
LECO thickness options differ |
|
6" x 0.020" x 1/2" Al₂O₃ Resin |
4063003 |
40000100 (50A15) |
809-314 |
80-11300 |
Struers hardness class HV 500–800 |
|
7" x 0.025" x 1/2" Al₂O₃ Resin |
4063004 |
N/A |
809-136 |
80-11505 |
LECO rubber bond and 25.4 mm arbor |
|
8" x 0.035" x 1/2" Al₂O₃ Resin |
4063005 |
N/A |
809-141 |
80-11510 |
LECO rubber bond and 25.4 mm arbor |
*Cross-references are provided for specification comparison only. Dimensional, mounting, and performance characteristics may differ by manufacturer and application
Resin Bond Cut-Off Blades - Silicon Carbide
Specification & Item Number Cross Reference Table
This table provides a direct specification and part number cross-reference between SMART CUT® silicon carbide resin bond cut-off blades and equivalent items from major metallography suppliers.
|
SMART CUT® SPECIFICATION |
SMART CUT® ITEM |
Struers ITEM |
LECO ITEM |
Allied High Tech ITEM |
NOTES / DIFFERENCES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
4" x 0.015" x 1/2" SiC Resin |
4063006 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
No 4 inch SiC resin bond equivalent listed |
|
5" x 0.020" x 1/2" SiC Resin |
4063007 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
No direct 125 mm SiC with 12.7 mm arbor |
|
6" x 0.020" x 1/2" SiC Resin |
4063008 |
40000103 (10S15) |
80-11400 |
80-11400 |
Struers and Allied are 0.61 mm thick |
|
7" x 0.025" x 1/2" SiC Resin |
4063009 |
N/A |
80-11605 |
80-11405 |
Allied thickness 0.76 mm |
|
8" x 0.035" x 1/2" SiC Resin |
4063010 |
N/A |
80-11610 |
80-11410 |
Allied thickness 0.76 mm |
*Cross-references are provided for specification comparison only. Dimensional, mounting, and performance characteristics may differ by manufacturer and application


Why Choose Us?
- Unmatched Selection For Many Applications
- Unmatched Technical Support & Expertise
- Superior Quality & Consistency
- Super Technology & innovation
- Immediate Worldwide Delivery
- American Based Manufacturer
-
Custom
Manufacturing - Better Value manufacturer Direct Price
Why Work With Us?
Read More
We produce diamond consumables for some of the leading world OEM manufacturers. We offer Manufacturers Direct Prices
We have the largest variety of diamond & cbn wafering blades available in stock. As well as large inventory of diamond & abrasive consumables. We also custom manufacture diamond and cbn tools, consumables and machines to better fit customer specific needs. Just about any tools & consumables can be designed and manufactured per client drawing or specificrtion
WE ARE A PARTNER IN YOUR SUCCESS
Our proprietory diamond chemistory , precision , manufacturing metods , quality control methods allow us to control and regulate the dozens of variables to that affect consumable life , quality , and consistency.
The more you understand about what we can do for you the better our partnership will be. Here you will find most comprehensive source of information and optimizing and improving your cutting , drilling , grinding and polishing on the web. find everything you ever wanted to know about diamond tools.
AMERICAN MANUFACTURER
"ONE OF THE MOST EXPERIENCED COMPANIES IN THE INDUSTRY"
Save Money Save up to 650%
COMPARE TO: BUEHLER , STRUERS , LECO & MANY OTHERS
Large Inventory & Custom Manufacturing
Umatched Technical Support
Developing close ties with our customers is the foundation of our business. At the core of
our company is a team of world class engineers, knowledgeable customer service personnel here to serve you. Whether is designing or manufacturing a special solution. We will go out of our way to optimizing your process to ultimate level of efficiency
Superior Quality & Consistency
EXPECT MORE FROM YOUR TOOLS
Comprehensive Source Of Information For Sample Preparation
Advanced Technology
As one of the few remaining independent U.S.Diamond Tool & machine builders. We have the experience & tradition to help you remain at frontier of technology Our experience has been further enhanced by acquiring assets and processes from some of the oldest American tool
manufacturers, along with their decades of experience and R& D. This has positioned us as one of the most experienced companies in the industry .Depend on us to bring you technology of tomorrow today.
Experience Makes All The Differences
Over the years we have worked with some of the leading Fortune 500 companies , thousands of universities , government and private research labs , and small organisations. We have made thousands of custom tools , built custom machines , work-holding fixtures , etc for hundreds of applications. Many of our staff members have been working in their respective fields for over 50 years and have gained a wealth of knowledge over the years
Let Us Help You
Related Products
SMART CUT® Abrasive Cut Off Blades
SMART CUT® CBN WAFERING BLADES SINTERED (METAL BOND)
SMART CUT® Series 3000R Resin Bond, Diamond Cut Off Blade
Resin Bond Diamond Cut off blades (Fine Size Diamond) for use on manual tile saws
SMART CUT® Series 3000R are the highest quality & most commonly used Resin Bond Diamond Cut off Blades / Cut Off Wheels available today. Finer Diamond Grit Size, and Slightly Higher Diamond Content then the SMART CUT Series 2000R blades. They are used for cutting very thin wall tubing, more fragile material, that need best surface finish possible to achieve. Cutting speed would be slower then the 2000R series. These blades cut more slowly due to their finer grit size, which provides less aggressive material removal. They are better suited for precision tasks where cut quality is prioritized over speed. The finer grit results in a much smoother surface finish with minimal chipping, making them ideal when a high-quality, clean cut is needed, especially for delicate materials The resin bond diamond cut off blades / cut off wheels excel in delivering superior cut quality compared to other diamond cutting blade, making them ideal for applications where cut quality and surface finish is highly important. They are designed to operate at higher speeds to minimize heat generation and improve surface finishes.SMART CUT® Series 400 Wafering Blade, Resin Bond
Resin Bond Diamond Wafering Blades for use on Precision & Laboratory type Cut off Saws
SMART CUT® Series 400 are Designed for Precision, Chip Free cutting of wide variety of materials These are very thin kerf blades and are very delicate. Must be used on high precision specialized laboratory cutting saws (not tile saws, trim saws, etc) The diamond section can be easily broken if the material moves while cutting, blade is dropped, material is feed to fast into the blade, material is not fed consistently straight into the blade (shifts position) etc. Diamond Size is Medium providing faster cutting speed, while still providing surface quality unmatched by 95% of other blades.SMART CUT 105N Diamond, Nickel Bond Wafering Blades INTERRUPTED RIM
SMART CUT™ Series 105N more freer cutting & aggressive than continuous rim nickel bond wafering blades. Best Suited for cutting larger variety of micro-electronics packages, pcb boards, plastics, composites, soft and precious metals, fish and human bones, graphite, GRP, FR4. Core steel with memory. Always snaps back to its original shape no matter how much bent.
Standard arbor size inside diameter is ½” (12.7mm) (* we can modify arbor size of any blade to anything you want same day for a small additional fee, if needed)
SMART CUT® Series 100N Wafering Blade, Nickel Bond
NICKEL BOND, DIAMOND CONTINUOUS RIM
SMART CUT® Series 100N will provide finer cut quality than interrupted rim nickel bond wafering blades. Best suited for cutting soft and fragile crystals, silicon wafers & substrates, fiberglass, glass fibers. made with stainless steel core Standard arbor size inside diameter is ½” (12.7mm) (* we can modify arbor size of any blade to anything you want same day for a small additional fee, if needed) Nickel Bond Diamond Cut off blades Blades usually have a single layer of diamonds, held by a tough durable nickel alloy. diamond particles to protrude from the bond matrix, providing a free, faster cutting action with minimum heat generation.Diamond, Nickel Bond Cut Off Blades for Laboratory & Other Saws
SMART CUT® Fully Sintered (Metal Bond) Diamond & CBN, Wafering Blades
SMART CUT® Fully Sintered (Metal Bond) diamond wafering blades are fully sintered from OD to ID of the blade. Meaning they have diamonds completely impregnated through the blade. Unlike standard diamond & cbn wafering blades with steel core and diamond section. Instead of having a steel core and small diamond bond edge (usually 1/8"/3.2mm). The diamond edge is all the way through the blade, from its Outside Diameter to Inside Diameter of the blade. You can use until the entire Outside Diameter of the blade is consumed.
Recently Viewed Products
ARE YOU USING ABRASIVE CUT OFF BLADES
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET US
HELP YOU
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT ABRASIVE CUT OFF BLADES?
Knowledge Center
02
Jun
How to Properly Use Precision Diamond & CBN Blades
The diamond blade itself is only a small factor in your cutting operation. Successful diamond sawing is both an art & science. Requiring proper use and understanding of the right: RPM's, Coolants, Equipment, Dressing Devices, Accessories...
02
Jun
Precision & Ultra Thin Diamond Blade Guide
Diamond and CBN blades are available in an extensive array of varieties, each differing in bond types, manufacturing methods, and design specifics. Ultra Thin & High Precision Diamond Blades are particularly versatile, applicable...
02
Jun
Troubleshooting Diamond Sawing Problems
Having issues with your diamond cutting operation? This Illustrated Guide can help. Learn the most common problems most people have in using diamond cutting blades. How to resolve them and avoid them in...
02
Jun
How to Improve & Optimize Your Diamond Sawing Operation
There are numerous variables that affect the performance of diamond and CBN cutting blades. Understanding these variables will help end users select the right diamond blade specifications for their applications and optimize their cutting operations...
02
Jun
Evaluating & Comparing Diamond Blades
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Proper testing procedures and methodologies must be set up and used to obtain accurate as well as repeatable testing results. This article will discuss several simple procedures which...
02
Jun
Selecting Right Wafering Blade for your application
Cross Sectioning is the first and most important step in the sample preparation process. Getting the best results involves obtaining a smooth surface finish, minimum chipping, material deformation, without sacrificing cutting speed. Today, most laboratories, work with dozens...
02
Jun
Wafering Blade Usage Recommendations
The wafering/sectioning blade itself is only a small factor in your sectioning operation. Successful wafering/sectioning operation is both an art & science. Requiring proper use and understanding of selecting the right diamond wafering/sectioning...
02
Jun
Wafering Blade Case Studies
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Case Studies
This study evaluates the cutting performance of SMART CUT® Diamond & CBN Wafering Blades compared to Conventional Wafering Blades under identical test conditions. The objective was to measure differences...
22
Apr
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Performance Metrics
When evaluating Diamond & CBN wafering blades, especially for metallography and sample preparation, it is critical to consider a set of key evaluation criteria and performance metrics. These factors help determine the effectiveness of a...
24
Apr
Understanding & Comparing Diamond & CBN Wafering Blades
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Diamond wafering blades are designed for sectioning a large variety of materials and sample types. In order to identify the best diamond wafering blade for your specific material/application,...
25
Apr
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Guide
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
All you need to know about wafering blades (understanding variables & specifications)
This guide is designed to help you navigate the various variables and possibilities associated with diamond wafering...
31
Jul
Top 5 Diamond & CBN Cutting Blade Performance Metrics
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
When evaluating diamond and cubic boron nitride (CBN) cutting blades, it's crucial to consider key performance metrics and criteria. Different applications have varying goals, making it...
01
Aug
Diamond & CBN Cutting Blade Performance Metrics that you Should Know
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
When evaluating diamond and cubic boron nitride (CBN) cutting blades, it's crucial to consider key performance metrics and criteria. Different applications have varying goals, making it important to...
02
Aug
Total Cost of Ownership & Why its Important
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Diamond and CBN cutting blades are available in a myriad of specifications, with virtually limitless options. The industry is saturated with numerous manufacturers, each professing to offer the...
19
Aug
Understanding & Calculating Return on Investment for Diamond & CBN Blades
The term "ROI" (Return On Investment) is frequently mentioned across various industries, often with different interpretations depending on the context. However, few take the time to thoroughly understand what ROI truly represents and its specific...
09
Sep
Understanding Tradeoffs – Searching for Perfect Diamond Drill & Tool
Choosing the right diamond drill or tool can significantly impact efficiency, cost, and quality. However, this is not a simple and clear-cut process. Selecting the optimal drill or tool involves navigating a complex landscape of...