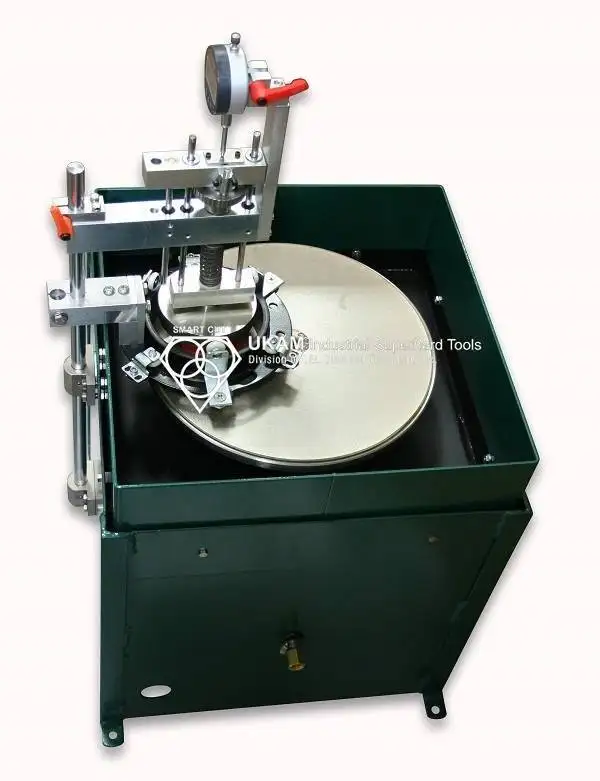
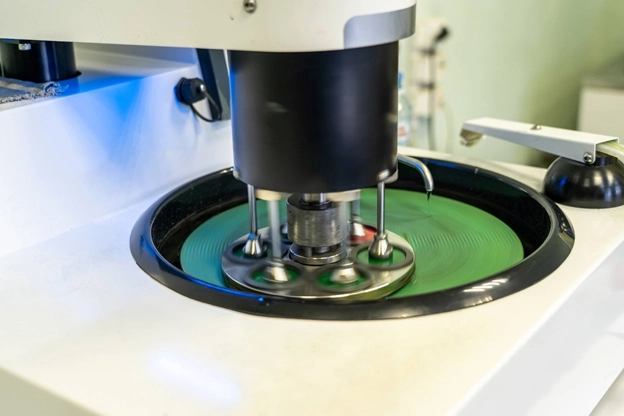
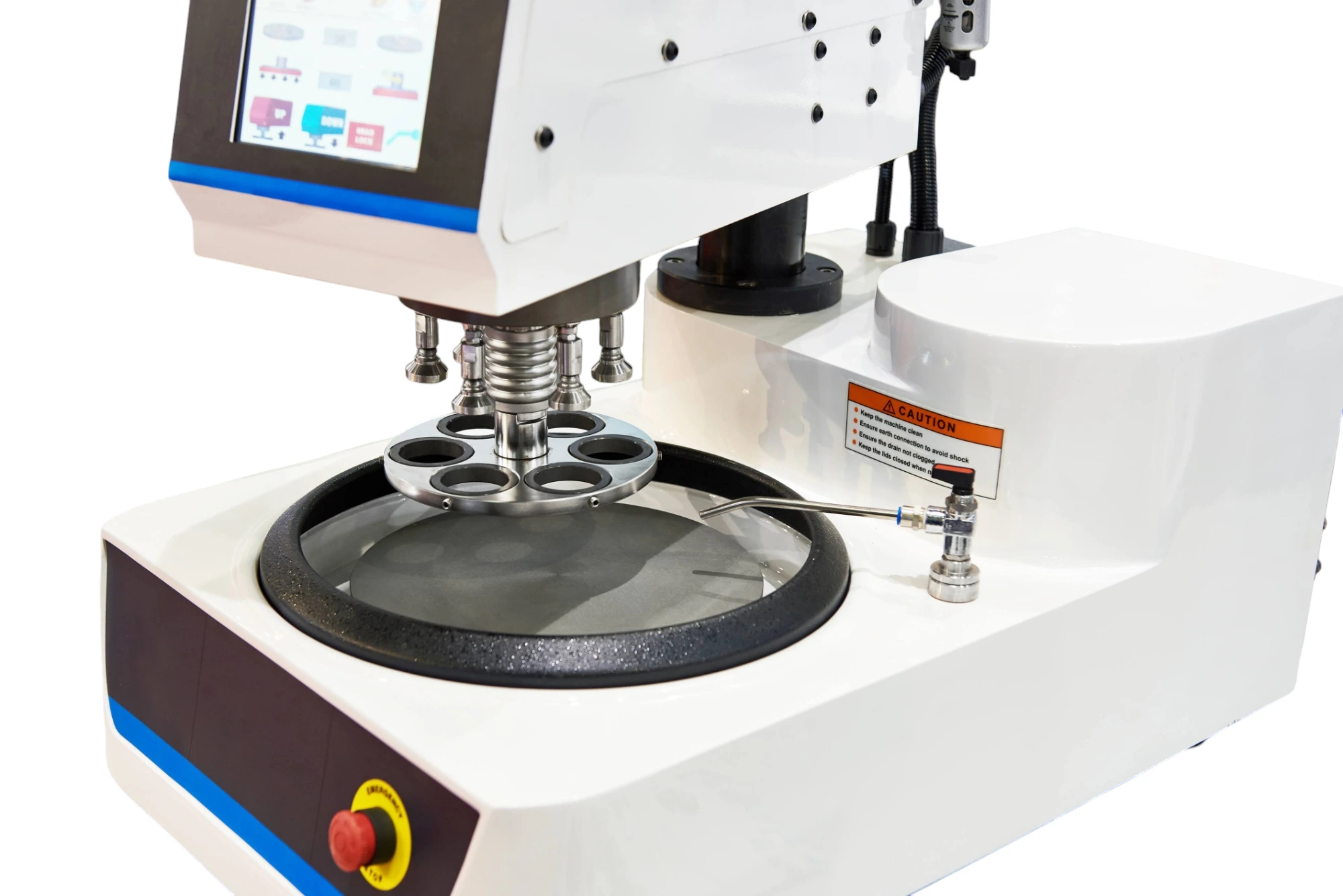
Grinding & Polishing Machines

Grinding & Polishing / Machines For
Industry and Research & Development
we manufacture and offer large verity of Grinding & Polishing machines for Laboratory & Industry. Typical applications include Research & Development, Sample Preparation, Failure Analysis, Materials Research, & many other industrial applications.
Examples include: ceramics, composites, plastics, quartz, metals, petrographic samples, and graphite. From high capacity Grinding of very large work pieces to Polishing of the most delicate samples
Why Choose Us?
- Unmatched Selection For Many Applications
- Unmatched Technical Support & Expertise
- Superior Quality & Consistency
- Super Technology & innovation
- Immediate Worldwide Delivery
- American Based Manufacturer
-
Custom
Manufacturing - Better Value manufacturer Direct Price
ENTRY LEVEL / SIMPLE
Grinding & Polishing Machines
Affordable Entry Level Laboratory Grinding & Polishing Machine. Designed for Mechanical Sample Preparation. What really sets these machines apart is their AFFORDIBILITY. For many applications SMART CUT® Grinding / Polishing Machines provide equal results and in less time, then many other much higher cost equipment. Which makes them a Perfect option for organizations of all sizes (manufacturing, R & D) that are on a Budget.

SMART CUT® LP-Grinding/Polishing Machine
SMART CUT® LP is Perfect for coarse & fine grinding and polishing of large variety of materials. Including: Ultra Hard & Brittle, Metals, Ceramics, Refractories, Cement, and Petrographic thin sections. As well as full range of optical materials, such as: Bk7, Fused Silica, Zeroder, Quartz, Soda Lime Glass, Yag, Sapphire, and Many Others. Its Variable Speed allows the operator the flexibility to move from high speed rough grinding to low speed final polishing. It’s molded plastic housing will never rust.

SMART CUT® LP – 12” (300MM) Grinding/Polishing Machines
SMART CUT® LP – 12” (300mm) is Perfect for coarse & fine grinding and polishing of large variety of materials. Including: Ultra Hard & Brittle, Metals, Ceramics, Refractories, Cement, and Petrographic thin sections. As well as full range of optical materials, such as: Bk7, Fused Silica, Zeroder, Quartz, Soda Lime Glass, Yag, Sapphire, and Many Others. Its Variable Speed allows the operator the flexibility to move from high speed rough grinding to low speed final polishing.

SMART CUT® LG Manual Metallurgical Grinder/Polisher with Single Wheel
SMART CUT® LG Bench Top Metallurgical Grinder/Polisher with Single Wheel offers an economical solution to your metallographic sample preparation needs. Available in 8” (200mm), 10” (250mm), and 12” (300mm) wheel size and comes with single wheel version with variable rotating wheel speed of 50-600 RPM OR 50-1,000 rpm. Detachable water sprayer for easy cleaning. A feather touch digital control panel as well as a fully molded FRP body with easy disc change design. 110V, 1 phase, 50/60 Hz and 230 V / 50Hz. This machine is ideal for fast manual grinding and polishing for small to large samples. This machine is incredibly robust while being easy to use and affordable in price. Perfect for organizations on a budget.

SMART CUT® NP Single Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher
SMART CUT® NP Single Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher embodies sophistication and precision engineering for metallographic specimen preparation. This robust unit is tailored to support the needs of both novice and expert technicians by simplifying complex grinding and polishing tasks through a user-friendly interface and superior design features.

SMART CUT® NP Dual Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher
SMART CUT® NP Dual Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher embodies sophistication and precision engineering for metallographic specimen preparation. This robust unit is tailored to support the needs of both novice and expert technicians by simplifying complex grinding and polishing tasks through a user-friendly interface and superior design features.

SMART CUT® MP Single Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher
SMART CUT® MP Single Wheel machine provides seamless grinding and polishing with a strong and variable speed drive ranging from 100 to 1000 RPM.

SMART CUT® MP-2A Single Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher
Single Control Double Wheel Grinder & Polisher Each wheel features independent speed controls, ensuring adaptability for various working steps and material requirements.

SMART CUT® MP-2B Single Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher
Dual Control Double Wheel Grinder & Polisher Each wheel features independent speed controls, ensuring adaptability for various working steps and material requirements.
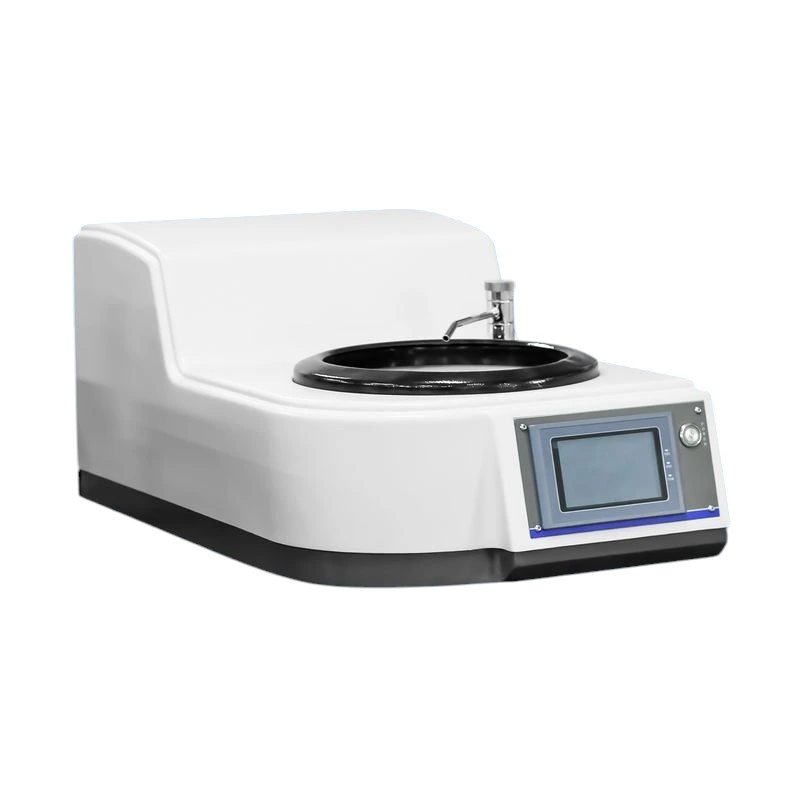

SMART CUT® RP Automatic Single Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher
SMART CUT® RP is a state-of-the-art, multi-functional machine designed to handle all stages of metallographic specimen preparation, including coarse grinding, fine grinding, and both coarse and fine polishing.
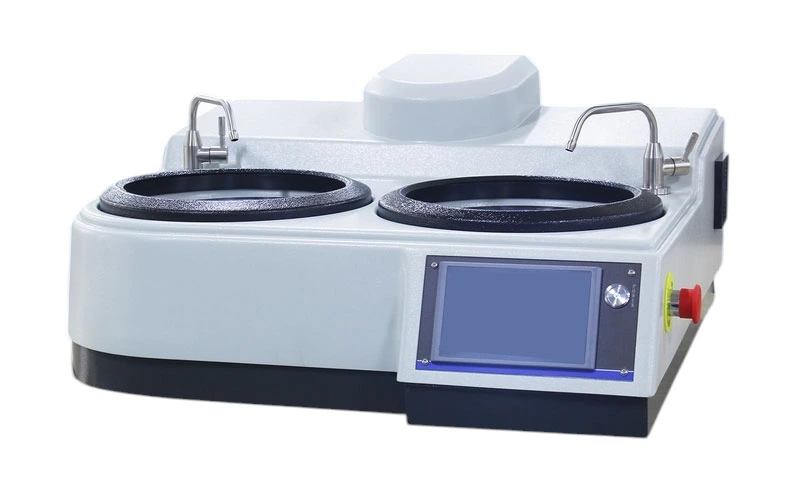

SMART CUT® RP Automatic Dual Wheel Metallographic Grinder and Polisher
SMART CUT® RP Dual Wheel is a state-of-the-art, multi-functional machine available in 8” (203mm) and 10” (254mm) is designed to handle all stages of metallographic specimen preparation, including coarse grinding, fine grinding, and both coarse and fine polishing.
Semi Automatic/Automatic
Grinding & Polishing Machines
Semi automatic & automatic grinding/polishing machines usually have grinding/polishing head that holds the sample and allows specified amount of pressure to be applied to the sample until desired amount of material has been removed. The operator may pre-set parameters or programmable settings to perform tasks automatically with minimal operator intervention.

SMART CUT® NP-1A Semi-Automatic Grinder/Polisher with Polishing Head
Single & Dual Grinder/ Polisher with adjustable spring pressure polishing head allows simultaneous processing of up to three specimens, with each one independently adjustable for optimal results.

SMART CUT® NP-2A Automatic Grinder/Polisher with Polishing Head
Single & Dual Grinding/Polishing Machine with Advanced features independently adjustable piston polishing heads, enabling the simultaneous processing of 1 to 6 specimens.

SMART CUT® AP Automatic Grinder/Polisher with Polishing Head
SMART CUT® AP is Central Pressure Single Disc AutomaticGrinder / Polisher, designed for finer polishing surface off Metallographic, Ceramic,and Petrographic Samples. This Metallographic grinder machine offers an economical solution to your metallographic sample preparation needs. Available in 10” (250mm) and 12″ (300mm) wheel size and comes with single wheel version with variable rotating wheel speed of 50-600 RPM. Detachable water sprayer for easy cleaning. A feather touch digital control panel as well as a fully molded FRP body with easy disc change design.This machine is incredibly robust while being easy to use and affordable in price. Perfect for organizations on a budget.
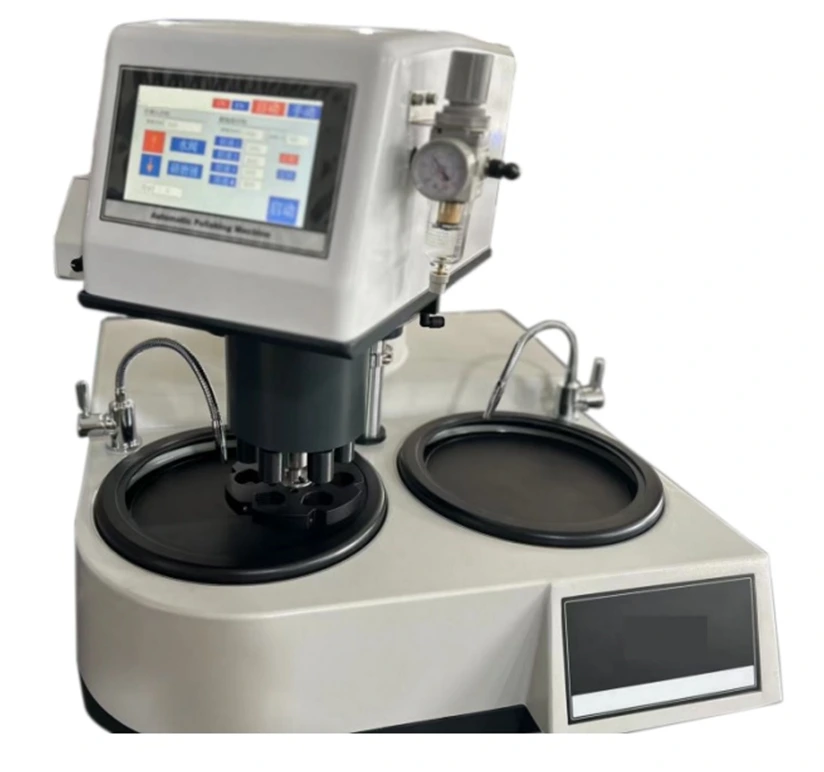

SMART CUT® NP-3A Automatic Grinder/Polisher with Polishing Head
Single & Dual Grinding/Polishing Machine with Advanced features independently adjustable piston polishing heads, enabling the simultaneous processing of 1 to 6 specimens.

SMART CUT® VP - Vibratory Polisher
SMART CUT® VP Vibratory Polisher is an advanced precision tool designed to meet the demanding requirements of materials processing, particularly where delicate surfaces and ultra-fine finishes are essential.
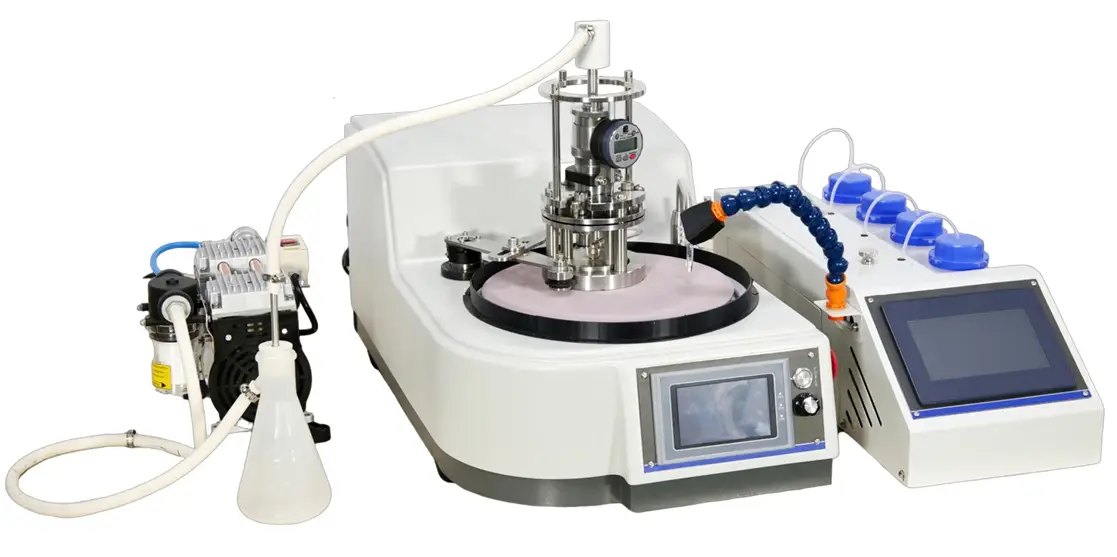

SMART CUT® RP 4000YX / 5000YX Precision Grinding & Polishing Machine
SMART CUT® RP 4000YX / 5000YX Precision Grinding & Polishing Machine is a next-generation semi-automatic system engineered for high-precision sample preparation in applications involving semiconductor wafers, advanced ceramics, metallographic specimens, and other hard or brittle materials requiring stringent surface finish tolerances and material removal accuracy.
Grinding and Polishing Head
Grinding & Polishing Machines
Grinding/Polishing Heads help remove material from the sample’s surface, typically through abrasive grinding. This step is necessary to achieve a flat, even, and precisely prepared surface and remove any remaining scratches or imperfections and provide the sample with a high-quality finish.

SMART CUT® Simple Precision Grinding/Polishing Head
The SMART CUT GP grinding/polishing SIMPLE head provides controllable level of pressure, flatness to insure uniform material removal. The operator set exactly the amount of pressure to apply and amount of material they wish to remove. The grinding/polishing head will apply the level of pressure pre set by the operator until the desired amount of material has been removed, automatically stopping when the objective has been achieved.

SMART CUT® High Precision Grinding/Polishing Head
SMART CUT® Grinding/Polishing Head Enables precise semiautomatic sample preparation of a wide range of materials for microscopic (optical, SEM, TEM, AFM, etc.) evaluation. Capabilities include parallel polishing, precise angle polishing, site specific polishing & others. It provides reproducible sample results by eliminating inconsistencies between users, regardless of their skill.

SMART CUT® SM Grinding/Polishing Head
SMART CUT® adjustable spring pressure polishing head allows simultaneous processing of up to three specimens, independently adjustable, RPM's 50 to 200 rpms.
Why Work With Us
Save Money Save up to 650%
We produce diamond consumables for some of the leading world OEM manufacturers. We offer Manufacturers Direct Prices
COMPARE TO: BUEHLER , STRUERS , LECO & MANY OTHERS
Large Inventory & Custom Manufacturing
We have the largest variety of diamond & cbn wafering blades available in stock. As well as large inventory of diamond & abrasive consumables. We also custom manufacture diamond and cbn tools, consumables and machines to better fit customer specific needs. Just about any tools & consumables can be designed and manufactured per client drawing or specificrtion
Umatched Technical Support
WE ARE A PARTNER IN YOUR SUCCESS
Developing close ties with our customers is the foundation of our business. At the core of
our company is a team of world class engineers, knowledgeable customer service personnel here to serve you. Whether is designing or manufacturing a special solution. We will go out of our way to optimizing your process to ultimate level of efficiency
Superior Quality & Consistency
Our proprietory diamond chemistory , precision , manufacturing metods , quality control methods allow us to control and regulate the dozens of variables to that affect consumable life , quality , and consistency.
EXPECT MORE FROM YOUR TOOLS
Comprehensive Source Of Information For Sample Preparation
The more you understand about what we can do for you the better our partnership will be. Here you will find most comprehensive source of information and optimizing and improving your cutting , drilling , grinding and polishing on the web. find everything you ever wanted to know about diamond tools.
Advanced
Technology
AMERICAN MANUFACTURER
As one of the few remaining independent U.S.Diamond Tool & machine builders. We have the experience & tradition to help you remain at frontier of technology Our experience has been further enhanced by acquiring assets and processes from some of the oldest American tool
manufacturers, along with their decades of experience and R& D. This has positioned us as one of the most experienced companies in the industry .Depend on us to bring you technology of tomorrow today.
Experience Makes All The Differences
"ONE OF THE MOST EXPERIENCED COMPANIES IN THE INDUSTRY"
Over the years we have worked with some of the leading Fortune 500 companies , thousands of universities , government and private research labs , and small organisations. We have made thousands of custom tools , built custom machines , work-holding fixtures , etc for hundreds of applications. Many of our staff members have been working in their respective fields for over 50 years and have gained a wealth of knowledge over the years
Precision Saws
- Obtain More Consistent Results
- Save Time & Money
- improve Surface Finish
- Preserve True Material Microstructure
- Improve Consumable Life & Overall Performance
- Reduce & eliminate Material Deformation