-
0 items in quote
No products in the Quote Basket.
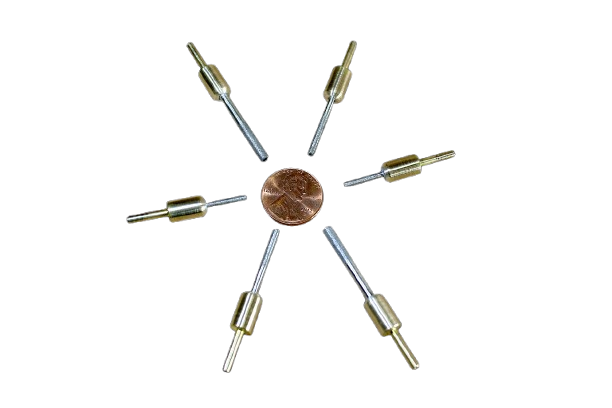
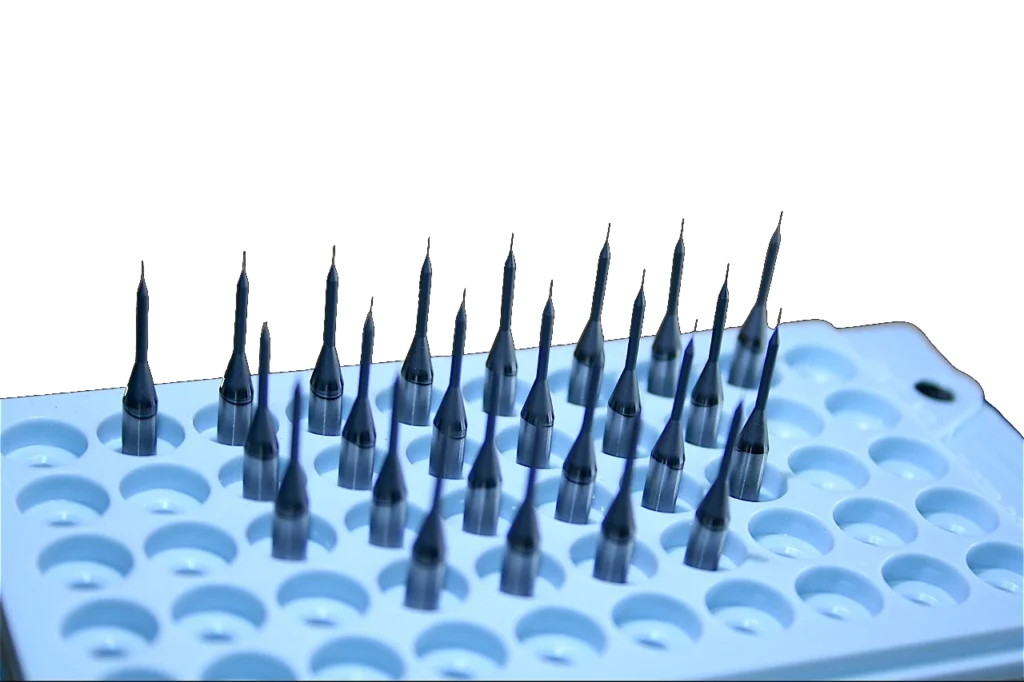
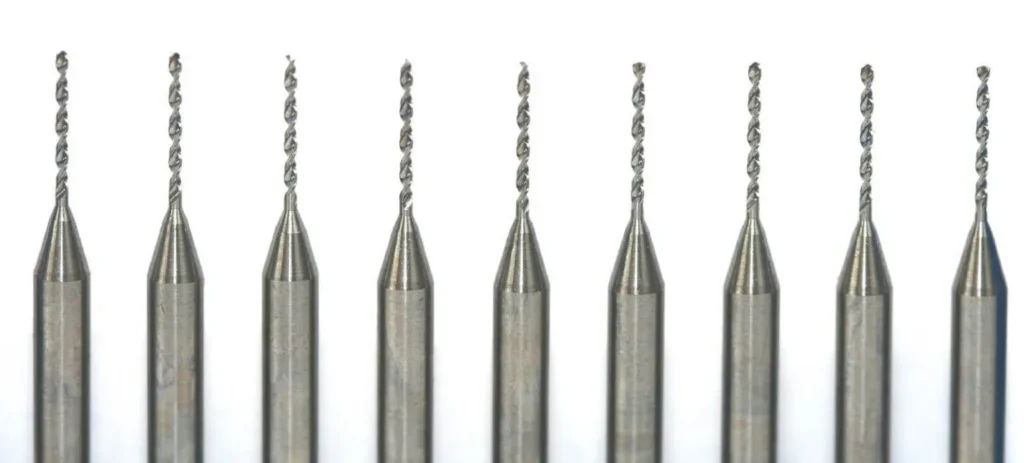
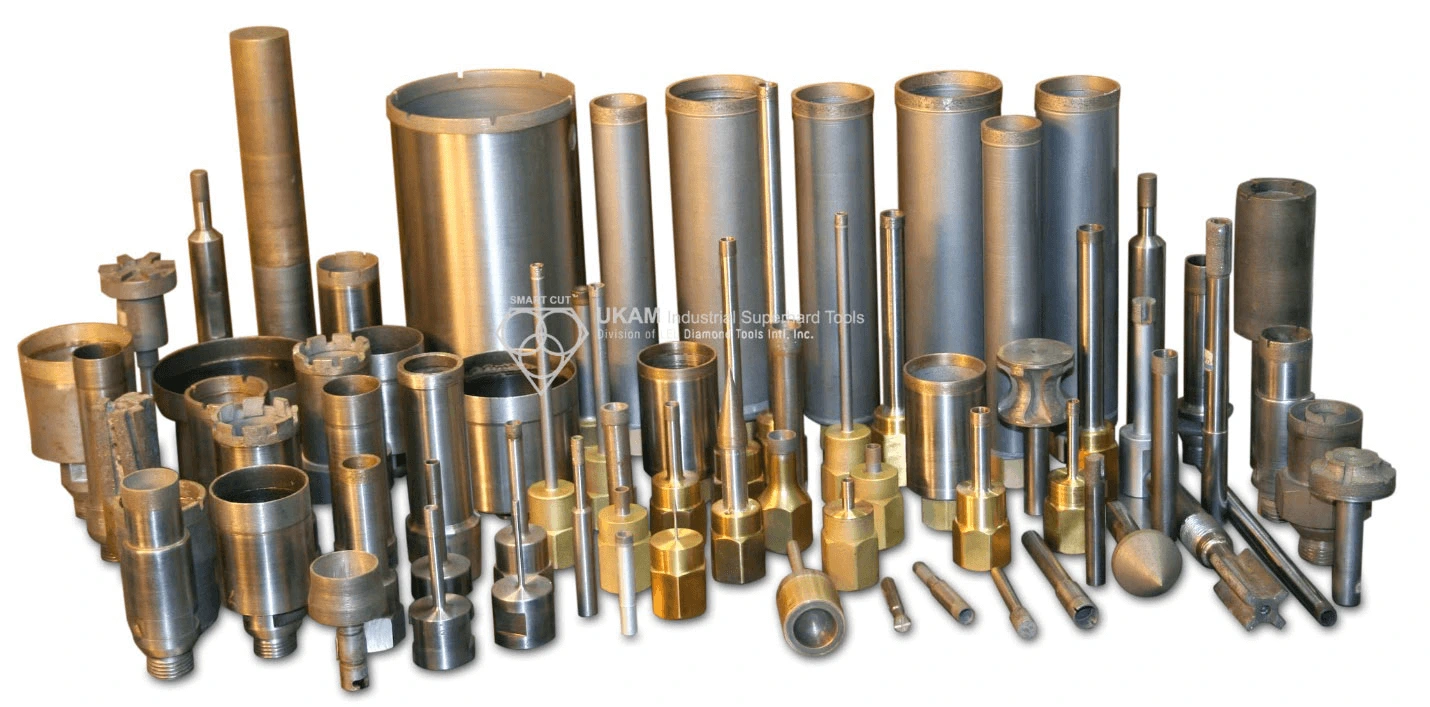
SMART CUT® Micro & Miniature Diamond Core Drills
SMART CUT® Micro & Miniature Diamond Core Drills, are sintered (metal bond) are designed for drilling very small diameter holes in large variety of ultra hard and brittle materials. Such as drilling glass, optical glass, silicon, ceramic, piezo, sapphire and other crystalline materials.
DESCRIPTION
SPECIFICATIONS
INDUSTRIES USED IN
FAQ
ACCESSORIES
DESCRIPTION
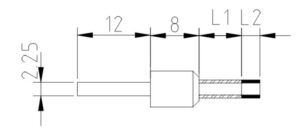
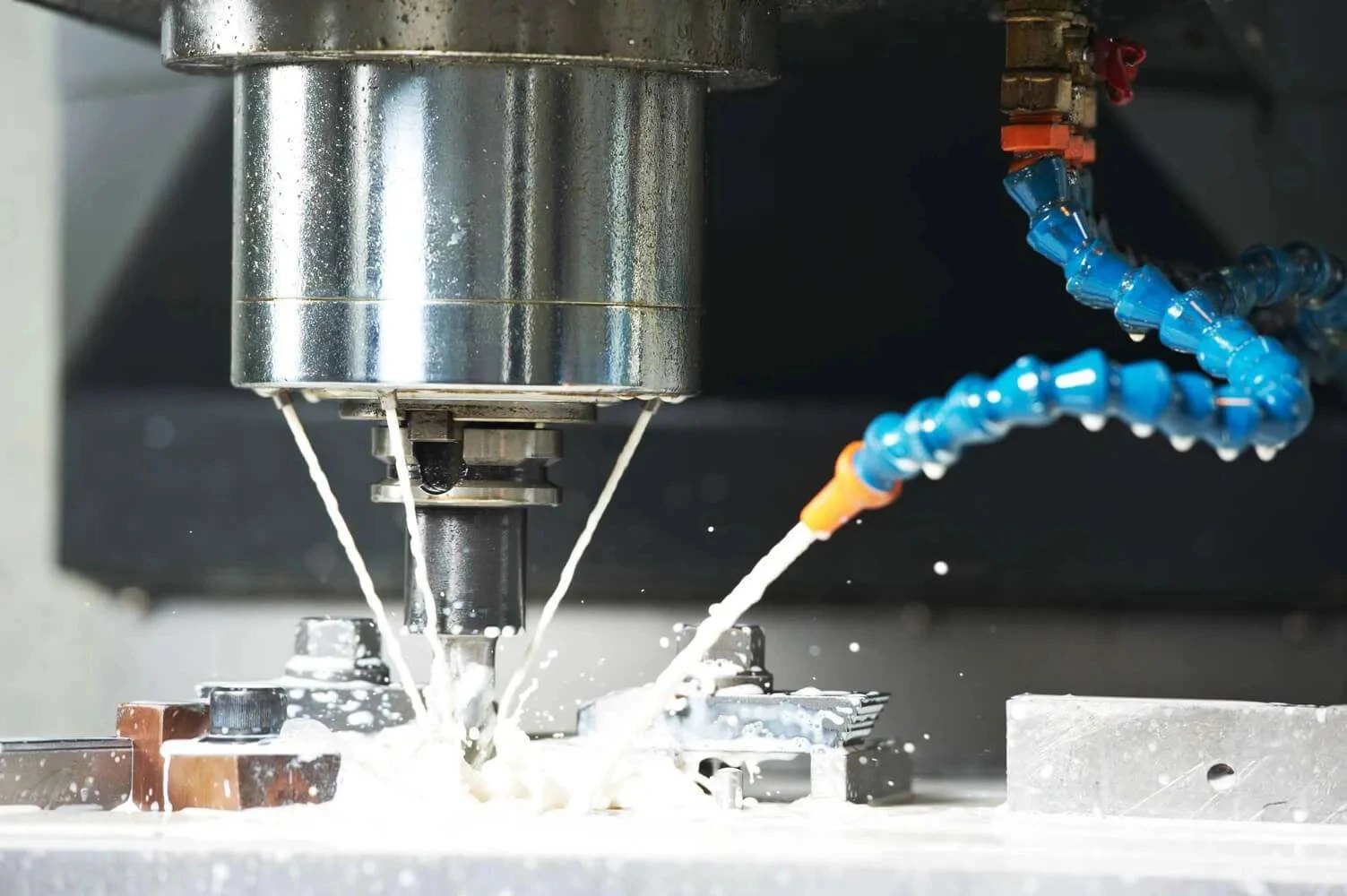
These core drills can be used for both drilling holes and obtaining core samples. Various mounting types are available. Custom specifications can be produced upon request. We always recommend using thru-hole coolant whenever possible. Flood cooling may be OK in certain situations, but this does not effectively remove swarf and does not cool the drill as well so drill life will typically be shorter.
These core drills weredeveloped especially for users with suspended motors and tools such as Dremel, proxxon, foredom, the These drills can be used on handpiece. Cooling in a water bath is always recommended. The shank of the drill has a through hole and thus allows a manual ejection of the core to ensure permanent safe and consistent results.
SPECIFICATIONS
- Bond Type: Sintered (Metal Bond)
- Tolerances on Outside Diameter: + / – 0.03mm or + / – .01mm
- Inside Diameter Tolerance: – 0 / + 0.01
- Run Out/Concentricity: 0.02- 0.03mm
- Diamond Depth:0.65mm
- Diamond Size:200 mesh (80 microns) to 1,000 mesh (15 micron)
- Diamond Depth: 4mm to 10mm
- Drill depth: 30mm to 40mm
- Life Span: hundreds of holes to over thousand
INDUSTRIES USED IN

Precision Optics

Hard to Medium Hard Ceramics

Alumina Ceramics

Glass, Quartz, BK7

Thin Wafers & Substrates such as Silicon & Galium Arsinide

Graphite

Glass, Quartz, & Pyrex
Tubing

Material Glass & Quartz
FAQ
These drills are designed for ultra-hard and brittle materials, including glass, optical glass, silicon, ceramic, piezo, sapphire, and other crystalline materials.
Yes, SMART CUT Diamond Core Drills are versatile and can be used for both drilling precise holes and extracting core samples from various materials.
The drills come in a range of sizes, with outside diameters ranging from 0.5mm to 3.2mm. Inside diameters and drill depths are matched accordingly.
The outside diameter tolerance is +/- 0.03mm or +/- 0.01mm, and the inside diameter tolerance is – 0 / + 0.01. This precision ensures accurate drilling.
These drills use a sintered (metal bond), which offers durability and a strong bond between the diamonds and the matrix
The lifespan varies based on usage and material but typically ranges from hundreds to over a thousand holes.
Yes, custom specifications can be produced upon request, allowing for tailored solutions for specific drilling needs.
Thru-hole coolant is recommended whenever possible. Flood cooling may be suitable in certain situations, but it is less effective in swarf removal and cooling.
The diamond size ranges from 200 mesh (80 microns) to 1,000 mesh (15 microns), allowing for a balance between drilling speed and finish quality. Diamond size used varies with diameter of the drill with smaller diameter drills having finer diamond sizes, and larger diamond drills having larger diamond sizes. We can customize diamond size to fit your particular application.
It’s important to use the recommended coolant method to prolong drill life and maintain performance. Also, ensuring the drill is correctly mounted and aligned can reduce wear and tear. And periodically dressing to maintain efficient drilling speed and diamond crystals exposed.
Yes, they can be used on standard drilling machines, but ensure the machine can accommodate the specific mounting type and operate within the required precision.
While there’s always a risk when drilling hard, brittle materials, these drills are designed to minimize cracking and damage, especially when used with proper techniques and coolant.
Yes, these drills are ideal for both industrial-scale operations and precise laboratory work, thanks to their durability and precision.
The diamond depth, which ranges from 4mm to 10mm, indicates the depth of the diamond-embedded segment. This depth impacts the drill’s longevity and its ability to maintain cutting efficiency over time.
The run out/concentricity, measured at 0.02-0.03mm, ensures the drill rotates evenly, leading to more precise holes, reduced risk of drill breakage, and overall better performance.
Using a slow, steady feed rate, maintaining consistent coolant flow, and avoiding excessive pressure are key techniques to optimize performance and prolong the drill’s life.
Material hardness, drilling speed, pressure applied, coolant used, and frequency of use are key factors that can affect the lifespan of these drills.
These drills are not recommended for use on ferrous metals. We can produce core drills using CBN (cubic boron nitride) instead of diamond that would help reduce amount of heat generated when drilling the tough materials. Diamond can be used but the effectiveness will not be as efficient compared to using CBN abrasive inside these core drills.
While possible, it’s not recommended due to the precision required. These drills are best used with stable, stationary drilling setups to ensure accuracy and safety.
Yes, they are designed for both high-precision tasks and repetitive, high-volume applications, provided the drills are used within their operational specifications.
Repairability depends on the extent of the damage. Minor wear might be addressable, but significant damage often requires replacement. Consult us for repair and retipping services.
Proper mounting, alignment, and using equipment with precise adjustment capabilities are key to maintaining concentricity.
Yes, SMART CUT Diamond Core Drills can be used for depth-controlled drilling, especially when used with precision drilling equipment that allows for depth settings.
these diamond core drills are ready to use right out of the box. These is no break in process or procedure that is needed.
Regular cleaning with appropriate solutions to remove debris and coolant residues is recommended. Store the drills in a dry, cool place and handle them carefully to avoid damage.
These drills are commonly used in industries like electronics, optics, semiconductors, materials research, and any other industry requiring precision drilling in hard materials.
The diameter of the drill determines the size of the hole it can create. Smaller diameters are used for precise, fine drilling, while larger diameters are used for bigger holes.
Yes, these drills are suitable for use on CNC machines, as long as the machine can accommodate the drill’s specifications and mounting requirements.
Common troubleshooting steps include checking for correct drill and material alignment, ensuring appropriate coolant flow, verifying speed settings, and inspecting the drill for wear or damage.
Store the drills in a dry, dust-free environment, away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Proper storage can significantly prolong the life of the drills.
The inside diameter tolerance affects the precision of the hole size. Tighter tolerances result in more accurate hole sizes, which is crucial in precision applications.
If the drill is not cutting efficiently, check for dullness, ensure proper coolant use, verify the material type being drilled, and adjust the drilling parameters accordingly.
These drills are designed for ultra-hard and brittle materials and may not be suitable for metals. Consult with the manufacturer for drills specifically designed for metal applications.
The choice of coolant is crucial as different materials may react differently to heat and stress during drilling. Using the correct coolant ensures optimal drilling performance and prevents material damage.
Yes, these drills are suitable for educational settings where precision drilling is taught or required, such as in material science or engineering courses.
Drill speed affects the quality and accuracy of the hole. Too fast may lead to overheating and material damage, while too slow may result in inefficient drilling. Optimal speed ensures a balance between efficiency and quality.
Accurate alignment requires a stable drilling setup, precise measurement tools, and careful setup procedures. Follow the drilling machine manufacturer’s guidelines and use appropriate jigs or alignment tools as needed.
Always use appropriate personal protective equipment, ensure a stable and safe working environment, and follow health and safety guidelines for handling sharp tools and dealing with drilling debris.
Material thickness affects the drill’s performance and the required drill depth. Thicker materials may require slower drilling speeds and more attention to heat dissipation.
These drills are designed for circular holes. For non-circular shapes, different tooling or techniques would be required.
The drill depth is limited by the drill’s length and design. The specifications include maximum drill depths, which should be adhered to for optimal performance. The drill depth is usually in proportion to diameter of the diamond core drill.
Yes, follow the equipment manufacturer’s guidelines for changing drills, ensuring that the replacement drill is properly mounted and aligned for safe and effective operation.
Yes, these drills can be used with robotic drilling systems, provided the system can accommodate their specific size and mounting requirements.
Higher diamond concentration typically offers longer life and a smoother finish, while lower concentration may allow for faster cutting but shorter drill life.
While these drills are designed for ultra-hard materials, drilling materials like diamond or carbide may require specialized drills. Consult with us for guidance on these specific applications.
In the event of drill bit breakage, immediately stop the operation, safely remove the broken pieces, and inspect the equipment for damage. Assess the cause of breakage to prevent future occurrences.
Yes, their high precision and quality make them ideal for use in precision engineering applications where exact tolerances and finishes are required.
Excessive runout can lead to holes that are larger than the drill’s nominal diameter, and can also cause uneven wear on the drill, reducing its life and precision.
The maximum material thickness these drills can handle effectively is determined by the drill depth specification. Exceeding this depth can lead to reduced effectiveness and potential damage to both the drill and the material.
The angle of entry affects the initial contact between the drill and the material. A perpendicular entry is generally recommended for precision, while angled entries require specialized setups to maintain accuracy.
Yes, these drills can be used for enlarging holes, but it requires careful alignment and control to ensure precision and avoid damage to both the drill and the material. Usually flat bottom type of drills are used for that application.
Regular cleaning, dressing, proper storage, and using them within their specified operational limits are key maintenance practices. Avoid dropping or mishandling the drills to prevent damage.
For the best hole quality, use the correct drill size and type for the material, maintain a stable drilling setup, use appropriate coolant, and drill at the recommended speed and feed rate.
Drilling on irregular surfaces can be challenging and requires a stable setup and possibly a specialized guide or jig to maintain accuracy.
Avoid using these drills in extreme temperatures, as it can affect both the material being drilled and the drill itself. Ensure the drilling environment is stable and within a reasonable temperature range.
The interior finish of holes drilled with these diamond core drills is typically smoother and more precise compared to other drilling methods, especially in hard and brittle materials.
If the drill becomes stuck, stop the drilling process immediately and carefully attempt to reverse the drill out. Avoid applying excessive force to prevent breaking the drill.
Yes, these drills can be used in both vertical and horizontal drilling setups, as long as the drill is properly aligned and securely mounted.
Using the drills at excessively high speeds can lead to overheating and rapid wear, reducing their lifespan. Conversely, too low speeds can result in inefficient drilling and unnecessary pressure on the drill.
Signs include a noticeable decrease in drilling efficiency, difficulty in achieving clean and precise holes, visible wear on the drill bit, and increased vibrations during drilling.
Drilling in a vacuum environment requires specialized equipment and considerations for drill cooling and debris removal. Consult with technical experts for guidance on such setups.
The mounting type affects how the drill is secured to the drilling equipment. The right mounting ensures stability and precision, and should be compatible with the drilling machine used.
Yes, their precision and ability to drill small, accurate holes make them suitable for microfabrication applications, particularly in electronics and materials research.
For shallow depths, precise control over the drill’s penetration is crucial. Using a drill press with depth stop settings and operating at lower speeds can help achieve accurate results.
Material density affects the drilling speed, feed rate, and coolant flow required. Denser materials typically require slower speeds and higher feed rates, along with efficient cooling.
Yes, but it requires careful consideration of the drill parameters for each layer’s hardness. Consistent coolant flow and controlled feed rates are essential to manage the transition between layers.
The right coolant reduces thermal stress and removes debris effectively, which can significantly extend the drill’s lifespan. Using inappropriate coolant can lead to premature wear or damage.
When drilling at high speeds, ensure the drill is well-cooled, the material is securely clamped, and the drill is properly aligned. It’s also important to gradually increase to high speeds to prevent shock to the drill and material.
Drilling in thin films or membranes requires extremely precise control and the right drill size to prevent material damage. Consult with us for recommendations on such applications.
Post-drilling treatments like deburring or polishing may be required, depending on the application and material. These treatments ensure the quality and functionality of the drilled holes.
Yes, these drills are suitable for composite ceramics. However, the specific drilling parameters should be adjusted based on the material’s properties.
The inside diameter of the drill determines the size of the core sample. It’s important to select a drill with an inside diameter that matches the required core sample size.
When drilling in extremely brittle materials, use lower feed rates, ensure stable support for the material, and maintain consistent coolant flow to prevent cracking or chipping.
While it’s possible to use these drills in hand-held drill presses, stationary equipment is recommended for greater stability and precision, especially for very small or precise holes.
The outside diameter tolerance impacts the accuracy of the hole size. Tighter tolerances ensure that the drilled hole closely matches the specified diameter, which is critical in precision applications.
These drills are designed for creating smooth holes. Creating threaded holes in hard materials typically requires additional specialized tools tools which we produce as well. Contact us for assistance
Assess the quality by examining the hole’s diameter accuracy, smoothness of the walls, and the absence of cracks or chips. Use precision measuring tools for accurate assessment.
Drilling angled holes in curved surfaces is challenging and requires specialized setup and equipment. Consult with technical experts for guidance on such specific applications.
Yes, with extreme precision and the right setup, these drills can be used for delicate materials like optical fibers. However, specialized techniques and handling are required to prevent damage.
For repeated drilling, ensure the material is stable and not overheated. Regularly check the drill for wear and adjust drilling parameters if necessary to maintain consistency and quality.
Proper drill alignment is crucial for achieving accurate hole locations and dimensions. Misalignment can lead to off-center holes, irregular shapes, or damage to the material. This is specially true for very small diamond core drills
Yes, but it’s important to manage heat effectively through appropriate coolant use and drilling parameters, as materials with high thermal conductivity can quickly dissipate heat, affecting drilling efficiency.
It’s generally recommended to proceed in gradual depth increments, especially for deeper holes, to allow for debris removal and prevent excessive heat buildup.
These drills are designed for standard, straight holes. Creating undercuts or non-standard profiles typically requires specialized tooling or techniques.
A smoother surface finish can aid in achieving more precise and clean holes, while a rough surface may require adjustments in drilling speed and pressure to maintain accuracy.
For crack-prone materials, use lower feed rates, ensure adequate support for the material, and apply consistent, gentle pressure. Also, using the appropriate coolant is crucial to prevent thermal stress.
Consistent hole diameters require regular monitoring of drill wear, maintaining stable drilling conditions, and replacing the drill once it shows signs of significant wear.
Yes, their precision and ability to drill hard, brittle materials make them suitable for medical device manufacturing, where exact dimensions and clean holes are critical.
Safety precautions include using protective eyewear and gloves, ensuring a stable drilling setup, and being aware of the high temperatures that can be generated during drilling
To manage vibrations, ensure the drill and material are securely mounted, use the correct drilling speed, and apply steady, controlled pressure. Excessive vibrations can indicate misalignment or an unsuitable drilling speed.
While they may be used for some advanced materials, it’s important to understand the specific properties of the material and adjust drilling techniques accordingly. Consult with experts for materials like nanocomposites.
Diamond core drills typically have a lower wear rate when used correctly, especially compared to standard drills, due to their hard diamond cutting surfaces and robust construction.
Yes, these drills are well-suited for automated manufacturing processes, especially where precision and repeatability are crucial. Ensure the automated system is compatible with the drill specifications.
The material hardness determines the required diamond grit size and bond type. Harder materials typically require a finer grit and a stronger bond to ensure effective drilling and longer drill life.
While diamond core drills are versatile, extreme drilling angles may require specialized equipment and setup for accurate and effective drilling.
While primarily designed for drilling, with the right setup and appropriate drill sizes, they can potentially be used for detailed work or engraving on hard materials.
The appropriate drill speed varies depending on the material’s hardness, thickness, and the desired finish. Refer to the our RPM’S guidelines and start with a lower speed, gradually increasing as needed.
Diamond core drills have good chemical resistance, but it’s important to use compatible coolants and be aware of any chemical interactions with the materials being drilled.
Yes, these drills are suitable for precision drilling in aerospace components where high accuracy and quality are essential. Ensure the drill specifications match the requirements of the aerospace materials.
In low-temperature environments, ensure the material and drill are not overly brittle. Adjust the drilling speed and pressure accordingly to account for potential changes in material properties.
The feed rate depends on the drill size, material hardness, and desired hole quality. For deeper holes, a slower feed rate may be necessary to prevent overheating and ensure effective debris removal.
Yes, their precision and ability to drill hard materials make them ideal for material science research, where controlled and accurate drilling is required.
First-time users should familiarize themselves with the drill specifications, start with lower speeds in the recommended rpm’s range and slower feed rates, and gradually adjust as they become more comfortable with the drill’s performance.
Diamond core drilling offers mechanical precision and is generally more cost-effective for bulk material removal compared to laser drilling with less surface deformation and stress to the materials. Specially when drilling deeper holes. However, laser drilling might provide better control for extremely small or complex features.
Dressing of diamond core drills can be done by drilling into dressing stone several times to wear away the metal layer in order to exposé the diamond crystals and sharpen the diamond crystal at the same time.
Diamond core drills are durable and long-lasting, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This durability can lead to less waste and a lower environmental impact over the tool’s lifetime.
Proper alignment involves carefully mounting the drill in the machine, checking for any runout or misalignment, and making necessary adjustments to ensure the drill is perfectly centered and stable
Yes, their precision makes them suitable for the fabrication of electronic components, especially when drilling is required in hard or brittle materials like ceramics or certain composites.
Larger diamond grit sizes typically allow for faster drilling but may result in a rougher finish, while finer grit sizes drill slower but produce a smoother finish.
Store the drills in a dry, stable environment away from extreme temperatures and humidity. Protective cases or holders can prevent physical damage and contamination
Thicker materials require more careful management of drilling parameters, such as speed and coolant flow, to ensure efficient drilling and prevent overheating or excessive wear.
Yes, these drills are well-suited for drilling in geological samples where precision and minimal sample disturbance are required.
Safety protocols include wearing protective gear, ensuring stable and secure drilling setups, and being aware of the high rotational speeds and potential for flying debris.
The diamond core drill design, particularly the relief/clearance between the steel tube and diamond section, greatly impacts how effectively debris is removed from the drilling site, which is crucial for maintaining drilling efficiency and preventing overheating.
Drilling advanced materials like graphene or carbon nanotubes requires specialized techniques. Consult with material experts and us for the suitability and optimal drilling parameters.
The primary lubrication for these drills comes from the coolant used during drilling. Using the right coolant is essential for both lubrication and temperature control.
Higher quality diamonds typically provide better cutting performance, longer life, and more consistent results. The quality of the diamonds is a key factor in the overall performance of the drill.
Drilling at oblique angles is possible but requires careful setup to ensure accuracy and prevent the drill from slipping or causing material damage.
Monitor drilling performance and efficiency regularly. Visible signs of wear, decreased drilling speed, or a reduction in hole quality
To reduce heat generation, use adequate coolant flow, drill at the recommended speed, and avoid excessive feed rates. Ensuring sharpness of the drill also helps in reducing heat by improving cutting efficiency.
While primarily designed for hard, brittle materials, with careful setup and appropriate parameters, these drills can be used on thin metal films on hard substrates. Consult with us for specific guidance.
Excessive feed pressure can lead to drill breakage or damage to the material. Conversely, insufficient pressure can result in inefficient drilling. It’s important to find a balance that allows efficient cutting without overstressing the drill or material.
High RPMs can increase the risk of overheating, while low RPMs may lead to inefficient drilling. It’s crucial to adjust the coolant flow and feed rate accordingly and to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for optimal RPMs.
For vibration-sensitive materials, use a stable drilling setup, appropriate drill speeds, and secure clamping to minimize vibration. It’s also helpful to select a drill with a design that inherently produces less vibration.
The appropriate diamond depth depends on the material’s hardness and abrasiveness, as well as the desired drilling lifespan. Harder, more abrasive materials typically benefit from a deeper diamond layer for extended durability. As they wear the diamond section much faster.
For temperature-sensitive materials, use coolants that maintain a consistent temperature and effectively remove heat from the drilling area. It’s also important to ensure that the coolant does not chemically react with the material.
Drilling in composite materials with mixed hardness requires careful selection of drilling parameters to account for the different material properties. Consult with the us for advice on handling such materials.
How does the interior diameter tolerance of these drills impact their use in precision applications?
The interior diameter tolerance directly affects the diameter tolerance of the core size and the uniformity of the core samples, if extracted. Tight tolerances are crucial for applications where dimensional accuracy is critical.
After use, clean the drills with an appropriate solvent to remove debris and coolant residues. Dry them thoroughly before storage, and handle them carefully to avoid any damage to the cutting edges.
Creating holes with a tapered profile typically requires specialized drill bits designed for that purpose. Standard diamond core drills are designed for creating straight, cylindrical holes. Consult with us for required tools for that application.
The outside diameter tolerance influences how precisely the hole will fit with other components, especially in applications requiring tight assembly tolerances. More precise tolerances lead to a better fit and alignment. More precision tolerances are available upon request at additional cost
Yes, diamond core drills can produce a high-quality surface finish inside the hole, but the finish quality also depends on the material being drilled and the drilling parameters used
The optimum diamond size and concentration depend on the material hardness, the required drilling speed, and the desired hole quality. Consult with us for recommendations based on your specific application.
ACCESSORIES
Showing 1 – -1 of 16 results Showing all 16 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Name A – Z
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
Image | Item No. | Description | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Color: 5/8″-11″ thread. Fits into drill press chuck. Shank adapter threads into 5/8″-11″ female thread of diamond drill. Can be used with any other tool with 5/8″-11″ thread. | $26.72 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
Color: 5/8″-11″ thread. Fits into drill press chuck. Shank adapter threads into 5/8″-11″ female thread of diamond drill. Can be used with any other tool with 5/8″-11″ thread. | $22.46 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1 Gallon Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $99.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1 Quart Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $34.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
5 Gallons Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $317.41 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
55 Gallons Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $1,745.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1/2″ x 1/2″ x 6.0″ White Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $8.65 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ White Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1/2″ x 1/2″ x 6.0″ White For use on diamond tools 150 to 220 Grit Size. | $8.65 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh size) or finer. | $15.39 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0″ x 2.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh size) or finer. | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0″ x 2.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
$154.87 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||
$154.87 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||
$235.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
Showing 1 – -1 of 26 results Showing all 26 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Price low to high
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
Image | Item No | Outside Diameter | Inside Diameter | Drill Depth | Diamond Depth | Quantity | Get Quote |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.0275” (0.7mm) | .0137” (0.35mm) | 3mm | 4mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
.0315” (0.8mm) | .016” (0.4mm) | 4mm | 4mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
.0355” (0.9mm) | .0175” (0.45mm) | 5mm | 4mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
.040” (1.0mm) | .020” (0.5mm) | 5mm | 5mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
.0435” (1.1mm) | .022” (0.55mm) | 5mm | 5mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
.047” (1.2mm) | ,0235” (0.6mm) | 6mm | 5mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
.051” (1.3mm) | .0255” (0.65mm) | 6mm | 5mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.4mm | 0.7mm | 8mm | 7mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.5mm | 0.75mm | 8mm | 7mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.6mm | 0.8mm | 9mm | 7mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.7mm | 0.85mm | 10mm | 7mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.8mm | 0.9mm | 10mm | 7mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.9mm | 0.95mm | 10mm | 7mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0mm | 1.0mm | 10mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.1mm | 1.05mm | 10mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.2mm | 1.1mm | 11mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.3mm | 1.15mm | 11mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.4mm | 1.2mm | 11mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.5mm | 1.25mm | 11mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.6mm | 1.3mm | 12mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.7mm | 1.35mm | 12mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.8mm | 1.4mm | 12mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.9mm | 1.45mm | 12mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
3.0mm | 1.5mm | 13mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
3.1mm | 1.55 | 13mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
3.2mm | 1.6mm | 13mm | 10mm | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
Advantages:
- Longer Life
- Less Chipping
- Faster & Freer cutting action
- Less Material Stress
- Consistent Performance
- Smoother Surface Finish
- Less Heat Generation
Features:
- High Quality Diamond Crystals & Materials
- High Quality & Consistent Manufacturing Process
- Preserves True Material Micro Structure
- Excellent Value (return on investment)
- High Quality & Consistent Manufacturing Process
- Dozens of Sizes available from stock
- Custom Manufacturing (almost any diameter, shape, head length)
Application (Materials Used on)
SMART CUTTM Series Micro & Miniature Diamond Core Drills provide the most excellent performance large spectrum of ultra hard, brittle, and dense materials such as:
- Alumina
- Glass
- Quartz
- Ruby
- Sapphire
- Yag
- Silicon
- Fused Quartz
- Bk7
- Many Other Materials
Equipment Used on:
- High Speed Drill Press Mounted Hand
- Piece Drill (such as: Foredom & Dremel),
- High Speed Air Spindles
How SMART CUT ® Bond Works?
Step 1
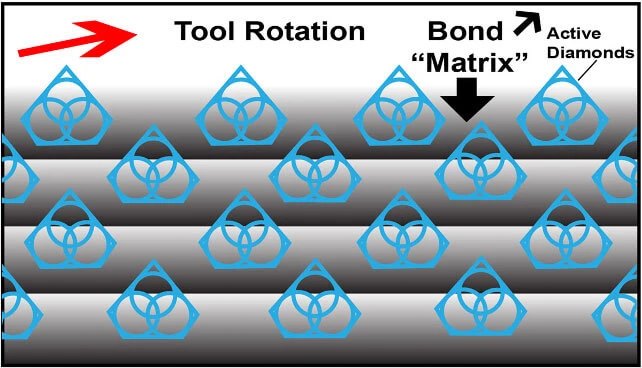
Diamonds or CBN Crystals
Diamonds or CBN Crystals are activated only at the exposed layer. As Bond Matrix layer begin to wear out, diamonds in a new Bond Matrix layer are immediately activated, substituting the already used up diamond layer. The SMART CUT® Diamond Hybrid Bond makes sure every diamond is in the right place and at the right time, working where you need it most.
Step 2
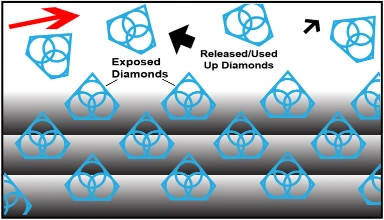
Sharpest And Finest Quality Diamonds
The newly exposed diamonds don’t effect diamonds already working on the material. Unlike many other diamond bonds, diamonds in a SMART CUT® Bond remains sharp and grow sharper with each cut, prolonging product life and consistent performance.
Step 3
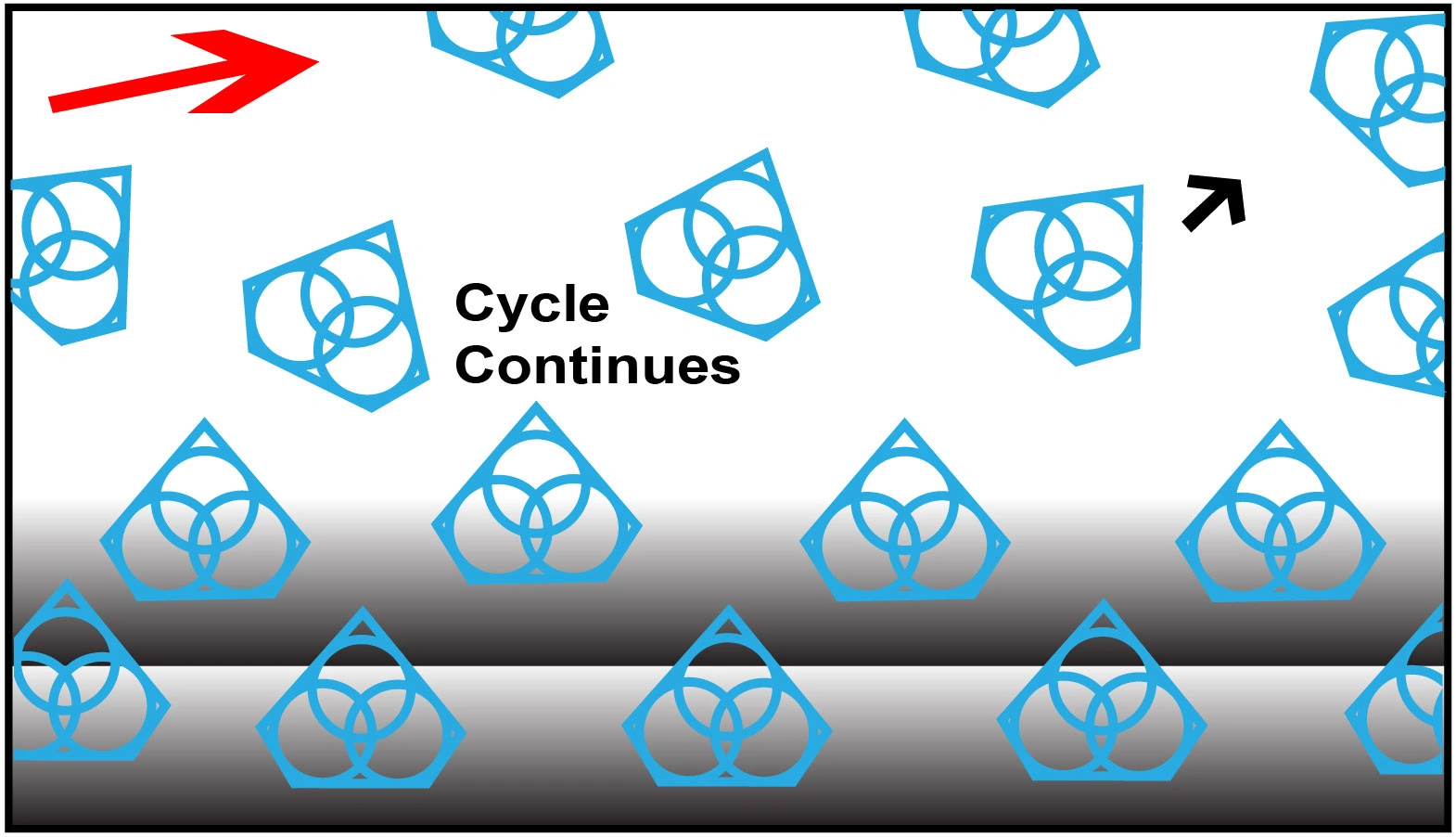
Advanced Formulated Open Diamond Bond Design
This advanced formulated open diamond bond design insures minimal chipping, fast cut, constant speed of cut, minimal cutting noise, and most important of all, consistent performance.
Diamond & Core Drill
Selection Variables

Diamond Concentration
Diamond concentration plays a critical role in determining the life and cutting speed of diamond core drills. Higher concentration offers longer tool life and faster cutting speeds, while lower concentration is typically used for softer materials that require a smoother finish.

Drilling Speed/RPMs
Diamond core drills generally operate at RPMs between 500 and 3,000, depending on the material being drilled. Softer materials allow for higher RPMs, while harder materials require slower speeds for improved cutting efficiency and to avoid damaging the tool or material. Always adjust RPM according to the specific characteristics of the material and drill size.

Diamond Particle/Grit size
The diamond grit size is crucial in determining the cutting speed, surface finish, and precision of diamond core drills. Finer grits provide a smoother surface finish, but may cut more slowly, while coarser grits offer faster cutting speeds but can leave a rougher surface. The choice of grit size depends on the material being drilled and the desired outcome.
Bond Type
The bond type used in diamond core drills influences the drill’s life, durability, and heat resistance. Common bond types for diamond core drills include: Sintered (Metal Bond): Provides a longer tool life and high resistance to wear and heat, making it ideal for drilling hard and abrasive materials. Electroplated: Offers a good combination of speed and precision, typically used for softer materials or applications where a smoother surface finish is needed. Braised Bond: Ideal for applications requiring higher strength, these bonds are used for tougher materials and applications where durability is key. PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond): Used for ultra-hard materials, PCD bond drills offer excellent wear resistance and are ideal for materials like ceramics and composite materials. CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Diamond: Offers exceptional cutting performance, often used in extremely hard materials like high-performance ceramics and advance.
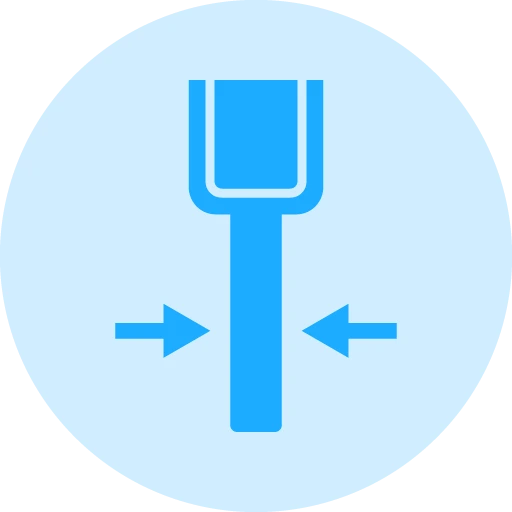
Kerf (Wall) Thickness
The kerf, or wall thickness, of diamond core drills is a key variable in determining the overall performance of the drill. Standard core drills typically feature a kerf thickness ranging from 0.5mm to 3.0mm, with thicker kerfs providing longer tool life and greater stability during drilling. Thinner kerfs allow for faster cutting but may wear out quicker and require more frequent maintenance. The selection of kerf thickness depends on the material being drilled and the precision required.

Feed Rates
The load/feed rate applied to diamond core drills significantly impacts their performance and lifespan. For tougher materials, feed rates typically range between 5-50 mm/min, while softer materials may allow for higher feed rates. Proper feed rate adjustment ensures optimal tool life and drilling speed, while preventing overheating or excessive wear.
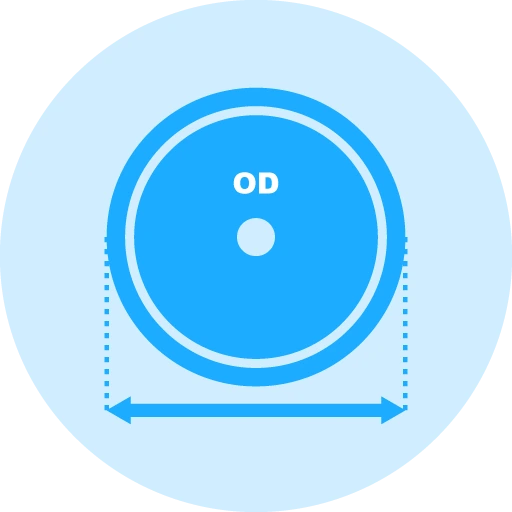
Core Drill Diameter
The diameter of the diamond core drill is directly related to the size of the hole you wish to create. Core drills typically range from small diameters (e.g., 3mm) up to large diameters (e.g., 200mm or more). Larger core drills offer greater drilling capacity, while smaller ones provide more precision for fine hole making.

Drilling depth
The depth of a diamond drill bit, often referred to as drilling depth, working length, or drilling length, is the maximum depth to which the drill can penetrate the workpiece. Drilling depth in diamond core drills depends on the material, drill size, and equipment. Softer materials allow for deeper holes with faster cutting, while harder materials require slower speeds and lower feed rates to prevent overheating. Larger drill diameters may reduce depth due to more material removal per rotation, often requiring multiple passes. Drilling equipment, including motor power and cooling systems, also plays a key role; more powerful motors and efficient cooling allow for deeper drilling.
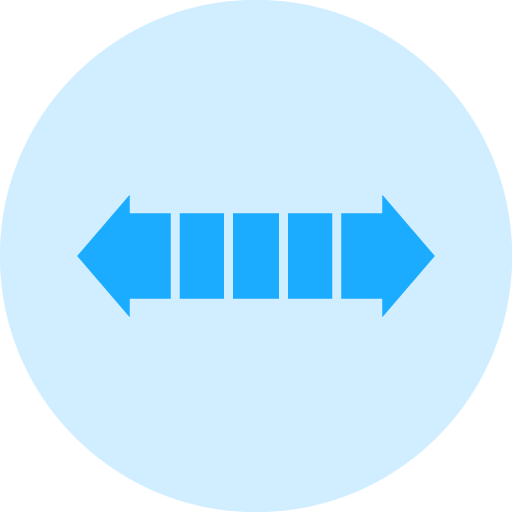
Bond Hardness
For diamond core drills, the bond hardness plays a crucial role in the performance and longevity of the drill. The bond matrix's ability to retain diamonds directly impacts the drilling efficiency and the tool's lifespan. As the hardness of the bond increases, the retention of diamonds improves, but the trade-off is typically a slower cutting speed. A harder bond matrix provides greater tool life but may lead to reduced cutting efficiency.
There are generally three categories for bond hardness in diamond core drills: Soft, Medium, and Hard. The bond's hardness is selected based on the material being drilled. For example, harder materials such as ceramics or hard metals often require a softer bond to allow the diamonds to be released at a controlled rate, preventing excessive wear and improving cutting performance. Conversely, softer and more brittle materials like concrete or certain composites benefit from a harder bond, which maintains the diamond's retention and extends the drill's lifespan, though it may slow the cutting process.
Using the right bond hardness for the material you're drilling is key to optimizing both cutting speed and tool life. A bond that is too soft will cause diamonds to be released too quickly, resulting in faster wear and a shorter drill life. On the other hand, a bond that is too hard may cause the drill to cut slower and require more frequent dressing to expose new diamonds.

Mounting Type
The mounting type of a diamond core drill refers to how the drill is secured to the drilling machine or equipment. The mounting type plays a significant role in stability, precision, and overall drilling performance. Here are the typical mounting types for diamond core drills:
Unmounted diamond core drills:
Unmounted diamond core drills are specialized tools designed for precision drilling without being pre-mounted to any specific holding mechanism such as a male, female, or straight shank. These drills comprise a steel tube paired with a diamond-embedded segment, offering flexibility in setup and application.
Shaft Mounting:
In this type, the diamond core drill is mounted directly onto a shaft or spindle of the drilling machine. The shaft typically has a locking mechanism (like a set screw or collar) to securely hold the drill in place. This mounting method ensures a stable connection and allows for precise drilling. Shaft mounting is commonly used in machines where the drill operates at high speeds and requires excellent stability.
Threaded Mounting:
Some diamond core drills feature a threaded arbor or core bit holder, allowing the drill to be screwed directly onto the machine's spindle. This method is commonly found in portable core drilling systems or for specific applications like wet drilling, where easy removal and installation are essential.
Choosing the right mounting type for your diamond core drill depends on factors such as the size of the drill, the type of drilling machine, and the specific application requirements. Proper mounting ensures optimal performance, stability, and safety during the drilling process.

Tolerances on Outside or Inside Diameter
The tolerance range for the outside diameter of diamond core drills varies depending on several factors including the drill's diameter, wall thickness, bond type, and the intended application. These tolerances are crucial as they determine the drill's suitability for precision tasks and influence how the drill interacts with the material it cuts.
For small diamond core drills with diameters less than 10mm, the diameter tolerance typically ranges from ±0.02 to ±0.05 mm. This tight tolerance is necessary for applications that require high accuracy, such as in electronics or medical device manufacturing, where small, precise holes are crucial.
Medium-sized drills, ranging from 10mm to 50mm in diameter, usually have a tolerance of ±0.05 to ±0.15 mm. These are commonly used in mechanical applications and construction where slightly larger variances are acceptable.

Run Out
Runout is a critical specification for diamond drills as it directly impacts the quality of the holes drilled and the longevity of the tool itself. The term "runout" refers to the degree to which a tool or workpiece deviates from perfect rotation along its central axis. High runout can lead to uneven wear on the tool, compromised hole quality, and increased heat generation, which are particularly detrimental when drilling hard, brittle materials such as glass, ceramics, and certain stones where precision is critical.
Standard and Precision Diamond Drills - Standard diamond drills typically exhibit runout ranging from 0.0005 inches (0.013mm) to 0.002 inches (0.05mm), which is acceptable for general-purpose drilling where absolute precision is not necessary. However, "standard" runout may vary based on the drill's manufacturer and specific applications. Precision diamond drills, manufactured to higher standards with stricter tolerances, usually have runout less than 0.0002 inches (0.005mm), with ultra-precision drills potentially having even tighter runout specifications.

Faster Cutting Action
Diamond & CBN tools made utilizing SMART CUT® technology are much more aggressive than your conventional tools. They can cut faster, while still leaving behind a smooth finish free of material deformation.

Longer Life
In most cases tools manufactured utilizing SMART CUT® technology, will outlast other conventional material (sintered), resin, and nickel bonded diamond & CBN tools. SMART CUT® diamond & CBN tools are more sturdy than tools manufactured with conventional technologies. They are capable to retain their form and bond configuration all the way through the tools life.

More Consistent Performance
SMART CUT Sintered (Metal Bond) Tools have diamonds crystals oriented and evenly positioned inside bond matrix. Unlike Many Other Tool Types, they wear evenly, and are known for their consistency. You will get consistent cutting speed, and overall consistent performance, with minimum amount of dressing even on the hardest to cut materials
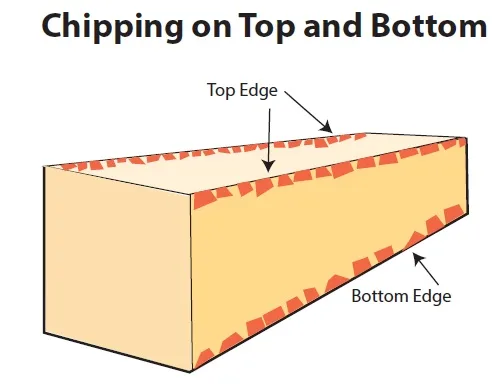
Minimize Chipping & Improve Surface Finish
SMART CUT® Sintered (Metal Bond) Tools have diamonds oriented and evenly distributed in a bond matrix. Providing faster, freer cutting action with minimum heat generation. This translates in improved surface finish and minimum chipping.

Best Performance & Value on the Market
SMART CUT® Sintered (Metal Bond) Diamond Tools are the best investment you can make! Although they may cost more than some Sintered (Metal Bond) Tools. They will more than pay for themselves in terms of overall performance and provide best Return on Investment.

Manufactured Using The Highest Quality Raw Materials
Only the highest quality synthetic diamonds and raw materials are used in the manufacturing process. The highest quality standards and product consistency is maintained, using sophisticated inspection and measurement equipment.
Related Products
SMART CUT® Micro & Miniature Core Drills
SMART CUT® Micro & Miniature Diamond Core Drills
SMART CUT® 010DME (SMCDU)
SMART CUT® 010DME Diamond Micro Drills represent a major advancement in precision micro-machining technology, specifically engineered to meet the challenges of drilling hard, brittle, and high-tech materials used across industries such as semiconductor, optics, advanced ceramics, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
These drills are widely used in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing for creating microscopic precision holes in wafers, essential for thermal management, electrical connectivity, and overall chip reliability. In optical engineering, they enable accurate hole placement in the assembly of lenses, mirrors, and optical components. In the medical field, they deliver consistent hole geometry and size control, which is vital for implant safety and precision assembly.
They are equally valuable in the aerospace and automotive industries, where components demand extremely tight tolerances and involve materials that are difficult to machine. The accuracy, stability, and repeatability of the SMART CUT® 010DME drills ensure defect-free holes in these critical applications, preventing system failures due to dimensional deviations.
CVD Micro Drills
Micro Drills
SMART CUT® CVD diamond micro drills are used for drilling micro holes in large variety of hard and brittle materials such as sapphire, high density ceramics, micro-circuit substrates, glass, silicon, various wafers, substrates, tubes etc We offer large variety of standard stock & custom micro drills from 0.05mm diameter to 6mm. with 3mm and 3.2mm shanks, and various heald lengths from 0.5mm and up, and flute specifications.PCD (Polycrystalline) Micro Drills
Diamond Micro Drills
SMART CUT® PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond) Micro Drills are precision-engineered tools designed for applications that demand exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional accuracy. They are available starting from 0.4 mm in diameter, with a wide selection of head lengths and standard shank diameters of 3 mm and 3.2 mm. Each drill features a sintered polycrystalline diamond tip bonded to a carbide or tungsten substrate, providing superior rigidity, heat resistance, and extended tool life. These micro drills are widely used in the semiconductor, electronics, EDM electrode manufacturing, and die and mold industries. In semiconductor production, they are used for machining monocrystalline silicon, inspection and cleaning jigs, and precision fixture fabrication. In EDM electrode manufacturing, they are ideal for drilling graphite electrodes and other hard-to-machine materials that quickly wear down conventional tools.SMART CUT® Diamond & CBN Micro Drills, Sintered (Metal Bond)
Carbide Micro Drills
SMART CUT® 005DME MCDU
SMART CUT® 005DME Diamond Micro Drills represent a major advancement in precision micro-machining technology, specifically engineered to meet the challenges of drilling hard, brittle, and high-tech materials used across industries such as semiconductor, optics, advanced ceramics, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
These drills are widely used in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing for creating microscopic precision holes in wafers, essential for thermal management, electrical connectivity, and overall chip reliability. In optical engineering, they enable accurate hole placement in the assembly of lenses, mirrors, and optical components. In the medical field, they deliver consistent hole geometry and size control, which is vital for implant safety and precision assembly.
They are equally valuable in the aerospace and automotive industries, where components demand extremely tight tolerances and involve materials that are difficult to machine. The accuracy, stability, and repeatability of the SMART CUT® 005DME drills ensure defect-free holes in these critical applications, preventing system failures due to dimensional deviations.
Recently Viewed Products
Related Products
Silicon Carbide Paper new
SMART CUT® Silicon Carbide Abrasive Paper is meticulously designed for preparing metallographic specimens, incorporating superior silicon carbide grains embedded in a resilient, waterproof backing for both dry and wet grinding. This versatile paper transitions smoothly from coarse cutting to fine polishing, ensuring that specimens are precisely prepared for microscopic analysis.
Recently Viewed Products

ARE YOU USING RIGHT DIAMOND CORE DRILLS & TOOLS
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET US
HELP YOU
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT DIAMOND CORE DRILLS & TOOLS?
Knowledge Center
02
Jun
Learn important diamond drill methodology. understand diamond drill specifications and their differences Selecting the right Diamond Drills/Bits for your application is key to obtaining desired diamond drilling results. Using the Right Diamond Drill will...
02
Jun
How to Properly Use Precision Diamond Drills
Step by step guide on how to properly use and care for your diamond drills. Selecting the right diamond drill/diamond drill bit parameters, often involves a trial and error process. Many which can be avoided...
02
Jun
Diamond Core Drills: Materials, Applications & Selection Guide
Diamond are used across large variety of industries and applications. This guide explores the wide range of diamond drill types, including hollow core drills designed for removing a cylindrical core, non-core formation drills that grind...
02
Jun
Diamond Tools Guide – Selecting Right Drills & Tools for your application
These tools are used for many different industries grinding and shaping material into different forms, expanding exiting inside diameters, grinding, finishing and polishing existing material. Grinding different angles and radius, creating cavities of various forms,...
02
Jun
Optimizing your Diamond Drilling Operation
There are numerous factors that influence the performance of diamond drills. Understanding these factors helps users select the appropriate diamond drill specifications for their specific applications, optimizing drilling operations to achieve maximum efficiency....
02
Jun
Micro Drilling Guide
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
In order for you to get the most out of your diamond micro drill or carbide / high speed steel micro drill, we strongly urge you to read...
02
Jun
Selecting Right Drilling Equipment for your Application. What you features & functionality you should look for?
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
There are hundreds or even thousands of different drilling equipment options. Selecting the right equipment for a specific application involves carefully considering several variables and attributes of the...
03
May
Diamond Core Drill & Drill Trouble Shooting Guide
Learn the most common problems most people have in using diamond drills. How to resolve them and avoid them in first place
https://ukam.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/diamond-drill-troublehsooting-guide.mp4
Troubleshooting Drilling Problems
Having issues with your diamond drilling operation? This Illustrated Guide...
09
Sep
Understanding & Calculating Return on Investment for Diamond Core Drills & Other Tools
The term "ROI" (Return On Investment) is widely used across industries, often interpreted differently depending on the context. However, few truly understand what ROI represents and its specific implications, particularly in the context of diamond...
09
Sep
Understanding Tradeoffs – Searching for Perfect Diamond Drill & Tool
Choosing the right diamond drill or tool can significantly impact efficiency, cost, and quality. However, this is not a simple and clear-cut process. Selecting the optimal drill or tool involves navigating a complex landscape of...
19
Sep
Why Use Diamond Drills?
Diamond, known as the hardest material on Earth, enables diamond drills and tools to grind away material at a micro (nano) scale. This extreme hardness allows diamond tools to effectively work on materials with a...