Wafering Blade Case Studies
-
Posted by
 Carlos Sanchez
Carlos Sanchez

Table of Contents
ToggleDiamond & CBN Wafering Blade Case Studies
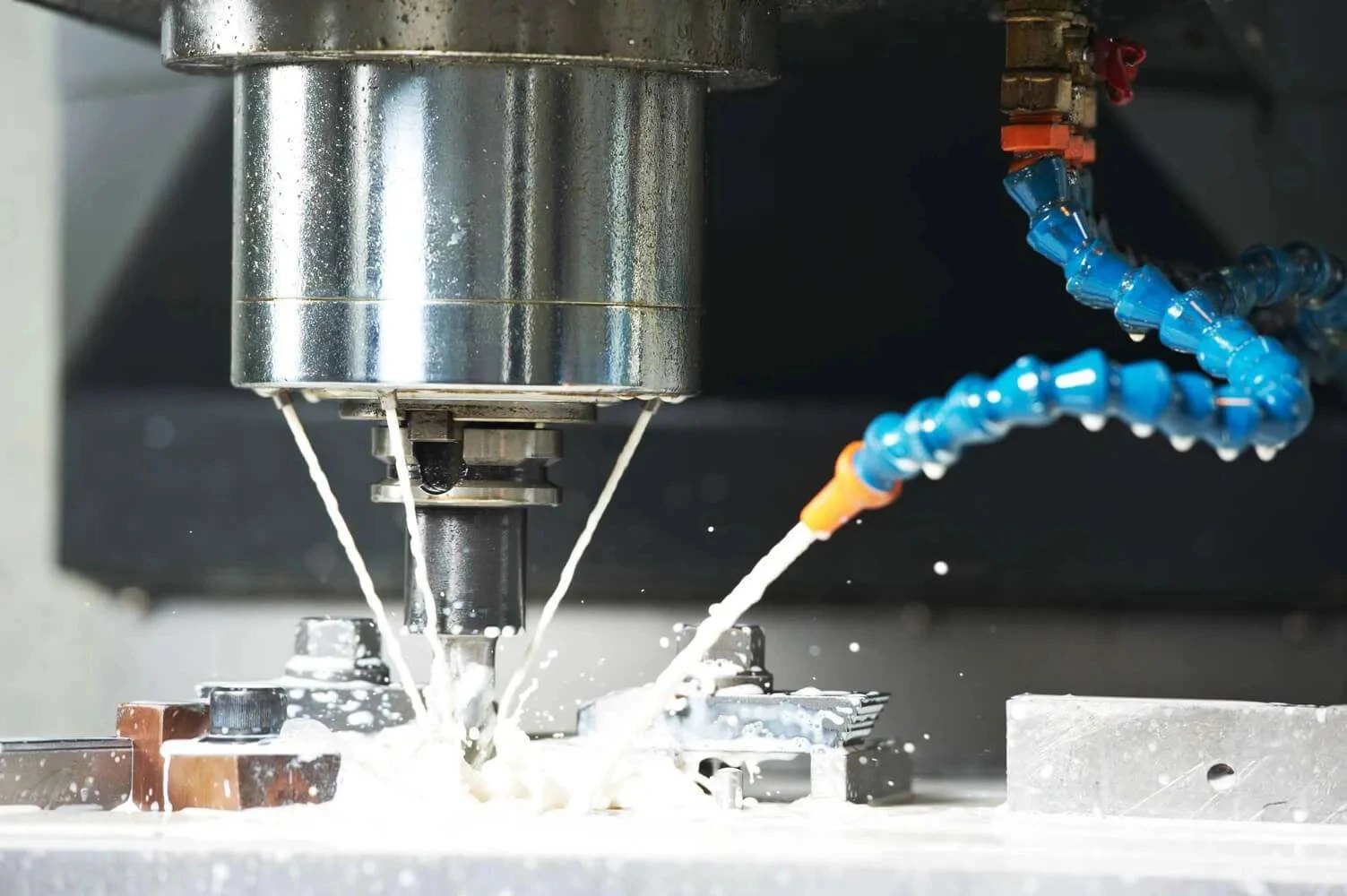
This study evaluates the cutting performance of SMART CUT® Diamond & CBN Wafering Blades compared to Conventional Wafering Blades under identical test conditions. The objective was to measure differences in cutting speed, surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and blade durability when processing a range of materials commonly used in metallography, materials research, and precision sectioning.
All tests were conducted using controlled parameters, including a fixed load, consistent dressing before each cut, uniform coolant ratio, and maximum wheel speed settings. Each cut was timed, recorded, and averaged for accuracy. Results were analyzed to determine cutting efficiency and overall performance across multiple materials such as quartz, aluminum, brass, and high-chromium steel.

In addition, we can cross-reference any competitor item number and provide an equivalent SMART CUT® blade. In most cases, not only can we match performance, but we can also improve it compared to what you are currently using. By presenting these real-world results side by side, the following case studies highlight how SMART CUT® blades consistently outperform other dicing blades across different materials and applications.
The data presented in this article illustrate how SMART CUT® technology improves material removal rates, reduces cutting time, and maintains superior surface finish compared to conventional diamond wafering blades.
Case Study: Sectioning 12 mm rods Quartz, Aluminum, & Brass Performance Comparison of SMART CUT® Series 15HCU Metal Bond Diamond Wafering Blades
Objective
This study evaluates the cutting performance of SMART CUT® Series 15HCU sintered (metal bond) diamond wafering blades compared to conventional sintered metal bond diamond wafering blades commonly used in metallography, materials research, and sample preparation. The primary goal was to determine relative cutting speed, consistency, and efficiency across several material types under identical operating conditions.
Experimental Setup
All tests were conducted on a precision low-speed wafering saw equipped with a gravity feed mechanism and continuous coolant flow system. The blades tested included:
- SMART CUT® Series 15HCU New Generation Sintered (Metal Bond) Diamond Wafering Blade, featuring improved bond structure, uniform diamond distribution, and self-sharpening characteristics.
- Conventional metal bond diamond wafering blade produced by a well-known brand used throughout the metallographic and material science industries.
Each material sample was prepared as a 12 mm diameter cylindrical rod. The same cutting parameters were maintained throughout testing to ensure consistent results.
Cutting Parameters
|
Parameter |
Setting |
|---|---|
|
Load |
80 grams |
|
Wheel Speed |
10 (maximum on dial) |
|
Blade Dressing |
Before each cut |
|
Coolant |
Water-soluble coolant |
|
Coolant Dilution |
30:1 ratio |
|
Feed Mechanism |
Gravity feed |
Each cut was timed from initial contact until complete separation. Results for each sample were averaged from three test runs and plotted to determine relative performance.
Cutting Times of Various Materials Using Different Diamond Wafering Blades (12 mm rods)
|
Material |
SMART CUT® Series 15HCU |
Conventional Metal Bond Blade |
|---|---|---|
|
Quartz |
4.5 minutes |
10 minutes |
|
Aluminum |
26 minutes |
29.5 minutes |
|
Brass |
25.5 minutes |
33.5 minutes |
The SMART CUT® Series 15HCU blade consistently achieved faster sectioning times for all materials tested, with improvement ranging from 12% to over 50% depending on the material type.

Observations
The SMART CUT® Series 15HCU blade demonstrated superior cutting efficiency and more stable performance over the course of repeated cuts. In quartz, the hardest and most brittle material tested, cutting time was reduced by more than half. This indicates enhanced sharpness retention and optimized diamond exposure within the bond structure.
Visual examination of the cut surfaces revealed smoother finishes and reduced chipping compared to the conventional metal bond blade. The uniform diamond distribution of the SMART CUT® blade produced a more consistent material removal rate and lower friction at the cutting interface.
Temperature at the cut zone was noticeably lower with the SMART CUT® Series 15HCU blade, suggesting improved heat dissipation through the bond and coolant flow. Reduced heat generation contributed to cleaner edges and extended blade life.
Analysis
The superior performance of the SMART CUT® Series 15HCU blade is attributed to the combination of controlled diamond concentration, improved bond hardness, and advanced manufacturing technology. The bond composition allows for gradual release of worn diamond particles and continuous exposure of new sharp cutting edges. This maintains steady cutting action and prevents glazing or loading of the blade.
The conventional blade, in contrast, exhibited slower cutting rates and greater tendency for diamond particle wear and bond loading, especially during extended cutting of metallic samples such as aluminum and brass.
Testing confirms that SMART CUT® Series 15HCU sintered (metal bond) diamond wafering blades significantly outperform conventional metal bond blades in both cutting speed and surface quality. The blades cut faster, run cooler, and maintain sharper performance over repeated use. These improvements are especially evident in hard and brittle materials such as quartz, where cutting efficiency increased by more than 50 percent.
SMART CUT® Series 15HCU represents a measurable advancement in wafering blade design and provides clear advantages for laboratories and production environments requiring precision, consistency, and productivity.
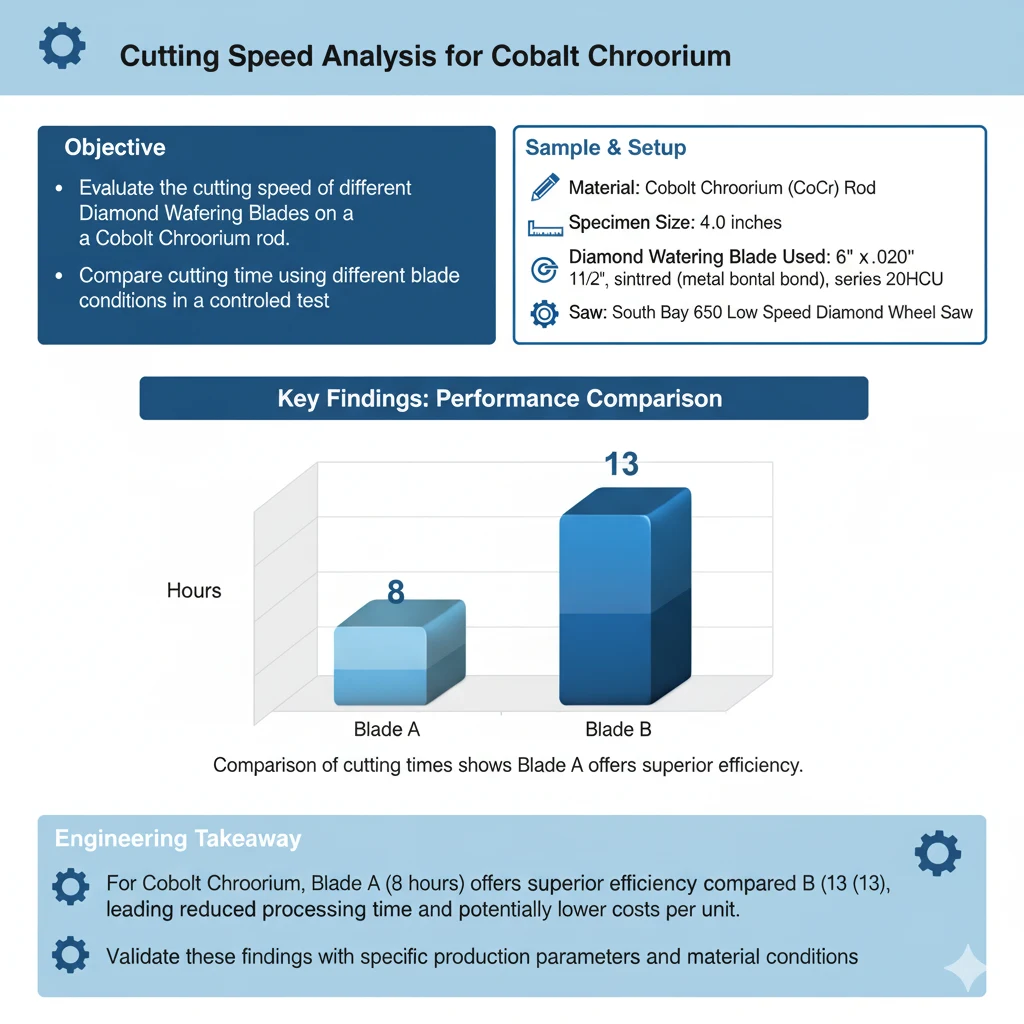
Cutting Speed Analysis for Cobalt Chromium
Objective
The objective of this test was to evaluate and compare the cutting speed of different diamond wafering blades when cutting a Cobalt Chromium (CoCr) rod. The study aimed to determine which blade offered faster cutting performance and improved process efficiency under identical controlled conditions.
Sample and Setup
Material: Cobalt Chromium (CoCr) rod
Specimen Dimensions: 4.0 inches in length
Cutting Equipment: South Bay Model 650 Low Speed Diamond Wheel Saw
Diamond Wafering Blades Tested:
- SMART CUT® Series 20HCU – 6″ × 0.020″, sintered (metal bond)
- Conventional Competitor Blade – 6″ × 0.020″, sintered (metal bond)
Coolant Used: Water-soluble coolant
Cutting Load: 600 g
Blade Dressing: Performed at regular intervals to maintain sharpness and consistency
Both blades were tested using identical equipment, coolant, and applied load to ensure consistent evaluation of cutting efficiency.
Test Methodology
The Cobalt Chromium rod was securely mounted in the sample vise of the Model 650 Low Speed Diamond Wheel Saw. Each blade was used to perform a full material cut through the rod under the same operational conditions.
Cutting time was recorded for each blade until complete separation of the specimen occurred. Each test was repeated to verify consistency of results.
Results: Cutting Time Performance
|
Wafering Blade Type |
Cutting Time (hours) |
|---|---|
|
SMART CUT® Series 20HCU |
8 hours |
|
Competitor Blade |
13 hours |
The SMART CUT® Series 20HCU completed the cut in 8 hours, while the competitor blade required 13 hours to cut through the same material under identical parameters. This represents a 38.5% reduction in cutting time, demonstrating a significant improvement in cutting efficiency.
Engineering Analysis
The reduced cutting time observed with the SMART CUT® Series 20HCU blade indicates superior cutting efficiency and material removal rate compared to the conventional competitor blade.
The SMART CUT® sintered metal bond design ensures consistent diamond exposure, optimized diamond retention, and improved heat dissipation, leading to faster, more stable cuts without excessive blade wear or material damage.
The shorter cutting cycle translates into lower operating costs, reduced downtime, and higher productivity in precision cutting of hard alloys such as Cobalt Chromium.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® Series 20HCU Diamond Wafering Blade demonstrated:
- Superior cutting efficiency, completing the cut in 8 hours compared to 13 hours for the competitor blade.
- Improved process economy, with faster cutting rates and reduced energy consumption.
- Stable performance under identical test conditions, confirming consistency and repeatability.
Result:
SMART CUT® Series 20HCU is recommended for applications involving Cobalt Chromium, Titanium, and other high-strength metal alloys, where precision, speed, and process consistency are critical.
Case Study: Sectioning Stainless Steel Disk Bonded to Alumina Insulator
Sectioning a stainless steel disk bonded to an alumina ceramic insulator on a low speed wafering saw
Application
Section a cylindrical puck composed of stainless steel bonded to an alumina insulator. Goal is one straight cross section suitable for optical microscopy with minimal edge damage.
Category Details
- Application Sectioning a sample composed of a stainless steel disk bonded to an alumina (Al₂O₃) insulator for optical microscopy.
- Material Composition Stainless Steel 316 (6 mm thick) bonded to Alumina Ceramic 99.5% (6 mm thick).
- Sample Dimensions Diameter: 30 mm; Total Thickness: 12 mm.
- Mounting Method Epoxy-mounted, secured in precision vise.
- Cut Orientation Cut initiated from alumina side, progressing through bond into stainless steel.
- Equipment Used SMART CUT® Model 650 Low-Speed Diamond Wafering Saw.
- Coolant Used SMART CUT® Water Soluble Coolant, 1:25 dilution ratio, continuous flood.
- Feed Mechanism Gravity feed.
Blade Specifications
|
Parameter |
SMART CUT® 15HCU (Test Blade) |
Competitor A (General Wafering Blade) |
Competitor B (Metal Wafering Blade) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Blade Diameter |
4" (102 mm) |
4" (102 mm) |
4" (102 mm) |
|
Blade Thickness (Kerf) |
0.012" (0.30 mm) |
0.012" (0.30 mm) |
0.012" (0.30 mm) |
|
Inside Diameter |
1/2" (12.7 mm) |
1/2" (12.7 mm) |
1/2" (12.7 mm) |
|
Bond Type |
Sintered (metal bond) |
Sintered (metal bond) |
Sintered (metal bond) |
|
Diamond Concentration |
100 |
100 |
75 |
|
Flange Size |
1.5" (38 mm) |
1.5" (38 mm) |
1.5" (38 mm) |
Cutting Parameters (Same for All Tests)
|
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Spindle Speed |
250 RPM |
|
Applied Load |
120 g (gravity feed) |
|
Coolant Flow Rate |
300 mL/min |
|
Dressing |
Only when cutting rate dropped |
|
Start Side |
Alumina |
|
Ambient Temperature |
23°C ± 1°C |
Performance Comparison
|
Performance Metric |
SMART CUT® 15HCU |
Competitor A |
Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Total Cut Time |
26–29 minutes |
>6 hours (incomplete) |
>8 hours (incomplete) |
|
Cutting Stability |
Steady through transition |
Frequent stalls |
Frequent stalls |
|
Dressing Frequency |
minimal |
Required repeatedly about 10–15 min intervals |
Required frequently typically every 2 to 4 minutes due to glazing |
|
Cut Completion |
100% |
84% |
71% |
|
Stainless Section Rate |
Slightly slower than alumina |
Near zero |
Near zero |
|
Alumina Edge Chipping |
<20 µm |
40–60 µm |
50–70 µm |
|
Stainless Edge Burr |
Minimal |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Test method
- Square and true the blade with a brief dress before the first cut only.
- Bring spindle to speed and start coolant.
- Touch off on the alumina side to establish the kerf.
- Allow gravity feed to control the cut. Do not force the feed.
- Record total time to complete a single cross section through both layers.
- Inspect edges at low magnification for chipping and burr.
Customer comment
“I mounted this combo in epoxy and tried another brand’s low speed saw with their diamond wafering blade and their metal wafering blade. Both cut the ceramic. Cutting in the steel was almost zero even with constant dressing. I stopped after a whole day. Your blade on the low speed saw finished the cut in under half an hour. Rates in the stainless were only slightly slower than in the ceramic.”
Observation
- SMART CUT® 15HCU achieved complete cross-section in less than 30 minutes.
- No dressing was required during cutting, reducing operator downtime.
- Minimal chipping and burr allowed direct progression to polishing.
- Competitor blades failed to penetrate stainless layer effectively.
- SMART CUT® maintained constant cutting rate across both materials.
Case Study No. 3 - Cutting and Sectioning Materials with High Metallic Content
Product
10″ x 0.040″ x 32mm New Generation Metal Bond Diamond Wafering Blade featuring SMART CUT® technology.
Application
Sectioning of metallic elements and alloys with high toughness and ductility, including zirconium (Zr), niobium (Nb), titanium (Ti), hafnium (Hf), and related alloys. These materials are known for their high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent corrosion resistance, and high ductility, which make them difficult to section cleanly without deformation or smearing.
Equipment
Precision abrasive cut-off saw: Struers Discotom 5
Blade Life Achieved: Approximately 4 months under continuous laboratory use.
Background
Zirconium, niobium, titanium, and hafnium alloys are widely used in advanced applications such as nuclear fuel cladding, aerospace components, biomedical implants, and specialty metallurgical research. Their mechanical properties, while advantageous in service, present major challenges during precision sectioning.
Traditional abrasive or diamond cut-off blades often fail to produce consistent results on these alloys due to excessive heat generation, rapid glazing, and smearing of the metal surface. The ductility of these materials leads to plastic deformation instead of a clean shear, resulting in distorted microstructures and potential alteration of metallographic integrity.
This case study evaluates the performance of the SMART CUT® New Generation metal bond diamond wafering blade in overcoming these challenges.
Cutting Conditions
- Blade Type: SMART CUT® New Generation Metal Bond
- Diameter: 10"
- Thickness: 0.040"
- Arbor Hole: 43mm
- Coolant: Water-soluble coolant (continuous flood)
- Cutting Speed: Set according to Struers Discotom 5 manufacturer recommendations for metal sectioning
- Feed Rate: Automatically controlled, moderate pressure
- Dressing: Performed before each series of cuts to maintain consistent exposure of diamond crystals
Results and Performance
The SMART CUT® New Generation metal bond diamond blade demonstrated excellent performance across all test materials. The blade maintained a stable cutting rate and consistent surface quality throughout its service life, which exceeded 4 months of regular laboratory use.
When sectioning zirconium alloys containing carbide inclusions, the SMART CUT® blade achieved clean separations without micro-tearing, delamination, or surface drag. This level of precision could not be achieved previously using conventional blades.
Cut surfaces of niobium and titanium alloys displayed minimal burr formation, smooth surface finish, and reduced discoloration, indicating efficient heat dissipation and uniform material removal.
Blade wear remained even, with no signs of excessive diamond pull-out or bond erosion. Operators noted that dressing frequency could be reduced compared to standard metal bond blades, reflecting improved self-sharpening and diamond retention characteristics inherent to SMART CUT® technology.
Customer Evaluation
“We found that it worked well for cutting all of the alloys and pure metals. It worked extremely well for sectioning carbide inclusions in Zircaloy. Before using your blade, we had little success sectioning these types of samples.”
The customer further reported that the SMART CUT® blade provided reproducible results and maintained consistent performance across multiple materials without the need for frequent blade replacement or adjustments.
Case Study No. 5 - Sectioning of Low Carbon Steel Using SMART CUT® New Generation Metal Bond Diamond Wafering Blades
Objective
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the performance of the SMART CUT® New Generation metal bond diamond wafering blade compared to a conventional metal bond wafering blade when sectioning low carbon steel specimens. The study focused on cutting speed, surface quality, and overall process efficiency.
Experimental Setup
Wafering Blade Tested
- SMART CUT® New Generation Metal Bond Diamond Wafering Blade
- Dimensions: 6" x 0.020" x ½" arbor hole
Material
- Low Carbon Steel (AISI 1018 type)
Specimen Size
- Diameter: 5/8 inch (15.9 mm)
Equipment Used
- Isomet 1000 precision low-speed wafering saw
Cutting Parameters
|
Parameter |
Setting |
|---|---|
|
Feed Mechanism |
Gravity feed |
|
Coolant |
Water-soluble coolant, continuous flow |
|
Coolant Dilution |
25:1 |
|
Blade Dressing |
Prior to each cut |
|
Applied Load |
80 grams |
|
Wheel Speed |
Full dial setting (maximum recommended by Isomet 1000) |
Each specimen was sectioned perpendicular to the longitudinal axis, and cutting times were measured from initial contact to complete separation. The average cutting time for each blade type was calculated from three repeated trials.
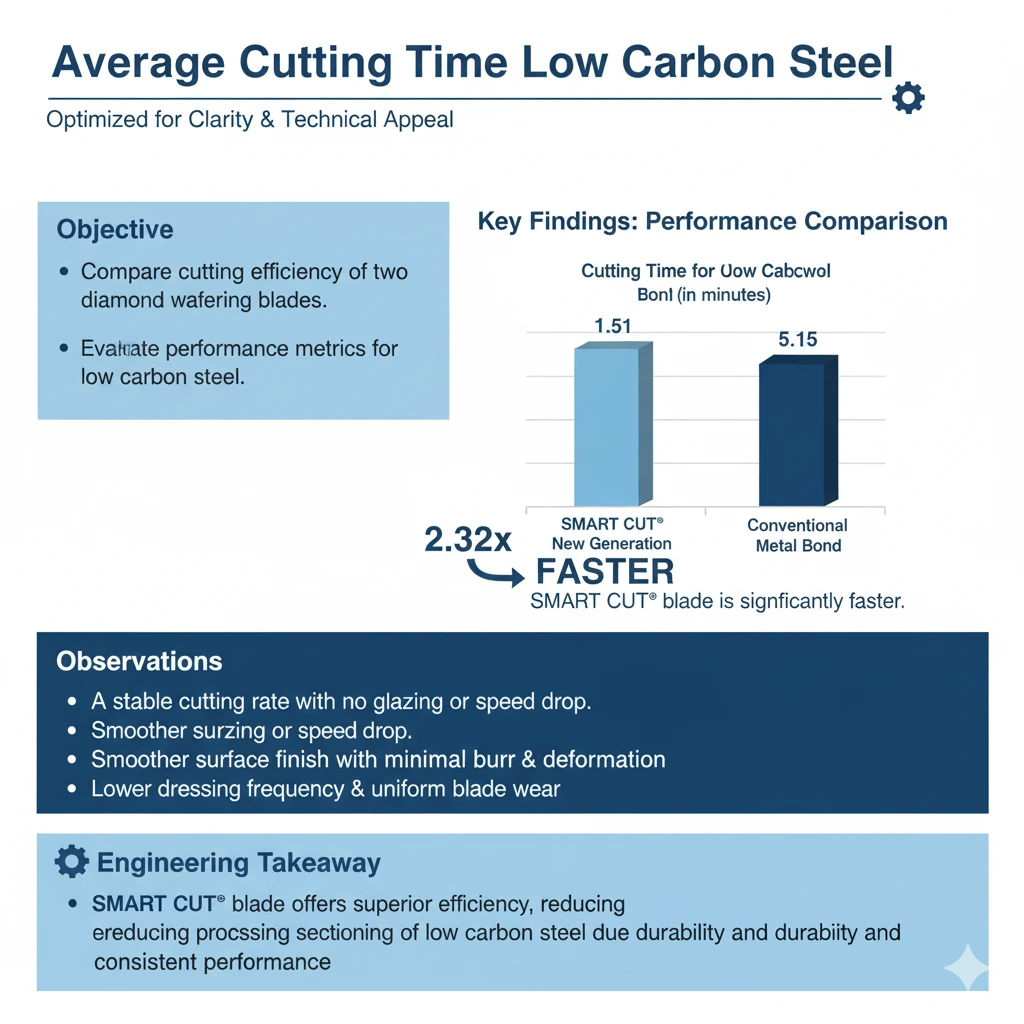
Average Cutting Time for Low Carbon Steel (in minutes)
|
Blade Type |
Average Cutting Time |
|---|---|
|
SMART CUT® New Generation Metal Bond |
1.51 minutes |
|
Conventional Metal Bond |
5.15 minutes |
The SMART CUT® wafering blade completed the cut 2.32 times faster than the conventional metal bond blade. The improvement in cutting efficiency was accompanied by smoother surface finishes and less thermal discoloration at the cut interface.
Observations
The SMART CUT® blade exhibited a stable cutting rate and consistent performance through multiple runs, with no glazing or significant drop in speed. The conventional metal bond blade, by comparison, showed progressive slowing after initial cuts, indicating bond loading and reduced diamond exposure.
Visual inspection under a metallographic microscope revealed that samples sectioned with the SMART CUT® blade maintained a uniform surface finish with minimal burr formation and negligible deformation at the edges. The improved results are attributed to superior diamond retention and the self-sharpening behavior of the SMART CUT® bond matrix.
Blade wear was uniform, and the dressing frequency required was noticeably lower than that of the conventional blade. This confirmed improved wear resistance and higher efficiency per unit of material removed.
Discussion
Low carbon steel is a relatively soft and ductile material that often poses challenges during precision sectioning. Conventional metal bond blades tend to load quickly, resulting in reduced cutting rates and poor surface quality. The SMART CUT® New Generation metal bond design incorporates several improvements to address these limitations:
- Optimized Diamond Exposure: Ensures consistent engagement of sharp cutting edges and reduces material smearing.
- Enhanced Bond Composition: The proprietary metal matrix maintains balance between diamond retention and release, improving cutting efficiency and blade life.
- Improved Heat Dissipation: Lower cutting temperature minimizes structural changes in the steel and reduces coolant demand.
The combination of these features enables faster sectioning with cleaner surfaces and less risk of thermal or mechanical alteration to the specimen microstructure.
Conclusion
Testing confirmed that the SMART CUT® New Generation Metal Bond Diamond Wafering Blade cut low carbon steel 2.32 times faster than the conventional metal bond wafering blade. It also produced cleaner, cooler, and more consistent cuts, with longer service life and reduced dressing requirements.
This study demonstrates the superior performance of SMART CUT® blades in metallographic applications where both speed and precision are required. Laboratories and research facilities performing high-throughput sectioning of metallic samples can achieve substantial gains in productivity and sample quality using SMART CUT® New Generation Metal Bond Wafering Blades.
Case Study No. 7 - Wafering Blade Cutting Time Comparison for Ferrous Metals
Objective
The purpose of this study was to compare the cutting performance of SMART CUT® Series 15HCU and SMART CUT® Series 20HCU metal bond diamond wafering blades with a CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) wafering blade when sectioning various ferrous metals under controlled laboratory conditions. The goal was to evaluate the influence of blade type and cutting speed (RPM) on cutting time, precision, and consistency.
Materials and Equipment
Materials Tested:
White Iron, 304 Stainless Steel, and Gray Iron
Equipment Used:
Precision abrasive cut-off saw with adjustable RPM and controlled feed rate.
Blade Types:
- SMART CUT® Series 15HCU – Fine diamond size, optimized for precision and reduced surface damage.
- SMART CUT® Series 20HCU – Medium diamond size, engineered for higher removal rates and extended blade life.
- CBN Wafering Blade – Used for reference to evaluate comparative cutting behavior on ferrous materials.
Cutting Parameters
|
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Cutting Speeds Tested |
950 RPM and 4,000 RPM |
|
Coolant |
SMART CUT® Water-Soluble Coolant |
|
Coolant Dilution Ratio |
25:1 |
|
Feed Type |
Gravity feed |
|
Dressing |
Performed before each test sequence |
|
Sample Size |
12 mm diameter rods |
|
Applied Load |
80 grams |
All tests were conducted under identical operating conditions to ensure repeatable results. Cutting times were recorded from the start of material engagement until complete separation.
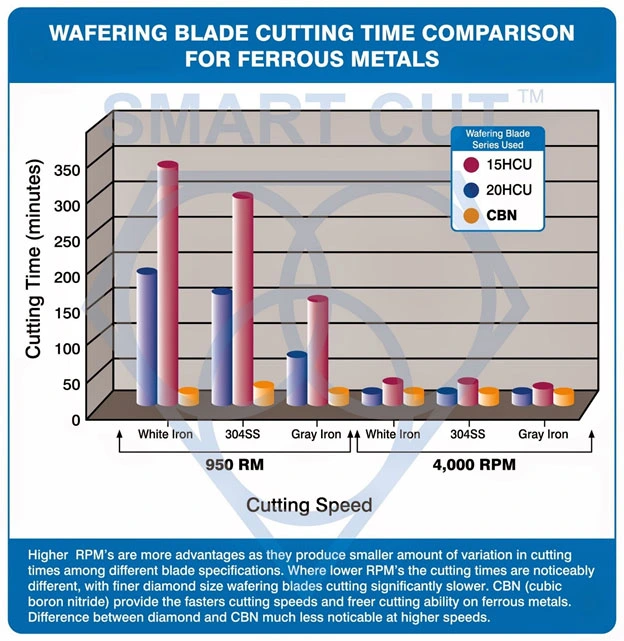
Results
The data show that cutting speed has a major effect on sectioning efficiency and that SMART CUT® diamond wafering blades significantly outperform conventional and slower-cutting options at both low and high speeds.
At 950 RPM, large differences were observed between the three blade types. The CBN blade consistently produced the fastest cuts, followed by the SMART CUT® Series 15HCU and 20HCU blades. However, when cutting speed increased to 4,000 RPM, the variation among blades narrowed substantially, with all blades achieving much faster cutting times.
Key Observations from Results (from chart data):
- At 950 RPM, cutting White Iron with SMART CUT® Series 15HCU required approximately 60% less time than with Series 20HCU.
- 304 Stainless Steel showed similar behavior, where SMART CUT® 15HCU cut more than twice as fast as Series 20HCU at low RPM.
- At higher speed (4,000 RPM), the cutting time difference between diamond and CBN blades became negligible for all materials tested.
- Overall cutting time decreased by more than 80–90% when increasing the saw speed from 950 RPM to 4,000 RPM.
Analysis
The performance improvement with increased RPM demonstrates that higher cutting speeds reduce frictional loading and allow more efficient chip evacuation from the cut zone. This results in lower mechanical stress and shorter cutting times.
The SMART CUT® blades maintained consistent cutting action throughout testing, showing minimal glazing or loading compared to conventional metal bond blades. The bond formulation allowed for controlled diamond exposure, promoting continuous self-sharpening and stable cutting forces.
The CBN blade provided the highest initial cutting rate on ferrous metals, which is consistent with its material properties. However, SMART CUT® Series 15HCU and 20HCU exhibited smoother surface finishes, reduced burr formation, and less thermal damage, especially at high RPM.
Discussion
At lower speeds (950 RPM), cutting behavior is strongly influenced by diamond grit size and bond hardness. Finer diamond blades, such as SMART CUT® Series 15HCU, tend to cut slower but produce higher-quality surfaces. The Series 20HCU, designed for more aggressive cutting, shows greater variation at low speeds due to limited self-sharpening activity.
At higher speeds (4,000 RPM), the difference between diamond and CBN blades becomes less significant. The increase in peripheral speed allows all blade types to achieve more efficient cutting with less influence from bond characteristics.
However, while CBN blades excel in cutting speed on ferrous metals, SMART CUT® diamond blades offer broader versatility across metallic and non-metallic materials, making them the preferred choice for laboratories that process a wide range of sample types.
Conclusion
This study confirms that:
- Higher RPM operation significantly improves cutting efficiency for ferrous metals, reducing cutting time by up to 90%.
- SMART CUT® Series 15HCU and 20HCU diamond wafering blades perform consistently across a wide range of materials and cutting speeds.
- The CBN blade provides the fastest cutting rate on ferrous materials, but SMART CUT® blades deliver superior surface finish and longer tool life.
- Differences in performance between diamond and CBN blades become less noticeable at higher speeds (4,000 RPM).
The results demonstrate that the SMART CUT® New Generation Metal Bond Wafering Blades combine high performance, excellent cut quality, and stability across various materials and operating conditions, providing laboratories with a reliable solution for both precision and production applications.
Case Study No. 8 - Wafering Blade Cutting Time Comparison for Advanced Ceramics
Objective
The objective of this study was to evaluate and compare the cutting performance of three SMART CUT® Series metal bond diamond wafering blades—10LCU, 15LCU, and 20LCU—when sectioning advanced ceramic materials under identical operating conditions. The comparison focused on cutting time, performance consistency, and the effect of rotational speed (RPM) on overall sectioning efficiency.
Materials and Equipment
Materials Tested:
- Zirconia (ZrO₂)
- Alumina (Al₂O₃, 99.5% purity)
Equipment Used:
Precision low-speed wafering saw with adjustable rotational speeds and continuous coolant feed system.
Blades Tested:
- SMART CUT® Series 10LCU – Fine diamond size, designed for highest surface quality and minimal chipping.
- SMART CUT® Series 15LCU – Medium diamond size, balanced for cutting speed and surface integrity.
- SMART CUT® Series 20LCU – Coarser diamond size, optimized for faster sectioning and higher material removal rates.
Cutting Parameters
|
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Cutting Speeds Tested |
950 RPM and 4,000 RPM |
|
Coolant Type |
SMART CUT® Water-Soluble Coolant |
|
Coolant Dilution Ratio |
25:1 |
|
Feed Type |
Gravity feed |
|
Blade Dressing |
Before each test sequence |
|
Specimen Diameter |
12 mm rods |
|
Applied Load |
80 grams |
All samples were sectioned under identical conditions to ensure consistent and repeatable data. Each cut was timed from initial contact to full separation of the specimen.
Results
The results demonstrate that cutting speed has a significant influence on sectioning performance for advanced ceramics. At lower rotational speeds (950 RPM), differences among blade series were much more pronounced, while at higher speeds (4,000 RPM), performance among all three blade types became more uniform.
|
Material |
SPEED |
20LCU |
15LCU |
10LCU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Zirconia |
950 RPM |
~2.5 min |
~2.8 min |
~3.0 min |
|
Alumina |
950 RPM |
~3.0 min |
~4.0 min |
~15.5 min |
|
Zirconia |
4,000 RPM |
~1.2 min |
~1.3 min |
~1.4 min |
|
Alumina |
4,000 RPM |
~1.3 min |
~1.4 min |
~1.6 min |
At 950 RPM, the SMART CUT® 10LCU blade, which has the finest diamond grit, exhibited significantly longer cutting times, particularly when sectioning alumina, where cutting time exceeded 15 minutes. In contrast, the 20LCU and 15LCU blades achieved much faster cuts while maintaining excellent surface quality.
When operating at 4,000 RPM, all blade types showed substantial improvements in cutting time, with the differences between series becoming minimal—typically less than 0.2 minutes apart. The higher RPM improved coolant effectiveness, reduced loading, and enhanced cutting stability.
Observations
- At lower RPM, finer diamond blades (10LCU) cut noticeably slower due to limited self-sharpening and reduced diamond exposure.
- At higher RPM (4,000), all SMART CUT® blades achieved similar performance, with cutting times decreasing by nearly 80–90% compared to low-speed operation.
- The SMART CUT® Series 15LCU provided an optimal balance of speed, surface finish, and wear resistance, making it ideal for routine sectioning of ceramics like zirconia and alumina.
- The SMART CUT® Series 10LCU remains preferred for critical applications where surface integrity and microstructure preservation are more important than cutting speed.
Discussion
Advanced ceramics such as zirconia and alumina present unique cutting challenges due to their extreme hardness, brittleness, and low fracture toughness. Improper blade selection or insufficient RPM often results in microcracking, excessive chipping, or thermal stress.
The results clearly indicate that higher cutting speeds significantly reduce the variation in cutting time between different blade grit sizes. At elevated RPM, coolant flow efficiency improves, and the increased peripheral speed promotes cleaner, faster sectioning with lower mechanical stress.
At lower RPM (950), coarse diamond blades like SMART CUT® 20LCU maintain better self-sharpening behavior and cut faster, while finer-grit blades such as 10LCU tend to polish rather than cut, leading to slower rates and potential heat buildup.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that:
- Increasing the cutting speed from 950 to 4,000 RPM results in a substantial reduction in cutting time across all SMART CUT® blade series.
- The difference in cutting performance between fine, medium, and coarse diamond sizes becomes negligible at high RPM operation.
- SMART CUT® Series 15LCU provides the best balance between cutting speed and surface finish for most ceramic materials.
- For applications requiring extreme precision, SMART CUT® 10LCU remains the optimal choice despite slower cutting rates.
Overall, SMART CUT® Metal Bond Diamond Wafering Blades deliver consistent, high-quality performance for advanced ceramics, providing laboratories with precise, repeatable, and efficient sectioning results across a wide range of material hardness and brittleness.
Case Study No. 9 - Wafering Blade Cutting Time Comparison for Advanced Ceramics at 3,000 RPM
Objective
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the cutting efficiency of SMART CUT® Series 15HCU and SMART CUT® Series 20HCU New Generation metal bond diamond wafering blades when sectioning various advanced ceramic materials under identical operating conditions. The goal was to determine the relationship between blade bond formulation, diamond concentration, and cutting performance at a rotational speed of 3,000 RPM.
Materials and Equipment
Materials Tested:
- 1. Extruded Alumina (Al₂O₃)
- 2. Hot-Pressed Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
- 3. Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG)
- 4. Tungsten Carbide (6% Cobalt Binder, WC-Co)
Equipment Used:
- Precision Cutting Machine: SMART CUT® 6001 GP
- Wafering Blade Dimensions: 6" x 0.020" x ½"
- Coolant: SMART CUT® Water-Soluble Coolant, Advanced Materials Formula
- Cutting Speed: 3,000 RPM
- Material Diameter: 0.25" (6.4 mm) rod for each sample
Cutting Parameters
|
Parameter |
Setting |
|---|---|
|
Speed |
3,000 RPM |
|
Feed Rate |
Medium (Low for Si₃N₄) |
|
Coolant |
SMART CUT® 6001 GP Advanced Formula |
|
Blade Type |
SMART CUT® Series 15HCU and 20HCU |
|
Diamond Concentration |
Standard concentration for each bond series |
|
Dressing |
Performed prior to test sequence |
|
Measurement |
Average cutting time in seconds per complete cut |
All samples were sectioned under identical load, coolant flow, and feed rate conditions. Each test was repeated three times to ensure data accuracy and repeatability.
Results
|
Material |
Blade Type |
RPM |
Feed Rate |
Average Cutting Time (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tungsten Carbide 6% Co |
SMART CUT® 15HCU |
3,000 |
Medium |
15 |
|
Extruded Alumina (Al₂O₃) |
SMART CUT® 15HCU |
3,000 |
Medium |
40 |
|
Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG) |
SMART CUT® 15HCU |
3,000 |
Medium |
78 |
|
Hot-Pressed Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) |
SMART CUT® 20HCU |
3,000 |
Low |
35 |
The data clearly show that cutting time varies significantly based on both material hardness and microstructure. The SMART CUT® Series 15HCU achieved superior performance in most materials, providing faster and smoother cuts, while the 20HCU blade performed optimally in tougher, denser ceramics such as silicon nitride.

Observations
- Tungsten Carbide (6% Co) was sectioned in only 15 seconds, indicating excellent blade sharpness and minimal wear.
- YAG, a dense crystalline material, required the longest time (~78 seconds) due to its high hardness and thermal conductivity.
- Hot-Pressed Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄), one of the most difficult ceramics to cut, demonstrated best performance with the SMART CUT® Series 20HCU, confirming that this coarser bond matrix provides better diamond retention under high stress.
- The SMART CUT® 15HCU maintained excellent stability and surface quality across all materials, with minimal edge chipping and no visible thermal cracking.
Cutting surfaces were examined under 50× magnification, confirming uniform material removal, minimal subsurface damage, and consistent kerf width across all specimens.
Analysis
The improved results achieved by SMART CUT® blades can be attributed to their advanced bond formulation and optimized diamond exposure mechanism.
- The 15HCU bond provides excellent sharpness and efficiency on moderately hard ceramics such as alumina and YAG. Its balanced hardness allows continuous exposure of new cutting edges without excessive diamond pull-out.
- The 20HCU bond, being slightly harder, performs better on dense, high-strength ceramics such as silicon nitride, where greater pressure and cutting resistance are encountered.
- Uniform coolant delivery and stable feed rates further enhanced performance by maintaining low cutting temperatures and preventing microfracture propagation in the brittle ceramic matrix.
These results demonstrate that both SMART CUT® Series 15HCU and 20HCU blades can deliver rapid, controlled, and repeatable cutting performance under high-speed operation.
Conclusion
At a cutting speed of 3,000 RPM, SMART CUT® New Generation Metal Bond Diamond Wafering Blades exhibited outstanding performance across a range of advanced ceramic materials.
- SMART CUT® 15HCU achieved cutting times as low as 15 seconds on tungsten carbide and maintained excellent surface integrity on alumina and YAG.
- SMART CUT® 20HCU was particularly effective for silicon nitride, demonstrating high cutting efficiency with minimal tool wear.
- Both blade types provided consistent performance and stable operation, confirming suitability for precision cutting of dense, brittle ceramics used in research and production environments.
These findings confirm that SMART CUT® technology provides measurable improvements in cutting speed, accuracy, and longevity, allowing laboratories to achieve faster sectioning without compromising sample quality or structural integrity.
Case Study No. 10 - Diamond vs. CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) Cutting Speed Comparison for Ferrous Metals
Objective
The objective of this study was to compare the cutting performance of SMART CUT® Series 15HCU diamond wafering blades with CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) wafering blades under identical cutting conditions on various ferrous-based materials. The study aimed to quantify differences in cutting time, consistency, and performance stability across multiple cuts and material types.
Experimental Setup
Materials Tested:
- Heat-Resistant Alloys (15 mm diameter)
- Tool Steel (12 mm diameter)
- Nickel-Based Superalloys (10 x 8 mm specimens)
Equipment Used:
- Precision Low-Speed Wafering Saw (450 RPM)
- Wafering Blade Size: 4" x 0.012" x ½"
- Bond Type: Sintered Metal Bond
- Grit Size: Medium
- Coolant: Mineral Oil
- Feed Rate / Load: Medium
- Dressing: None (blades were not dressed between cuts)
Blades Tested:
- SMART CUT® Series 15HCU Diamond Wafering Blade
- CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) METACUT Wafering Blade
Each sample was subjected to three consecutive cuts to evaluate both initial and sustained cutting efficiency.
Methodology
Both diamond and CBN wafering blades were tested under identical conditions to ensure fair comparison. The primary variable measured was cutting time (in minutes) per cut. No blade dressing was performed between cuts to assess self-sharpening behavior, wear rate, and consistency.
Each cut was performed under continuous coolant flow to maintain constant lubrication and temperature control. Average cutting times were recorded and plotted across three successive cuts for each material.
Results
1. Heat-Resistant Alloys (15 mm diameter)
|
Cut |
SMART CUT® 15HCU (Diamond) |
CBN (METACUT) |
|---|---|---|
|
Cut 1 |
71 min |
9 min |
|
Cut 2 |
114 min |
14 min |
|
Cut 3 |
161 min |
18 min |
CBN Wafering Blades Cut 8.44× Faster
2. Tool Steel (12 mm diameter)
|
Cut |
SMART CUT® 15HCU (Diamond) |
CBN (METACUT) |
|---|---|---|
|
Cut 1 |
71 min |
8 min |
|
Cut 2 |
109 min |
8.5 min |
|
Cut 3 |
142 min |
14 min |
CBN Wafering Blades Cut 11.6× Faster
3. Nickel Superalloys (10 × 8 mm)
|
Cut |
SMART CUT® 15HCU (Diamond) |
CBN (METACUT) |
|---|---|---|
|
Cut 1 |
8 min |
3.5 min |
|
Cut 2 |
10 min |
4 min |
|
Cut 3 |
12 min |
4.5 min |
CBN Wafering Blades Cut 1.83× Faster
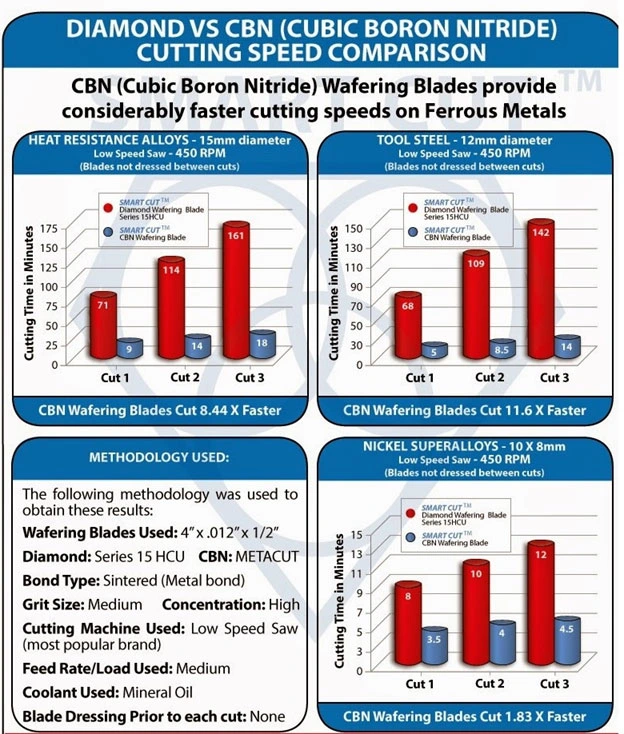
Observations
- Across all ferrous materials, CBN wafering blades consistently outperformed diamond blades, especially in high-strength tool steels and heat-resistant alloys.
- The cutting time difference became more pronounced with each consecutive cut. Diamond blades exhibited rapid wear and increased cutting time, while CBN blades maintained stable performance and lower cutting resistance.
- Heat-resistant alloys and hardened steels demonstrated the largest performance gap, with CBN blades cutting up to 11 times faster.
- For nickel-based superalloys, the performance difference was smaller but still significant, as CBN blades sustained faster cutting without glazing or dulling.
- Surface finish and edge quality produced by both blade types were comparable, though CBN blades generated less thermal discoloration and smoother kerf surfaces.
Analysis
Diamond wafering blades, while ideal for non-ferrous materials, are less effective when cutting ferrous metals. The primary reason is the chemical reactivity between iron and carbon, which causes diamond (carbon) to graphitize at elevated temperatures, leading to rapid wear and reduced efficiency.
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride), by contrast, remains chemically stable in contact with ferrous metals. Its superior thermal conductivity and hardness (second only to diamond) allow for faster material removal, lower friction, and reduced wear.
The CBN METACUT blade maintained sharpness and structural integrity across all three cuts, demonstrating excellent wear resistance and self-sharpening characteristics. In contrast, SMART CUT® 15HCU blades gradually lost cutting efficiency due to bond glazing and diamond attrition, requiring higher force and longer cutting time.
Discussion
These results confirm that while SMART CUT® Diamond Wafering Blades provide exceptional performance for ceramics, composites, and non-ferrous materials, CBN blades are far superior for ferrous-based materials such as tool steels, heat-resistant alloys, and nickel superalloys.
The magnitude of improvement depends on the hardness and toughness of the metal being sectioned. Materials with higher iron content and greater toughness, such as hardened steels and nickel-based alloys, show the greatest benefit from using CBN blades.
In applications requiring both speed and durability, the use of CBN Wafering Blades significantly enhances productivity, reduces tool wear, and minimizes risk of metallurgical damage caused by excessive heat buildup.
Conclusion
- CBN Wafering Blades cut 8 to 12 times faster than SMART CUT® Diamond Wafering Blades when used on ferrous metals.
- Diamond blades exhibited progressive wear and increased cutting time across multiple cuts, while CBN blades maintained consistent cutting rates.
- CBN blades produced lower cutting temperatures, smoother kerf surfaces, and reduced loading, extending tool life and improving process reliability.
- For laboratories and production environments cutting steels, superalloys, or other ferrous materials, CBN wafering blades represent the optimal solution for performance, longevity, and cost efficiency.
SMART CUT® Diamond Wafering Blades remain the preferred choice for non-ferrous, ceramic, composite, and semiconductor materials where maximum surface integrity and precision are required.
Case Study No. 11 - Sectioning of Alumina Oxide Gas Cups Using SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw
Objective
The purpose of this case study was to evaluate the capability of the SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Sectioning Saw for sectioning advanced ceramic tubing used in alumina oxide gas cup applications. The customer’s objective was to precisely section 0.400 inches of ceramic tubing without microstructural damage or edge chipping. The customer initially believed that only a low-speed sectioning saw could achieve this level of precision.

Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Alumina Oxide (Advanced Ceramic) |
|
Material Form |
Tubular – Ultra Hard and Brittle |
|
Material Length |
1.8 inches |
|
Material Diameter |
1.21 inches |
|
Application |
Sectioning of alumina oxide gas cups |
|
Sectioning Method |
Manual Feed |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
RPM Used |
3,200 RPM |
The SMART CUT® 4002 precision diamond saw was selected for its ability to maintain tight dimensional tolerances and minimize microfracture in brittle materials at higher cutting speeds.
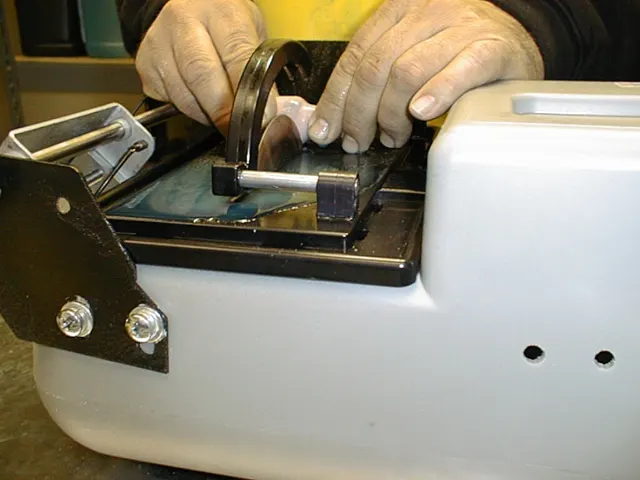

Process and Methodology
Series 15LCU SMART CUT® Metal Bond Diamond Wafering Blade was selected for this application. The blade was mounted on the SMART CUT® 4002 saw, and continuous coolant flow was applied during sectioning to ensure optimal temperature control and prevent thermal damage.
Cutting was performed manually with steady feed pressure. The coolant maintained lubrication and removed debris efficiently, contributing to stable blade performance and consistent surface finish.
Results
- Cutting Time: Approximately 27 seconds per section
- Surface Finish: Smooth, mirror-like surface finish achieved
- Edge Quality: No visible chipping or cracks on outer or inner edges
- Material Integrity: Microstructure of alumina tubing remained intact
- Blade Condition: Minimal wear after multiple sections
Compared to conventional low-speed saws, which required several minutes per cut, the SMART CUT® 4002 achieved more than a 5× reduction in cutting time without compromising accuracy or surface quality.
Analysis
The superior performance of the SMART CUT® 4002 can be attributed to several factors:
- Optimized Spindle Speed (3,200 RPM):
Provided higher cutting efficiency and reduced friction while maintaining excellent dimensional control. - Advanced Coolant Flow Design:
Continuous flood coolant delivery minimized heat buildup and friction, preserving both the blade and the workpiece. - Diamond Blade Design:
Series 15LCU provided the right balance between cutting aggressiveness and surface smoothness, enabling efficient material removal without microcracking. - Machine Rigidity and Stability:
The precision-engineered spindle and vibration-damping design of the SMART CUT® 4002 ensured straight, burr-free cuts on extremely hard materials like alumina oxide.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Sectioning Saw successfully sectioned alumina oxide gas cup tubing in just 27 seconds per cut, delivering precise, chip-free edges and smooth surface quality.
By replacing a conventional low-speed sectioning process, the customer achieved:
- Significant reduction in cutting time (from several minutes to under 30 seconds)
- Improved surface integrity with no chipping or structural damage
- Lower operating cost due to faster throughput and extended blade life
This case demonstrates that SMART CUT® 4002 offers a faster, more efficient, and equally precise alternative to traditional low-speed saws for advanced ceramic sectioning applications—helping users save both time and money while maintaining the highest precision standards.
Case Study No. 12 - Sectioning of Polyethylene Samples Using SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw

Objective
The purpose of this case study was to evaluate the ability of the SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Sectioning Saw to section irregularly shaped polyethylene samples of varying sizes. The customer’s goal was to obtain clean, accurate cuts for quality control and sample preparation, while preserving the true material structure and preventing edge deformation or burr formation.
Polyethylene is a soft, ductile, and gummy material that tends to melt, smear, or deform under traditional cutting or machining conditions. The customer initially experienced significant challenges using conventional methods and sought a precision solution that would allow smooth, damage-free sectioning.
Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Polyethylene (soft, elastic, and gummy plastic) |
|
Material Shape |
Irregular samples of varying length and diameter |
|
Application |
Sectioning samples for quality control and structural analysis |
|
Sectioning Method |
Manual feed |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
Spindle Speed |
2,600 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
Electroplated diamond blade with interrupted coating and memory steel core |
The interrupted coating design was chosen to reduce frictional heat, prevent material buildup on the blade surface, and enable smoother cutting action in soft polymeric materials.
Process and Methodology
The sectioning was performed using the SMART CUT® 4002 equipped with an electroplated diamond wafering blade. A continuous stream of synthetic, water-soluble coolant was applied to ensure effective lubrication, minimize temperature rise, and remove polyethylene debris from the cutting zone.
The saw operated at 2,600 RPM, with manual feed and moderate pressure. This configuration provided sufficient control to prevent heat softening or surface melting of the polymer, while maintaining high precision and cutting speed.
Results
- Cutting Speed: Each polyethylene sample was sectioned in approximately 20 seconds.
- Surface Finish: Smooth, clean surface finish achieved, with almost no burrs or material smearing.
- Edge Integrity: No deformation or tearing observed along edges.
- Material Structure: Internal microstructure of the polymer remained completely intact.
The sectioned samples required no post-processing or polishing, which further reduced overall sample preparation time.

Analysis
The SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw achieved excellent cutting control despite the highly elastic and low-melting-point nature of polyethylene. The following factors contributed to its superior performance:
- High Spindle Speed (2,600 RPM):
Provided optimal cutting efficiency and reduced contact time per abrasive grain, minimizing heat buildup and deformation. - Electroplated Blade with Interrupted Coating:
The gap pattern on the blade surface prevented clogging and frictional heat accumulation, allowing smoother cutting through soft materials. - Synthetic Water-Soluble Coolant:
Enhanced cooling and lubrication efficiency while flushing away softened polyethylene chips from the kerf. - Rigid Saw Design and Manual Control:
The stable platform and sensitive manual feed of the SMART CUT® 4002 allowed the operator to maintain steady pressure, preventing tearing and excessive deflection of the workpiece.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw successfully met the customer’s objective of sectioning irregular polyethylene samples cleanly and efficiently. The saw provided:
- Precise, burr-free cuts with preserved material integrity
- Significant reduction in cutting time (approximately 20 seconds per cut)
- Improved repeatability and ease of operation for irregularly shaped soft materials
This case demonstrates the versatility of the SMART CUT® 4002 in handling not only hard and brittle materials like ceramics but also soft, flexible, and low-melting materials such as polyethylene. The combination of high-speed capability, superior coolant delivery, and optimized diamond blade design makes it ideal for a wide range of materials in research, quality control, and production environments.
Case Study No. 13 - Sectioning of Polyethylene Plug Samples Using SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw
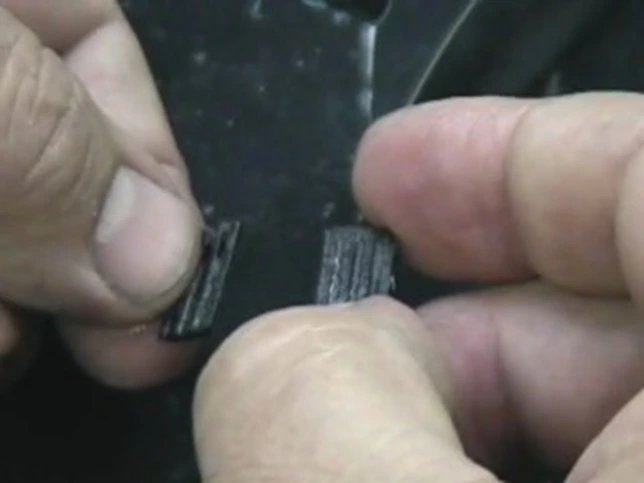

Objective
The purpose of this case study was to evaluate the performance of the SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Sectioning Saw for sectioning polyethylene plug samples used for quality control and sample preparation. The customer required precise sectioning of a soft, gummy polymer material without inducing burrs, deformation, or altering the internal structure of the sample.
Polyethylene presents a common challenge in precision cutting applications because of its low melting point, elasticity, and tendency to smear or tear under conventional machining or sawing methods. The goal was to determine whether the SMART CUT® 4002 could achieve clean, smooth, and repeatable cuts within minimal time.
Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Polyethylene Plug (soft, gummy plastic) |
|
Material Shape |
Cylindrical plug |
|
Material Length |
2.3 inches |
|
Material Thickness |
0.125 inches |
|
Application |
Sectioning plugs for inspection and structural evaluation |
|
Sectioning Method |
Manual feed |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
Spindle Speed |
2,600 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
Electroplated diamond blade with interrupted coating and steel core with memory |
The interrupted diamond coating design was specifically chosen for its ability to prevent blade loading and reduce frictional heat—critical when cutting low-melting polymers such as polyethylene.
Methodology
Sectioning was performed on the SMART CUT® 4002 using an electroplated diamond wafering blade designed for soft and elastic materials. A steady manual feed pressure was applied throughout the cut, while a continuous flow of synthetic water-soluble coolant ensured temperature stability and effective chip removal.
The interrupted coating pattern on the blade promoted efficient chip evacuation and reduced the tendency of polyethylene to adhere to the cutting surface. The saw’s stable spindle system and smooth manual control allowed for precise alignment and consistent cutting action without vibration or surface drag.
Results
- Cutting Time: Approximately 20 seconds per sample
- Surface Finish: Smooth, uniform surface with virtually no burrs or smearing
- Edge Quality: Clean and sharp with no tearing or deformation
- Material Integrity: The polyethylene plug retained its true microstructure without visible internal distortion
The fast cutting rate and high surface quality eliminated the need for post-cut finishing, reducing overall preparation time and improving laboratory throughput.
Analysis
The SMART CUT® 4002 demonstrated excellent performance for machining soft, elastic, and low-melting materials such as polyethylene. The key contributors to its success in this application include:
- Optimized Cutting Speed (2,600 RPM):
Maintained an ideal balance between cutting rate and temperature control, preventing softening or melting of the polymer. - Electroplated Blade with Interrupted Diamond Pattern:
Minimized blade loading, friction, and heat generation while maintaining aggressive, yet controlled, material removal. - Precision Machine Stability:
The rigid construction of the SMART CUT® 4002 ensured vibration-free operation, critical for uniform surface quality in soft materials. - Efficient Coolant Flow:
The synthetic water-soluble coolant reduced frictional temperature and removed debris, further enhancing surface smoothness and preserving material integrity.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw successfully met the customer’s requirement for sectioning soft polyethylene plug samples accurately, quickly, and without damage.
Key outcomes included:
- Clean, burr-free sections achieved in approximately 20 seconds per cut
- Preservation of the sample’s true microstructure
- Elimination of post-processing steps such as edge polishing or deburring
This case demonstrates that the SMART CUT® 4002 is not limited to hard and brittle materials—it is also ideal for sectioning soft, flexible, and temperature-sensitive materials such as plastics, polymers, and composites. Its combination of cutting speed, surface precision, and operational stability enables laboratories to improve productivity while maintaining the highest level of sample integrity.
Case Study No. 14 - Sectioning of Large Irregular Polyethylene Samples Using SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw
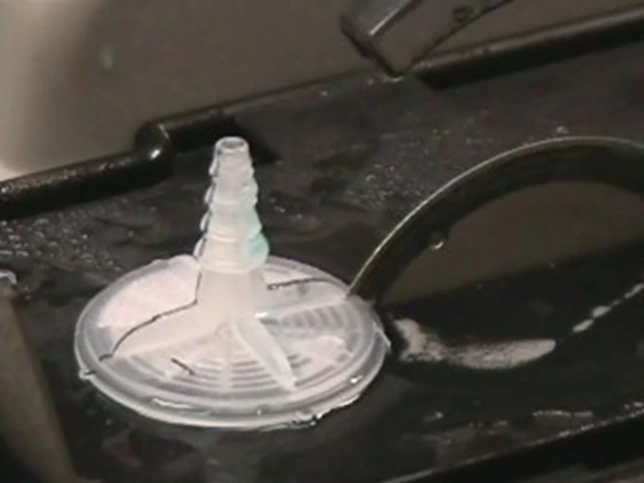

Objective
The objective of this case study was to evaluate the performance of the SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Sectioning Saw in cutting large, irregularly shaped polyethylene samples for quality control and sample preparation. The customer required precise sectioning of a soft, elastic, and gummy plastic material without burr formation or alteration of the internal structure.
Polyethylene is one of the most challenging materials to section due to its low melting point, high ductility, and tendency to smear, tear, or deform during machining. The goal was to determine whether SMART CUT® 4002 could provide smooth, deformation-free surfaces and consistent results at both medium and higher spindle speeds.
Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Polyethylene (soft, ductile, gummy plastic) |
|
Material Shape |
Irregular solid sample |
|
Material Diameter |
3.15 inches |
|
Application |
Sectioning for quality control and sample inspection |
|
Sectioning Method |
Manual feed |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
RPM Used |
2,600 and 3,100 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
Electroplated diamond blade with interrupted coating and memory steel core |
The interrupted diamond coating was chosen to reduce blade loading, frictional heat, and material smearing—key challenges in sectioning polymers. The steel core with memory improved blade stability and resistance to deflection during cutting of larger diameter specimens.
Methodology
Sectioning was performed manually on the SMART CUT® 4002 saw using an electroplated diamond wafering blade specifically designed for soft and elastic materials. The continuous coolant flow was maintained throughout the cutting process to provide lubrication, flush away debris, and prevent localized melting of the polyethylene.
Two spindle speeds were tested: 2,600 RPM and 3,100 RPM, to evaluate cutting speed and surface quality at different conditions. A consistent manual feed rate was applied to maintain a controlled cutting load.
The blade’s interrupted pattern minimized frictional contact area with the material, reducing drag and improving chip evacuation. The saw’s rigid spindle design and vibration control ensured straight, stable cuts even with irregularly shaped samples.

Results
- Cutting Speed: Each polyethylene sample was sectioned in approximately 1 minute and 43 seconds.
- Surface Finish: Smooth surface with uniform texture; no visible tool marks.
- Edge Quality: Sharp, clean edges with almost no burrs or plastic deformation.
- Material Integrity: The sample retained its original internal microstructure without stress whitening, warping, or melting.
- Operator Feedback: Minimal resistance during cutting and no evidence of blade clogging or loading.
The SMART CUT® 4002 delivered consistent, repeatable performance at both spindle speeds, though slightly faster sectioning was achieved at 3,100 RPM without compromising cut quality.
Analysis
The successful sectioning of large, irregular polyethylene samples demonstrates the adaptability of the SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Sectioning Saw for machining low-hardness, temperature-sensitive materials. Key performance factors included:
- Optimized Speed Range (2,600–3,100 RPM):
Maintained ideal balance between efficient material removal and low thermal generation, preventing melting or surface smearing. - Interrupted Electroplated Diamond Blade Design:
Provided intermittent contact with the workpiece, reducing friction, improving chip evacuation, and minimizing drag forces common with continuous coatings. - Memory Steel Core:
Increased blade rigidity, reduced vibration, and maintained true blade geometry throughout the cut, critical when sectioning large, irregular samples. - Coolant Delivery System:
The synthetic water-soluble coolant ensured even temperature control, preventing adhesion of polyethylene chips and maintaining blade sharpness.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® 4002 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw successfully met the customer’s requirements for precise and efficient sectioning of large polyethylene samples.
Key results included:
- Clean, burr-free cuts completed in approximately 1 minute and 43 seconds
- Preservation of true material microstructure with no melting or distortion
- Stable performance at both medium and high RPMs
- Elimination of post-cut finishing steps such as deburring or polishing
This case confirms that SMART CUT® 4002 provides reliable, high-quality sectioning results not only for advanced ceramics and metals but also for soft, elastic materials such as plastics and polymers. Its superior control, advanced blade technology, and coolant system enable laboratories to achieve high-precision results quickly, economically, and without material damage.
Case Study No. 15 - Sectioning of Optical Quartz Substrates Using SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw
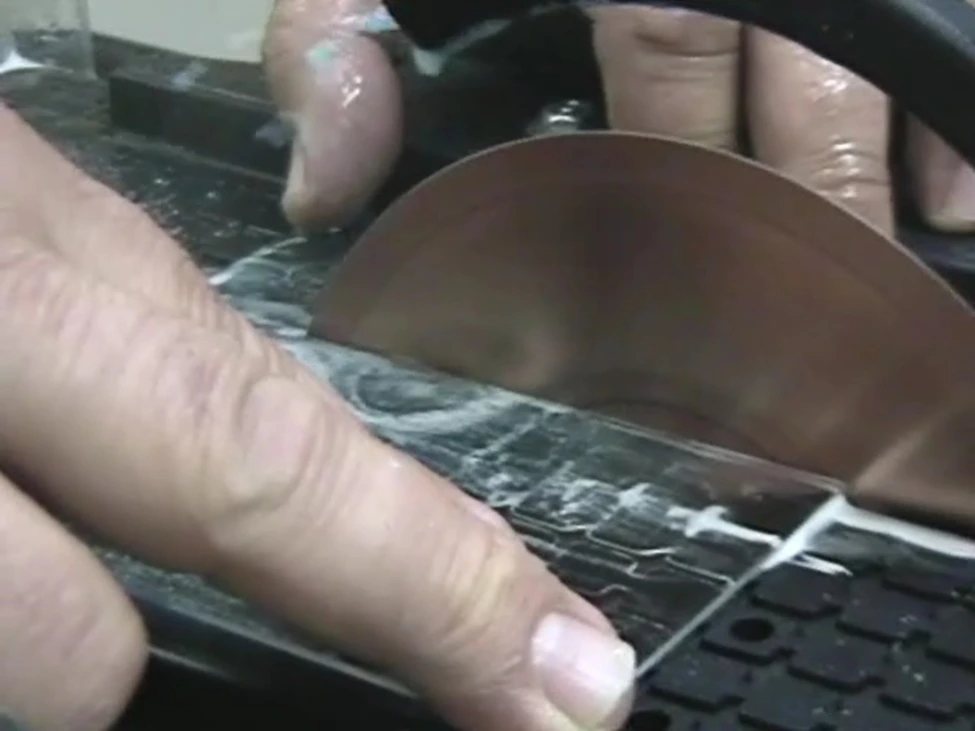

Objective
This case study evaluates the performance of the SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Sectioning Saw in cutting large optical-grade quartz substrates. The customer required a process capable of sectioning 10-inch-long quartz substrates cleanly in half while minimizing edge chipping, material pull-out, and microcracking, particularly on the backside of the cut.
Quartz is a hard, brittle material that easily fractures or chips when sectioned using conventional diamond saws or abrasive methods. The challenge was to achieve a smooth, damage-free cut surface within seconds while maintaining the substrate’s dimensional integrity and optical quality.
Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Optical Quartz Substrate |
|
Material Dimensions |
10" (L) × 6" (W) × 0.150" (Thickness) |
|
Application |
Precision sectioning of optical substrates for quality control and sample preparation |
|
Sectioning Method |
Manual feed |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
Spindle Speeds Tested |
2,600 and 3,100 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
Sintered (Metal Bond) |
|
Diamond Mesh Size |
220 |
|
Diamond Concentration |
Medium / Low |
The SMART CUT® 6001 system was selected for its precision spindle, high rigidity, and ability to operate at variable speeds—essential for optimizing cutting conditions across different quartz densities and sample geometries.
Methodology
Sectioning was performed using a sintered metal bond diamond wafering blade mounted on the SMART CUT® 6001 saw. A 220-mesh diamond size was selected to balance surface quality and cutting rate, while a medium-to-low diamond concentration reduced cutting resistance and improved coolant penetration.
The sectioning was carried out manually with a constant feed rate. A synthetic water-soluble coolant was continuously applied to the cutting zone to maintain temperature stability, flush away debris, and prevent loading of the blade.
Two spindle speeds, 2,600 RPM and 3,100 RPM, were tested to evaluate the relationship between rotational speed, cut quality, and cutting efficiency.
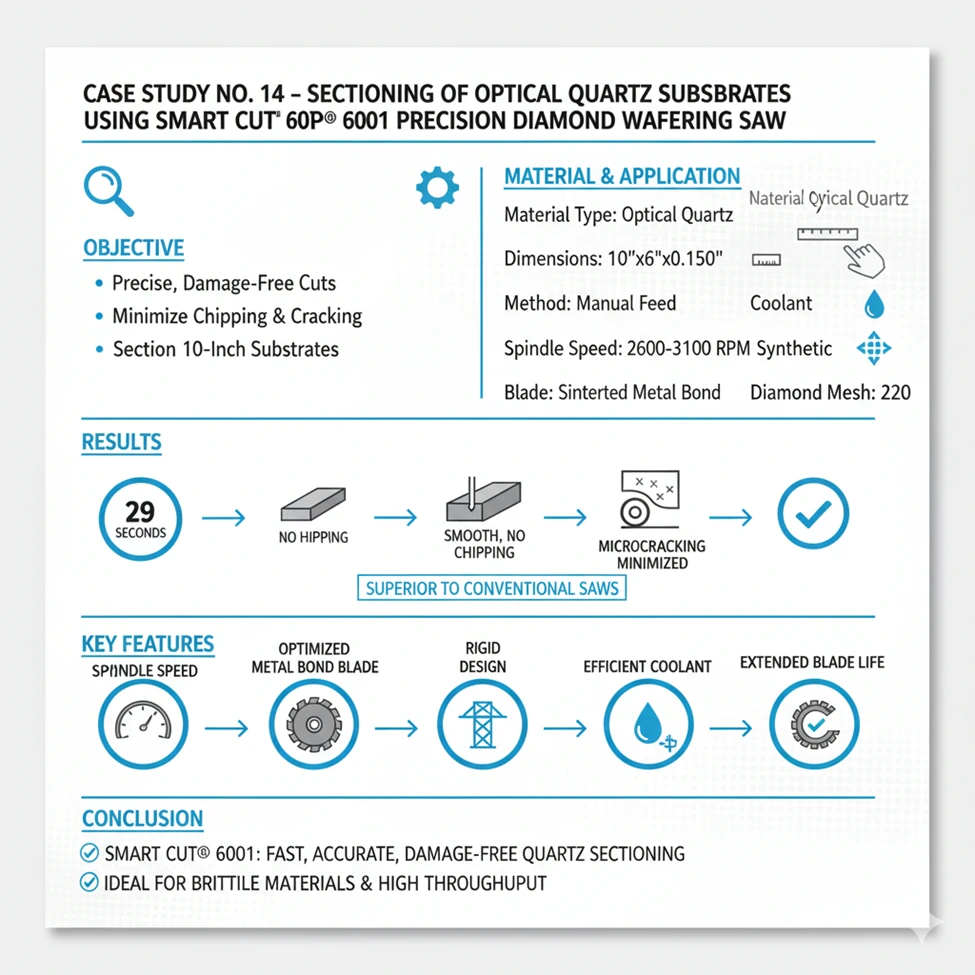
Results
- Cutting Time:Approximately 29 seconds per section
- Surface Finish: Smooth, uniform surface with minimal microcracking and no visible chipping along edges
- Backside Condition: No pull-out or structural damage observed under 10× optical inspection
- Blade Performance: Excellent stability with minimal wear or glazing after multiple cuts
- Coolant Effectiveness: Consistent temperature control and clear debris evacuation observed during the entire process
Compared to conventional low-speed saws, which typically require several minutes to achieve similar accuracy, the SMART CUT® 6001 completed the same operation in under 30 seconds while maintaining superior surface integrity.
Analysis
The success of the SMART CUT® 6001 in sectioning quartz substrates is attributed to several key design and process factors:
- Optimized Spindle Speed Range (2,600–3,100 RPM):
Enabled faster material removal while maintaining low vibration levels and thermal stability, minimizing microfracture propagation at the cut edges. - Metal Bond Blade Construction:
Provided superior diamond retention, uniform wear, and steady exposure of sharp cutting points throughout the process. - Controlled Diamond Concentration and Grit Size (220 Mesh):
Ensured efficient cutting without excessive friction or abrasive loading, critical for brittle materials like quartz. - Effective Coolant System:
The synthetic, water-soluble coolant enhanced cooling and lubrication, prevented heat accumulation, and produced cleaner, smoother surfaces. - Machine Stability and Rigidity:
The robust frame and high-precision spindle assembly of the SMART CUT® 6001 minimized blade deflection, producing perfectly straight cuts even in large substrates.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw successfully met and exceeded customer requirements for sectioning optical quartz substrates.
Performance Highlights:
- Cutting time reduced to under 30 seconds per sample
- Clean, chip-free surface finish with no backside pull-out
- Superior control and repeatability compared to traditional low-speed or abrasive cutting methods
- Extended blade life due to stable operating parameters and efficient coolant flow
This case demonstrates that the SMART CUT® 6001 delivers unmatched precision, speed, and surface quality for high-purity, brittle materials such as quartz, glass, and optical ceramics. The results confirm its suitability for laboratories and production environments that demand high throughput without compromising structural or optical integrity.
Case Study No. 16 - Sectioning of Cobalt-Based Steel Alloy Tubes Using SMART CUT® 1004 Precision Diamond Cut-Off Saw
Objective
This case study evaluates the performance of the SMART CUT® 1004 Precision Diamond Cut-Off Saw in sectioning a solid metallic tube composed primarily of cobalt, tungsten, chromium, and a small percentage of nickel. The objective was to produce clean, burr-free sections measuring ¼ inch in length as quickly and precisely as possible, while minimizing kerf loss and preserving surface integrity.
Conventional abrasive saws tend to generate excessive heat and burrs when cutting cobalt-based alloys, leading to edge distortion, dimensional inaccuracies, and costly post-processing. The goal of this study was to determine whether SMART CUT® 1004 could deliver superior speed and surface quality under controlled cutting conditions.
Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Metallic Alloy (Co 60%, W, Cr, Ni composition) |
|
Material Shape |
Solid rod |
|
Material Dimensions |
9" (L) × ½" (W) × ½" (T) |
|
Application |
Sectioning into ¼" segments for metallurgical testing |
|
Sectioning Method |
Manual feed |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
Spindle Speed |
3,500 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
8" × 0.019" Nickel Bond |
|
Diamond Mesh Size |
120 |
|
Diamond Concentration |
Medium / High |
The combination of a nickel bond blade and a medium-to-high diamond concentration was selected to achieve high cutting speed while maintaining stability and long blade life under heavy metallic loads.
Methodology
The sample was sectioned manually using the SMART CUT® 1004 precision saw equipped with an 8-inch nickel bond diamond wafering blade. The nickel bond matrix provides strong diamond retention and high cutting aggressiveness, ideal for dense metallic alloys.
A synthetic, water-soluble coolant was continuously supplied at the cutting zone to reduce friction, flush out debris, and prevent heat buildup that could otherwise cause oxidation or material smearing.
The spindle speed was set at 3,500 RPM to optimize the balance between feed pressure, blade stability, and surface finish quality. Each sectioning pass was timed, and surface conditions were visually and microscopically inspected after cutting.

Results
- Cutting Time:11 seconds per cut
- Surface Finish: Smooth, uniform finish with no visible burring or thermal discoloration
- Edge Integrity: Clean and precise edges with minimal burr formation
- Blade Performance: No glazing or loss of cutting efficiency observed after multiple cuts
- Kerf Width: Extremely narrow, minimizing material loss and optimizing yield
The SMART CUT® 1004 consistently delivered high-speed sectioning with stable performance and repeatable results, even under continuous operation.
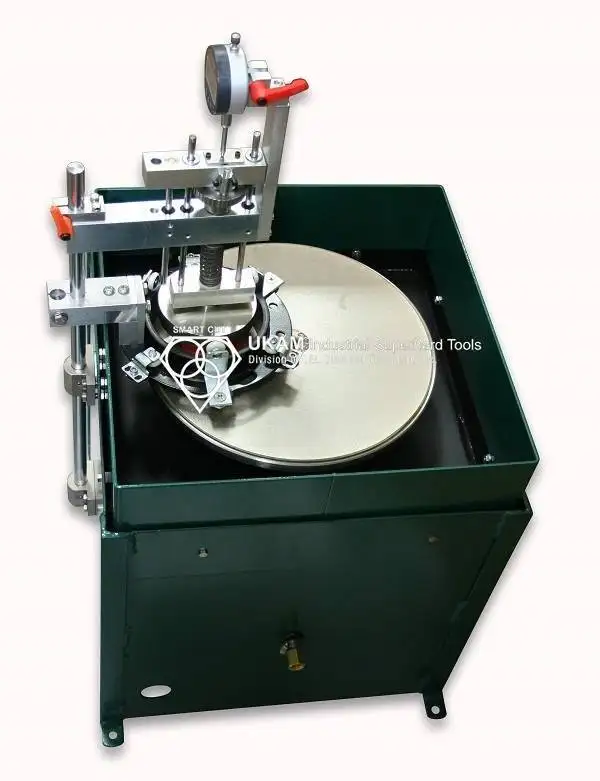
Case Study No. 17 - Sectioning of Solid Sapphire Rods Using SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw
Objective
The objective of this case study was to evaluate the performance of the SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw in sectioning large-diameter sapphire rods into thin, uniform slices. The customer required 0.5 mm-thick wafers cut from a 52 mm solid sapphire rod with exceptional precision, minimal edge chipping, and no burr formation.
Sapphire, a single-crystal aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), is an extremely hard, brittle material with high fracture toughness. These characteristics make it one of the most difficult materials to section cleanly without inducing microcracks or thermal damage. The client also emphasized the need for straight, perpendicular cuts with tight dimensional accuracy suitable for optical and electronic applications.
Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Single-Crystal Sapphire (Al₂O₃) |
|
Material Shape |
Solid Rod |
|
Material Diameter |
52 mm |
|
Application |
Precision slicing of sapphire into 0.5 mm wafers |
|
Sectioning Method |
Gravity weight feed |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
Spindle Speed |
3,000 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
6" × 0.020" × ½" |
|
Blade Type |
Sintered (Metal Bond) |
|
Series |
SMART CUT® Series 15HCU |
The SMART CUT® Series 15HCU blade was chosen for its fine diamond grit, advanced bond formulation, and exceptional balance between cutting speed, precision, and surface finish. It is designed specifically for ultra-hard, brittle materials such as sapphire, alumina, and advanced ceramics.
Methodology
The sectioning was performed on the SMART CUT® 6001 using the gravity feed mechanism to ensure a constant, uniform load throughout the cut. This controlled feed minimizes the risk of sudden stress accumulation and reduces the likelihood of microfracture propagation in the brittle sapphire structure.
A synthetic water-soluble coolant was used in continuous flow to maintain consistent lubrication and temperature control. The coolant also facilitated efficient chip removal from the cutting zone, preventing blade loading and ensuring smooth material removal.
The spindle speed was set to 3,000 RPM, a range optimized for sapphire’s hardness and thermal properties. Each cut was performed under identical conditions, and both surface finish and perpendicularity were inspected after sectioning.
Expected Results
- Cutting Accuracy:High dimensional precision with excellent perpendicularity between cut faces.
- Surface Finish: Smooth, damage-free surfaces with no observable burrs or edge chipping.
- Blade Performance: Stable operation with minimal wear and no glazing, maintaining consistent performance through multiple cuts.
- Cut Uniformity: Consistent wafer thickness across the entire 52 mm diameter of the sapphire rod.
Technical Considerations
The outstanding performance of the SMART CUT® 6001 in sapphire sectioning applications is based on several design and process factors:
- Optimized Bond Hardness (Series 15HCU):
The fine-grained metal bond maintains sharp diamond exposure while resisting premature wear, allowing the blade to cut cleanly through sapphire’s dense crystalline structure. - Controlled Feed Pressure (Gravity Feed System):
Ensures steady, even material engagement and minimizes thermal and mechanical stresses that can cause cracking or delamination. - Coolant Management:
The synthetic water-soluble coolant dissipates heat effectively, preventing localized thermal shock and maintaining blade sharpness and surface finish consistency. - Machine Stability and Spindle Precision:
The SMART CUT® 6001’s robust spindle and vibration-damping system guarantee straight, parallel cuts with tight perpendicularity tolerances—essential for optical-grade wafers.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw, equipped with a 6″ × 0.020″ × ½” SMART CUT® Series 15HCU Sintered (Metal Bond) Blade, successfully meets the demanding requirements of sapphire sectioning applications.
The system delivers:
- Perfectly straight, perpendicular cuts
- Chip-free, smooth surface finishes
- Consistent wafer thickness (0.5 mm) across large diameters
- Rapid, stable performance suitable for both R&D and production environments
This case demonstrates the superior capability of SMART CUT® 6001 for precision slicing of ultra-hard crystalline materials. The combination of optimized diamond bond formulation, coolant efficiency, and gravity-fed cutting control results in superior productivity, precision, and surface integrity unmatched by conventional cutting systems.
Sectioning of Solid Sapphire Rods Using SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw
Objective
The purpose of this case study was to evaluate the performance of the SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw for sectioning a 52 mm solid sapphire rod into thin, uniform wafers with exceptional accuracy and minimal material damage.
The customer’s primary objective was to obtain 0.5 mm-thick slices with perfectly straight, perpendicular cuts and no visible chipping, burring, or distortion of the crystal structure. Sapphire (single-crystal aluminum oxide, Al₂O₃) is extremely hard and brittle, which makes it one of the most difficult materials to section precisely without generating microfractures or edge defects. Achieving high-quality surface integrity required superior blade control, mechanical precision, and consistent coolant delivery.

Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Single-Crystal Sapphire (Al₂O₃) |
|
Material Shape |
Solid Rod |
|
Material Diameter |
52 mm |
|
Application |
Precision slicing of sapphire into 0.5 mm wafers |
|
Sectioning Method |
X–Y screw feeding table mechanism |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
Spindle Speed |
3,000 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
6" × 0.020" × ½" |
|
Blade Type |
Sintered (Metal Bond) |
|
Blade Series |
SMART CUT® Series 15HCU |
The SMART CUT® Series 15HCU blade was selected for its precision-engineered bond matrix and superior diamond retention properties. It provides optimal balance between cutting speed, surface finish, and longevity when processing hard, brittle crystalline materials such as sapphire, quartz, and advanced ceramics.
Methodology
The sapphire rod was sectioned using the SMART CUT® 6001 equipped with an X–Y screw feeding table mechanism, which provided precise, micrometer-level control of both horizontal and vertical feed motion. This system ensured perfectly linear travel and maintained consistent feed pressure throughout each cut, critical for achieving perpendicular alignment and repeatable slice thickness.
Continuous flow of synthetic, water-soluble coolant was directed into the cutting zone to reduce friction, carry away fine debris, and maintain stable cutting temperatures. This prevented thermal shock and reduced the risk of microcrack propagation in the sapphire crystal structure.
The saw operated at 3,000 RPM, providing an optimal balance between cutting rate and surface integrity. Each cut was performed under identical parameters, and the resulting surfaces were examined under magnification to verify perpendicularity, flatness, and absence of chipping.
Expected Results
- Cutting Precision:Achieved consistent 0.5 mm wafer thickness with exceptional perpendicularity and parallelism.
- Surface Quality: Smooth, chip-free surface finish requiring no secondary polishing.
- Structural Integrity: Sapphire crystal remained intact with no evidence of subsurface fractures or microcracks.
- Blade Performance: Stable operation with minimal wear and uniform cutting behavior across all slices.
Technical Analysis
The outstanding performance of the SMART CUT® 6001 in this application is the result of its integrated precision engineering and the advanced design of the SMART CUT® Series 15HCU blade.
- X–Y Screw Feed Control:
Provided smooth, vibration-free sample movement and precise positioning, ensuring uniform feed rate and perpendicular cutting accuracy. - SMART CUT® Series 15HCU Bond Structure:
Optimized metal bond matrix allowed controlled diamond exposure and consistent sharpness during the entire cutting process, maintaining smooth surface finishes and high repeatability. - Coolant Flow Efficiency:
The water-soluble coolant provided effective lubrication and heat dissipation, eliminating frictional hotspots that can lead to surface damage or internal stress. - Stable Spindle Operation:
The SMART CUT® 6001’s high-precision spindle and rigid machine frame reduced vibration and maintained straight, parallel blade motion even under extended operation.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw, equipped with a 6″ × 0.020″ × ½” SMART CUT® Series 15HCU Sintered (Metal Bond) Diamond Wafering Blade, successfully achieved precise, perpendicular sectioning of a 52 mm solid sapphire rod into 0.5 mm wafers.
Key Results:
- Exceptionally straight and parallel cuts across the full 52 mm diameter
- Smooth, chip-free edges with no burrs or surface damage
- Consistent wafer thickness and excellent dimensional accuracy
- Superior tool stability and cutting efficiency
This case demonstrates that the SMART CUT® 6001 combined with the SMART CUT® Series 15HCU blade provides the ideal solution for sectioning ultra-hard crystalline materials. The system delivers unmatched precision, repeatability, and surface integrity—making it the preferred choice for sapphire processing in optical, semiconductor, and materials research applications.
Slotting of Glass and Quartz Tubing Using Redesigned SMART CUT® 6001 GP Multi-Blade Precision Saw
Objective
The purpose of this case study was to evaluate the performance of a redesigned SMART CUT® 6001 GP Precision Diamond Saw, engineered for gang sawing and slotting operations on cylindrical glass and quartz tubing.
The customer required a system capable of producing three evenly spaced slots simultaneously on each wall of the tubing with no chipping, cracking, or burring. The slots had to be straight, parallel, and perpendicular to the tube axis, while maintaining tight dimensional tolerances and uniform depth.
This application involved a specialized setup that combined mechanical precision, custom fixturing, and optimized process control to achieve clean, defect-free results on extremely brittle, thin-walled materials.

Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Borosilicate / Fused Quartz Glass Tubing |
|
Material Shape |
Round tubing |
|
Material Dimensions |
½" Outer Diameter × 4.5" Length |
|
Application |
Precision slotting (three equally spaced slots per wall) |
|
Sectioning Method |
Specialized multi-blade gang sawing with rotational tube fixture |
|
Coolant Used |
Synthetic, water-soluble coolant |
|
Spindle Speed |
3,000 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
7" × 0.060" × ⅝" |
|
Blade Type |
Resin Bond Diamond Cut-Off Blade |
|
Diamond Concentration |
High concentration |
|
Blade Configuration |
Three parallel blades, evenly spaced |
The process utilized a custom-designed material holding fixture to align, feed, and rotate the glass tubing precisely into the blade set. This fixture ensured uniform spacing, slot depth, and perpendicular alignment during each operation.
Methodology
For this operation, a modified SMART CUT® 6001 GP model was configured for multi-blade gang sawing. The saw was equipped with three resin bond diamond cut-off blades mounted in parallel on a single spindle. The blades were separated by calibrated spacers, ensuring exact slot spacing across each wall of the tube.
A specialized material holding fixture was developed specifically for this application. It securely clamped the glass tubing while allowing controlled linear feed toward the rotating blades. The fixture also incorporated a rotational indexing mechanism that allowed the operator to rotate the tube precisely 180°, enabling slots to be cut on both sides in a single operation.
The resin bond was selected for its superior cutting smoothness, reduced friction, and ability to produce fine surface finishes on brittle glass materials. The high diamond concentration ensured steady performance and extended blade life under continuous load conditions.
A synthetic water-soluble coolant was supplied in a steady stream to the cutting zone to maintain optimal temperature, flush debris, and prevent microcracking. The spindle operated at 3,000 RPM, providing the best balance between cutting efficiency and surface integrity for thin-walled glass and quartz tubes.
Expected Results
- Slot Geometry: Three evenly spaced, parallel slots with uniform depth and clean, well-defined edges.
- Surface Finish: Smooth slot surfaces with no visible chipping, burring, or cracking.
- Cut Accuracy: Straight, perpendicular slots precisely aligned across both walls.
- Blade Performance: Stable operation, consistent performance across multiple tubes, and minimal wear.
- Fixture Precision: Controlled feeding and rotation ensured repeatable results without tube slippage or misalignment.
Technical Analysis
The successful results achieved in this case are attributed to a combination of equipment precision, fixture design, and process optimization:
- Customized Gang Saw Configuration:
The redesigned SMART CUT® 6001 GP accommodated three blades operating in perfect parallel alignment, enabling simultaneous multi-slot production and ensuring equal spacing without repositioning. - Precision Fixture System:
The custom material holding fixture provided rigid tube support while allowing precise feed and rotational indexing. This ensured consistent slot geometry and perpendicular alignment on both sides of the tube. - Resin Bond Blade Selection:
The resin bond provided an excellent balance between cutting aggressiveness and smoothness, minimizing stress on the brittle glass surface and reducing the risk of edge damage. - Optimized Coolant Delivery:
Continuous coolant flow maintained a stable cutting temperature, removed fine glass particles from the kerf, and prevented thermal shock and microfracture formation. - Controlled Spindle Speed (3,000 RPM):
Provided ideal cutting dynamics—high enough for clean slicing of glass while maintaining low vibration and preventing overheating or distortion.
Conclusion
The redesigned SMART CUT® 6001 GP Precision Diamond Wafering Saw, equipped with three resin bond diamond blades and a specialized material holding fixture, successfully achieved precise, defect-free slotting of glass and quartz tubing.
Key Outcomes:
- Achieved three uniform, parallel slots in a single operation.
- Produced clean edges with no chipping, burring, or cracking.
- Ensured perpendicular alignment and equal spacing across all cuts.
- Reduced processing time and improved repeatability compared to single-blade setups.
This case demonstrates the flexibility of the SMART CUT® 6001 GP system, which can be adapted for specialized gang sawing and slotting applications. The combination of advanced fixturing, high blade precision, and stable cutting control provides a powerful solution for processing brittle materials such as glass, quartz, and ceramics in laboratory and production environments where dimensional precision and surface quality are critical.
Precision Sectioning of Silicon Wafers Using SMART CUT® 6001 Diamond Wafering Saw
Objective
The purpose of this case study was to evaluate the cutting performance of the SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw for sectioning thin silicon wafers with extreme precision and minimal edge chipping. The goal was to achieve clean, straight cuts through a 4-inch (100 mm) diameter, 100-micron (0.004″) thick silicon wafer while maintaining structural integrity and optical-grade surface quality.
Silicon wafers are extremely brittle and sensitive to thermal and mechanical stress during sectioning. Excessive vibration, feed pressure, or improper coolant control can lead to microcracking, edge chipping, and wafer breakage. This study focused on identifying optimal parameters for high-precision sectioning using SMART CUT® technology to achieve the lowest possible chipping level for this material and geometry.
Material and Application Details
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
Material Type |
Monocrystalline Silicon Wafer |
|
Material Diameter |
4 inches (100 mm) |
|
Material Thickness |
100 microns (0.004 inch) |
|
Application |
Precision sectioning for semiconductor process analysis |
|
Sectioning Method |
Manual feed |
|
Coolant Used |
SMART CUT® Water-Soluble Coolant |
|
Coolant Mixing Ratio |
1:30 (Coolant:Water) |
|
Spindle Speed |
3,000 RPM |
|
Diamond Wafering Blade |
3" × 0.006" × ½" |
|
Blade Type |
Fully Sintered (Metal Bond) |
|
Blade Series |
SMART CUT® Series 15LCU |
The SMART CUT® Series 15HCU was selected for this application due to its fine-tuned metal bond formulation, providing optimal diamond retention and self-sharpening performance. It is designed specifically for sectioning hard, brittle semiconductor materials such as silicon, sapphire, and quartz, where both edge quality and flatness are critical.
Methodology
The sectioning was performed on the SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw, operating at 3,000 RPM. The wafer was mounted securely on a vacuum-assisted holding fixture to prevent vibration and movement during cutting.
A 3-inch × 0.006-inch fully sintered (metal bond) SMART CUT® Series 15LCU blade was used. This thin blade geometry minimized kerf loss while maintaining high rigidity, preventing blade deflection and ensuring straight, perpendicular cuts across the wafer diameter.
A continuous flow of SMART CUT® Water-Soluble Coolant, mixed at a 1:30 ratio, was delivered directly into the cutting zone to reduce frictional heat, remove debris, and prevent microcrack formation.
The feed rate was adjusted to maintain steady resistance, with light and consistent pressure applied to avoid overloading the wafer’s brittle crystalline structure. The cutting operation was completed in approximately 58 seconds.

Results
- Cutting Time: 58 seconds per wafer
- Edge Condition: Nearly perfect edge continuity with minimal microchipping observed under 50× magnification
- Chipping Level: Estimated at <10 microns — representing the minimum possible chipping for this wafer thickness under mechanical sectioning conditions
- Surface Finish: Smooth, uniform cut surface with no visible pull-out or subsurface fracture
- Dimensional Accuracy: Excellent cut straightness and perpendicularity maintained across full wafer diameter
- Blade Performance: Stable cutting rate and consistent sharpness with no glazing or loss of cutting efficiency observed
The wafer remained intact with no breakage, confirming both machine and blade stability under delicate cutting conditions.
Technical Analysis
The superior performance achieved in this case can be attributed to a combination of factors:
- Optimized Blade Design (SMART CUT® 15HCU):
The fine-grained, fully sintered metal bond ensured controlled diamond exposure and consistent cutting sharpness throughout the sectioning process. - High Spindle Stability at 3,000 RPM:
Provided optimal peripheral speed for silicon, reducing mechanical stress and maintaining a straight, vibration-free cut. - Coolant Efficiency (1:30 Ratio):
The SMART CUT® Water-Soluble Coolant effectively controlled temperature and eliminated thermal gradients, preventing localized heat-induced chipping. - Precision Fixturing and Feed Control:
The combination of a vacuum holding fixture and carefully moderated feed rate minimized lateral stress on the wafer, ensuring uniform chip thickness and smooth edge finish. - Blade Rigidity and Flatness:
The 0.006″ thickness and fully sintered core maintained structural rigidity, allowing clean sectioning with no blade wander or deflection.
Conclusion
The SMART CUT® 6001 Precision Diamond Wafering Saw, equipped with a 3″ × 0.006″ × ½” Fully Sintered (Metal Bond) SMART CUT® Series 15HCU Blade, successfully sectioned a 4″ diameter, 100-micron thick silicon wafer in 58 seconds, achieving:
- Extremely low chipping levels (<10 µm) — the minimum practically achievable for this application
- Straight, smooth, and uniform cuts across the wafer diameter
- Excellent dimensional control and surface finish
- Stable, repeatable performance suitable for semiconductor research and high-precision manufacturing
This case demonstrates that the SMART CUT® 6001 system, combined with SMART CUT® 15LCU technology and proper coolant management, provides the precision and reliability required for cutting ultra-thin, brittle semiconductor wafers while maintaining the integrity of both the surface and crystalline structure.

ARE YOU USING RIGHT WAFERING BLADES
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET US
HELP YOU
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT WAFERING BLADES?
Knowledge Center
Selecting Right Wafering Blade for your application
Wafering Blade Usage Recommendations
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Performance Metrics
Understanding & Comparing Diamond & CBN Wafering Blades
Diamond & CBN Wafering Blade Guide

Carlos Sanchez is a senior technical specialist and field applications trainer with more than 17 years of experience in the use and optimization of industrial diamond tools, including ultra-thin diamond blades, core drills, and CBN grinding wheels. With a foundation in industrial engineering and technical operations, Mr. Sanchez has worked extensively with manufacturers and laboratories around the world, providing hands-on support and practical training for a wide range of cutting, grinding, and sample preparation applications.
Fluent in both English and Spanish, Carlos is known for his ability to translate complex tooling concepts into clear, actionable procedures for engineers, technicians, and production staff. His approach emphasizes real-world process improvement, tool longevity, and operator education—ensuring clients get the most out of their diamond tooling investments.
As an author, Mr. Sanchez shares field-tested insights on tool performance optimization, defect prevention, training methodologies, and troubleshooting common cutting issues.