SMART CUT® Cut‑Off Wheels Designed for High‑Performance Cutting Applications
-
Posted by
 Brian Farberov
Brian Farberov
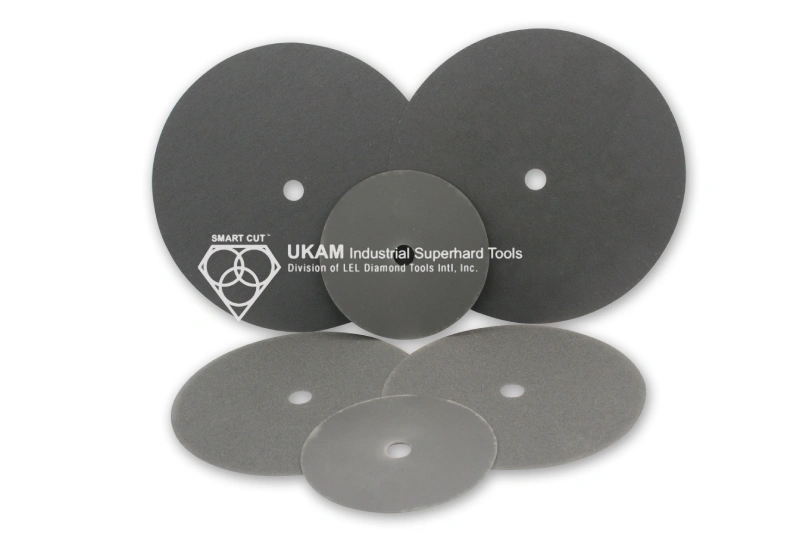

Table of Contents
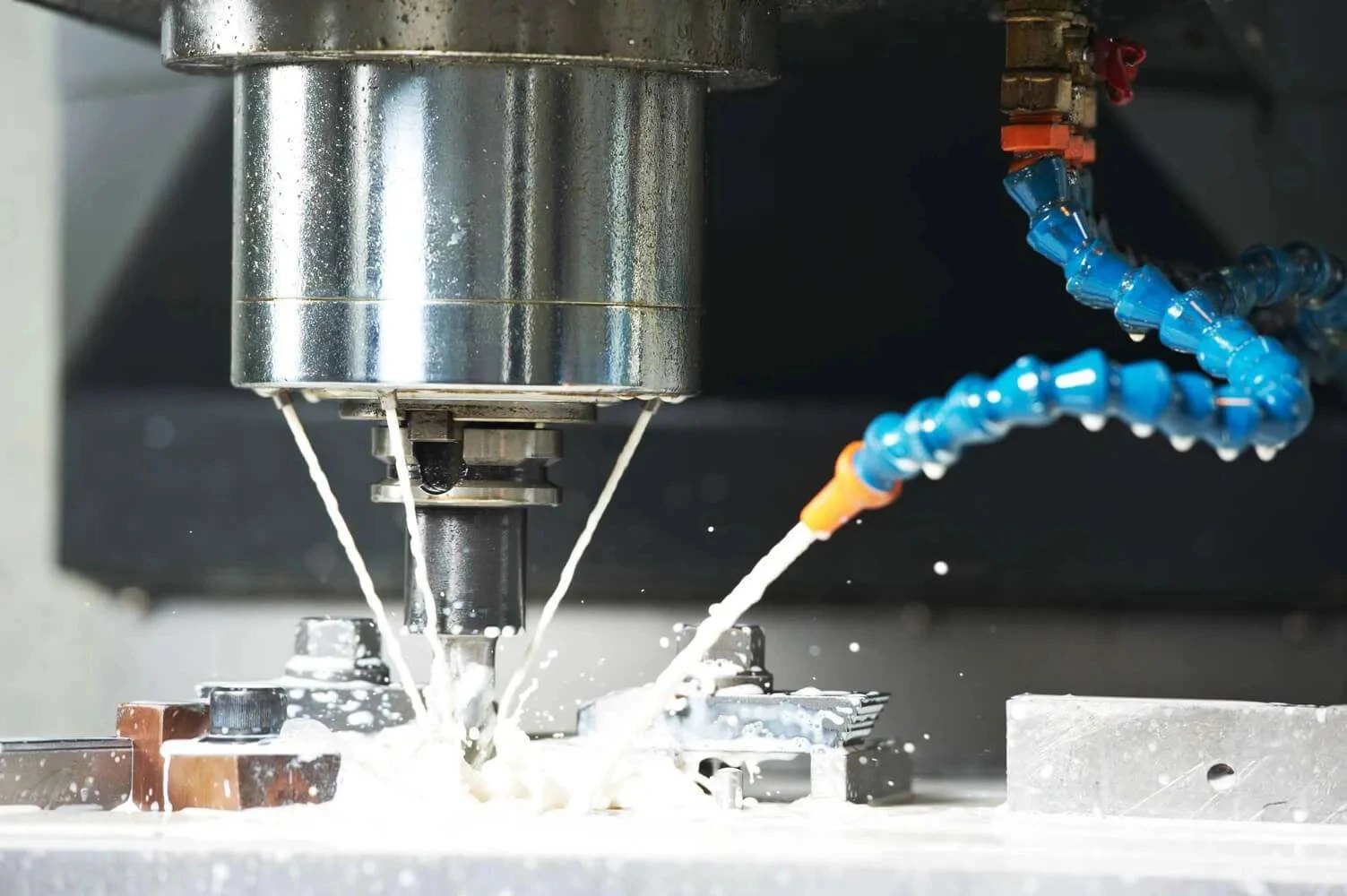
ToggleAbrasive cut‑off wheels are a necessary tool within industrial manufacturing and metal fabrication operations. Critical is the accuracy, performance, and safety in the workplace. Whether you need to cut iron, steel, or stainless steel rod or tubing, CNC cutting systems produce metal products from their best side: with clean separation edges of the highest quality. However, even though they are important, cut‑off applications continue to be carried out with all-purpose grinding wheels that are not intended for continuous cutting.
To achieve consistent results and long‑term performance, cut‑off applications require wheels engineered specifically for cutting, not adapted from standard grinding solutions. SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels are designed to meet these demands, delivering precision, durability, and safety across a wide range of industrial cutting applications.
The Unique Nature of Cut‑Off Applications
Cut‑off applications differ significantly from surface grinding, deburring, or finishing processes. Instead of removing material laterally, cut‑off wheels penetrate directly into the workpiece and maintain constant engagement throughout the cut. This creates a unique set of mechanical and thermal stresses that place extreme demands on wheel performance.
Key characteristics of cut‑off applications include:
- High RPM and peripheral speed
- Thin wheel profiles with minimal tolerance for deflection
- Concentrated cutting forces at the wheel edge
- Continuous heat generation in a narrow cutting zone
- High stability requirements to ensure straight, accurate cuts
Because of these conditions, even minor compromises in wheel design—such as improper abrasive selection or insufficient reinforcement—can lead to glazing, excessive heat buildup, vibration, or premature wheel failure.

Why General‑Purpose Wheels Fall Short
General‑purpose grinding wheels are designed for surface contact and lateral stock removal. When used as cut‑off wheels, they are forced to operate outside their intended design parameters. This often results in poor performance and safety concerns.
Common problems include:
- Slow cutting rates that reduce productivity
- Excessive heat generation leading to workpiece discoloration or metallurgical damage
- Glazing caused by dull abrasive grains
- Increased vibration and loss of cut accuracy
- Short wheel life and frequent wheel changes
- Greater risk of cracking or catastrophic wheel failure
In industrial environments where efficiency and safety are critical, these issues increase downtime, raise operating costs, and compromise overall process stability.
The Importance of Application‑Specific Cut‑Off Wheel Design
Cut‑off wheels must be engineered with a different design philosophy than grinding wheels. Every component—abrasive type, grain size, bond formulation, reinforcement, and wheel geometry—must be optimized specifically for cutting.
- Application‑specific cut‑off wheels are designed to:
- Maintain sharp cutting edges throughout the cut
- Minimize friction and control heat generation
- Resist deflection in thin profiles
- Deliver consistent cutting performance from start to finish
- Provide predictable wear and longer service life
This level of engineering ensures reliable operation even under demanding cutting conditions.

SMART CUT® Cut‑Off Wheels: Engineered Specifically for Cutting

SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels are designed from the ground up to meet the challenges of modern cut‑off applications. Rather than modifying standard grinding wheel designs, SMART CUT® focuses on application‑driven engineering, ensuring each wheel delivers optimal cutting efficiency, stability, and safety.
Precision Abrasive Selection
SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels are made to deliver sharp cutting points under high contact pressure. The grits of these abrasives are melded on this premise – to achieve a quick and aggressive cut without reducing the longevity of each sheet by grinding along with too much friction that produces heat.
Because sharp grain geometry is preserved through the entire cut, SMART CUT® cut-off wheels require less force to cut and help to lower user fatigue, as well as wheel wear.
Optimized Bond Systems
The bond system plays a critical role in cut‑off wheel performance. SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels use advanced bond formulations designed to balance grain retention with controlled release.
As abrasive grains become dull, the bond allows them to release at the appropriate time, exposing fresh cutting edges. This self‑sharpening behavior prevents glazing, maintains consistent cutting efficiency, and reduces the risk of overheating or burning the workpiece.
Reinforced Thin‑Wheel Construction
Thin cut‑off wheels must maintain structural integrity at high speeds. SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels incorporate advanced reinforcement to ensure stability, even under high mechanical stress.
This reinforced construction:
- Reduces vibration during cutting
- Improves straightness and cut accuracy
- Enhances operator control
- Increases overall safety
These features are particularly important in automated and high‑speed cutting systems, where consistency and reliability are essential.
Heat Control and Workpiece Protection
Excessive heat is one of the most common causes of poor cut quality and premature wheel failure. SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels are engineered to minimize heat generation and promote efficient heat dissipation.
Improved thermal control helps prevent:
- Workpiece discoloration
- Metallurgical damage
- Micro‑cracking
- Surface distortion
This is especially important when cutting hardened steels, stainless steels, tool steels, and heat‑sensitive alloys.
Benefits of Using SMART CUT® Cut‑Off Wheels

Using cut‑off wheels engineered specifically for cutting delivers measurable advantages across industrial operations:
- Faster, cleaner cuts with improved accuracy
- Reduced heat buildup and lower burn risk
- Longer wheel life and fewer changeovers
- Improved stability and operator safety
- Consistent performance throughout the wheel’s life
- Lower total cost per cut
These benefits make SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels an ideal choice for both high‑volume production and precision cutting environments.
Industrial Applications for SMART CUT® Cut‑Off Wheels

SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels are used across a wide range of industries and cutting applications, including:
- Metal fabrication and industrial manufacturing
- Cutting carbon steel, stainless steel, and tool steels
- Hardened alloys and specialty metals
- Aerospace and automotive components
- Tool and die manufacturing
- Precision cutting of rods, tubes, pipes, and profiles
Their consistent performance makes them suitable for manual, semi‑automated, and fully automated cutting systems.
Why Choosing the Right Cut‑Off Wheels Matters

Choosing the right cut‑off wheels is more than a tooling decision; it affects productivity, safety, and product quality. Wheels developed exclusively for cut‑off applications give you lower downtime, less waste, and fewer changes to increase productivity.
When you select SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels for your manufacturing process, you have more latitude in how to control the cut, lower the cost per part, and make more predictable, repeatable cuts.
Table of Comparison for SMART CUT®
Abrasive Cut Off Blades
|
Attribute |
Resin Bond (Aluminum Oxide) |
Resin Bond (Silicon Carbide) |
Rubber Bond (Aluminum Oxide) |
Rubber Bond (Silicon Carbide) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Abrasive Material |
Aluminum Oxide |
Silicon Carbide |
Aluminum Oxide |
Silicon Carbide |
|
Bond Type |
Resin (phenolic, epoxy) |
Resin (phenolic, epoxy) |
Rubber (natural or synthetic) |
Rubber (natural or synthetic) |
|
Cutting Speed |
High |
High |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
Flexibility |
Low |
Low |
High |
High |
|
Heat Resistance |
Moderate |
Moderate |
High |
High |
|
Water Resistance |
Low |
Low |
High |
High |
|
Durability |
High |
High |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
Material Compatibility |
Hard, brittle materials |
Very hard materials |
Softer, more sensitive materials |
Softer, more sensitive materials |
|
Cut Quality |
Smooth, minimal deformation |
Smooth, minimal deformation |
Very smooth, minimal chipping |
Very smooth, minimal chipping |
|
Application |
Dry cutting |
Dry cutting |
Wet or dry cutting |
Wet or dry cutting |
|
Cost |
Low to Moderate |
Low to Moderate |
Moderate to high |
Moderate to high |
|
Maintenance |
Low |
Low |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
Noise Level |
Higher |
Higher |
Lower |
Lower |
|
Thermal Stability |
Good |
Good |
Excellent |
Excellent |
|
Impact Resistance |
Low |
Low |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
Cutting Precision |
High |
High |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
Suitability for Delicate Materials |
Poor |
Poor |
Excellent |
Excellent |
|
Wear Rate |
Moderate |
Moderate |
High |
High |
|
Vibration Damping |
Low |
Low |
High |
High |
|
Environmental Suitability |
Best in controlled environments |
Best in controlled environments |
Versatile in various settings |
Versatile in various settings |
|
Ease of Use |
Easy for skilled operators |
User-friendly for all levels |
User-friendly for all levels |
User-friendly for all levels |
Conclusion
Applications such as cut‑off drive abrasives to the limit of their mechanical and thermal capabilities. When performing such operations with a general‑purpose wheel, it is not uncommon to end up with lost productivity, significantly faster wear of the wheel, and safety issues. SMART CUT® cut off wheels are made for cutting, extending the life and performance of hundreds of other varieties of failure-prone, low‑quality wheels even in the most demanding industrial conditions.
Selecting application‑tailored cutoff wheels is more than just an added value—it’s a smart strategy designed to help you improve productivity, quality, and long‑term profitability.
FAQs
Cut‑off wheels are used for precise cutting of metals such as steel, alloys, rods, tubes, and pipes.
SMART CUT® cut‑off wheels are engineered specifically for cutting, offering faster cuts, better heat control, and longer life.
Application‑specific cut‑off wheels improve cutting efficiency, safety, accuracy, and overall tool life.
Yes, they are designed to reduce friction and control heat during cutting.
They can cut carbon steel, stainless steel, hardened alloys, and other industrial metals.
Yes, they are reinforced for stability and safe operation at high speeds when used correctly.
Trusted by Tens of Thousands of Manufacturers, Laboratories,
Research Institutions Worldwide Since 1990

Established in 1990

Brian is an experienced professional in the field of precision cutting tools, with over 27 years of experience in technical support. Over the years, he has helped engineers, manufacturers, researchers, and contractors find the right solutions for working with advanced and hard-to-cut materials. He’s passionate about bridging technical knowledge with real-world applications to improve efficiency and accuracy.
As an author, Brian Farberov writes extensively on diamond tool design, application engineering, return on investment strategies, and process optimization, combining technical depth with a strong understanding of customer needs and market dynamics.