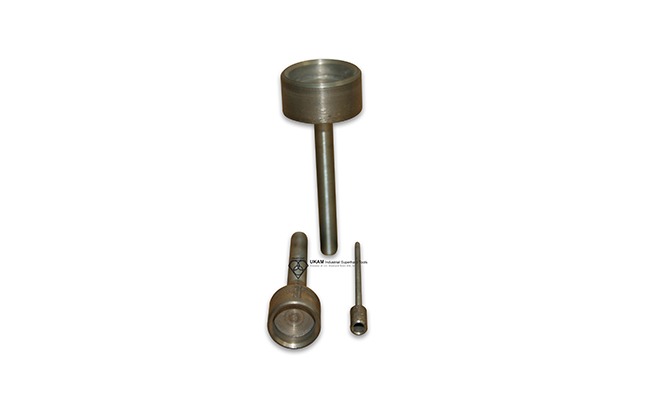
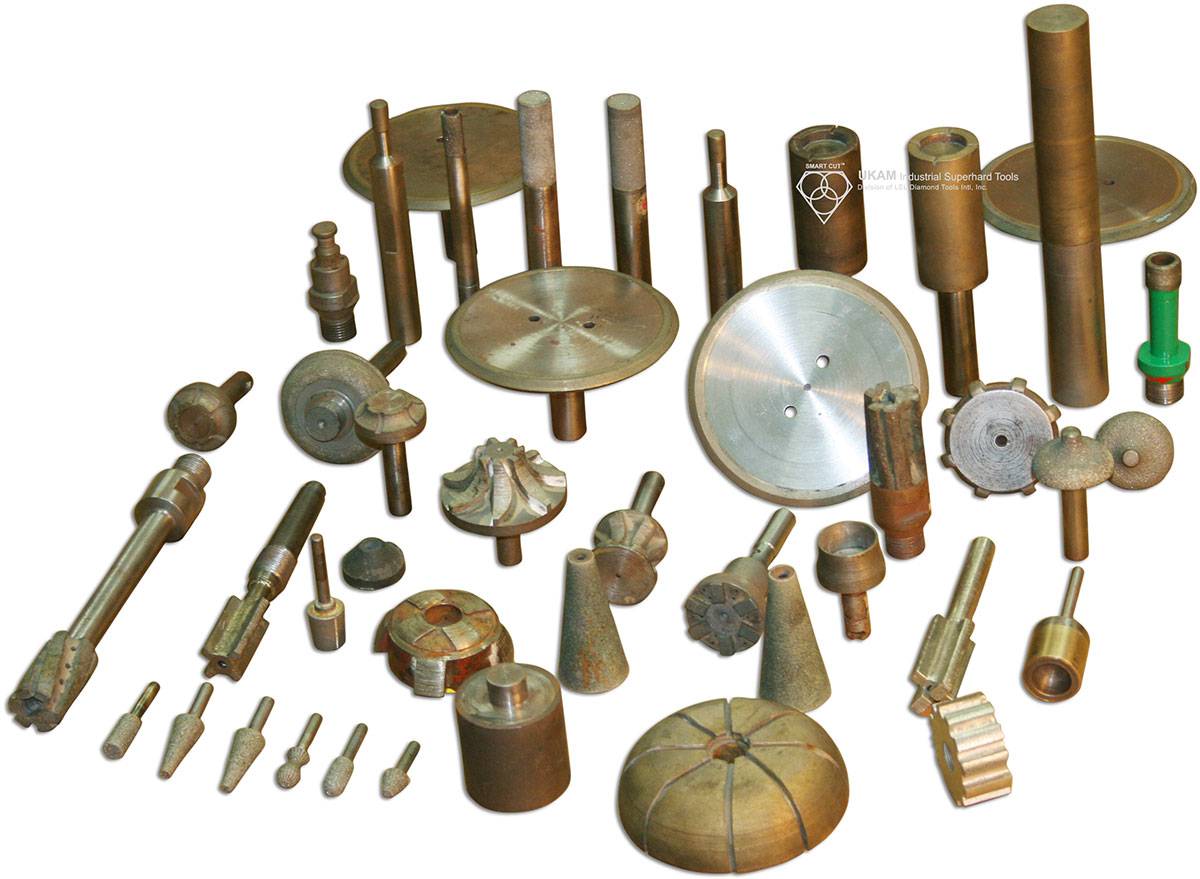
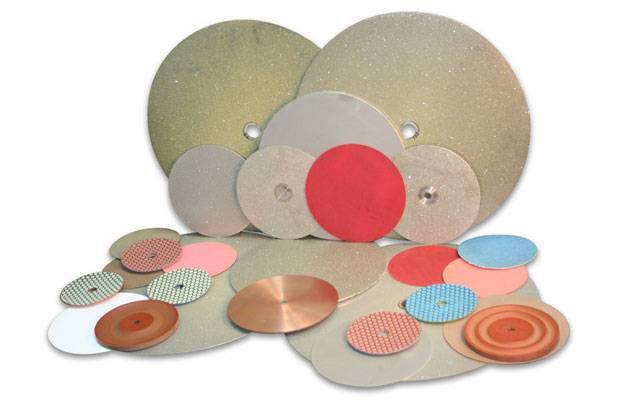
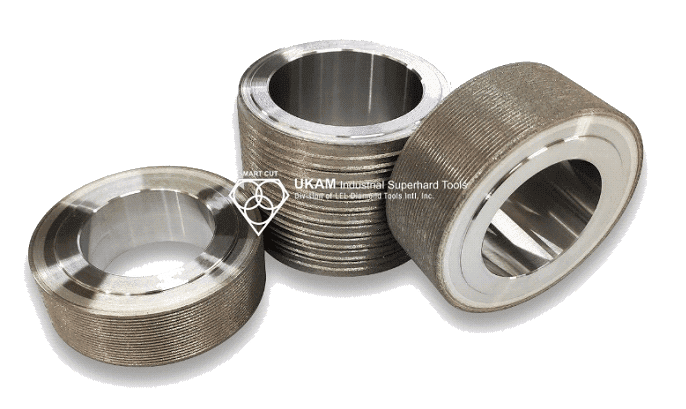
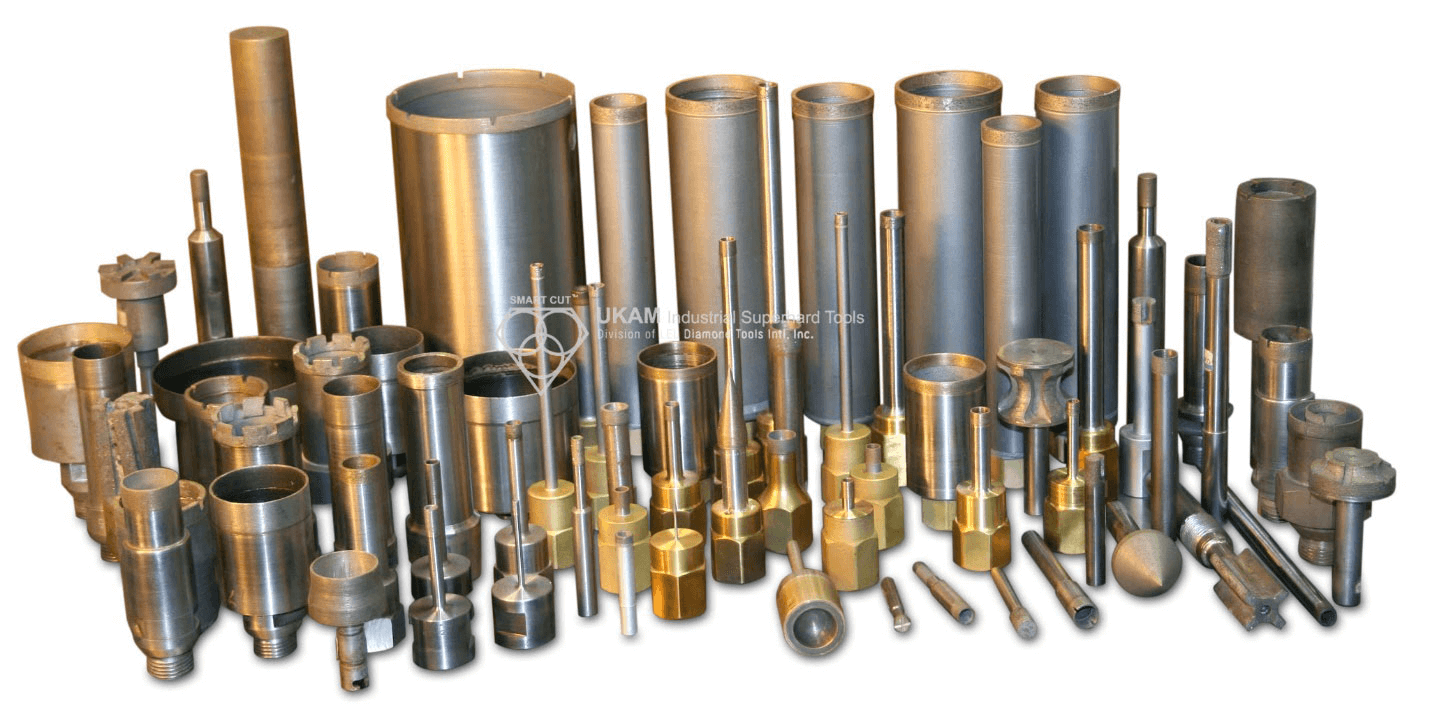
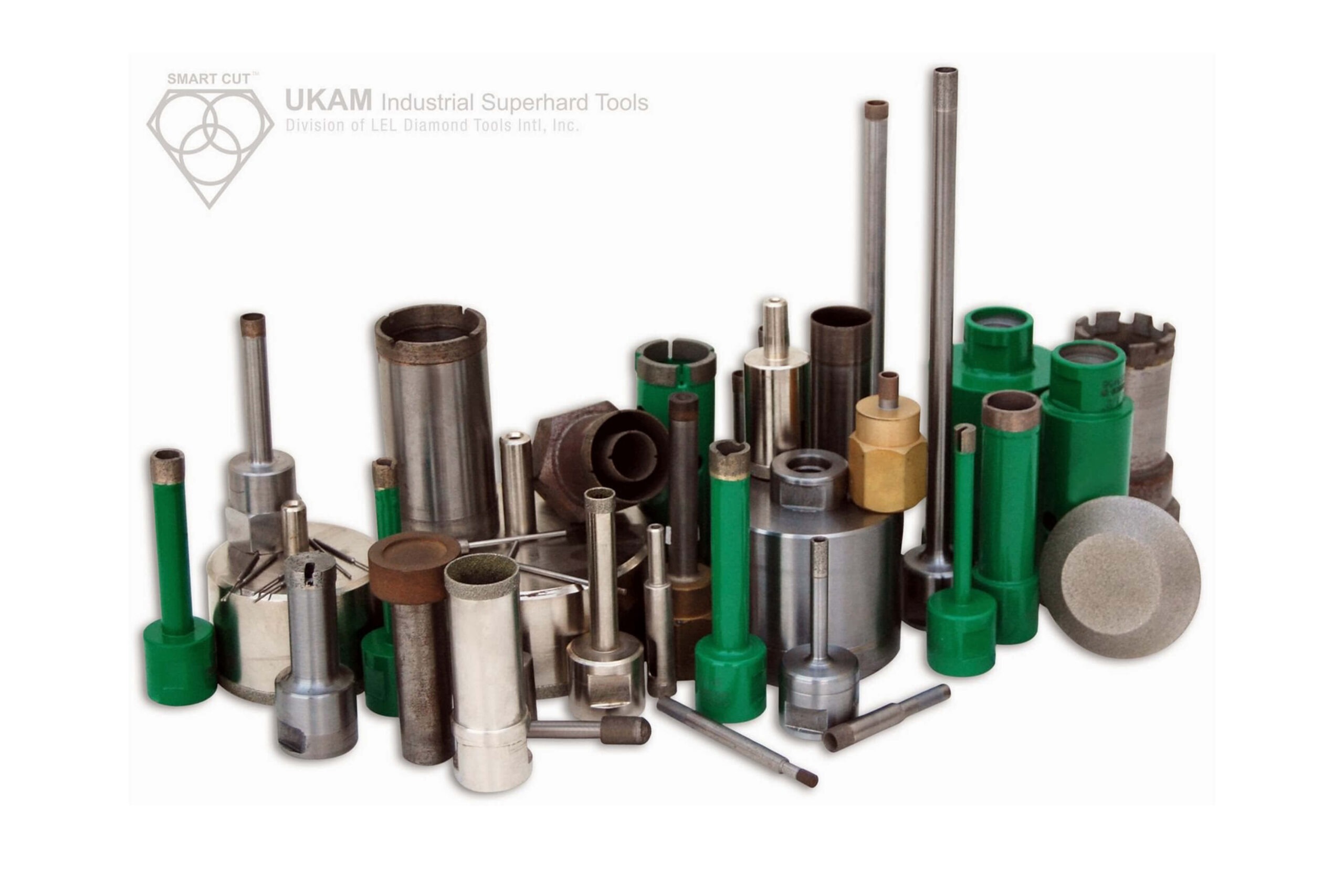
Diamond Tools Guide – Selecting Right Drills & Tools for your application
-
Posted by
contactor6
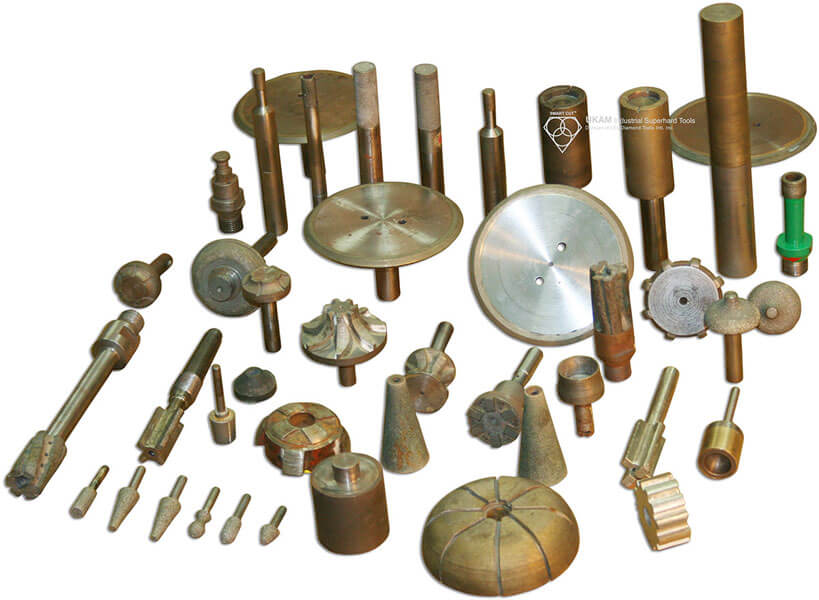

These tools are used for many different industries grinding and shaping material into different forms, expanding exiting inside diameters, grinding, finishing and polishing existing material. Grinding different angles and radius, creating cavities of various forms, milling, deburring, Thread grinding.
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
- Diamond carving points
- Diamond mounted points
- Diamond counter tools
- Diamond grinding pins
- Diamond routers
- Diamond ID grinding points
- Diamond jig grinding mandrels/pins
- Diamond countersinks
- Diamond counter bores etc
- Diamond Generating Tools
- Diamond Milling Tools
- Diamond face grinding tools
- Diamond Chamfer Tools
- Diamond Radius Tools
- Diamond Profiling Tools
- Diamond Ball Nose Tools
- Diamond Round End Tools
- Diamond Full Ball Tools
- Diamond Bottom Grinding Tools
- Diamond Reamers
- Diamond Honing Tools
- Diamond Tapered Hones
- Diamond Threading tools
- Diamond hole/bore finishing tools
- Diamond cone grinding tools
- Diamond burs for industry/hobby
- Diamond Profile Tools
- Diamond Radois Tools
- Diamond Radius Tools,
- Diamond Chamfer Tools
- Diamond expanding laps/mandrels
- Diamond Engraving Tools & Diamond CNC Engraving Tools
We offer a wide range of precision tools, including Diamond, CBN, PCD, and CVD milling tools; Diamond chamfer tools; Diamond radius tools; profiling tools; ball nose tools; full ball tools; bottom grinding tools; reamers; threading tools; engraving tools; and other custom tools tailored to your specifications.
These tools are designed for various industrial applications, including grinding, shaping, expanding inside diameters, finishing, polishing, milling, deburring, and thread grinding. They are ideal for working on a broad spectrum of ultra-hard, dense, and brittle materials, such as advanced ceramics (e.g., alumina, silicon carbide, boron nitride, boron carbide, PZT), sapphire, silicon, YAG, quartz, glass, crystals, a wide variety of natural and semi-precious stones, composite materials, ferrous and non-ferrous metals, carbide, ferrites, tough alloys, cements, and many more.
These tools can be effectively used with routers, jig grinding machines, handpieces, milling machines, and other equipment, operating at speeds ranging from 15,000 to 35,000 RPM. Available in four different bond types, they are designed to provide precision and efficiency in any machining operation.
When choosing the right diamond tool for a specific application, the first step is to identify the material to be machined. Understanding its hardness, density, and brittleness will help in selecting the right tool and bond type. Next, clarify the application, whether it's milling, engraving, polishing, shaping, or drilling, as this will guide the choice of tool type and shape. It’s also important to consider the desired surface finish, tolerance, and precision. For rough shaping, a coarser grit and more durable bond, like a metal bond, may be suitable, while fine polishing or engraving might require a resin or electroplated tool with a finer grit.
Ensuring that the tool is compatible with the machine being used and that the machine can reach the appropriate RPMs is another key factor. Selecting the correct bond type is also crucial; for example, a metal-bond tool is appropriate for fast material removal on tough materials, while resin or electroplated bonds are better for achieving a fine finish with precision. In some cases, custom-made diamond tools may be necessary to meet the unique requirements of an application, such as specialized shapes, sizes, or bond types tailored to your specifications.
Diamond Bond Types Avaialble:
-
 Sintered (metal bond)
Sintered (metal bond)
-
 Resin Bond
Resin Bond
-
 Nickel Bond (electroplated/galvanic)
Nickel Bond (electroplated/galvanic)
-
 Brazed Bond
Brazed Bond
-
 PCD (polycrystalline diamond)
PCD (polycrystalline diamond)
-
 CVD (chemical vapor deposition) diamond
CVD (chemical vapor deposition) diamond
Tool Types And Their Applications
|
Tool Type |
Applications |
|---|---|
|
Diamond Carving Points |
Carving, shaping, fine detailing |
|
Diamond Mounted Points |
Precision grinding, surface finishing |
|
Diamond Counter Tools |
Internal counterbore shaping |
|
Diamond Grinding Pins |
Internal grinding, deburring |
|
Diamond Routers |
Routing intricate patterns |
|
Diamond ID Grinding Points |
ID grinding of small diameters |
|
Diamond Jig Grinding Mandrels/Pins |
Precision internal grinding |
|
Diamond Countersinks |
Countersinking holes |
|
Diamond Counter Bores |
Expanding countersunk holes |
|
Diamond Generating Tools |
Surface generation, pattern shaping |
|
Diamond Milling Tools |
Milling complex forms and surfaces |
|
Diamond Face Grinding Tools |
Face grinding, flat surface preparation |
|
Diamond Chamfer Tools |
Chamfering edges, deburring |
|
Diamond Radius Tools |
Creating rounded edges and shapes |
|
Diamond Profiling Tools |
Profiling complex contours |
|
Diamond Ball Nose Tools |
3D contour milling, fine detailing |
|
Diamond Round End Tools |
Finishing rounded surfaces |
|
Diamond Full Ball Tools |
Milling complete hemispheres or balls |
|
Diamond Bottom Grinding Tools |
Bottom face grinding, surface smoothing |
|
Diamond Reamers |
Reaming holes to tight tolerances |
|
Diamond Honing Tools |
Honing internal diameters |
|
Diamond Tapered Hones |
Precision honing with tapered geometry |
|
Diamond Threading Tools |
Thread forming and grinding |
|
Diamond Hole/Bore Finishing Tools |
Finishing bores, fine hole finishing |
|
Diamond Cone Grinding Tools |
Conical grinding applications |
|
Diamond Burs for Industry/Hobby |
Deburring, carving in small details |
|
Diamond Profile Tools |
Profiling complex shapes |
|
Diamond Radius Tools |
Creating precise radii |
|
Diamond Chamfer Tools |
Deburring and chamfering edges |
|
Diamond Expanding Laps/Mandrels |
Expanding internal diameters |
|
Diamond Engraving Tools |
Engraving fine details |
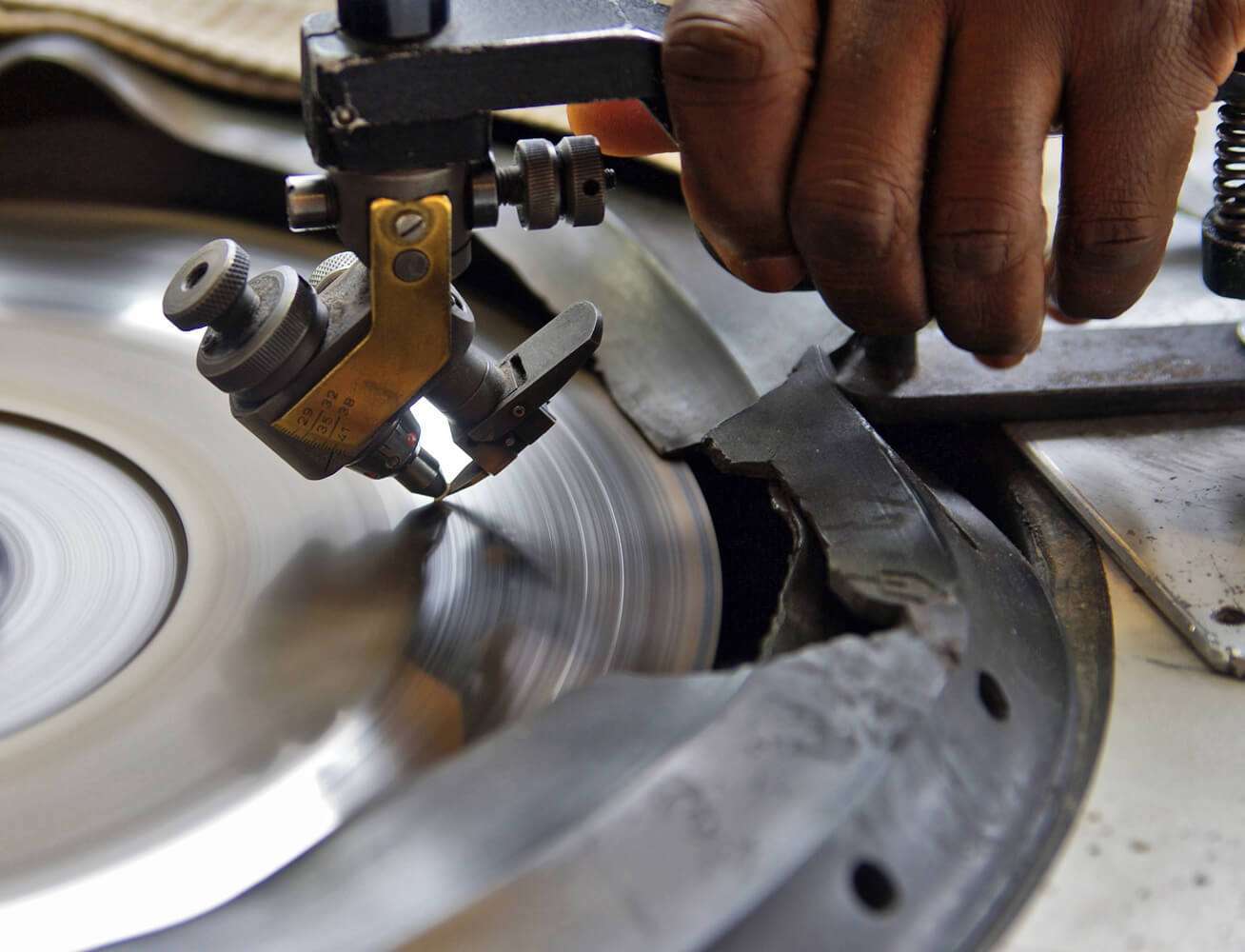
Diamond countersinks, diamond counterbores, and diamond chamfer tools
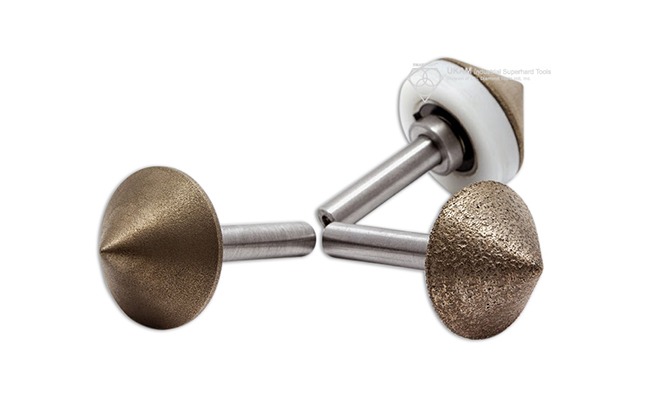
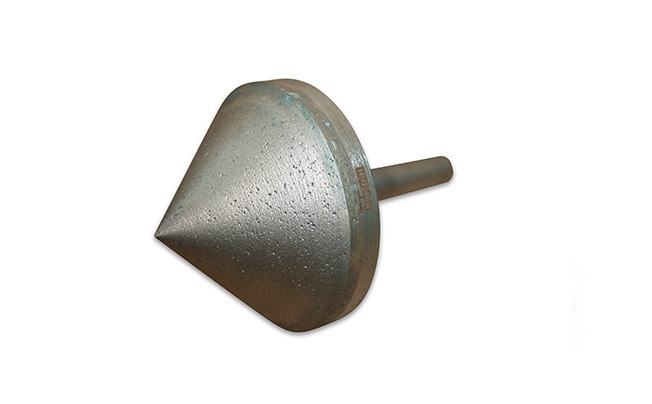






Diamond countersinks, diamond counterbores, and diamond chamfer tools are essential components in precision machining, used to create conical holes, expand existing holes, break corners, chamfer edges, and polish holes in a wide array of materials. These tools are available in various specifications and can be customized to meet specific industrial needs, including adjustments in diameters, angles, radii, bond types, diamond grit sizes, lengths, and shank sizes. This customization ensures that the tools are perfectly suited to the specific requirements of any given application.
Diamond and CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) countersinks are particularly effective for detailed and finish-oriented machining tasks. They are used across various industries, from aerospace engineering, where precision is critical, to the production of electronics and automotive parts, where clean and accurate chamfers and holes are required for assembly. The ability to modify the characteristics of these tools allows them to be tailored for materials ranging from soft composites to ultra-hard ceramics.
These tools can be designed to be solid for use submerged in coolant, or with a coolant slot in the diamond section, which allows coolant to pass through the center of the tool. This feature is especially recommended for operations involving ultra-hard and dense materials, as it helps reduce heat and prevent material damage during the machining process. The flexibility in the mounting system, whether it be female or male collets (threads) or straight shanks, adds to their adaptability in various machinery setups.
Bond Types and Material Compatibility
-
 Sintered (Metal Bond): Ideal for harder and denser materials such as ceramics, due to its durability and ability to maintain form under extreme conditions.
Sintered (Metal Bond): Ideal for harder and denser materials such as ceramics, due to its durability and ability to maintain form under extreme conditions.
-
 Nickel Bond (Electroplated/Galvanic): Suitable for softer materials such as composites, glass, and marble, offering fast material removal rates.
Nickel Bond (Electroplated/Galvanic): Suitable for softer materials such as composites, glass, and marble, offering fast material removal rates.
-
 Brazed Bond: Known for its robust attachment of the diamond grains, providing a strong bond that is suitable for demanding applications.
Brazed Bond: Known for its robust attachment of the diamond grains, providing a strong bond that is suitable for demanding applications.
-
 PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond): Excellent for high abrasion resistance required in non-ferrous metal machining.
PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond): Excellent for high abrasion resistance required in non-ferrous metal machining.
-
 CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Diamond: Provides an extremely hard coating that is suitable for high-precision machining tasks.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Diamond: Provides an extremely hard coating that is suitable for high-precision machining tasks.
Advantages
-
 Durability: They maintain sharpness over long periods.
Durability: They maintain sharpness over long periods.
-
 Smooth Finish: Ensure clean and precise countersink holes.
Smooth Finish: Ensure clean and precise countersink holes.
-
 Reduced Heat: Minimize friction and heat buildup during use.
Reduced Heat: Minimize friction and heat buildup during use.
-
 Versatility: Effective on a range of tough materials.
Versatility: Effective on a range of tough materials.
-
 Efficiency: Quickly and cleanly remove material.
Efficiency: Quickly and cleanly remove material.
-
 Precision: Offer precise control over hole dimensions.
Precision: Offer precise control over hole dimensions.
Sintered Diamond Tools: .030" (0.75mm) to .250” (6.0mm)





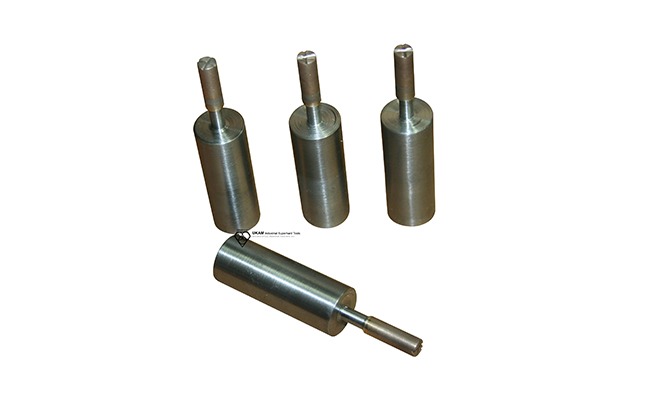
Sintered diamond tools, crafted using a robust metal bond process, encompass a diverse range of precision instruments including miniature diamond points, reamers, mandrels, counter tools, carving tools, and routers. These tools are tailored for detailed work across various industries such as jewelry making, precision engineering, and art restoration, ensuring high precision and durability.
Diamond Points and Reamers serve as essential tools for engraving, detailing, and finishing work, particularly useful in precision applications on hard materials such as gemstones and hardened alloys. Diamond points are perfect for intricate detailing due to their sharp tips and sturdy construction, while reamers are employed to refine, enlarge, and smooth drilled holes, ensuring high precision necessary for jewelry design and fine metalworking.
Diamond Mandrels and Counter Tools are used for grinding, shaping, and smoothing tough materials, commonly paired with rotary tools to work on intricate parts. Diamond mandrels enhance detailed accuracy and surface quality, whereas counter tools are indispensable for creating precise countersinks or counterbores required in metal fabrication and woodworking.
Diamond Carving Tools and Routers are pivotal for artists and craftspeople. Diamond carving tools allow for precision in sculpting and texturing stone, ceramics, or hardwoods, enabling fine artistic details and complex designs. Diamond routers are crucial in the stone and construction industries, utilized for shaping, cutting, and finishing robust materials like granite and marble, essential in countertop fabrication and decorative stonework.
The durability and longevity of these tools are marked by the sintered metal bond that embeds diamond particles within a resilient matrix, allowing the tools to withstand rigorous pressures and temperatures. This attribute not only extends their service life but also enhances their efficiency. The metal bond also permits a finer distribution of diamond grit, resulting in higher cutting accuracy and smoother finishes on workpieces.
Customizability is another significant advantage, as these tools can be engineered to specific geometries and sizes to cater to unique project demands, increasing their utility in specialized tasks. Sintered diamond tools find extensive applications in industries that demand meticulous precision and durability, ranging from jewelry manufacturing to automotive, aerospace, art, sculpture, construction, and stone masonry.
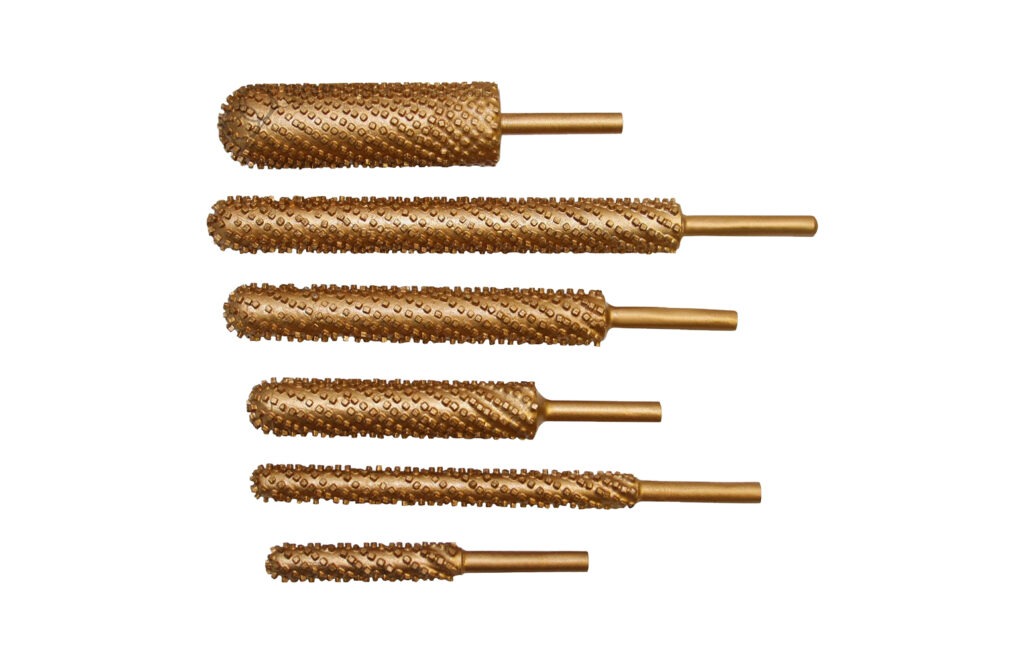
Diamond Carving Points
Diamond carving points are versatile precision tools designed for a wide range of industrial applications, such as grinding, shaping, and expanding inside diameters. They are highly effective for material removal, angle grinding, contouring, cavity creation, milling, deburring, thread grinding, finishing, and polishing, making them essential in industries that require intricate work on complex shapes and fine details.
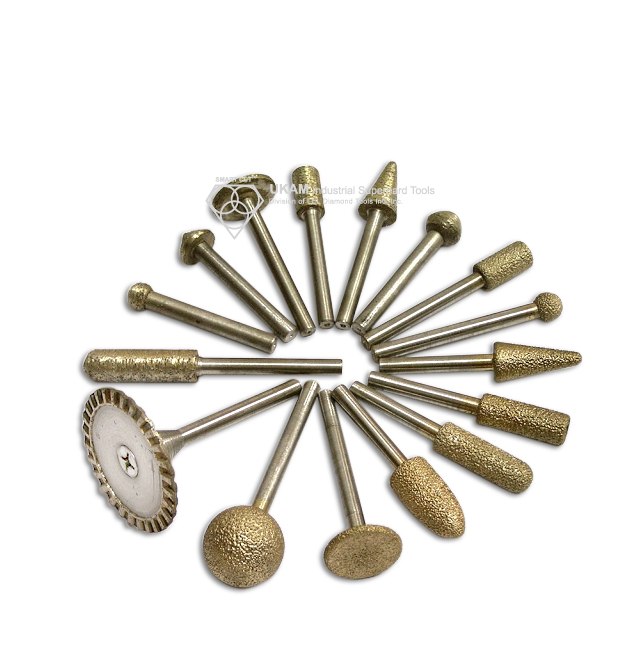
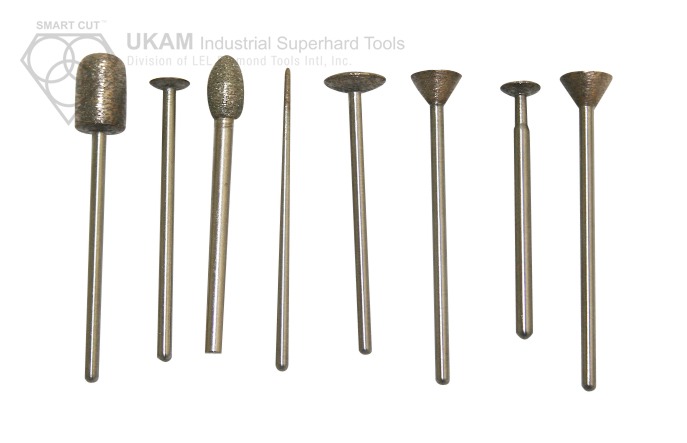


These carving points are specifically engineered to handle a broad spectrum of ultra-hard, dense, and brittle materials, offering efficient results across advanced ceramics like alumina, silicon carbide, boron nitride, boron carbide, and PZT. They are also well-suited for processing both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, tough alloys, cements, quartz, sapphire, and other crystals, as well as a variety of natural and semi-precious stones. Their capability extends to composite materials, carbides, ferrites, and ceramics, making them highly adaptable to different material requirements.
Designed for compatibility with an array of machinery, diamond carving points can be used effectively with routers, jig grinding machines, handpieces, and milling machines. These machines are utilized based on the specific needs of the application, whether it involves detailed shaping, precision grinding, intricate carving, or bulk material removal.
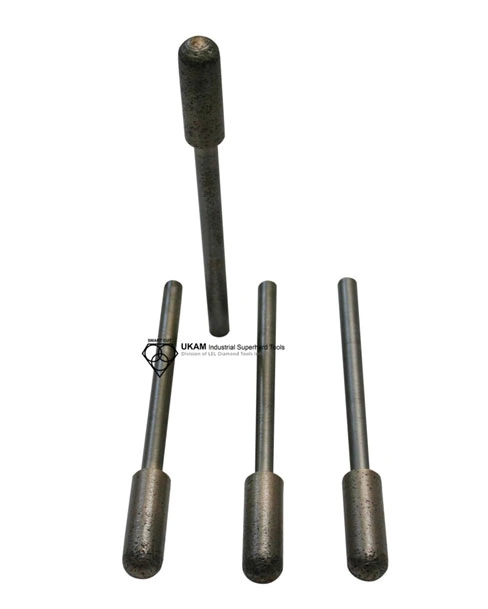
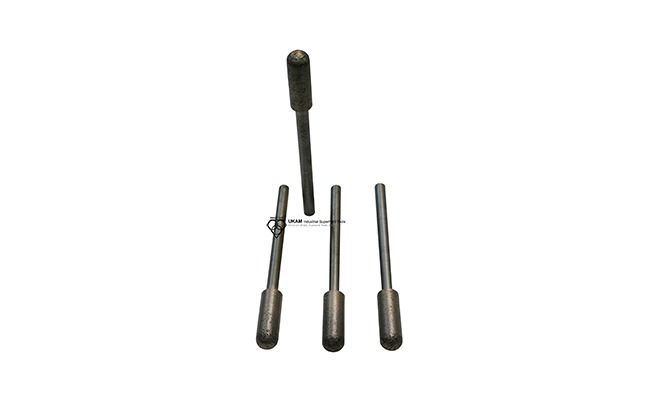
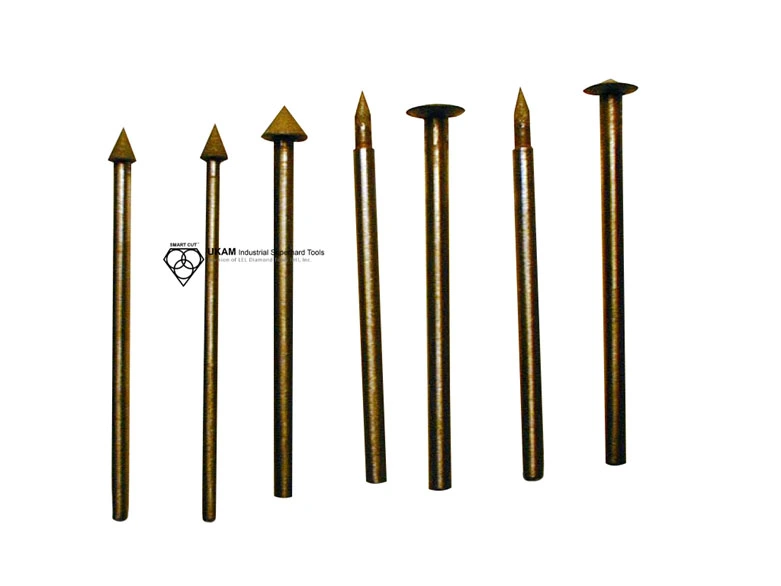



Operating efficiently at high speeds ranging from 15,000 to 35,000 RPM, these tools are optimized for both performance and tool life. The choice of operating speed depends on the type of material, the intricacy of the work, and the desired finish. Proper speed selection plays a crucial role in achieving optimal efficiency and high-quality results.
To cater to different applications and material properties, diamond carving points are available in four different bond types. The resin bond provides smooth and fine finishes, making it ideal for precision work on softer and more delicate materials. The metal bond is known for its durability and toughness, which allows for aggressive material removal on harder substances. Electroplated bonds offer sharp cutting action, perfect for detailed work and applications requiring a free-cutting tool,
Diamond Engraving Tools
Diamond engraving tools are specialized cutting instruments equipped with diamond tips or edges, designed to inscribe, etch, or carve intricate designs on various materials. Integrating CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology enhances the precision and repeatability of the engraving process, making these tools ideal for detailed work and high-volume production.
Diamonds, known for their unmatched hardness, enable these tools to engrave a broad spectrum of materials including metals like aluminum and copper, as well as hard ceramics, glass, gemstones, and some hard plastics. There are two main types of diamond tips used in these tools. Drag (or non-rotating) engravers have a diamond tip that does not rotate but is instead dragged across the material to scribe or scratch a line. Rotating engravers, in contrast, feature a diamond tip that rotates, allowing for deeper and broader engravings akin to traditional drill bits but specifically designed for detailing.
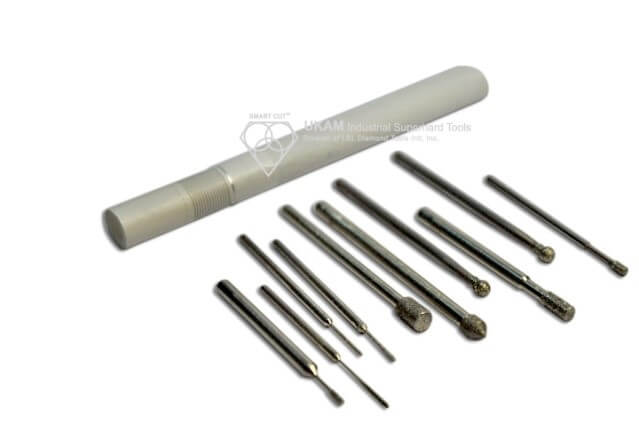

These tools are employed in various applications such as nameplate engraving, jewelry design, intricate designs on glassware, etching barcodes or QR codes on industrial components, and decorative engraving on stone or tiles. CNC diamond engraving tools stand out due to their precision and repeatability; CNC technology ensures each engraving is consistent and precise, which is particularly crucial for intricate designs and logos. Users can also program designs into the CNC system, which then guides the diamond engraving tool with high accuracy, enhancing both speed and efficiency. This capability is especially valuable in high-volume production settings, where the same design can be engraved repeatedly with minimal manual intervention.
Furthermore, CNC systems are versatile enough to work with various diamond engraving tools, enabling a wide range of engraving depths, styles, and finishes. This versatility finds applications in high-volume jewelry production, engraving serial numbers on industrial components, and creating intricate designs on electronics housings, such as phone and laptop exteriors, as well as detailed artwork on glass or ceramics.
The design and construction of these tools are also critical. The geometry of the diamond tip, including points, conical shapes, and pyramidal tips, plays a crucial role in determining the style of engraving. The type of shank used, which can vary from straight shanks to threaded designs depending on the CNC machine or engraving setup, is another important consideration. Additionally, the use of coolants or lubricants, especially when engraving metals, can prevent overheating and extend the tool’s life.
When selecting diamond engraving tools, it is essential to consider the suitability of the tool for the material, the desired depth of engraving, and the tool's wear. Regular inspection of the diamond tip is necessary to ensure it remains sharp and free from damage. In summary, diamond engraving tools, particularly when combined with CNC technology, provide industries with an advanced method for executing precision engraving tasks on a diverse range of materials, serving purposes that span from artistry to identification and functionality.
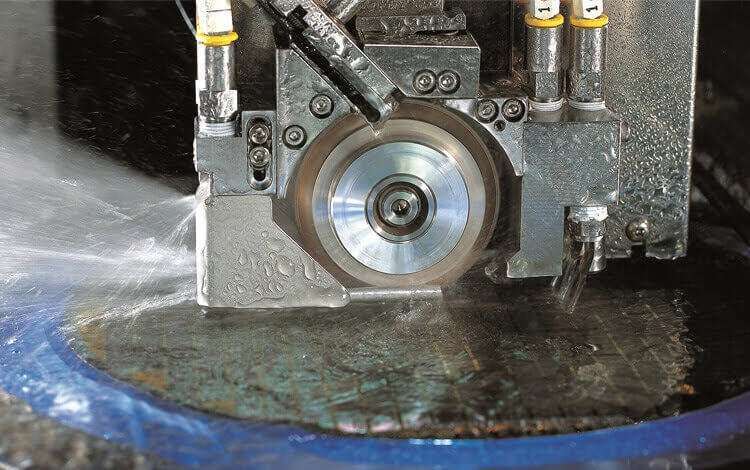
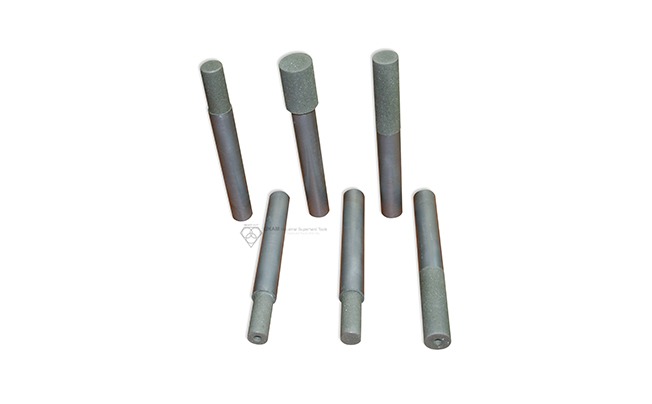
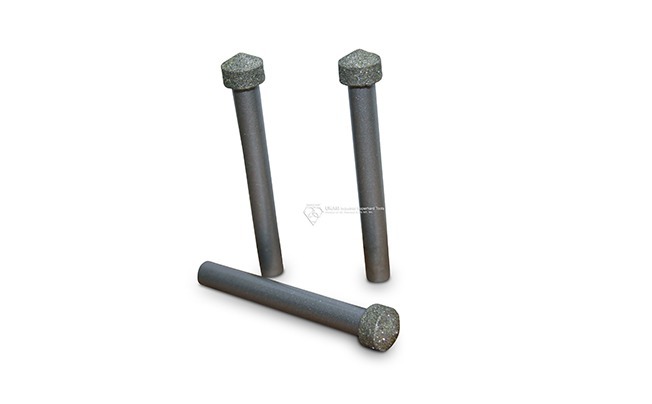
Diamond grinding pins
Diamond grinding pins are precision tools designed for internal grinding, deburring, and finishing ultra-hard materials. With diamond abrasives, they efficiently cut and shape advanced ceramics, hardened steels, carbides, glass, and composites, providing excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances. Compatible with jig grinders, die grinders, CNC machines, and rotary tools, they operate at speeds up to 60,000 RPM for precise grinding in intricate spaces.


Diamond Cone Grinding Tools
Diamond cone grinding tools are uniquely shaped to enable precise grinding, shaping, and deburring in areas that may be challenging to access with standard flat or cylindrical grinding tools. With their cone-shaped design embedded with diamond particles, they excel at working on complex contours, tight spaces, and intricate details across a variety of hard materials. The hardness and durability of the diamond particles make these tools highly effective for grinding through hard and brittle materials, while the conical shape allows for flexibility in shaping different profiles.






Diamond cone grinding tools are widely used in metalworking, particularly for detailed deburring, chamfering, and finishing of complex parts after machining, welding, or casting. The pointed cone shape is especially effective for reaching into grooves, corners, and threads to refine intricate features, leaving a smooth and precise finish.
In the stone and tile industry, these cone tools play an important role in detailed sculpting and shaping of materials like granite, marble, and porcelain. They are ideal for creating fine details, smoothing intricate designs, and achieving a high-quality finish in areas that are difficult to reach with other grinding tools.
When working with glass, diamond cone grinding tools are used to shape and finish delicate edges or internal contours, ensuring precision while minimizing the risk of cracking or chipping. They are particularly useful in applications that require shaping curved surfaces or detailed glass art, where accuracy and a smooth finish are paramount.
For ceramics, diamond cone grinders are essential for refining and deburring, especially when working on complex, detailed parts such as ceramic fixtures, art pieces, or engineering components. Their conical shape allows them to navigate intricate surfaces and provide a polished edge that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
In the field of composite materials, which includes advanced materials like carbon fiber, fiberglass, and other reinforced composites, diamond cone tools are used to grind, shape, and finish these tough and often abrasive materials. The diamond-embedded surface ensures efficient grinding without compromising the integrity of the composite structure, making these tools ideal for aerospace, automotive, and advanced manufacturing applications.
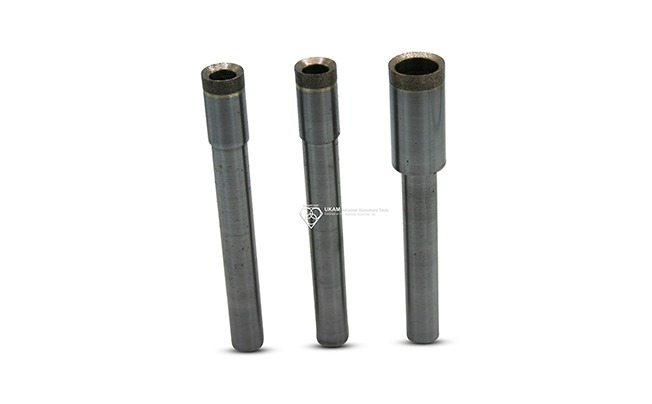
Diamond Hole and Bore Finishing Tools
Diamond hole or bore finishing tools are specially designed for creating precise and smooth internal surfaces in bores or drilled holes. Using diamond as the abrasive ensures durability and high-quality finishes, making these tools particularly effective for hard and abrasive materials. The fine cutting action provided by diamond abrasives enables the tools to achieve a superior surface finish and maintain tight tolerances, which are essential for ensuring optimal performance in mechanical and engineering applications.
Types of Diamond Hole/Bore Finishing Tools
Diamond honing tools are designed to improve both the geometric form and surface texture of a bore. These tools typically have one or more honing stones embedded with diamond abrasives. The honing process involves the tool rotating and reciprocating inside the bore, with the diamond stones pressed against the surface. This action progressively refines the hole's internal dimensions, achieving a highly accurate and smooth surface finish.
Diamond reamers are rotary cutting tools designed to accurately finish holes that have already been drilled or bored. They are particularly effective in creating precision bore sizes while maintaining excellent surface quality. Diamond reamers remove minimal material, providing a highly refined surface and improved accuracy, making them suitable for achieving tight tolerances in applications requiring high precision.

Diamond lapping tools utilize a lapping paste containing diamond particles to achieve ultra-fine finishes within bores or holes. The tool moves back and forth inside the bore, with the diamond paste acting as the abrasive between the tool and the material. This process is ideal for creating extremely smooth and polished internal surfaces, improving both form and function in precision components.
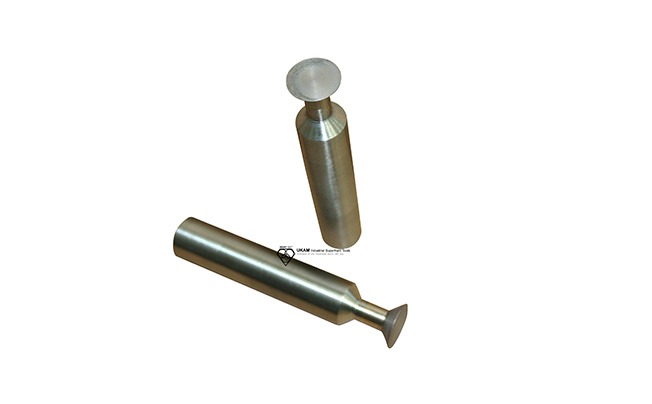
Diamond Chamfer Tools
Diamond chamfer tools are specialized instruments used to create a beveled edge or chamfer at the intersection of two surfaces. The diamond-coated edges of these tools allow for the precise shaping and smoothing of hard materials, providing a refined finish and improving both the functionality and aesthetic appeal of a component. By beveling or smoothing sharp edges, diamond chamfer tools help to create safer, more durable surfaces that are less prone to chipping or damage.
In the stone and tile industry, diamond chamfer tools are widely used for creating beveled edges on countertops, tiles, monuments, and other stone surfaces. The beveled edges provide a smooth transition between surfaces, enhancing the visual appeal of the finished product.
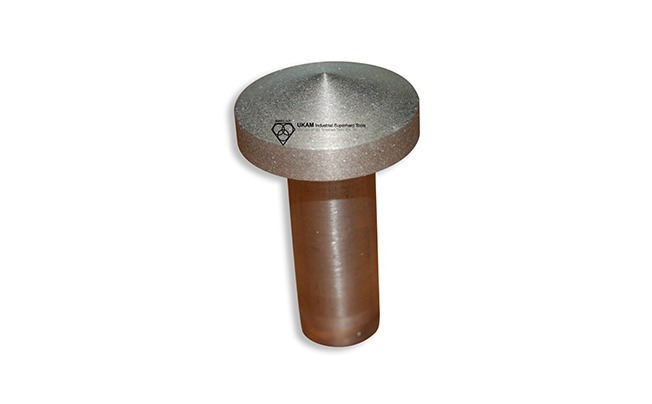


These chamfers not only improve aesthetics but also add functional benefits by preventing the edges from chipping or cracking over time, making them especially useful for high-traffic areas or decorative stonework.
In the glass industry, diamond chamfer tools are used to shape and refine the edges of glass sheets. A beveled edge is particularly important when the glass will be exposed in the final product, such as in glass tables, windows, mirrors, and display cases. The chamfering process smooths sharp edges, making them safer to handle and improving the overall appearance of the glass, ensuring a polished and professional finish.
For machining and metalworking, especially in precision industries, diamond chamfer tools are used to create bevels on metal parts, particularly those made of hard alloys and difficult-to-machine metals. The diamond abrasive allows for precise and consistent chamfering, achieving clean edges without compromising the material's integrity. This process is crucial in situations where exact dimensions, fine finishes, and edge integrity are required for the functionality of the part.
In the electronics sector, chamfer tools are used to refine and bevel the edges of various components, such as ceramic substrates and semiconductor parts. The use of diamond allows for high precision and fine finishing, which is essential for fitting and assembly in electronic devices. The chamfered edges help prevent damage during handling and improve the fit and integration of components within assemblies.

Concrete and masonry applications also benefit from diamond chamfer tools. They are used to create beveled edges in concrete surfaces, particularly in decorative concrete work or when creating joints. These beveled edges provide a smoother transition between surfaces and enhance the structural integrity of joints, making them more resistant to wear and damage over time.
Diamond Radius Tools
Diamond radius tools are designed to shape and finish materials by creating rounded edges or profiles. The diamond-embedded cutting surface of these tools allows for smooth, precise shaping of hard and brittle materials, achieving a high-quality finish that not only enhances aesthetics but also improves durability. A rounded edge created by these tools is typically more resistant to damage than sharp edges, reducing the risk of chipping or cracking, and adding to the material’s functional lifespan.
In the stone and tile industry, diamond radius tools are frequently used to add rounded edges to countertops, tiles, stone monuments, and other natural stone surfaces.

A rounded edge enhances both the appearance and durability of these materials, providing a sleek, finished look while minimizing the risk of chipping, which can be common with sharp, square edges.
For the glass industry, these tools play a vital role in safety and aesthetics. By creating a smooth, rounded edge on glass sheets, furniture, mirrors, or display cases, the risk of injury from sharp edges is significantly reduced. This is particularly important for glass pieces that are intended to be exposed or handled frequently. The resulting rounded profile also adds to the visual appeal of the glass, contributing to its polished, high-quality appearance.
When working with ceramics and porcelain, diamond radius tools are used to refine and finish the edges of decorative or functional pieces. Whether shaping pottery, tiles, or art pieces, the smooth, rounded edges produced by these tools add elegance to the finished product and help prevent damage during handling and installation. This makes diamond radius tools particularly valuable for detailed work in ceramics.
In metalworking, diamond radius tools are less commonly used but can be particularly effective for shaping and rounding edges on abrasive hard alloys or metals that are difficult to machine. The hardness of the diamond abrasive makes it suitable for these challenging applications, where conventional tools might wear out quickly. Although not typically the first choice for all metals, diamond radius tools provide excellent finishing options for tough and abrasive alloys requiring smooth, rounded profiles.
For composite materials, which often include hard and abrasive components like carbon fiber or fiberglass, diamond radius tools are used to shape and finish edges with precision. These tools allow for the smooth profiling of composites, helping to refine parts for industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where exact tolerances and clean finishes are crucial.
Diamond Profile Tools
Diamond profile tools are designed for creating specific shapes, contours, and edge profiles on a variety of hard materials. These tools are embedded with diamond abrasives to deliver smooth and precise shaping, making them indispensable in applications where detailed finishing and complex contours are required. Diamond profile tools provide high efficiency and durability, particularly when working with hard and brittle materials that demand precisionIn the stone industry, diamond profile tools are widely used to shape and contour surfaces like countertops, table edges, and decorative stone details. They can create a wide range of edge profiles, from rounded to more complex shapes, to enhance the functionality and appearance of stone products such as granite or marble surfaces.

For ceramics and porcelain, diamond profile tools are essential for creating intricate designs, shaped edges, and fine finishes on both functional and decorative ceramic pieces. They are frequently used in tile manufacturing, pottery, and porcelain detailing, where clean, precise lines are required for both aesthetics and structural purposes.
In glass manufacturing, these tools are employed to detail and shape glass items, allowing for smooth, complex edge profiles that not only improve the visual appeal but also reduce the risk of sharp edges that could lead to breakage or safety issues. Glass tables, mirrors, and display items often require such profiles to achieve a refined, polished appearance.
For concrete and masonry, diamond profile tools are used in decorative concrete applications and to create specialized masonry detailing. They allow for shaping and refining concrete edges, corners, and joints, whether for functional structural elements or aesthetic design. This is particularly important in architectural concrete work, garden stones, or custom masonry pieces.
Types of Profiles Created by Diamond Profile Tools
-
 A full bullnose profile produces a completely rounded edge, offering a soft, smooth contour that is frequently used in countertops and other surface edges for both aesthetic and safety purposes.
A full bullnose profile produces a completely rounded edge, offering a soft, smooth contour that is frequently used in countertops and other surface edges for both aesthetic and safety purposes.
-
 A half bullnose creates a semi-circular profile, rounding only one side of the material while leaving the other side flat. This provides a more subtle contour while still enhancing the material's edge for both design and durability.
A half bullnose creates a semi-circular profile, rounding only one side of the material while leaving the other side flat. This provides a more subtle contour while still enhancing the material's edge for both design and durability.
-
 The ogee profile is a classic "S" shape often found in countertop edges and detailed stonework. This sophisticated, curved design adds an elegant touch and is commonly used in upscale architectural elements and furnishings.
The ogee profile is a classic "S" shape often found in countertop edges and detailed stonework. This sophisticated, curved design adds an elegant touch and is commonly used in upscale architectural elements and furnishings.
-
 A bevel profile features a straight incline cut into the material, usually at a 45-degree angle. This sharp yet refined edge is practical and stylish, commonly applied to both stone and glass items for a clean, angled finish.
A bevel profile features a straight incline cut into the material, usually at a 45-degree angle. This sharp yet refined edge is practical and stylish, commonly applied to both stone and glass items for a clean, angled finish.
-
 The Dupont profile is characterized by a straight drop that transitions into a rounded or curved edge. This intricate profile adds depth and style to the material, making it popular for detailed work on countertops and custom stone designs.
The Dupont profile is characterized by a straight drop that transitions into a rounded or curved edge. This intricate profile adds depth and style to the material, making it popular for detailed work on countertops and custom stone designs.
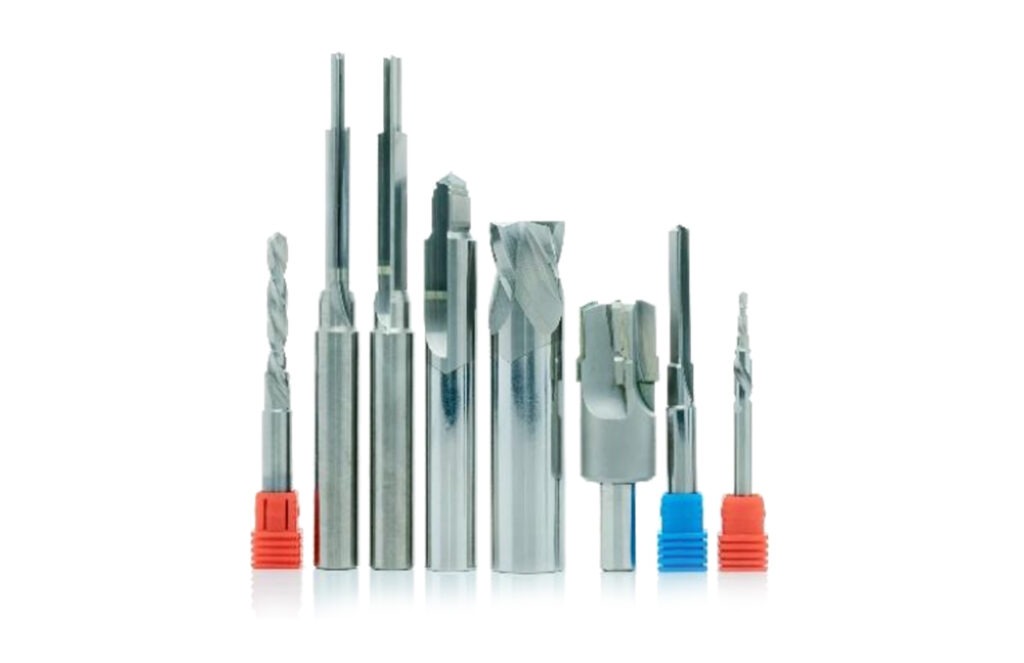
Diamond milling & form tools
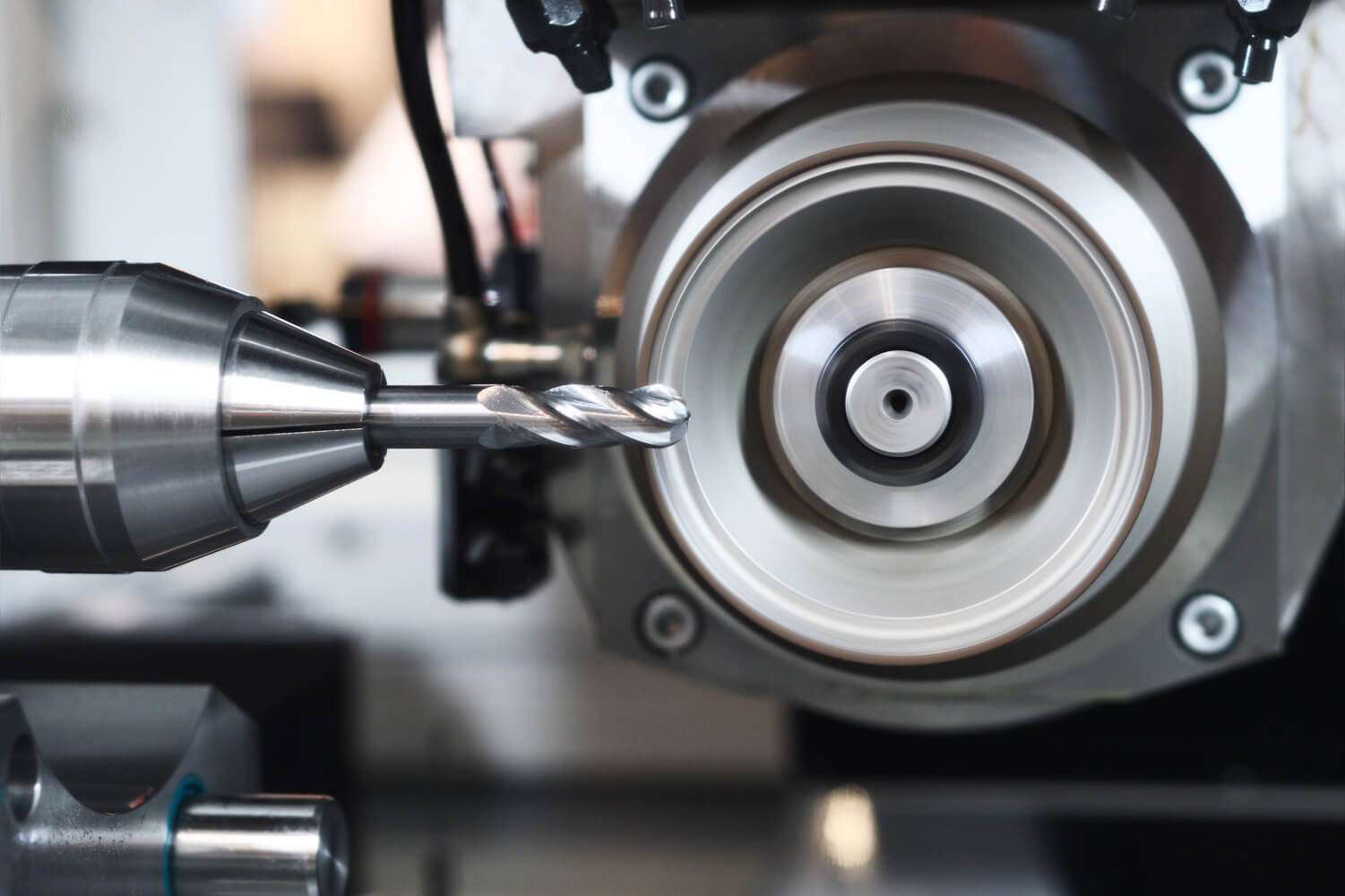
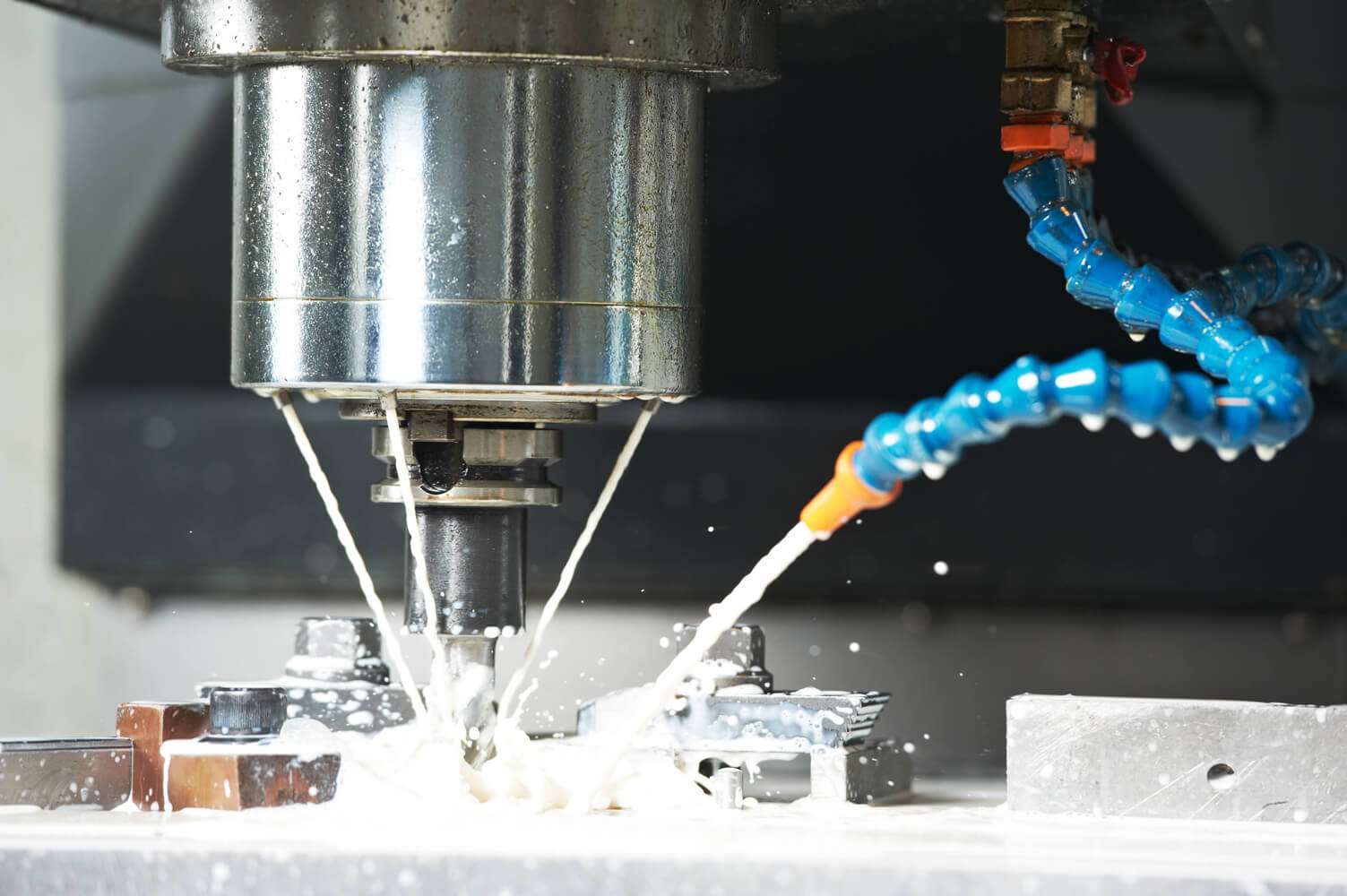
Diamond milling tools are precision-engineered for machining operations where durability and performance are crucial. diamond milling & form tools are used to create complex geometries and fine details in large variety of materials ranging from advanced ceramics, composites, optical glass, glass, semiconductor materials, stone, semi precious stone and many other applications. These tools are manufactured to order based on your requirements and specifications. These tools can be produced in almost any diameter, shape, length, edge geometry, radius, diamond grit size, and mounting type. The geometry of diamond milling tools is crafted to maximize cutting efficiency and surface finish.
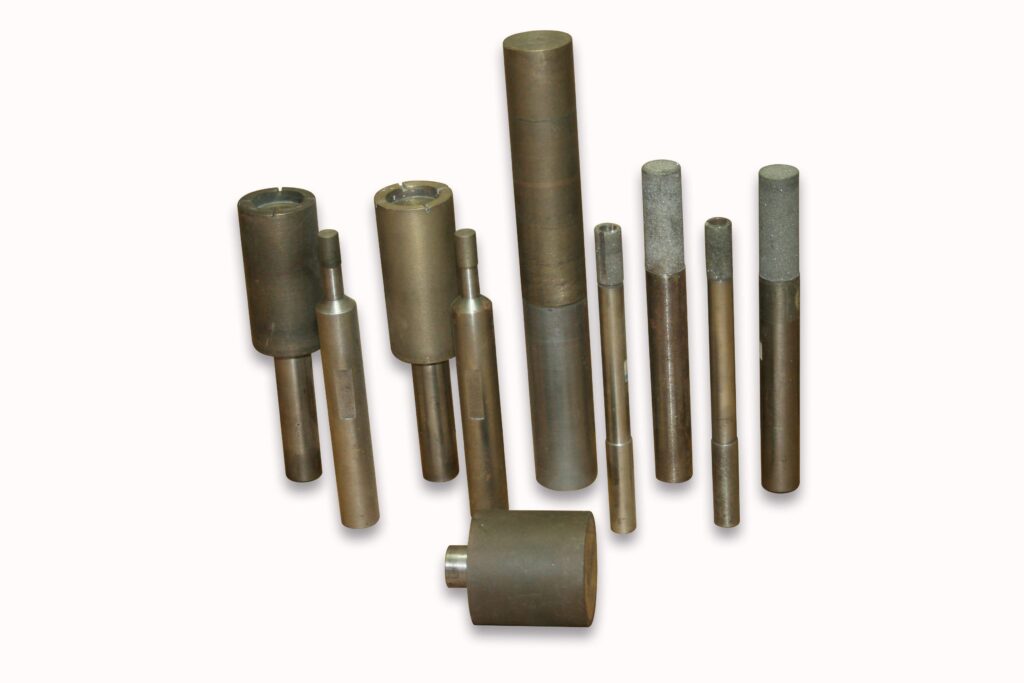

Diamond milling & form tools come in various forms and shapes to meet different machining needs. Some of the common shapes include flat end, ball nose, radius, and profile forms. Flat-end milling tools are ideal for creating sharp edges, flat surfaces, and fine details, while ball nose milling tools are designed for contouring, 3D profiling, and creating smooth curved surfaces. Radius tools, on the other hand, have rounded corners to reduce stress concentration during cutting and to create smoother transitions and contours on the workpiece. Profile tools are specifically shaped for forming and shaping complex geometries, such as custom angles, curves, or detailed mold features.
Diamond milling tools come in various types, including PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond), CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Diamond, and Monocrystalline Diamond tools. PCD tools are used for long-term production runs requiring high wear resistance, CVD tools provide an ultra-hard coating for high-precision tasks, and Monocrystalline tools offer exceptional hardness for ultra-precision machining.
These tools are employed across aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries for tasks like machining composites without fraying, achieving fine finishes on ceramics and hard metals, and creating intricate features in electronics manufacturing. Their durability means less frequent tool changes, their heat resistance allows for higher operational speeds, and their enhanced precision leads to improved product quality.
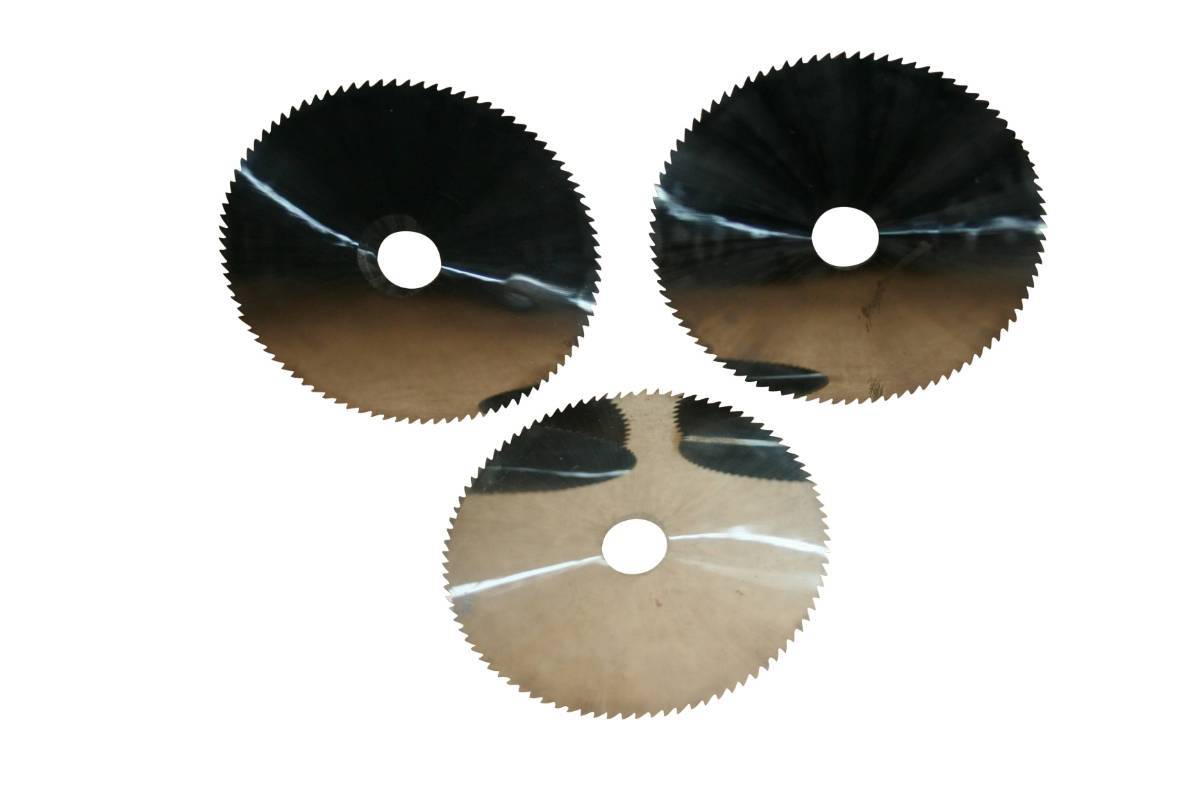
Diamond Routers
Diamond routers in larger variety of shapes, diameters, profiles, radiuses, geometries, in many different diamond bond types, diamond grit sizes, to fit many different types of equipment. These tools are used for grinding and shaping large variety of materials from ultra hard such advanced ceramics to very soft such as glass and composites. Many Tools are available from stock and we also provide custom manufacturing.
These tools are manufactured to order based on your requirements and specifications. These tools can be produced in almost any diameter, shape, length, edge geometry, radius, diamond grit size, and mounting type.
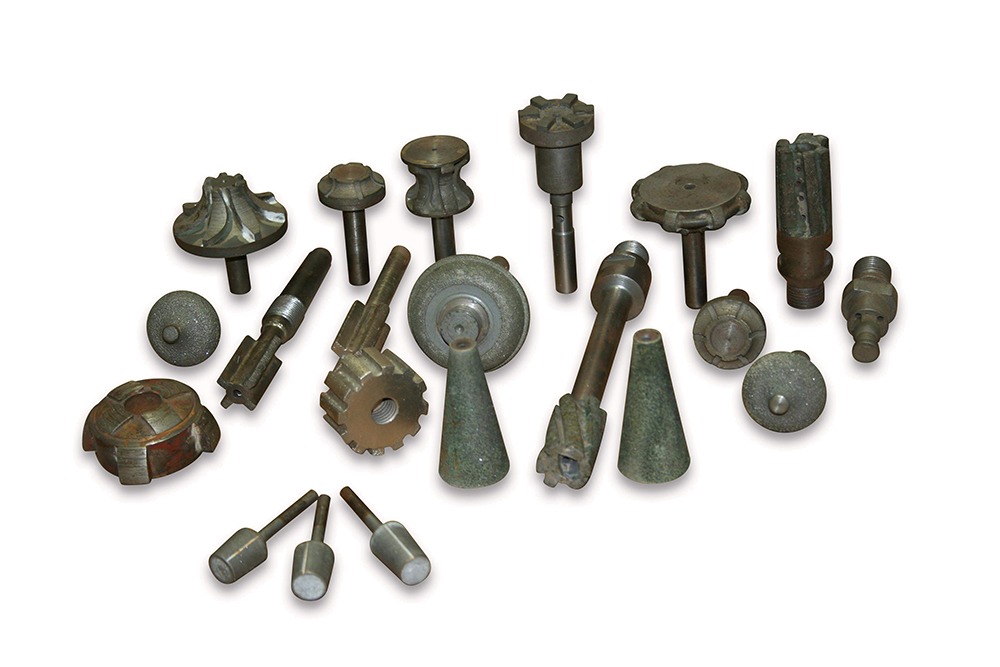

Diamond Router Types:
- Ball Rutters
- Rounded Head Helical Mill
- Segmented Router Bits for Solid Hollowing
- Segmented Milling Wheels
- Milling Wheels
- Diamond Routers for Edge Profiling
- Round Tip Diamond Routers
- Diamond Routers for Laminates
- Diamond Pattern Routers
- Finger Router Bits
- Diamond Routers for 3D Carving
- Diamond Router Bits for Composites
- Diamond Bevel Bullnose Routers
- Diamond Radius Routers
- Diamond Face Routers
- Diamond Slotting Routers
- Diamond V-Groove Routers
- Diamond Sink Routers
- Diamond Cone Routers
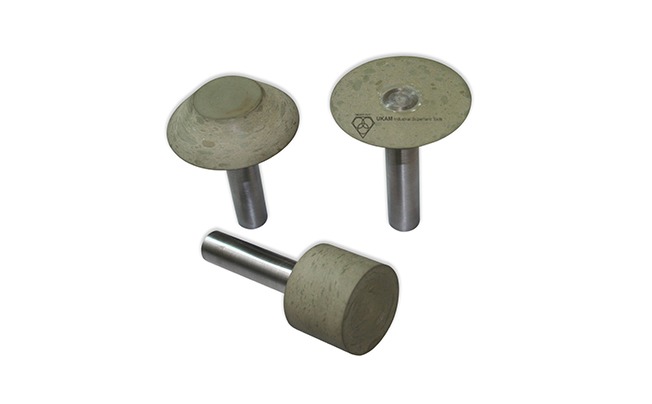
Diamond Ball Nose Tools
Diamond ball nose tools are specialized cutting instruments designed for precision machining of contoured surfaces, complex geometries, and intricate features on a variety of ultra-hard, dense, and brittle materials. Their spherical cutting surface is ideal for achieving smooth, accurate finishes on curved surfaces, carving detailed designs, and milling complex 3D profiles. These tools are highly effective for applications requiring both roughing and fine finishing in industries like aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical devices, and jewelry.
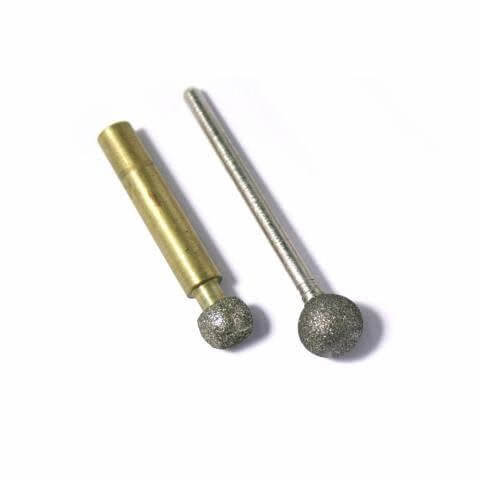


Engineered to work on advanced ceramics, crystals, glasses, composites, and hard metals, diamond ball nose tools deliver clean finishes without chipping or excessive tool wear. They operate efficiently on CNC machines, routers, jig grinders, and milling machines, typically at speeds of 15,000 to 35,000 RPM. The correct speed and cutting parameters are crucial to achieving optimal performance and surface quality.
The tools are available in various bond types, each providing different benefits. Metal bonds offer durability for aggressive cutting, resin bonds ensure fine finishes for precision tasks, electroplated bonds deliver sharp cutting for intricate detailing, and brazed bonds offer high efficiency for machining tough materials.
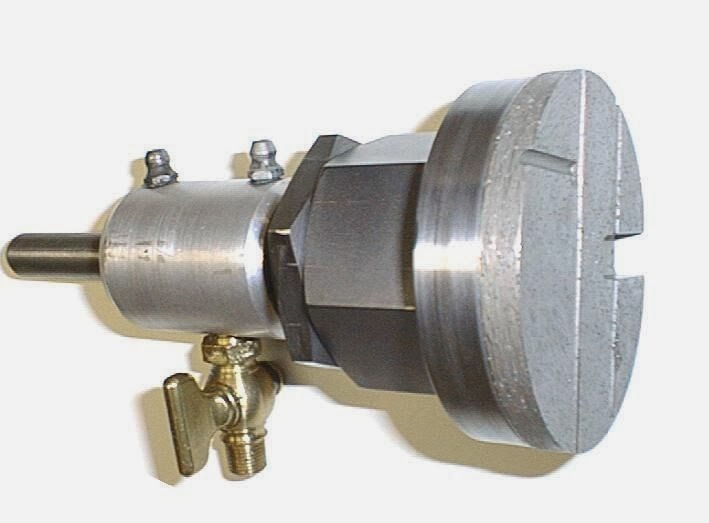
Diamond Bottoming tools/Drills
Diamond bottoming drills/tools are specialized cutting instruments designed for creating flat-bottomed holes or features in a variety of ultra-hard and brittle materials. Unlike standard drills that produce conical or pointed holes, bottoming drills have a flat cutting surface at the tip, allowing for the creation of clean, even bottoms in drilled holes. This design makes them ideal for applications where a precise, flat-bottom finish is required, such as in countersinking flat surfaces, milling pockets, or producing specific hole geometries in advanced materials.


These tools are commonly used in industries like aerospace, electronics, jewelry, ceramics, and optics, where materials like advanced ceramics (alumina, zirconia, silicon carbide), composites, glass, gemstones, and metals require precise hole finishing. Diamond bottoming drills are highly effective in maintaining sharpness and producing clean finishes due to the hardness and wear resistance of diamond, providing longer tool life and better surface quality compared to conventional tools.
In practice, diamond bottoming tools are often used in applications like counterboring, where the goal is to create a flat area at the bottom of a hole, or in sample preparation, where a consistent hole depth and finish are critical. The tools come in different sizes and geometries, depending on the diameter and depth of the hole required, and can be used in a range of machinery, including CNC mills, rotary drills, and precision machining equipment.

Diamond Bottoming/Non Core Formation
Custom Manufacturing Capabilities
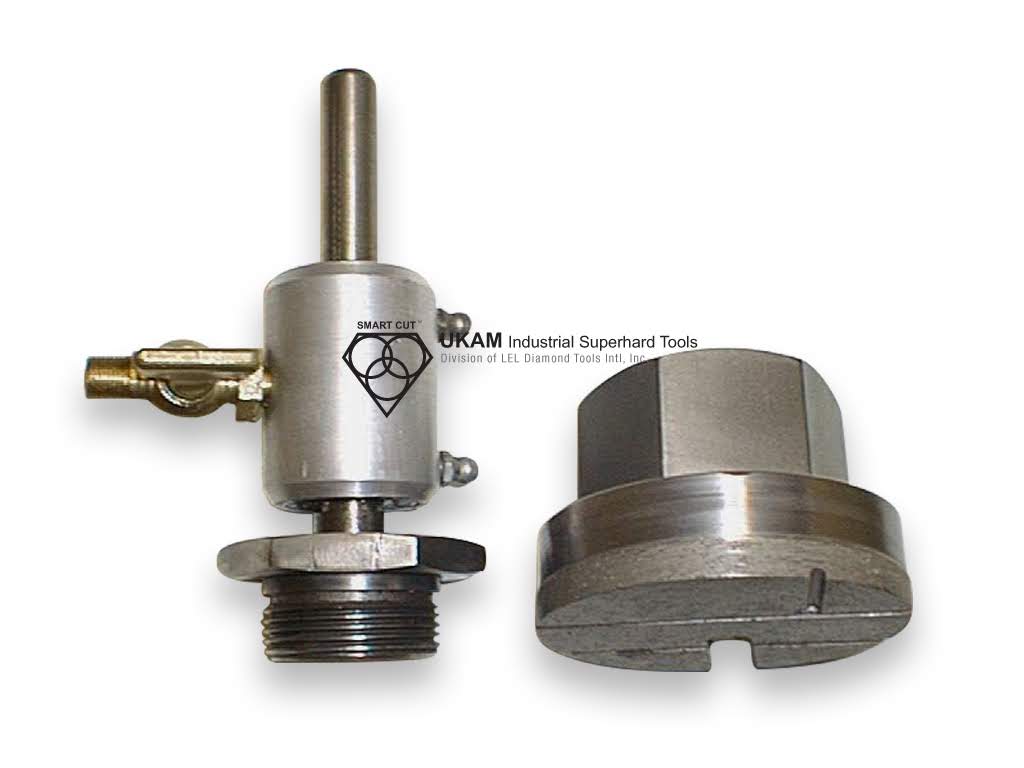
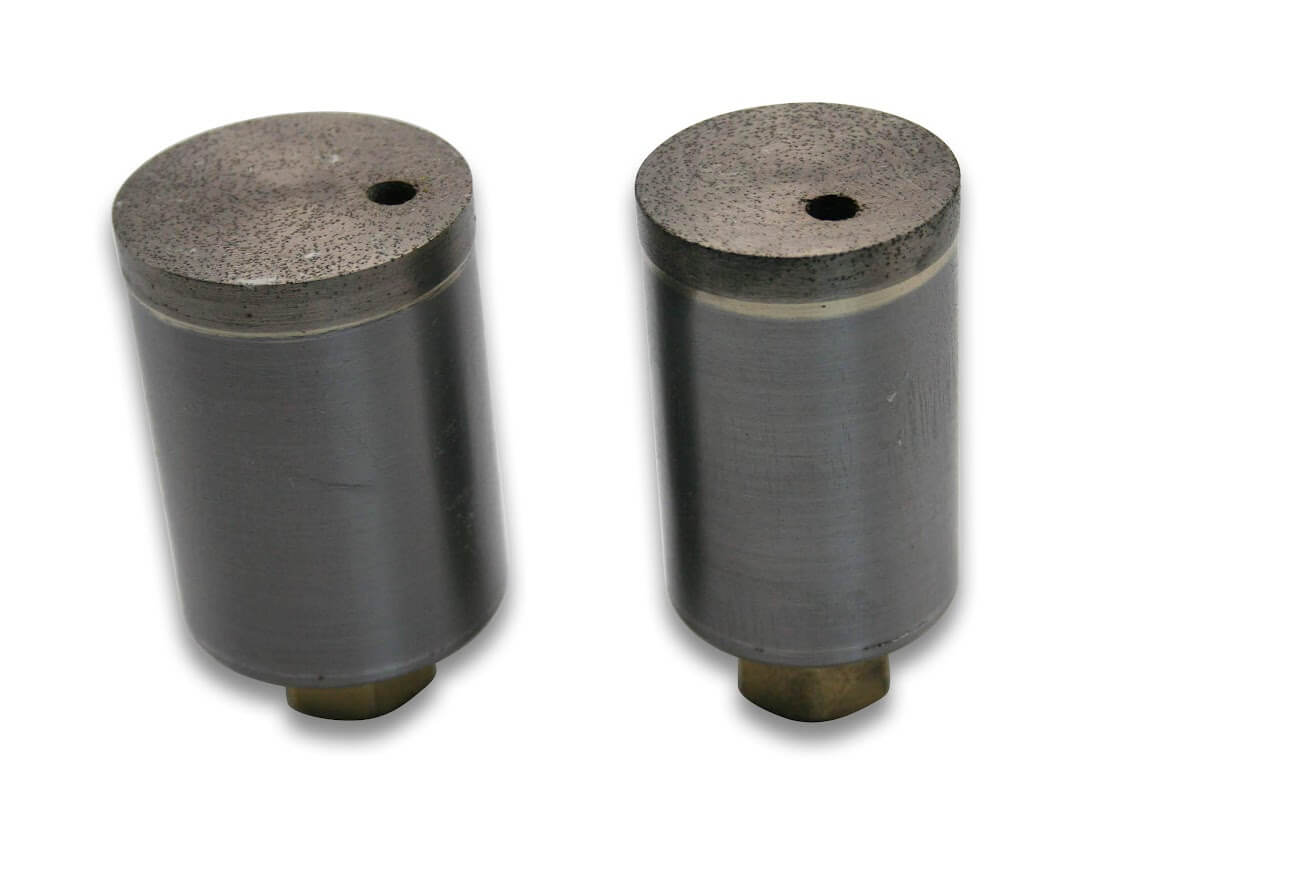
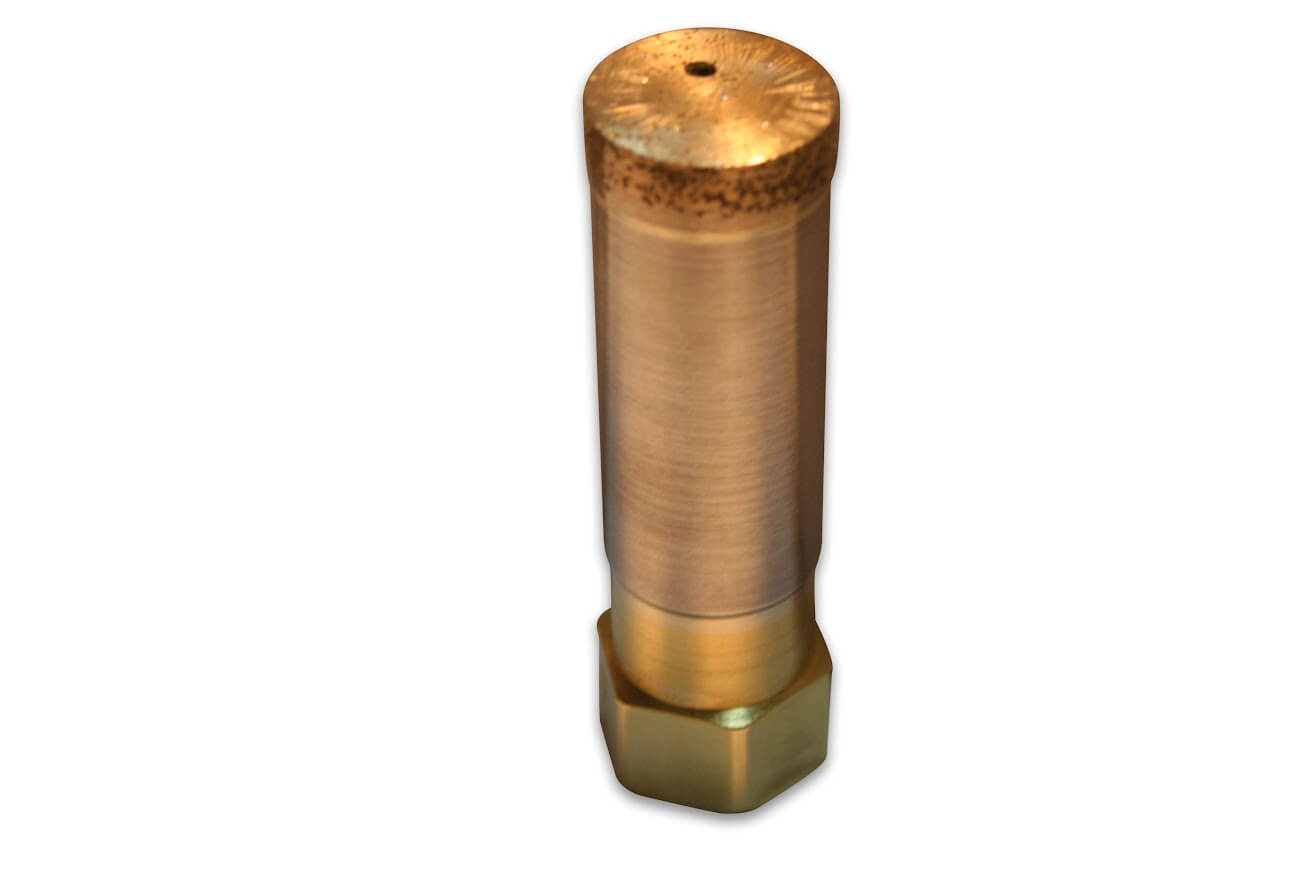
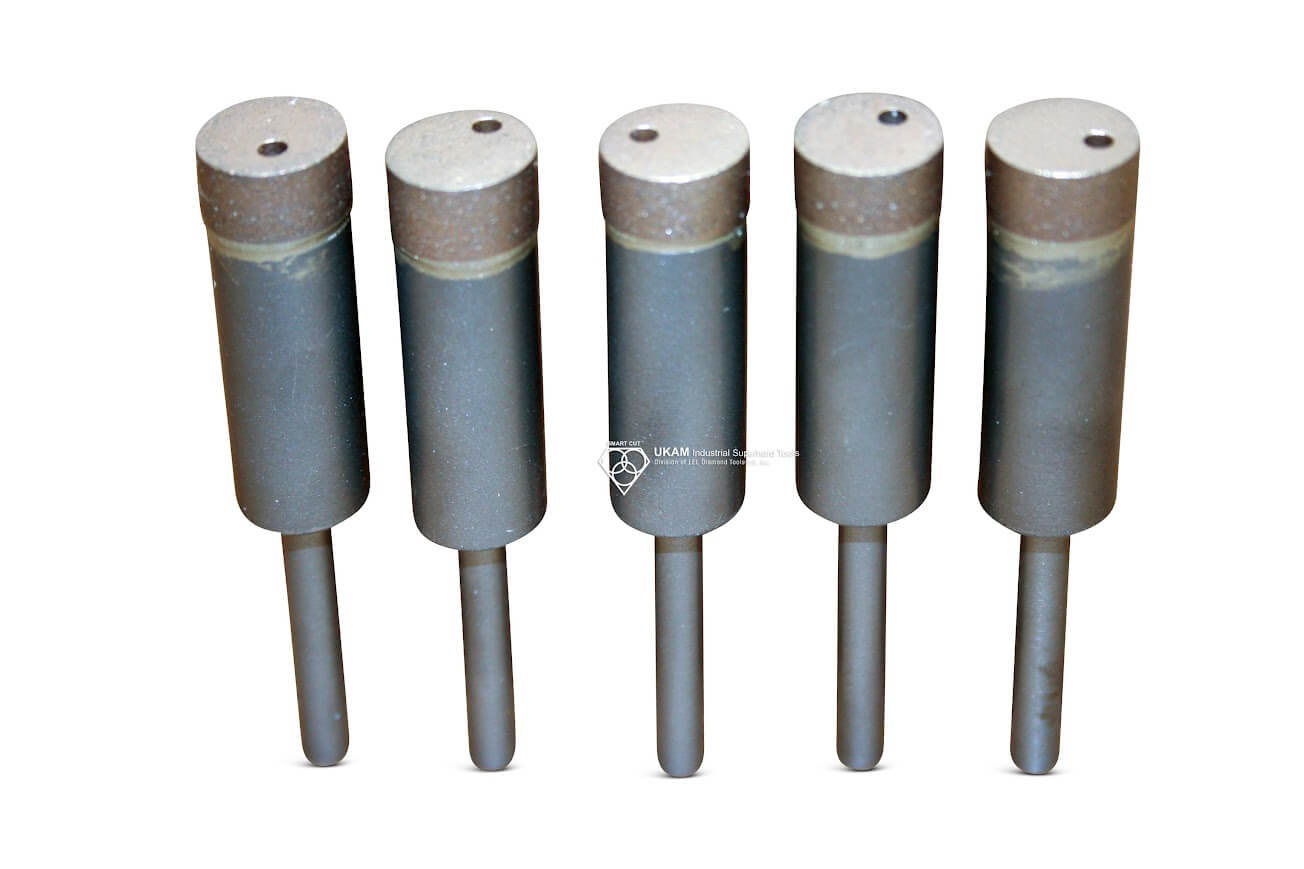
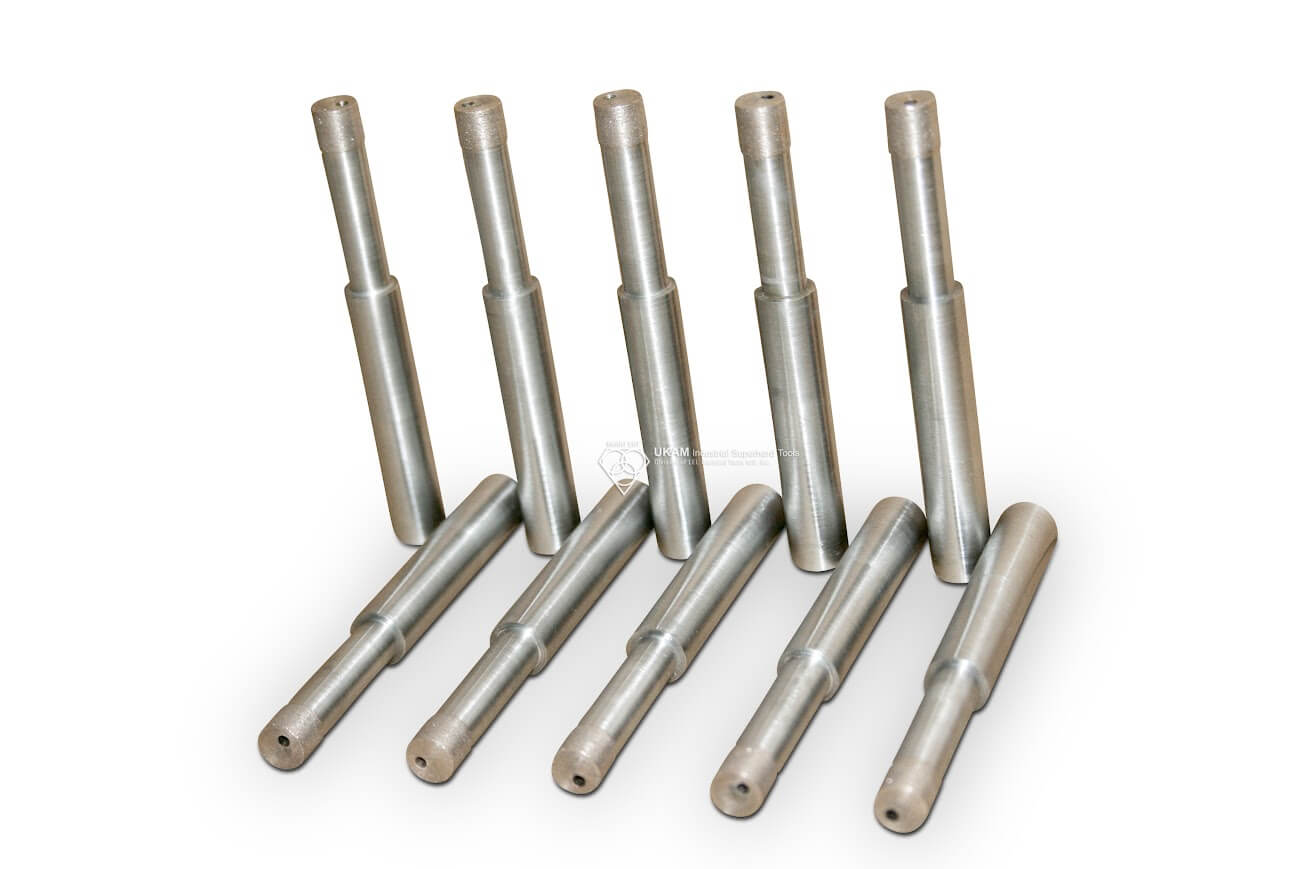
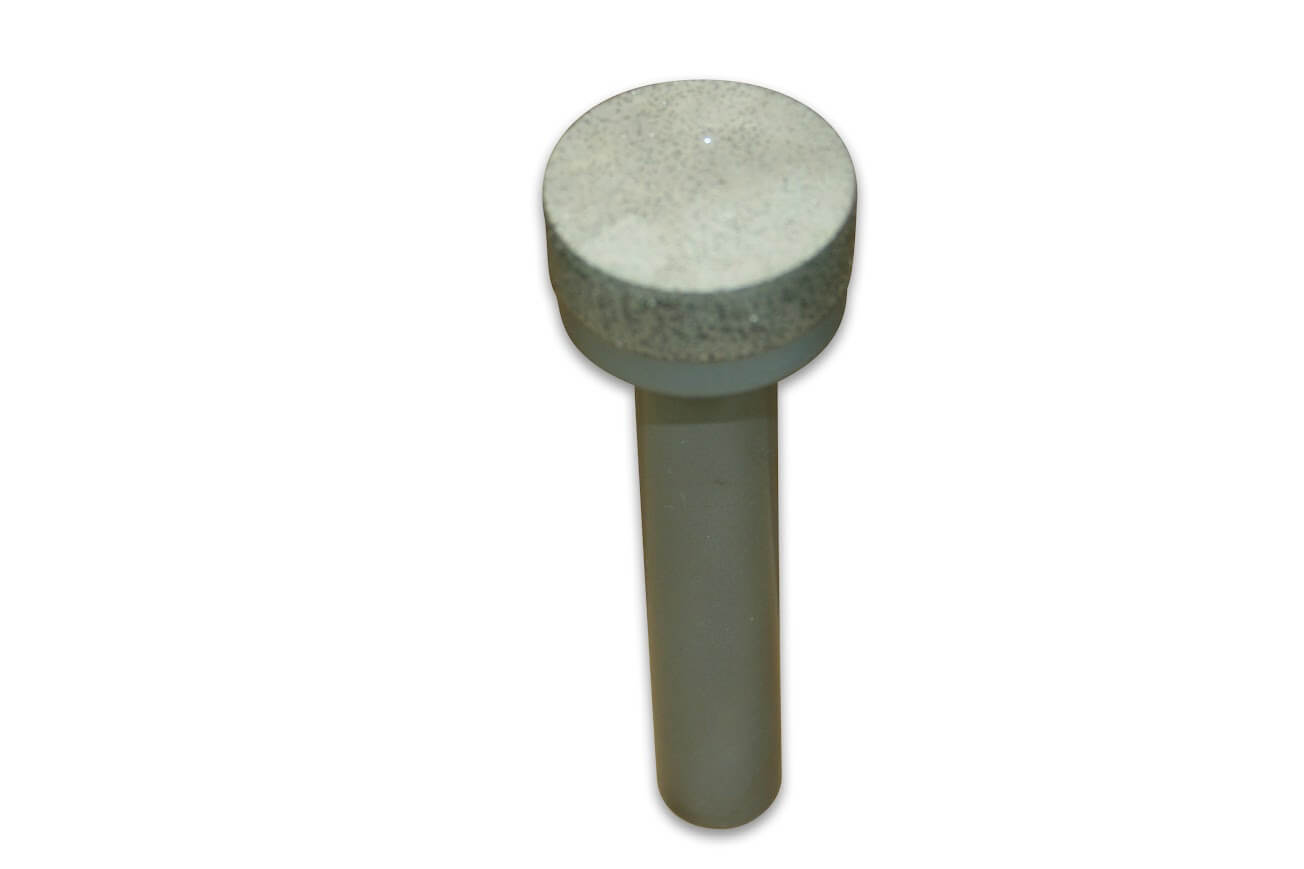
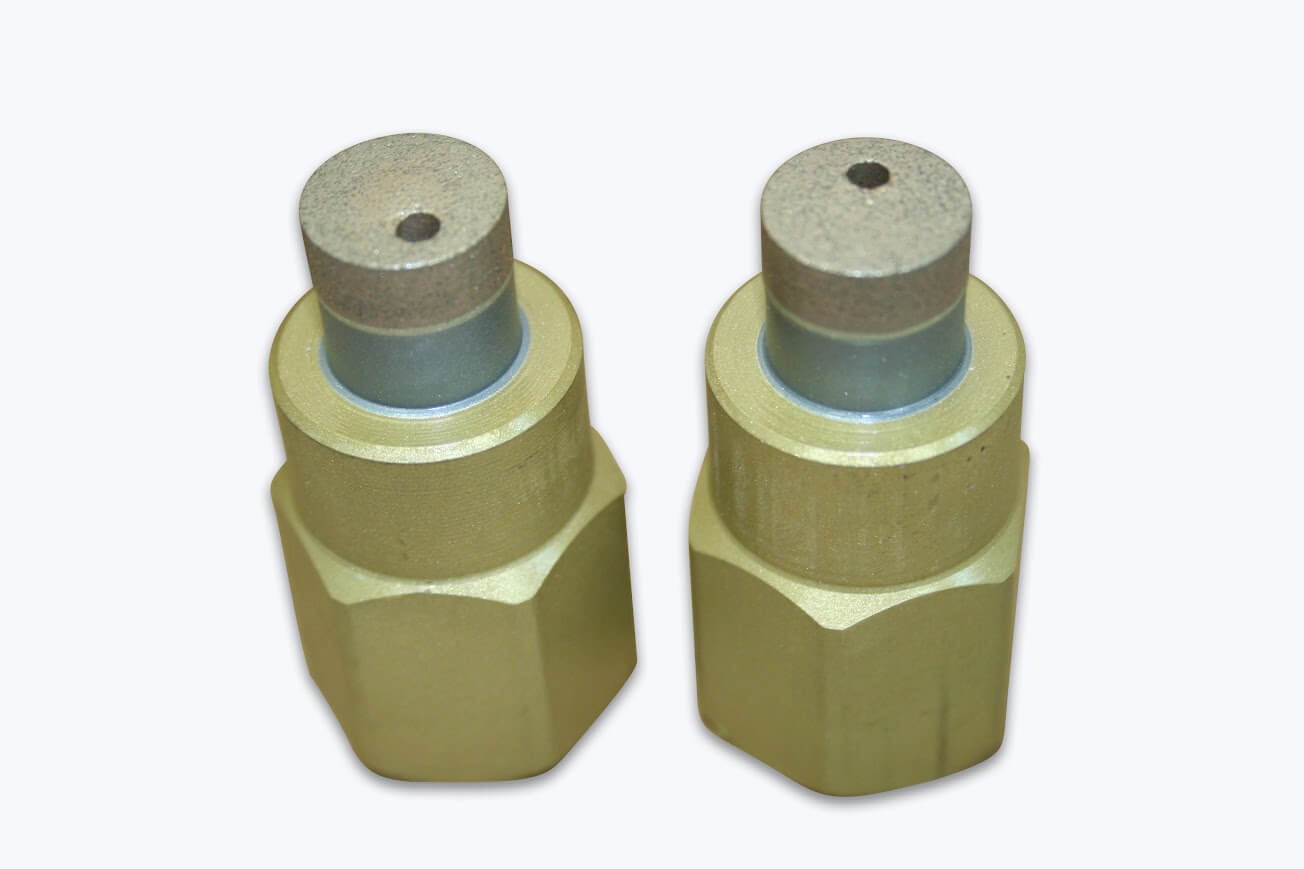
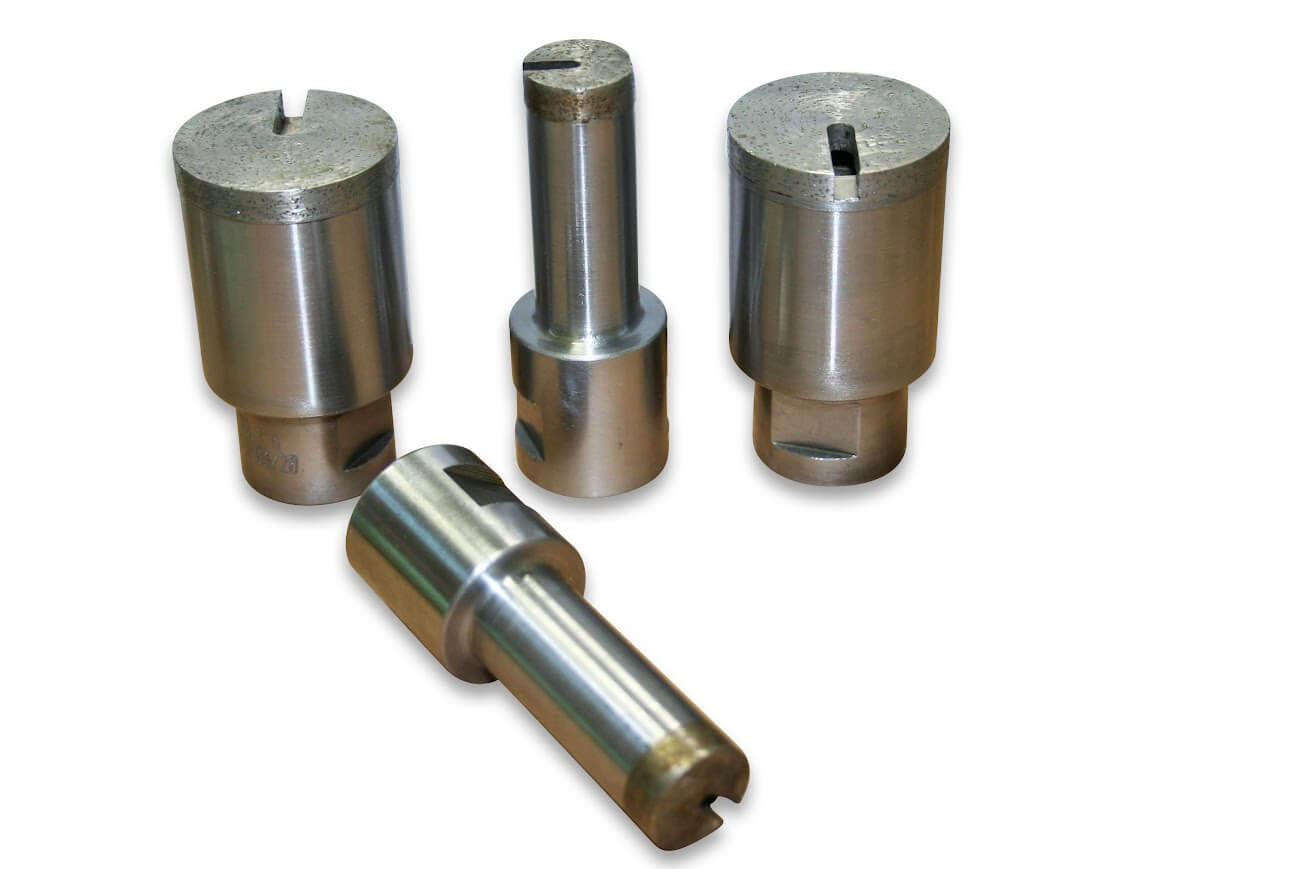
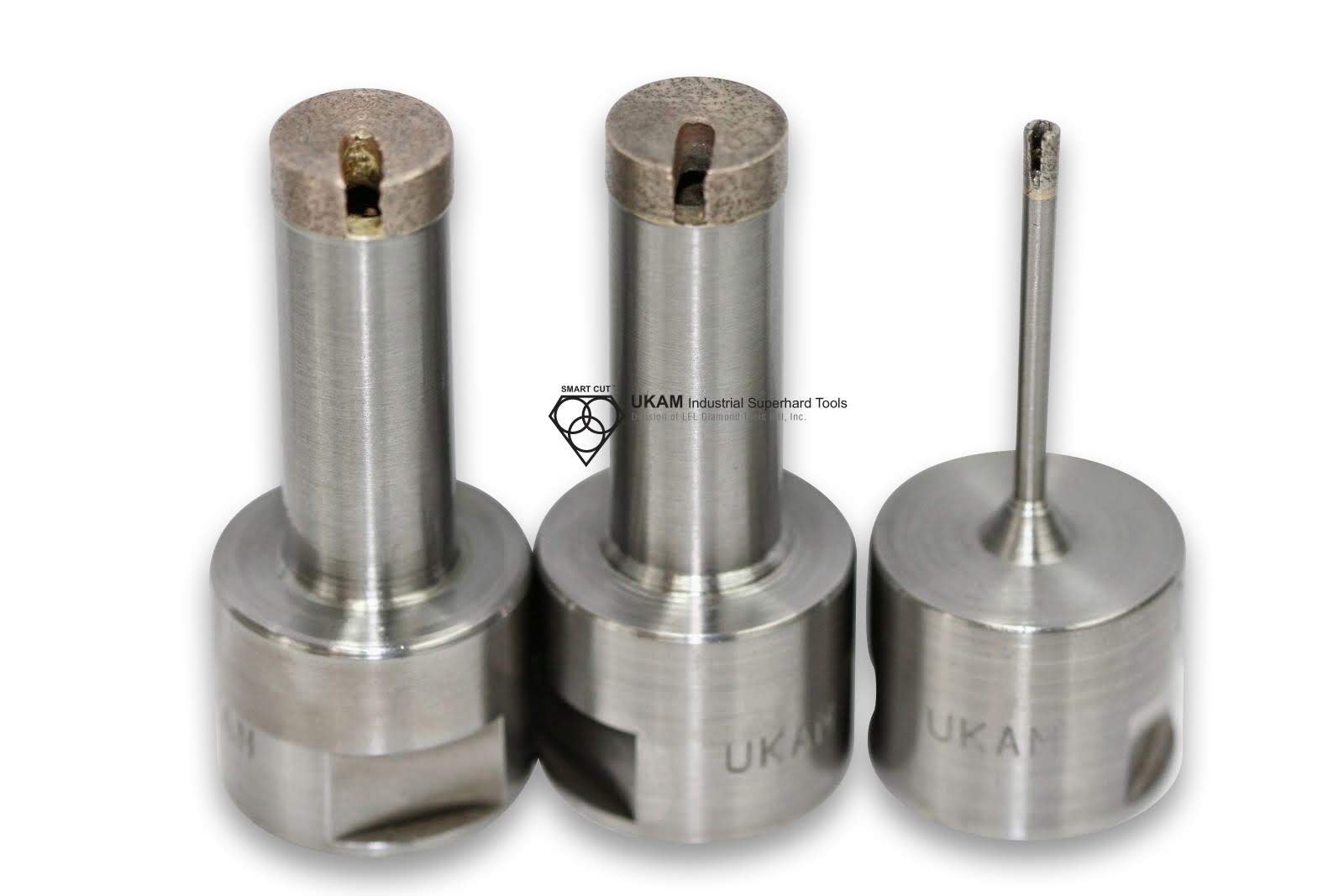













In addition to the standard SMART CUT series Diamond Bottoming/Non Core Formation typically available from stock. We can produce large variety of custom Diamond Bottoming/Non Core Formation and tools per your specification or drawing
- Almost any diameter
- Head geometry (anygle/radius)
- Diamond Section Slotts or Channels
- Custom drill lengths
- Custom shank diameters & Mounting Types
- Almost any diamond or cbn size in proportion to diameter of the tool
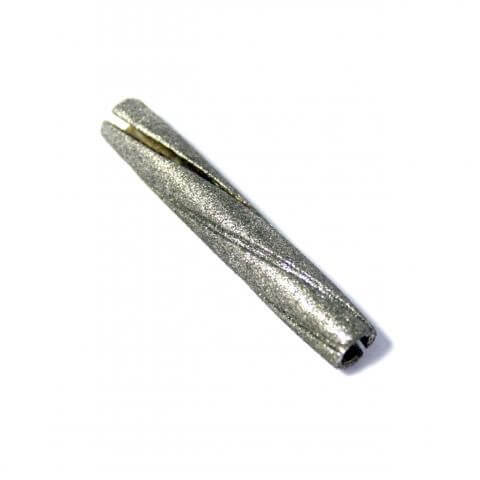
Diamond expanding lap or mandrel
Diamond expanding laps/mandrels are designed for precision honing, lapping, and finishing of internal diameters. The grooves or slits on the body suggest that it is adjustable, allowing it to expand to fit the internal bore of a workpiece accurately. The diamond coating provides efficient material removal and a fine finish on ultra-hard materials like ceramics, glass, and metals.
Expanding laps/mandrels are commonly used for fine-tuning bore sizes, achieving tight tolerances, and polishing internal surfaces to a very smooth finish. The spiral or fluted design allows for even distribution of the diamond abrasive, enhancing the tool’s efficiency and performance during the honing process.


Diamond threading tools
Diamond threading tools are specialized for cutting precise threads on hard, abrasive, or brittle materials like ceramics, composites, metals, and glass. Utilizing diamond as the cutting edge, these tools provide exceptional wear resistance and produce high-quality, smooth threads with consistent accuracy. They are designed to match specific thread profiles, such as V-threads or ACME threads, and come in various forms like single-point tools for intricate thread cutting or thread mills for efficient threading.
The tools are available with different bond types, including metal, resin, and electroplated bonds, to cater to the specific application and material. Operating in CNC machines or lathes, they require careful setup, proper speed, feed rate, and coolant use to achieve the best results and maximize tool life. Diamond threading tools are widely used in aerospace, medical devices, optics, and automotive industries where precision and durability are crucial for threading hard and delicate materials.
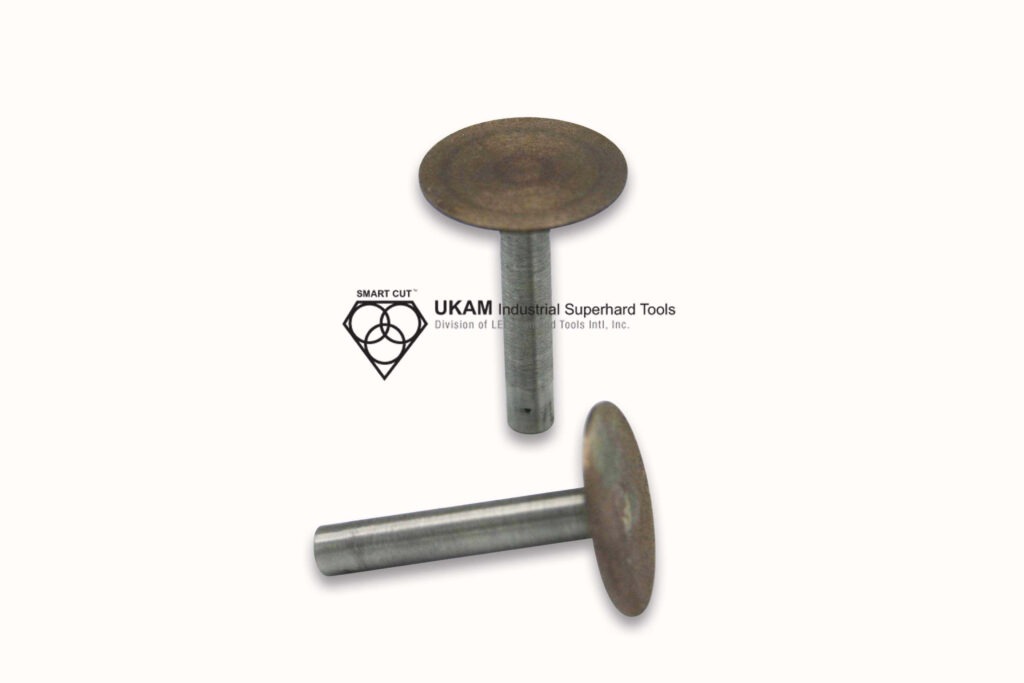
Diamond face grinding tools
These tools are used for surface grinding, leveling, and finishing flat surfaces on hard materials like ceramics, glass, metals, and composites. The flat, circular design with diamond abrasive on the face allows for efficient material removal and produces smooth, flat finishes.
They are typically mounted on grinding machines or other precision equipment and are used in applications requiring high surface quality and precise tolerances. The design of these tools makes them particularly suitable for preparing surfaces, removing excess material, and achieving consistent flatness and smoothness.


Diamond Endmills
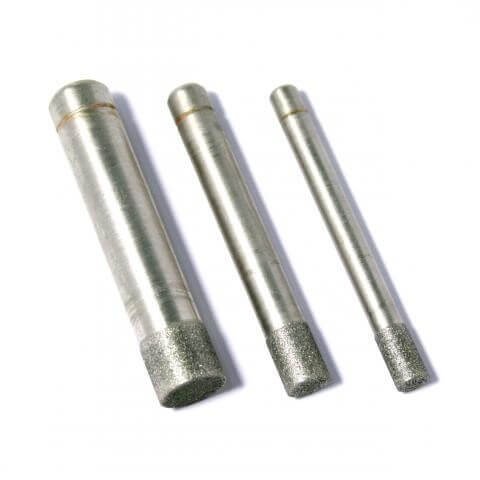
Diamond end mills are designed for precision milling, grinding, and finishing operations on extremely hard and abrasive materials, such as ceramics, glass, carbide, and composites. They are used to produce detailed features, slots, pockets, and contours in these challenging materials.
The solid design, with diamond abrasive coating on the end, allows for efficient cutting, shaping, and fine surface finishing. Unlike traditional end mills, diamond end mills are particularly effective in applications where wear resistance and durability are critical for maintaining precision and prolonging tool life.
Diamond- Grinding Pins
These are designed primarily for internal grinding, deburring, and finishing applications. Their flat bottom is specifically meant for working inside holes, bores, or cavities, producing a flat and smooth bottom surface. They are used for precision shaping and surface finishing, rather than for general milling.
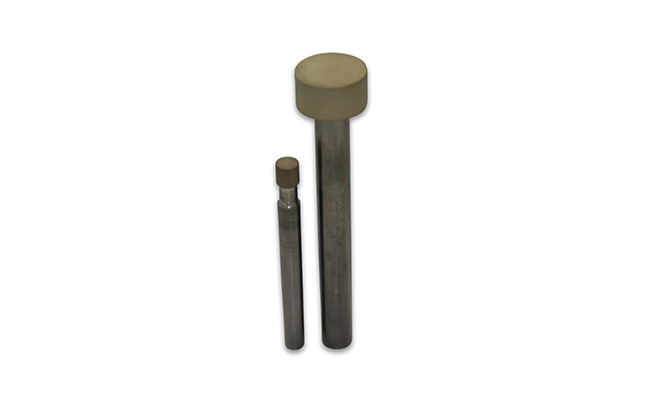


Diamond Grinding Hones
Diamond grinding hones are precision tools used for finishing, polishing, and achieving exact dimensions on hard materials like ceramics, glass, and metals. Unlike traditional grinding, which focuses on substantial material removal, honing with diamond abrasives is aimed at producing smooth surfaces, correcting minor imperfections, and enhancing dimensional accuracy. The diamond abrasive embedded within the hone offers exceptional hardness, allowing for effective surface refinement and consistency across various workpieces.
Resin, metal, or vitrified bonds are commonly used to hold the diamond abrasive, which enables the hone to provide a controlled and gentle grinding action, reducing the risk of damaging the material being honed. Diamond grinding hones can achieve a high level of precision, creating extremely fine surface finishes that are essential in applications demanding tight tolerances and superior surface quality, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. These hones are typically employed in honing machines or hand-held rotary tools to provide smooth finishes and fine-tuned dimensions without significant material removal.
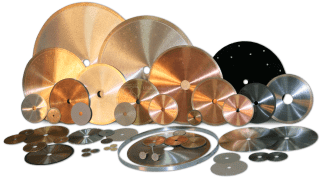
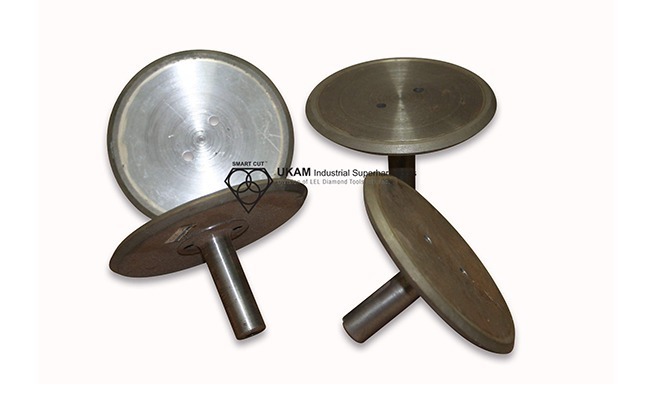
Mounted diamond slitting wheels
Fully sintered (metal bond) mounted diamond slitting wheels are precision cutting tools designed for high-performance slitting, cutting, and slotting applications on ultra-hard and brittle materials. The term "fully sintered" refers to the method of manufacturing, where diamond particles are thoroughly bonded within a metal matrix, resulting in a highly durable tool with excellent cutting efficiency and extended life. Unlike plated or resin-bonded wheels, sintered metal bond wheels offer greater strength, longevity, and resistance to wear, making them suitable for challenging and continuous-use applications.
These wheels are made to order and can be customized to meet a wide variety of specifications, including any diameter, shank size, height, radius, and angle requirements. The flexibility in customization ensures that the diamond slitting wheels are tailored to meet the exact needs of the material, machine, and application.

The ability to fabricate these wheels in almost any diameter makes them suitable for a broad range of cutting tasks, from fine, intricate slitting to wider, deeper cuts. Customizable shank diameters ensure compatibility with different machines, from high-precision CNC equipment to manual grinders. The height and thickness of the wheel can be adapted based on the depth of cut or specific slitting requirements, while custom angles and radii allow for specialized applications like V-grooving, chamfering, or shaping complex profiles.
These metal-bonded diamond wheels are commonly used for cutting, trimming, or slotting a wide array of materials, such as ceramics, glass, gemstones, composites, carbide, ferrites, and hardened metals. Their exceptional durability ensures that they maintain sharp cutting edges over long production runs, providing consistent performance with minimal downtime for tool changes.
Diamond bottoming reamers
They are designed for precision bottoming and shaping of flat-bottomed holes or for expanding existing holes to achieve a smooth, flat surface at the bottom.
The cup-like design allows these tools to create flat-bottom holes or to shape the interior of a bore to specific dimensions, often with minimal chipping or cracking on hard materials such as ceramics, glass, metals, or composites. These tools are typically used for precision work in applications where the shape, depth, and bottom surface finish of the hole are critical, such as in manufacturing and sample preparation. The cylindrical body and flat grinding surface allow for smooth and accurate cutting.