-
0 items in quote
No products in the Quote Basket.
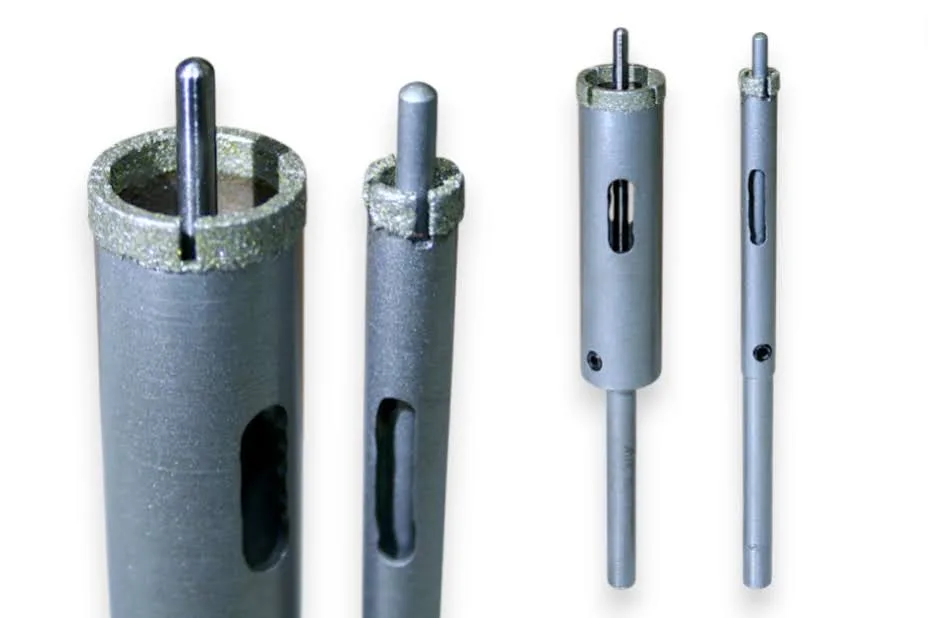
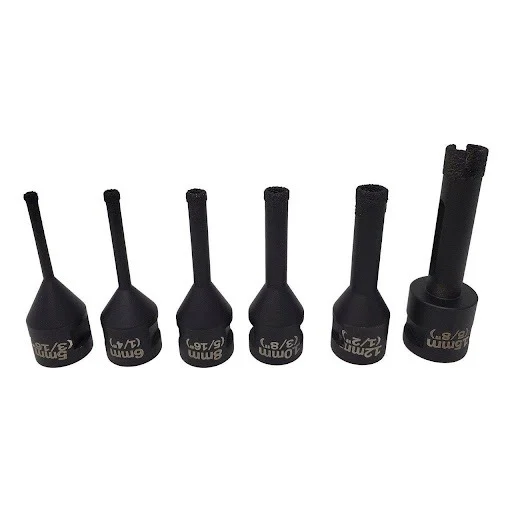
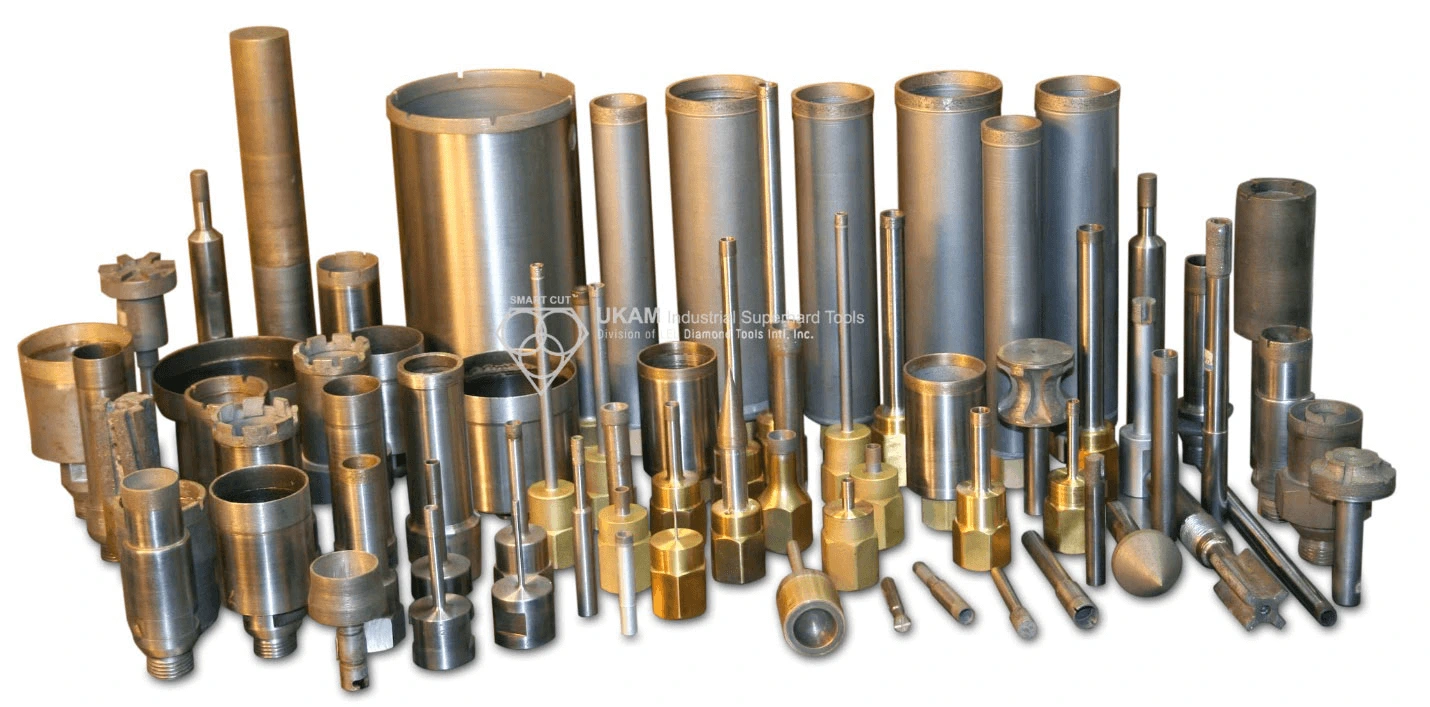
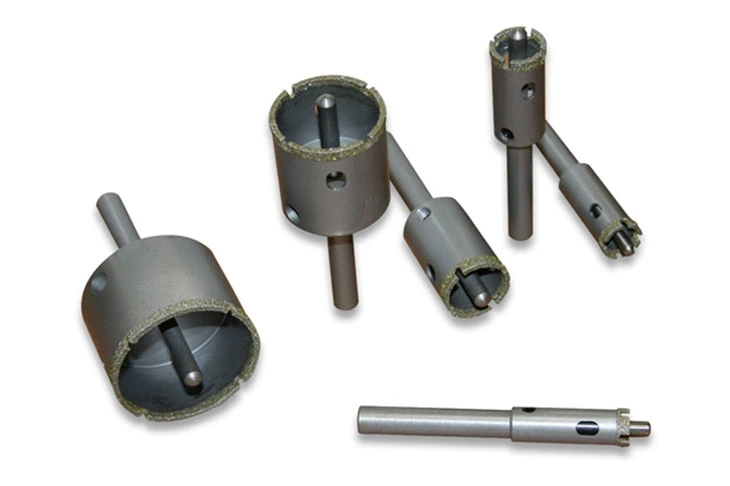
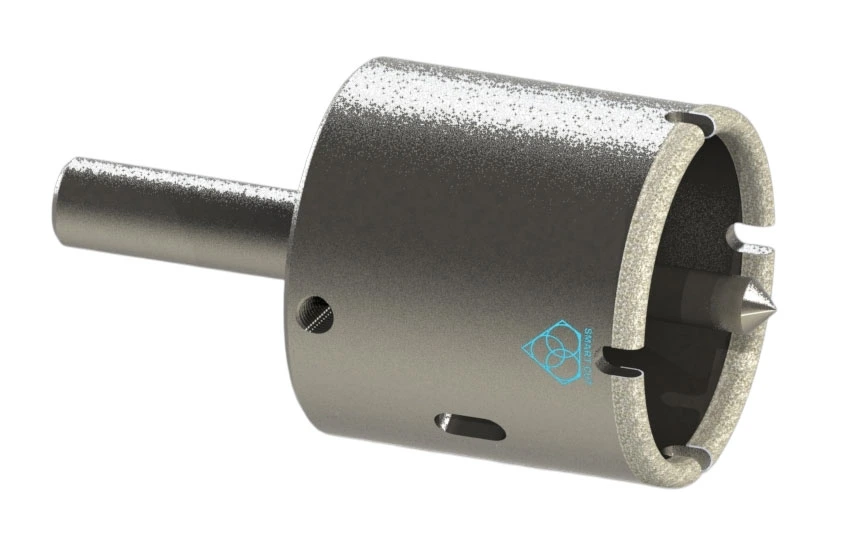
SMART CUT® Diamond Plated Electroplated (NICKEL BOND) Hole Saws / Core Drills with Pilot
SMART CUT® Diamond Electroplated Hole Saws and Core Drills with optional Pilots. These diamond hole saws feature diamond electroplating with a nickel bond and are available with windows and slots for enhanced performance.
SMART CUT® Diamond Plated Hole Saws and Core Drills are designed for fast, accurate drilling in composites, fiberglass, laminates, plastics, and other abrasive non-metallic materials. These tools utilize a nickel electroplated diamond bond that exposes sharp diamond crystals on the surface, delivering aggressive cutting action with low drilling pressure.
Available with or without pilot drills, these diamond plated hole saws are engineered to provide excellent positional accuracy, clean entry, and reduced walking when starting holes. Optional windows and slots in the steel body improve coolant flow, assist chip evacuation, and allow easy core removal.
SMART CUT® diamond plated hole saws construction offers a cost-effective solution for applications that require high cutting speed, good surface finish, and consistent hole size.
DESCRIPTION
SPECIFICATIONS
FAQ
INDUSTRIES USED IN
ACCESSORIES
USAGE RECOMMENDATION
ADVANTAGES
DESCRIPTION
Wall Thickness Specifications:
- For diameters smaller than 1 inch: 0.050 inches
- For diameters of 1 inch and larger: 0.090 inches
Diamond Grit Size: 40/60, Choose between diamond coated pilots or uncoated pilots at no extra cost. When selecting pilots, please specify the diameter and diamond grit, and whether you prefer a removable or permanent pilot.
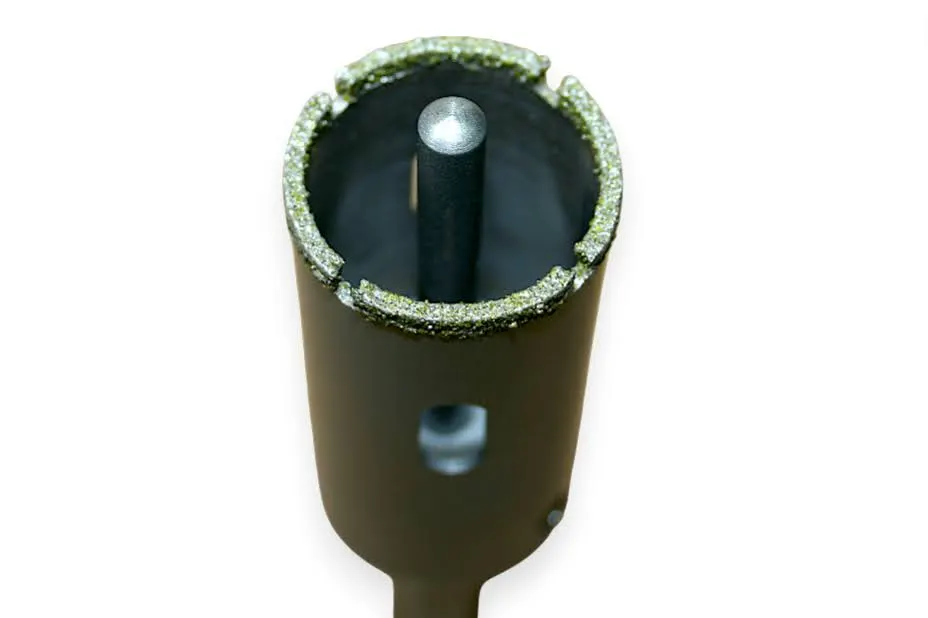
Our SMART CUT® electroplated diamond hole saws are crafted from a single block of metal, ensuring precise core drilling and perfect concentricity. Unlike bi-metal saws with seams, our core drills are seamless, offering faster and smoother drilling in a variety of materials, including composite materials, glass-reinforced plastic, carbon fiber, plastic composites, fiberglass, graphite, and more. They are suitable for dry drilling on various drilling equipment. These diamond hole saws are also available for recoating, offering a cost-saving option if the original blank is reusable.
SPECIFICATIONS
Bond Type: Electroplated (Nickel Bond)
Outside Diameters Available: 1/2″ (12.7mm) to 6″ (150mm)
Wall Thickness Specifications:
- For diameters smaller than 1 inch: 0.050 inches
- For diameters of 1 inch and larger: 0.090 inches
- Diamond Grit Size: 40/60
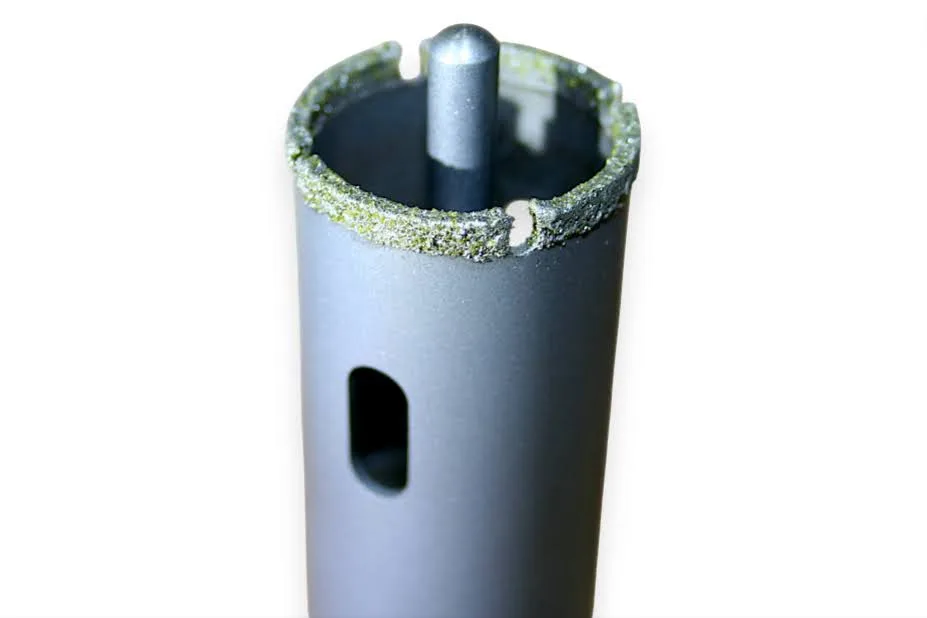
- Rim Type: Continuous Rim, Sloted
- Available with or without pilot
Pilot Type: can be electroplated or non coated
Drill Depth: 2″ (50mm)
Shank Length: 2″ (50mm)
Shank Diameter: Any typically 1/4″ (6.4mm), 3/8″ (9.75mm), 1/2″ (12.7mm)
Diamond Depth/Height: 1/8″ (3.2mm)
Steel Body Composition: Metal
Core Drill Body Design: Key Holes to help remove core
Application: composite materials, glass-reinforced plastic, carbon fiber, plastic composites, fiberglass, graphite, and more
Coolant Used: Wet or Dry
RPM’s Range: 250 to 2,100
FAQ
- Wall Thickness: 0.050 inches for diameters < 1 inch, 0.090 inches for diameters ≥ 1 inch.
- Diamond Grit Size: 40/60.
- Pilot Options: Diamond coated or uncoated (no extra charge).
- Construction: One-piece, seamless metal construction.
Yes, customization options include:
- Continuous rim or slotted designs.
- Various pilot diameters, with or without diamond coating.
- Custom sizes, drilling depths, shank diameters and lengths, diamond depths, grit sizes, and keyhole configurations.
They are designed for materials like composite materials, glass-reinforced plastic, carbon fiber, plastic composites, fiberglass, graphite, and more.
Yes, they are suitable for dry drilling without coolant on a variety of drilling equipment.
Yes, recoating is available at a 5 to 10% savings, provided the original blank is reusable.
- 1/2″ to 1-1/4″: 2100 RPM
- 1-1/4″ to 2″: 1500 to 1700 RPM
- 2″ to 3″: 1100 RPM
- 4-1/2″: 600 RPM
- Larger than 4-1/2″: 250 to 400 RPM
Their one-piece construction ensures precision and reduces vibration, while the diamond electroplating enhances cutting speed and durability.
Yes, they are compatible with a wide range of drilling equipment.
Yes, always adhere to recommended RPMs and use appropriate safety gear. The diamond hole saws are designed to minimize breakage risk but always follow standard safety protocols.
When ordering, specify the pilot diameter, whether you want it coated with diamond grit, and if you prefer a removable or permanent pilot.
The option to recoat and reuse the diamond hole saws reduces waste, making them a more sustainable choice compared to single-use alternatives.
Absolutely. The diamond hole saws can hold precision tolerances, making them suitable for specialized or intricate drilling applications.
The 40/60 diamond grit size is optimized for a balance between cutting speed and finish quality. It provides efficient cutting while maintaining a smooth surface finish on the drilled material.
Yes, their robust design and customization options make them suitable for both small-scale and large-scale industrial applications, including specialized manufacturing processes.
Yes, their seamless construction and precision manufacturing allow for highly accurate and precise drilling, essential for tasks requiring exact hole dimensions.
Regular cleaning and proper storage are key. Avoid overexerting the diamond hole saws at speeds or materials outside its recommended range, and consider recoating when the diamond grit shows signs of wear.
Unlike bi-metal saws that have seams and are prone to breakage, the SMART CUT diamond hole saws are seamless, offering greater strength and stability for high-demand drilling tasks.
A diamond-coated pilot enhances the drilling start, providing better stability and accuracy at the beginning of the drilling process, especially in hard or slippery materials.
Yes, but ensure that the drill is securely handled and that all safety precautions for overhead work are strictly followed.
Avoid using these diamond hole saws on materials that are significantly harder than the diamond hole saws’s capacity or materials that might cause rapid wear, like certain metals or abrasive ceramics.
The specified wall thicknesses are designed to provide optimal balance between strength and cutting efficiency for different diameters, ensuring effective drilling in various materials.
Yes, start with a slow, steady speed to establish the hole, then gradually increase to the recommended RPM. This technique ensures stability and precision at the start of the drilling process.
Yes, but it requires skill and proper setup to maintain the angle consistently. A guide may be necessary for precise angled drilling.
Windows and slots aid in cooling and ejecting debris during drilling, which prevents overheating and maintains the cutting efficiency of the diamond hole saws.
If the diamond hole saws’s performance decreases, consider having it recoated. This can extend its life and is more cost-effective than purchasing a new one.
Measure the thickness of the material you’re drilling and choose a diamond hole saws with an appropriate drilling depth to ensure complete penetration without overextending the diamond hole saws
The lifespan varies based on usage frequency, material drilled, and adherence to recommended practices. Proper maintenance and occasional recoating can significantly extend their life.
Store them in a dry, cool place, ideally in a protective casing to prevent damage to the diamond coating. Avoid stacking heavy items on top of them.
Avoid using them in extremely high temperatures or in environments with abrasive materials in the air, as these conditions can prematurely wear down the diamond coating.
For extended drilling sessions, periodically withdraw the diamond hole saws from the material to allow air cooling. If the diamond hole saws is designed for wet use, a coolant can also be applied to prevent overheating.
Yes, they can be used with standard hand drills, but ensure that the drill’s specifications match the diamond hole saws’s requirements, particularly the chuck size and RPM capacity.
The 40/60 diamond grit size is a general-purpose size suitable for most materials. For finer finishes or harder materials, a finer grit may be necessary.
If the drill bit gets stuck, stop drilling immediately. Gently rotate the drill back and forth to loosen the bit, but avoid applying excessive force to prevent breaking the bit.
While carbide-tipped drills are effective, the diamond electroplating on the SMART CUT diamond hole saws offers superior durability and performance on harder and more abrasive materials.
Yes, they are suitable for use in automated drilling machinery, provided the machinery is compatible with the diamond hole saws’s specifications.
No significant break-in period is required, but it’s advisable to start with less demanding applications to get a feel for the diamond hole saw performance.
Yes, they can be used in high-humidity environments, but ensure that they are dried and stored properly after use to prevent rust or corrosion.
The pilot hole size is crucial for centering the drill and ensuring a clean, accurate hole. Choose a size appropriate for your specific drilling needs.
Yes, but ensure that the diamond hole saws is properly aligned and stable to maintain the desired angle throughout the drilling process.
Extremely hard or abrasive materials can wear down the diamond coating faster. It’s important to match the diamond hole saws to the material’s hardness.
The wall thickness affects the stability and heat dissipation of the diamond hole saws. Thicker walls provide more stability and are better for tougher materials, while thinner walls are more suitable for softer materials and require less power.
The material hardness dictates the speed. Harder materials require slower speeds to prevent overheating and wear, while softer materials can be drilled at higher speeds.
While primarily designed for core drilling, they can be used for countersinking if the diamond hole saws’s size and specifications match the requirements of the task.
Composite materials can be tricky due to their layered structure. Use steady, moderate pressure and appropriate speeds to prevent delamination or damage to the material.
Clean the diamond hole saws with a brush to remove debris and store it in a dry place. Regularly check for wear and damage, especially on the diamond coating.
When drilling these materials, wear protective gear to avoid irritation from small fibers. Also, use steady, controlled drilling to prevent splintering or damage.
A seamless construction offers greater structural integrity, reducing the risk of breakage and ensuring a consistent, uninterrupted cutting edge for cleaner, more accurate drilling.
Yes, they are suitable for plunge cutting, but ensure steady pressure and appropriate speeds for the material being cut.
Signs include decreased performance, visible wear on the diamond coating, or difficulty in achieving clean cuts.
Larger diameters are suitable for bigger, deeper holes but require more power and stability. Smaller diameters offer more precision and are easier to handle, especially in tight spaces.
Yes, but extra care should be taken to ensure the diamond hole saws is stable and the pilot bit is properly engaged before drilling.
Use a drill guide or a drill press to ensure alignment, and start with a pilot hole for additional accuracy.
Store the diamond hole saws in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Also, avoid storing them in an environment where they might be exposed to corrosive chemicals.
Yes, as long as the chuck size matches the shank size of the diamond hole saws.
Consider the material, hole size, depth requirements, and any specific features like the need for a slotted design or a particular pilot size.
Yes, but ensure you have stable support for the drill and use safety equipment to protect against falling debris.
The pilot bit guides the main drill bit and helps maintain accuracy, especially at the start of the drilling process. It’s essential for precise and stable drilling.
The maximum drilling depth depends on the specific diamond hole saws model and size. Usually the drill depth most popular is 2” (50mm). Custom sizes are available for deeper drilling requirements.
It’s possible, but periodically cooling the diamond hole saws, especially during intensive drilling, will prolong its life and maintain optimal performance.
If the performance drops significantly, it’s time to dress the drill, if this does not help it may be time to consider recoating the drill bit. Continuing with a dull bit can damage both the hole saw and the material.
The nickel bond in the diamond coating provides additional strength and durability, enhancing the diamond hole saws’s overall performance and lifespan.
They are not recommended for use with impact drivers, as the percussive action can damage the diamond coating.
A diamond-coated pilot offers better penetration and stability in harder materials, while an uncoated pilot may be sufficient for softer materials.
Use the recommended RPMs, allow for periodic cooling, and if applicable, use a coolant or water to dissipate heat.
They are designed for circular holes; for non-circular shapes, other specialized diamond hole saws or methods would be more appropriate.
Slotted designs offer better heat dissipation and chip removal, while continuous rims provide smoother cuts.
Avoid pushing the diamond hole saws beyond its recommended limits, use the correct speeds for the material, and store it properly when not in use.
While designed primarily for non-metallic materials, they can be used on certain metals, but expect faster wear and a shorter lifespan of the diamond hole saws. Using lubricant such as oil would be recommended for this application.
Use lower speeds, apply steady pressure without forcing the diamond hole saws, and consider using a coolant to prevent overheating.
Match the diamond hole saws size to the diameter of the hole required, considering the wall thickness for stability based on the material’s hardness. Most Composite materials have minimal hardness. If the material is ultra hard consider using other types of diamond drills that we offer for these applications.
They are not typically used for engraving or shaping, as they are designed for core drilling and hole cutting.
The pilot diameter should match the core drill size for optimal stability and accuracy. A mismatch can lead to off-center drilling or reduced stability.
Dressing the drills is possible, however note since these diamond hole saws have single or multi layered diamond coating. They will wear out prematurely if frequently dressed. Recoating is the recommended approach when the diamond hole saws becomes blunt.
A protective case or holder that keeps the diamond hole saws secure and separated is ideal to prevent damage to the diamond coating.
A removable pilot offers flexibility for different applications, while a permanent pilot provides consistent stability and is ideal for repetitive tasks.
These have a straight shank. Usually most angle grinders have 5/-11” thread. So the hole saws will not fit.
Recoating is subject to the condition of the diamond hole saws. Severely damaged or deformed diamond hole saws may not be suitable for recoating.
Reduce pressure, lower the drilling speed, and ensure the diamond hole saws is aligned correctly. Chipping often occurs due to excessive force or misalignment.
Yes, they are suitable for CNC machines, provided the diamond hole saws’s specifications match the machine’s capabilities. There are different core drill designs that we make more suited for cnc machines.
Excessive wear, uneven cutting edges, or frequent chipping indicate improper use, such as using incorrect speeds or forcing the diamond hole saws.
Use the recommended RPM, apply steady, moderate pressure, and ensure the material is securely clamped and the diamond hole saws is properly aligned.
Yes, but ensure the diamond hole saws length and design are appropriate for the depth required, and periodically withdraw the diamond hole saws to clear debris.
Yes they can be used bot wet or dry. Many composite applications require dry drilling.
Ensure the diamond hole saws is properly aligned, use a steady feed rate, and avoid applying lateral force to prevent deflection.
An uneven diamond coating can lead to inconsistent drilling. Consider recoating the diamond hole saws if the unevenness affects performance.
Yes, but extra care and stability are required. Consider using a guide or jig for non-flat surfaces to maintain accuracy.
Use a pilot drill or a center punch to create a guide hole, ensuring the drill starts precisely where intended.
Yes, their durability and precision make them ideal for high-volume applications,specially for composites applications but regular maintenance checks are recommended.
Yes, but it’s important to adjust the drilling speed and pressure according to the layers’ hardness as you progress through the material.
If the diamond hole saws’s body is damaged or severely worn, recoating may not be feasible, and replacement would be the better option.
Only moderate pressure is needed. The diamond coating does most of the work, so excessive force is unnecessary and can be detrimental. Composite Materials usually have several layers its important to reduce amount of pressure applied when existing the hole in order to minimize delamination and stress to material.
Extreme temperatures can affect the metal body, while humidity can impact the longevity of the diamond coating. Store in a controlled environment to maintain optimal condition.
Use a center punch to create a starting point, ensuring the drill bit does not slip when initiating the hole.
Yes, they can be used for this purpose, but ensure the diamond hole saws’s diameter is suitable for the desired expansion size.
Match the shank size of the diamond hole saws to the chuck size of your drill for a secure fit and optimal performance.
Vibration may indicate misalignment or an unsuitable speed. Adjust the alignment and speed, and check if the diamond hole saws is securely mounted.
Use a slow, steady speed, apply consistent pressure, and consider using a coolant to facilitate the drilling process.
Yes, they are well-suited for use in a vertical drill press, which provides stability and precision for drilling.
Worn pilot bits can lead to off-center drilling and reduced accuracy. Replace or recoat the pilot bit if it shows significant wear.
Regularly withdraw the diamond hole saws to clear debris and avoid forcing the diamond hole saws into the material. If it gets stuck, gently rotate and withdraw it.
Yes, but expect faster wear on the diamond coating. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial. Would not recommend using these for abrasive materials.
Yes, they are suitable for tiles and ceramics, but there are different diamond core drills designed for that application that will do better job. These diamond hole saws are specifically designed for composites.
Common risks include flying debris, diamond hole saws breakage, and overheating. Always use protective gear and follow safety guidelines.
Longer diamond hole saws allow for deeper holes but require more stability during drilling, while shorter diamond hole saws offer more control for shallow drilling.
Clean the diamond hole saws with a brush or compressed air to remove debris and grit, and then store it in a clean, dry place.
Yes, they can be used for automotive parts, especially those made from composite materials, plastics, or fiberglass.
Inspect the diamond hole saws for dullness, reduced cutting efficiency, and visible wear on the diamond surface. Regular inspection helps determine when recoating or replacement is needed.
- Wall Thickness: 0.050 inches for diameters < 1 inch, 0.090 inches for diameters ≥ 1 inch.
- Diamond Grit Size: 40/60.
- Pilot Options: Diamond coated or uncoated (no extra charge).
- Construction: One-piece, seamless metal construction.
Yes, customization options include:
- Continuous rim or slotted designs.
- Various pilot diameters, with or without diamond coating.
- Custom sizes, drilling depths, shank diameters and lengths, diamond depths, grit sizes, and keyhole configurations.
They are designed for materials like composite materials, glass-reinforced plastic, carbon fiber, plastic composites, fiberglass, graphite, and more.
Yes, they are suitable for dry drilling without coolant on a variety of drilling equipment.
Yes, recoating is available at a 5 to 10% savings, provided the original blank is reusable.
- 1/2″ to 1-1/4″: 2100 RPM
- 1-1/4″ to 2″: 1500 to 1700 RPM
- 2″ to 3″: 1100 RPM
- 4-1/2″: 600 RPM
- Larger than 4-1/2″: 250 to 400 RPM
Their one-piece construction ensures precision and reduces vibration, while the diamond electroplating enhances cutting speed and durability.
Yes, they are compatible with a wide range of drilling equipment.
Yes, always adhere to recommended RPMs and use appropriate safety gear. The diamond hole saws are designed to minimize breakage risk but always follow standard safety protocols.
When ordering, specify the pilot diameter, whether you want it coated with diamond grit, and if you prefer a removable or permanent pilot.
The option to recoat and reuse the diamond hole saws reduces waste, making them a more sustainable choice compared to single-use alternatives.
Absolutely. The diamond hole saws can hold precision tolerances, making them suitable for specialized or intricate drilling applications.
The 40/60 diamond grit size is optimized for a balance between cutting speed and finish quality. It provides efficient cutting while maintaining a smooth surface finish on the drilled material.
Yes, their robust design and customization options make them suitable for both small-scale and large-scale industrial applications, including specialized manufacturing processes.
Yes, their seamless construction and precision manufacturing allow for highly accurate and precise drilling, essential for tasks requiring exact hole dimensions.
Regular cleaning and proper storage are key. Avoid overexerting the diamond hole saws at speeds or materials outside its recommended range, and consider recoating when the diamond grit shows signs of wear.
Unlike bi-metal saws that have seams and are prone to breakage, the SMART CUT diamond hole saws are seamless, offering greater strength and stability for high-demand drilling tasks.
A diamond-coated pilot enhances the drilling start, providing better stability and accuracy at the beginning of the drilling process, especially in hard or slippery materials.
Yes, but ensure that the drill is securely handled and that all safety precautions for overhead work are strictly followed.
Avoid using these diamond hole saws on materials that are significantly harder than the diamond hole saws’s capacity or materials that might cause rapid wear, like certain metals or abrasive ceramics.
The specified wall thicknesses are designed to provide optimal balance between strength and cutting efficiency for different diameters, ensuring effective drilling in various materials.
Yes, start with a slow, steady speed to establish the hole, then gradually increase to the recommended RPM. This technique ensures stability and precision at the start of the drilling process.
Yes, but it requires skill and proper setup to maintain the angle consistently. A guide may be necessary for precise angled drilling.
Windows and slots aid in cooling and ejecting debris during drilling, which prevents overheating and maintains the cutting efficiency of the diamond hole saws.
If the diamond hole saws’s performance decreases, consider having it recoated. This can extend its life and is more cost-effective than purchasing a new one.
Measure the thickness of the material you’re drilling and choose a diamond hole saws with an appropriate drilling depth to ensure complete penetration without overextending the diamond hole saws
The lifespan varies based on usage frequency, material drilled, and adherence to recommended practices. Proper maintenance and occasional recoating can significantly extend their life.
Store them in a dry, cool place, ideally in a protective casing to prevent damage to the diamond coating. Avoid stacking heavy items on top of them.
Avoid using them in extremely high temperatures or in environments with abrasive materials in the air, as these conditions can prematurely wear down the diamond coating.
For extended drilling sessions, periodically withdraw the diamond hole saws from the material to allow air cooling. If the diamond hole saws is designed for wet use, a coolant can also be applied to prevent overheating.
Yes, they can be used with standard hand drills, but ensure that the drill’s specifications match the diamond hole saws’s requirements, particularly the chuck size and RPM capacity.
The 40/60 diamond grit size is a general-purpose size suitable for most materials. For finer finishes or harder materials, a finer grit may be necessary.
If the drill bit gets stuck, stop drilling immediately. Gently rotate the drill back and forth to loosen the bit, but avoid applying excessive force to prevent breaking the bit.
While carbide-tipped drills are effective, the diamond electroplating on the SMART CUT diamond hole saws offers superior durability and performance on harder and more abrasive materials.
Yes, they are suitable for use in automated drilling machinery, provided the machinery is compatible with the diamond hole saws’s specifications.
No significant break-in period is required, but it’s advisable to start with less demanding applications to get a feel for the diamond hole saw performance.
Yes, they can be used in high-humidity environments, but ensure that they are dried and stored properly after use to prevent rust or corrosion.
The pilot hole size is crucial for centering the drill and ensuring a clean, accurate hole. Choose a size appropriate for your specific drilling needs.
Yes, but ensure that the diamond hole saws is properly aligned and stable to maintain the desired angle throughout the drilling process.
Extremely hard or abrasive materials can wear down the diamond coating faster. It’s important to match the diamond hole saws to the material’s hardness.
The wall thickness affects the stability and heat dissipation of the diamond hole saws. Thicker walls provide more stability and are better for tougher materials, while thinner walls are more suitable for softer materials and require less power.
The material hardness dictates the speed. Harder materials require slower speeds to prevent overheating and wear, while softer materials can be drilled at higher speeds.
While primarily designed for core drilling, they can be used for countersinking if the diamond hole saws’s size and specifications match the requirements of the task.
Composite materials can be tricky due to their layered structure. Use steady, moderate pressure and appropriate speeds to prevent delamination or damage to the material.
Clean the diamond hole saws with a brush to remove debris and store it in a dry place. Regularly check for wear and damage, especially on the diamond coating.
When drilling these materials, wear protective gear to avoid irritation from small fibers. Also, use steady, controlled drilling to prevent splintering or damage.
A seamless construction offers greater structural integrity, reducing the risk of breakage and ensuring a consistent, uninterrupted cutting edge for cleaner, more accurate drilling.
Yes, they are suitable for plunge cutting, but ensure steady pressure and appropriate speeds for the material being cut.
Signs include decreased performance, visible wear on the diamond coating, or difficulty in achieving clean cuts.
Larger diameters are suitable for bigger, deeper holes but require more power and stability. Smaller diameters offer more precision and are easier to handle, especially in tight spaces.
Yes, but extra care should be taken to ensure the diamond hole saws is stable and the pilot bit is properly engaged before drilling.
Use a drill guide or a drill press to ensure alignment, and start with a pilot hole for additional accuracy.
Store the diamond hole saws in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Also, avoid storing them in an environment where they might be exposed to corrosive chemicals.
Yes, as long as the chuck size matches the shank size of the diamond hole saws.
Consider the material, hole size, depth requirements, and any specific features like the need for a slotted design or a particular pilot size.
Yes, but ensure you have stable support for the drill and use safety equipment to protect against falling debris.
The pilot bit guides the main drill bit and helps maintain accuracy, especially at the start of the drilling process. It’s essential for precise and stable drilling.
The maximum drilling depth depends on the specific diamond hole saws model and size. Usually the drill depth most popular is 2” (50mm). Custom sizes are available for deeper drilling requirements.
It’s possible, but periodically cooling the diamond hole saws, especially during intensive drilling, will prolong its life and maintain optimal performance.
If the performance drops significantly, it’s time to dress the drill, if this does not help it may be time to consider recoating the drill bit. Continuing with a dull bit can damage both the hole saw and the material.
The nickel bond in the diamond coating provides additional strength and durability, enhancing the diamond hole saws’s overall performance and lifespan.
They are not recommended for use with impact drivers, as the percussive action can damage the diamond coating.
A diamond-coated pilot offers better penetration and stability in harder materials, while an uncoated pilot may be sufficient for softer materials.
Use the recommended RPMs, allow for periodic cooling, and if applicable, use a coolant or water to dissipate heat.
They are designed for circular holes; for non-circular shapes, other specialized diamond hole saws or methods would be more appropriate.
Slotted designs offer better heat dissipation and chip removal, while continuous rims provide smoother cuts.
Avoid pushing the diamond hole saws beyond its recommended limits, use the correct speeds for the material, and store it properly when not in use.
While designed primarily for non-metallic materials, they can be used on certain metals, but expect faster wear and a shorter lifespan of the diamond hole saws. Using lubricant such as oil would be recommended for this application.
Use lower speeds, apply steady pressure without forcing the diamond hole saws, and consider using a coolant to prevent overheating.
Match the diamond hole saws size to the diameter of the hole required, considering the wall thickness for stability based on the material’s hardness. Most Composite materials have minimal hardness. If the material is ultra hard consider using other types of diamond drills that we offer for these applications.
They are not typically used for engraving or shaping, as they are designed for core drilling and hole cutting.
The pilot diameter should match the core drill size for optimal stability and accuracy. A mismatch can lead to off-center drilling or reduced stability.
Dressing the drills is possible, however note since these diamond hole saws have single or multi layered diamond coating. They will wear out prematurely if frequently dressed. Recoating is the recommended approach when the diamond hole saws becomes blunt.
A protective case or holder that keeps the diamond hole saws secure and separated is ideal to prevent damage to the diamond coating.
A removable pilot offers flexibility for different applications, while a permanent pilot provides consistent stability and is ideal for repetitive tasks.
These have a straight shank. Usually most angle grinders have 5/-11” thread. So the hole saws will not fit.
Recoating is subject to the condition of the diamond hole saws. Severely damaged or deformed diamond hole saws may not be suitable for recoating.
Reduce pressure, lower the drilling speed, and ensure the diamond hole saws is aligned correctly. Chipping often occurs due to excessive force or misalignment.
Yes, they are suitable for CNC machines, provided the diamond hole saws’s specifications match the machine’s capabilities. There are different core drill designs that we make more suited for cnc machines.
Excessive wear, uneven cutting edges, or frequent chipping indicate improper use, such as using incorrect speeds or forcing the diamond hole saws.
Use the recommended RPM, apply steady, moderate pressure, and ensure the material is securely clamped and the diamond hole saws is properly aligned.
Yes, but ensure the diamond hole saws length and design are appropriate for the depth required, and periodically withdraw the diamond hole saws to clear debris.
Yes they can be used bot wet or dry. Many composite applications require dry drilling.
Ensure the diamond hole saws is properly aligned, use a steady feed rate, and avoid applying lateral force to prevent deflection.
An uneven diamond coating can lead to inconsistent drilling. Consider recoating the diamond hole saws if the unevenness affects performance.
Yes, but extra care and stability are required. Consider using a guide or jig for non-flat surfaces to maintain accuracy.
Use a pilot drill or a center punch to create a guide hole, ensuring the drill starts precisely where intended.
Yes, their durability and precision make them ideal for high-volume applications,specially for composites applications but regular maintenance checks are recommended.
Yes, but it’s important to adjust the drilling speed and pressure according to the layers’ hardness as you progress through the material.
If the diamond hole saws’s body is damaged or severely worn, recoating may not be feasible, and replacement would be the better option.
Only moderate pressure is needed. The diamond coating does most of the work, so excessive force is unnecessary and can be detrimental. Composite Materials usually have several layers its important to reduce amount of pressure applied when existing the hole in order to minimize delamination and stress to material.
Extreme temperatures can affect the metal body, while humidity can impact the longevity of the diamond coating. Store in a controlled environment to maintain optimal condition.
Use a center punch to create a starting point, ensuring the drill bit does not slip when initiating the hole.
Yes, they can be used for this purpose, but ensure the diamond hole saws’s diameter is suitable for the desired expansion size.
Match the shank size of the diamond hole saws to the chuck size of your drill for a secure fit and optimal performance.
Vibration may indicate misalignment or an unsuitable speed. Adjust the alignment and speed, and check if the diamond hole saws is securely mounted.
Use a slow, steady speed, apply consistent pressure, and consider using a coolant to facilitate the drilling process.
Yes, they are well-suited for use in a vertical drill press, which provides stability and precision for drilling.
Worn pilot bits can lead to off-center drilling and reduced accuracy. Replace or recoat the pilot bit if it shows significant wear.
Regularly withdraw the diamond hole saws to clear debris and avoid forcing the diamond hole saws into the material. If it gets stuck, gently rotate and withdraw it.
Yes, but expect faster wear on the diamond coating. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial. Would not recommend using these for abrasive materials.
Yes, they are suitable for tiles and ceramics, but there are different diamond core drills designed for that application that will do better job. These diamond hole saws are specifically designed for composites.
Common risks include flying debris, diamond hole saws breakage, and overheating. Always use protective gear and follow safety guidelines.
Longer diamond hole saws allow for deeper holes but require more stability during drilling, while shorter diamond hole saws offer more control for shallow drilling.
Clean the diamond hole saws with a brush or compressed air to remove debris and grit, and then store it in a clean, dry place.
Yes, they can be used for automotive parts, especially those made from composite materials, plastics, or fiberglass.
Inspect the diamond hole saws for dullness, reduced cutting efficiency, and visible wear on the diamond surface. Regular inspection helps determine when recoating or replacement is needed.
INDUSTRIES USED IN
Composite Materials

- Resin
- Aramid
- Carbon Fibers
- Boron
- E-Glass
- S-Glass
- Polymer Matrix Composites
- Metal Matrix Composites
- Ceramic Matrix Composites
- Graphite
- Honeycomb
- Fiber
- SiC
- Si3N4
- Titanium
- Diboride
- Thermoplastic Honeycomb
- FRP Composite
- Al2O3
- Aluminium
- Normex Honeycomb
- Hormex Honeycomb
- Silicon Carbide Fibers
- Many Others
ACCESSORIES
Showing 1 – -1 of 16 results Showing all 16 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Name A – Z
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
Image | Item No. | Description | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Color: 5/8″-11″ thread. Fits into drill press chuck. Shank adapter threads into 5/8″-11″ female thread of diamond drill. Can be used with any other tool with 5/8″-11″ thread. | $26.72 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
Color: 5/8″-11″ thread. Fits into drill press chuck. Shank adapter threads into 5/8″-11″ female thread of diamond drill. Can be used with any other tool with 5/8″-11″ thread. | $22.46 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1 Gallon Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $99.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1 Quart Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $34.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
5 Gallons Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $317.41 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
55 Gallons Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $1,745.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1/2″ x 1/2″ x 6.0″ White Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $8.65 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ White Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1/2″ x 1/2″ x 6.0″ White For use on diamond tools 150 to 220 Grit Size. | $8.65 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh size) or finer. | $15.39 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0″ x 2.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh size) or finer. | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0″ x 2.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
$154.87 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||
$154.87 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||
$235.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
USAGE RECOMMENDATION
Diamond Hole Saw / Core Drill Usage Recommendations for Drilling Composites and other similar materials
1. Diamond Hole Saw / Core Drill Selection
 Choose the appropriate diamond hole saw size based on the desired hole diameter.
Choose the appropriate diamond hole saw size based on the desired hole diameter. Select the pilot type (diamond coated or uncoated) based on the material hardness.
Select the pilot type (diamond coated or uncoated) based on the material hardness. Use a diamond hole saw with an appropriate angle for the type of composite material. Different fiber orientations and matrix materials may require different angles for optimal drilling.
Use a diamond hole saw with an appropriate angle for the type of composite material. Different fiber orientations and matrix materials may require different angles for optimal drilling. Avoid using the same drill bit on different types of materials, as this can lead to cross-contamination and potential damage to both the material and the tool.
Avoid using the same drill bit on different types of materials, as this can lead to cross-contamination and potential damage to both the material and the tool. In projects requiring multiple holes, plan the drilling sequence to minimize material stress and deformation.
In projects requiring multiple holes, plan the drilling sequence to minimize material stress and deformation. Use techniques to reduce the burden on the diamond hole saw, like starting with smaller diameter bits and gradually increasing to the desired size.
Use techniques to reduce the burden on the diamond hole saw, like starting with smaller diameter bits and gradually increasing to the desired size.
2. Preparing to Drill & Drilling Surface
 If the surface is slippery or hard, use a center punch to create a starting point.
If the surface is slippery or hard, use a center punch to create a starting point. Ensure the material is securely clamped and stable.
Ensure the material is securely clamped and stable. Mark the drilling point clearly on the composite material.
Mark the drilling point clearly on the composite material. Conduct a pre-drilling analysis of the composite material to understand its structure and properties, like fiber orientation, which can affect drilling strategy.
Conduct a pre-drilling analysis of the composite material to understand its structure and properties, like fiber orientation, which can affect drilling strategy. Always wear appropriate safety equipment: eye protection, gloves, and hearing protection.
Always wear appropriate safety equipment: eye protection, gloves, and hearing protection. Ensure the work area is well-lit and free from hazards.
Ensure the work area is well-lit and free from hazards. For smooth or hard materials where the drill might wander, start with a smaller pilot drill to create a guide hole.
For smooth or hard materials where the drill might wander, start with a smaller pilot drill to create a guide hole. Ensure that the drill and the material remain stable throughout the process.
Ensure that the drill and the material remain stable throughout the process. Use clamps or vices to secure the material firmly.
Use clamps or vices to secure the material firmly. If the hole depth is critical, use a depth stop or mark the drill bit with tape as a visual guide.
If the hole depth is critical, use a depth stop or mark the drill bit with tape as a visual guide. For angled holes, double-check alignment before drilling, as errors can be more pronounced.
For angled holes, double-check alignment before drilling, as errors can be more pronounced. Familiarize yourself with the properties of the material being drilled, as this knowledge will guide your choice of drilling parameters.
Familiarize yourself with the properties of the material being drilled, as this knowledge will guide your choice of drilling parameters. When drilling vertically, ensure the drill is perfectly perpendicular to the surface. Use a drill stand or press for greater accuracy.
When drilling vertically, ensure the drill is perfectly perpendicular to the surface. Use a drill stand or press for greater accuracy. For larger diameter drills, increase the support for the material being drilled, and consider using a more powerful drill to handle the extra load.
For larger diameter drills, increase the support for the material being drilled, and consider using a more powerful drill to handle the extra load. When drilling thin materials, use a backing board to prevent material deformation and to achieve a clean exit.
When drilling thin materials, use a backing board to prevent material deformation and to achieve a clean exit. For cleaner cuts, consider using tape over the drilling area to reduce splintering.
For cleaner cuts, consider using tape over the drilling area to reduce splintering. Mark the drilling area with a non-permanent marker or masking tape to enhance visibility and precision, especially on dark or textured composites.
Mark the drilling area with a non-permanent marker or masking tape to enhance visibility and precision, especially on dark or textured composites. Be attentive to tool deflection, particularly in thin composite materials. Supporting the material adequately and using correct drill speeds can mitigate this.
Be attentive to tool deflection, particularly in thin composite materials. Supporting the material adequately and using correct drill speeds can mitigate this.
3. Install the Diamond Hole Saw
 Fit the tool into the drill chuck and tighten securely.
Fit the tool into the drill chuck and tighten securely. Ensure the shank size matches the chuck size of your drill.
Ensure the shank size matches the chuck size of your drill. Clamp down the composite material firmly to prevent movement or flexing during drilling.
Clamp down the composite material firmly to prevent movement or flexing during drilling. Position the drill perpendicular to the material surface for a straight hole, or at the desired angle for angled holes.
Position the drill perpendicular to the material surface for a straight hole, or at the desired angle for angled holes. Use a drill guide if available, especially for precise or angled holes.
Use a drill guide if available, especially for precise or angled holes. For hard-to-reach areas, consider using drill extensions but be aware of the increased difficulty in maintaining stability and alignment.
For hard-to-reach areas, consider using drill extensions but be aware of the increased difficulty in maintaining stability and alignment.
4. Recommended Drilling Speeds for Composite Materials(RPM Recommendations)
Set a moderate RPM based on the density and type of composite material. Composite materials often require lower RPMs to prevent overheating and delamination.
 Start the drill at a low speed to initiate the hole.
Start the drill at a low speed to initiate the hole. Gradually increase speed while maintaining steady pressure.
Gradually increase speed while maintaining steady pressure. Adjust the drilling speed based on the type of composite (e.g., carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.), as different materials respond differently to drilling.
Adjust the drilling speed based on the type of composite (e.g., carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.), as different materials respond differently to drilling. Be prepared to adjust drilling speeds dynamically based on the feedback from the material, such as changes in sound or resistance.
Be prepared to adjust drilling speeds dynamically based on the feedback from the material, such as changes in sound or resistance. On uneven or rough surfaces, use a slower feed rate and RPM to maintain control and accuracy.
On uneven or rough surfaces, use a slower feed rate and RPM to maintain control and accuracy. Reduce feed rate and RPM for very hard or abrasive materials to minimize wear on the diamond coating.
Reduce feed rate and RPM for very hard or abrasive materials to minimize wear on the diamond coating. If drilling through materials with different hardness layers, adjust feed rate and RPM as each layer is encountered.
If drilling through materials with different hardness layers, adjust feed rate and RPM as each layer is encountered. Be prepared for sudden changes in resistance.
Be prepared for sudden changes in resistance. To achieve clean, burr-free holes, maintain a consistent drilling speed and avoid abrupt movements.
To achieve clean, burr-free holes, maintain a consistent drilling speed and avoid abrupt movements. In areas where precision is critical, such as near edges or corners, reduce speed and feed rate to prevent chipping or cracking.
In areas where precision is critical, such as near edges or corners, reduce speed and feed rate to prevent chipping or cracking. If the composite has different layers of materials, adjust speed and pressure as you drill through each layer.
If the composite has different layers of materials, adjust speed and pressure as you drill through each layer. In resin-rich composites, use lower speeds to prevent excessive heat that can melt or distort the resin.
In resin-rich composites, use lower speeds to prevent excessive heat that can melt or distort the resin. For fragile or thin composite materials, consider using a sandwich technique with a backing material to reinforce the area during drilling.
For fragile or thin composite materials, consider using a sandwich technique with a backing material to reinforce the area during drilling. Strive to balance the drilling speed with the quality of the hole. Faster drilling can lead to reduced quality and potential damage to the composite.
Strive to balance the drilling speed with the quality of the hole. Faster drilling can lead to reduced quality and potential damage to the composite. Utilize proper workholding techniques to securely hold the composite material without inducing stress or deformation.
Utilize proper workholding techniques to securely hold the composite material without inducing stress or deformation. To ensure clean entry and exit points, make sure the diamond crystals are exposed. Use appropriate backing materials. This is crucial for preventing delamination and fraying.
To ensure clean entry and exit points, make sure the diamond crystals are exposed. Use appropriate backing materials. This is crucial for preventing delamination and fraying. Experiment with varying the tool speed to find the optimal RPM for different types of composites, as they may respond differently to drilling.
Experiment with varying the tool speed to find the optimal RPM for different types of composites, as they may respond differently to drilling. Pay attention to the orientation of different layers within the composite material, as this can significantly impact the drilling dynamics.
Pay attention to the orientation of different layers within the composite material, as this can significantly impact the drilling dynamics.
Recommended RPM’s (for starting point)
 1/2″ to 1-1/4″: 2100 RPM.
1/2″ to 1-1/4″: 2100 RPM. 1-1/4″ to 2″: 1500 to 1700 RPM.
1-1/4″ to 2″: 1500 to 1700 RPM. 2″ to 3″: 1100 RPM.
2″ to 3″: 1100 RPM. 4-1/2″: 600 RPM.
4-1/2″: 600 RPM. Larger than 4-1/2″: 250 to 400 RPM.
Larger than 4-1/2″: 250 to 400 RPM. Adjust the speed according to the material hardness (lower speed for harder materials).
Adjust the speed according to the material hardness (lower speed for harder materials).
5. Starting the Drill
 Begin with a gentle touch. Let the tool’s diamond coating start cutting the material without applying excessive force.
Begin with a gentle touch. Let the tool’s diamond coating start cutting the material without applying excessive force. Maintain a stable grip and position to prevent the tool from wandering.
Maintain a stable grip and position to prevent the tool from wandering. Start the drill at a low speed to establish the hole.
Start the drill at a low speed to establish the hole. Gradually increase to the recommended RPM.
Gradually increase to the recommended RPM. Apply moderate, steady pressure. Do not force the tool into the material.
Apply moderate, steady pressure. Do not force the tool into the material. In some cases, drilling a pilot hole before using the core drill can help in maintaining accuracy and reducing material stress.
In some cases, drilling a pilot hole before using the core drill can help in maintaining accuracy and reducing material stress. Start with smaller pilot holes and progressively move to larger diameters if needed. This step-by-step approach can reduce stress on the material.
Start with smaller pilot holes and progressively move to larger diameters if needed. This step-by-step approach can reduce stress on the material. When drilling near the edges of a composite material, reinforce or support the area to prevent chipping or cracking.
When drilling near the edges of a composite material, reinforce or support the area to prevent chipping or cracking.
6. Use of Coolants
 For extended drilling or hard materials, use a coolant or water to prevent overheating.
For extended drilling or hard materials, use a coolant or water to prevent overheating. Apply coolant to both the tool and the material.
Apply coolant to both the tool and the material. For materials like ceramics or glass, keep the drilling area wet to prevent cracking.
For materials like ceramics or glass, keep the drilling area wet to prevent cracking. In metal drilling, a continuous stream of coolant is ideal for heat management.
In metal drilling, a continuous stream of coolant is ideal for heat management. For thick or high-density composites, use a coolant to prevent overheating.
For thick or high-density composites, use a coolant to prevent overheating. Water or water-soluble oils are effective coolants for composite materials.
Water or water-soluble oils are effective coolants for composite materials. Apply coolant evenly and directly to both the drill bit and the material surface for effective heat dissipation.
Apply coolant evenly and directly to both the drill bit and the material surface for effective heat dissipation. In dry drilling scenarios, particularly with hard materials, take frequent breaks to prevent overheating of both the tool and the material.
In dry drilling scenarios, particularly with hard materials, take frequent breaks to prevent overheating of both the tool and the material. In the absence of liquid coolants, compressed air can be used to help cool the bit and remove debris.
In the absence of liquid coolants, compressed air can be used to help cool the bit and remove debris.
7. Pecking Cycles
 Periodically withdraw the tool to clear debris, especially in deep drilling or when working with dense materials.
Periodically withdraw the tool to clear debris, especially in deep drilling or when working with dense materials. This pecking motion aids in heat dissipation and prolongs tool life.
This pecking motion aids in heat dissipation and prolongs tool life. Use pecking cycles more frequently to clear debris and reduce heat.
Use pecking cycles more frequently to clear debris and reduce heat. During prolonged drilling tasks, take regular breaks to allow the tool to cool down and to check its condition.
During prolonged drilling tasks, take regular breaks to allow the tool to cool down and to check its condition. Approach the final depth slowly to ensure precision.
Approach the final depth slowly to ensure precision. Use peck drilling for deeper holes, periodically withdrawing the tool to allow debris to clear and reduce heat buildup.
Use peck drilling for deeper holes, periodically withdrawing the tool to allow debris to clear and reduce heat buildup. If the composite has different layers of materials, adjust speed and pressure as you drill through each layer.
If the composite has different layers of materials, adjust speed and pressure as you drill through each layer. Utilize peck drilling (intermittent drilling and withdrawing) for deeper holes to facilitate debris removal and reduce heat buildup.
Utilize peck drilling (intermittent drilling and withdrawing) for deeper holes to facilitate debris removal and reduce heat buildup. For thicker composite materials, increase the frequency of peck drilling to allow chips to escape and prevent heat buildup.
For thicker composite materials, increase the frequency of peck drilling to allow chips to escape and prevent heat buildup. Optimize the depth of each peck cycle based on material thickness and density, allowing for efficient chip removal and cooling.
Optimize the depth of each peck cycle based on material thickness and density, allowing for efficient chip removal and cooling.
8. Feed Rates
 Maintain a consistent feed rate that matches the tool’s capability and the material’s hardness.
Maintain a consistent feed rate that matches the tool’s capability and the material’s hardness. Avoid rapid feed rates that might overload the tool or cause chipping.
Avoid rapid feed rates that might overload the tool or cause chipping. Increase the feed rate gradually as the hole deepens, but never exceed the tool’s capacity.
Increase the feed rate gradually as the hole deepens, but never exceed the tool’s capacity. Listen to the sound of the drill and feel for vibration to gauge the appropriate feed rate.
Listen to the sound of the drill and feel for vibration to gauge the appropriate feed rate. Reduce feed rate and RPM for very hard or abrasive materials to minimize wear on the diamond coating.
Reduce feed rate and RPM for very hard or abrasive materials to minimize wear on the diamond coating. In areas where precision is critical, such as near edges or corners, reduce speed and feed rate to prevent chipping or cracking.
In areas where precision is critical, such as near edges or corners, reduce speed and feed rate to prevent chipping or cracking. Maintain a consistent, moderate feed rate. Avoid forcing the tool too quickly into the material, as this can cause delamination or fiber pull-out in composites.
Maintain a consistent, moderate feed rate. Avoid forcing the tool too quickly into the material, as this can cause delamination or fiber pull-out in composites. Lower feed rates can be more effective for precise control, especially when dealing with composites that have a tendency to chip or fray.
Lower feed rates can be more effective for precise control, especially when dealing with composites that have a tendency to chip or fray. For heat-sensitive composites, use intermittent drilling with short bursts to prevent heat buildup that can alter the properties of the material
For heat-sensitive composites, use intermittent drilling with short bursts to prevent heat buildup that can alter the properties of the material If the composite surface is rough or uneven, adjust the drill pressure and speed to account for varying resistance.
If the composite surface is rough or uneven, adjust the drill pressure and speed to account for varying resistance. In some cases, specialty coolants or lubricants designed for composites can enhance the drilling process by reducing heat and improving bit life.
In some cases, specialty coolants or lubricants designed for composites can enhance the drilling process by reducing heat and improving bit life. Apply only the necessary force to engage the diamond hole saw with the material. Excessive force can lead to delamination, fiber damage, cracking. especially in layered or fiber-reinforced composites.
Apply only the necessary force to engage the diamond hole saw with the material. Excessive force can lead to delamination, fiber damage, cracking. especially in layered or fiber-reinforced composites. Customize feed rate and speed settings for each type of composite material based on its specific characteristics and drilling response.
Customize feed rate and speed settings for each type of composite material based on its specific characteristics and drilling response. For composites with high fiber content, use lower RPM and higher feed rates to prevent fiber pullout and ensure clean cuts.
For composites with high fiber content, use lower RPM and higher feed rates to prevent fiber pullout and ensure clean cuts. Control chip size through drill speed and feed rate. Smaller chips are preferable as they are easier to evacuate and reduce the risk of clogging.
Control chip size through drill speed and feed rate. Smaller chips are preferable as they are easier to evacuate and reduce the risk of clogging. Gradually increase pressure when starting to drill to prevent sudden stress on the composite material.
Gradually increase pressure when starting to drill to prevent sudden stress on the composite material. Be cautious of applying excessive pressure which can induce cracks or damage, particularly in more brittle composite materials.
Be cautious of applying excessive pressure which can induce cracks or damage, particularly in more brittle composite materials.
9. Monitoring and Adjustments
 Continuously monitor the drilling process for signs of overheating, vibration, or unusual resistance.
Continuously monitor the drilling process for signs of overheating, vibration, or unusual resistance. Adjust the speed, feed rate, or coolant flow as necessary.
Adjust the speed, feed rate, or coolant flow as necessary. Clear chips and debris regularly, especially when drilling deep holes, to prevent clogging and overheating.
Clear chips and debris regularly, especially when drilling deep holes, to prevent clogging and overheating. In addition to using coolants, ensure that the drilling speed and feed rate are optimized to minimize heat generation.
In addition to using coolants, ensure that the drilling speed and feed rate are optimized to minimize heat generation. If excessive vibration occurs, check the tool and drill alignment, and ensure everything is properly secured and balanced.
If excessive vibration occurs, check the tool and drill alignment, and ensure everything is properly secured and balanced. When drilling at an angle, use a drill guide or jig to maintain the angle consistently throughout the drilling process.
When drilling at an angle, use a drill guide or jig to maintain the angle consistently throughout the drilling process. Do not apply side pressure as it can cause the drill bit to break. Always drill straight in line with the bit.
Do not apply side pressure as it can cause the drill bit to break. Always drill straight in line with the bit. Monitor the condition of the pilot bit. Replace it if it becomes worn out to maintain drilling accuracy.
Monitor the condition of the pilot bit. Replace it if it becomes worn out to maintain drilling accuracy. Stay focused on the task, especially when handling tough materials or complex drilling tasks.
Stay focused on the task, especially when handling tough materials or complex drilling tasks. Periodically check the alignment of the drill, especially after changing the setup or drilling multiple holes.
Periodically check the alignment of the drill, especially after changing the setup or drilling multiple holes. Avoid pushing the drill too hard or too fast, as this can accelerate wear on the diamond coating.
Avoid pushing the drill too hard or too fast, as this can accelerate wear on the diamond coating. Keep the tool clean and avoid contact with materials that could clog or contaminate the diamond coating, such as adhesives or soft metals.
Keep the tool clean and avoid contact with materials that could clog or contaminate the diamond coating, such as adhesives or soft metals. Find the right balance between drill speed and pressure for each material to maximize efficiency and tool life.
Find the right balance between drill speed and pressure for each material to maximize efficiency and tool life. When drilling overhead, wear protective headgear and ensure that loose material cannot fall and cause injury.
When drilling overhead, wear protective headgear and ensure that loose material cannot fall and cause injury. Regularly check the temperature of both the tool and the material. Excessive heat can damage the composite material.
Regularly check the temperature of both the tool and the material. Excessive heat can damage the composite material. Watch for signs of delamination or fraying, which indicate too much pressure or speed.
Watch for signs of delamination or fraying, which indicate too much pressure or speed. Continuously monitor the temperature during drilling. If the bit or material becomes too hot, pause to let it cool.
Continuously monitor the temperature during drilling. If the bit or material becomes too hot, pause to let it cool. If excessive vibration occurs, reduce the drilling speed and check the tool’s alignment and the material’s stability.
If excessive vibration occurs, reduce the drilling speed and check the tool’s alignment and the material’s stability. When drilling through composites with multiple layers, be aware of potential changes in resistance as you move through different layers, and adjust your technique accordingly.
When drilling through composites with multiple layers, be aware of potential changes in resistance as you move through different layers, and adjust your technique accordingly. Frequently inspect the diamond hole saw for signs of wear or damage, as diamond hole saws can cause damage to the composite material.
Frequently inspect the diamond hole saw for signs of wear or damage, as diamond hole saws can cause damage to the composite material. To minimize fiber pull-out, especially in fiber-reinforced composites, ensure the diamond crystal coating on diamond hole saw are sharp and exposed and the drilling speed is not too high.
To minimize fiber pull-out, especially in fiber-reinforced composites, ensure the diamond crystal coating on diamond hole saw are sharp and exposed and the drilling speed is not too high. Keep the diamond coating clean and free from material build-up to maintain effectiveness.
Keep the diamond coating clean and free from material build-up to maintain effectiveness. Implement cool down periods in long drilling sessions to prevent overheating of both the tool and the composite material.
Implement cool down periods in long drilling sessions to prevent overheating of both the tool and the composite material. Closely monitor the wear on the diamond hole saw during extensive use, as composite materials can be abrasive and may accelerate wear.
Closely monitor the wear on the diamond hole saw during extensive use, as composite materials can be abrasive and may accelerate wear. Alternate between drilling and cooling periods to prevent overheating, especially in high-tensile composites.
Alternate between drilling and cooling periods to prevent overheating, especially in high-tensile composites. Adjust drill parameters like speed and feed rate based on the thickness of the composite material to prevent overheating and ensure thorough penetration.
Adjust drill parameters like speed and feed rate based on the thickness of the composite material to prevent overheating and ensure thorough penetration. Ensure that the drill bit is clean and free of contaminants that could transfer to the composite material during drilling.
Ensure that the drill bit is clean and free of contaminants that could transfer to the composite material during drilling. For composites with varying densities, be prepared to adjust drilling parameters on the fly as you encounter different densities within the material.
For composites with varying densities, be prepared to adjust drilling parameters on the fly as you encounter different densities within the material. When dealing with multi-layer composites, employ a sequential drilling approach, adjusting parameters as you progress through different layers.
When dealing with multi-layer composites, employ a sequential drilling approach, adjusting parameters as you progress through different layers. Be aware of moisture content in certain composites, as it can affect drilling dynamics and diamond hole saw longevity.
Be aware of moisture content in certain composites, as it can affect drilling dynamics and diamond hole saw longevity. For transparent composites, extra care should be taken to prevent scratches or marks that could impair visibility.
For transparent composites, extra care should be taken to prevent scratches or marks that could impair visibility. Be aware of thermal expansion in composites during drilling, as heat can cause materials to expand and affect hole dimensions.
Be aware of thermal expansion in composites during drilling, as heat can cause materials to expand and affect hole dimensions. Consider the impact of environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, on both the composite material and the drilling process.
Consider the impact of environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, on both the composite material and the drilling process. Take special care when drilling composite sandwich panels to avoid damaging the core material and maintain structural integrity.
Take special care when drilling composite sandwich panels to avoid damaging the core material and maintain structural integrity. When drilling carbon fiber composites, be especially cautious about heat generation, as it can degrade the fiber-matrix interface.
When drilling carbon fiber composites, be especially cautious about heat generation, as it can degrade the fiber-matrix interface. Keep the diamond hole saw clean, especially from resin or fiber build-up, to maintain efficiency and prevent material contamination.
Keep the diamond hole saw clean, especially from resin or fiber build-up, to maintain efficiency and prevent material contamination. When drilling fiberglass composites, be extra cautious about dust and fibers, which can be irritating to the skin and respiratory system.
When drilling fiberglass composites, be extra cautious about dust and fibers, which can be irritating to the skin and respiratory system.
10. Drilling Completion
 Slow down as you approach the end of the drill depth to prevent breakout on back side of the material
Slow down as you approach the end of the drill depth to prevent breakout on back side of the material Once drilling is complete, turn off the drill and carefully withdraw the tool.
Once drilling is complete, turn off the drill and carefully withdraw the tool. Once the desired depth is reached, reduce the RPM and gently withdraw the tool from the hole.
Once the desired depth is reached, reduce the RPM and gently withdraw the tool from the hole. Avoid abrupt movements that might damage the hole or the tool.
Avoid abrupt movements that might damage the hole or the tool. Inspect the hole for smoothness and absence of delamination.
Inspect the hole for smoothness and absence of delamination. Check the tool for wear, and clean it thoroughly after use.
Check the tool for wear, and clean it thoroughly after use. After completing the drilling, clean the work area to remove any hazardous debris or shards.
After completing the drilling, clean the work area to remove any hazardous debris or shards. As the drill approaches the end of the material, reduce pressure to prevent blowout or damage on the exit side.
As the drill approaches the end of the material, reduce pressure to prevent blowout or damage on the exit side. Use appropriate deburring or countering tools to clean up the edges of the hole, ensuring a smooth finish and removing any potential sharp edges.
Use appropriate deburring or countering tools to clean up the edges of the hole, ensuring a smooth finish and removing any potential sharp edges.
11. Post-Drilling Care
 Clean the hole saw with a brush or compressed air to remove any debris. Use appropriate solvents to remove any resin or composite material that may have adhered to the bit.
Clean the hole saw with a brush or compressed air to remove any debris. Use appropriate solvents to remove any resin or composite material that may have adhered to the bit. Inspect the tool for wear and store it in a dry, cool place.
Inspect the tool for wear and store it in a dry, cool place. After use, inspect the tool for any signs of damage or unusual wear.
After use, inspect the tool for any signs of damage or unusual wear. Clean the tool thoroughly and apply a light oil if storing for an extended period to prevent corrosion.
Clean the tool thoroughly and apply a light oil if storing for an extended period to prevent corrosion. After heavy or prolonged use, inspect the tool for any signs of overheating, such as discoloration or loss of diamond grit.
After heavy or prolonged use, inspect the tool for any signs of overheating, such as discoloration or loss of diamond grit. After drilling, evaluate the quality of the hole for any signs of material damage, such as fraying, splintering, or delamination.
After drilling, evaluate the quality of the hole for any signs of material damage, such as fraying, splintering, or delamination. Post-drilling, assess the integrity of the hole, checking for any signs of material compromise, such as splintering or de-bonding.
Post-drilling, assess the integrity of the hole, checking for any signs of material compromise, such as splintering or de-bonding. Inspect the composite material after drilling for any hidden cracks, delamination, or other damage that might not be immediately visible.
Inspect the composite material after drilling for any hidden cracks, delamination, or other damage that might not be immediately visible.
ADVANTAGES
- Precision & Concentricity: Manufactured from a single block of metal, these diamond hole saws ensure highly precise core drilling and perfect concentricity. This leads to accurate and clean drilling performance.
- Long Life & Durability: The diamond electroplating with a nickel bond enhances the durability and strength of the diamond hole saws, allowing them to withstand rigorous use and offering a longer service life compared to standard hole saws.
- Perfect for Composites & Related Materials: These diamond hole saws are designed to drill through a wide range of materials, including composite materials, glass-reinforced plastic, carbon fiber, plastic composites, fiberglass, graphite, and more, making them suitable large variety of aerospace, turbine, boat building, and many other applications
- Customization Options: With options for continuous rim or slotted designs, various pilot diameters, and other customizable features, these hole saws can be tailored to specific drilling needs and applications, ensuring optimal performance for any task.
- Seamless Design: Unlike bi-metal saws that have seams, these core drills are seamless, reducing the risk of breakage and enhancing the quality of the cut.
- Dry Drilling Capability: They can be used for dry drilling without coolant, which is convenient and reduces the need for additional equipment or materials.
- Enhanced Cooling and Waste Removal: The design with windows and slots aids in cooling the cutting surface and facilitates the removal of drilling waste. This feature helps in maintaining the effectiveness of the drill bit over longer periods and prevents overheating, which is crucial when working with materials that are sensitive to high temperatures.
- Reduced Vibration: The one-piece construction minimizes vibration during drilling. This not only makes the drilling process smoother but also reduces operator fatigue and enhances safety, especially during extended use.
- Increased Cutting Speed: The diamond grit size of 40/60 is optimized for efficient cutting, allowing for faster drilling without sacrificing precision. This leads to increased productivity, especially in professional settings where time efficiency is crucial.
- Lower Maintenance Requirements: The robust construction and quality materials used in these diamond hole saws reduce the need for frequent maintenance, saving both time and resources for users.
Typical Applications:
- Composites
- Fiberglass
- Plastics and polymers
- Carbon fiber(CFRP)
- GFRP laminates
- Phenolics and epoxy materials
Benefits:
- Faster & Freer Drilling
- Minimum Heat Generation
- Reduce Fiber Pull Out
- Minimize Material Delamination
- Minimum Amount of Material Stress
- Preserve Material Micro Structure
- Minimum Dust Generation
- More Accurate Holes
Features:
- Nickel electroplated diamond bond (single-layer diamond)
- Fast cutting and low drilling pressure
- Clean entry and exit with minimal chipping
- Optional pilot drill for improved starting technology
- Optional windows/slots for coolant access and debris removal
- Steel body construction for rigidity and stability
- Designed for wet or dry use (wet recommended for longer life)
Showing 1 – -1 of 25 results Showing all 25 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Price low to high
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
Image | Item No | Outside Diameter | Quantity | Get Quote |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1/2" (12.7mm) | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
9/16" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
5/8" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
7/8" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-1/16" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-1/8" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-1/8" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-1/8" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-3/16" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-3/16" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-1/4" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-3/4" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1-7/8" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2-1/4" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2-1/2" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
3" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
3-1/4" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
3-1/2" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
4" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
4-1/4" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
4-1/2" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
5" | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
6” | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
Customization Options:
- Continuous rim or slotted designs
- Customizable pilot diameters, with or without diamond coating
- Fully customizable sizes, drilling depths, rim types, shank diameters and lengths, pilot sizes, diamond depths, grit sizes, and keyhole configurations
- Precision tolerances available for specialized tasks
We also offer customization using standard hole saw brands like STARRETT, NICKLESON, BLACK & DECKER, MILLER FALLS, MILWAUKEE, and DO-ALL. For these, the teeth are replaced with a diamond-plated cutting surface.
Recommended RPMs:
- 1/2″ to 1-1/4″: 2100 RPM
- 1-1/4″ to 2″: 1500 to 1700 RPM
- 2″ to 3″: 1100 RPM
- 4-1/2″: 600 RPM
- Larger than 4-1/2″: 250 to 400 RPM (Note: Lower speeds are recommended for harder materials.)
Benefits:
- Faster & Freer Drilling
- Minimum Heat Generation
- Reduce Fiber Pull Out
- Minimize Material Delamination
- Minimum Amount of Material Stress
- Preserve Material Micro Structure
- Minimum Dust Generation
- More Accurate Holes
Example of
Custom Diamond Tool for Composites
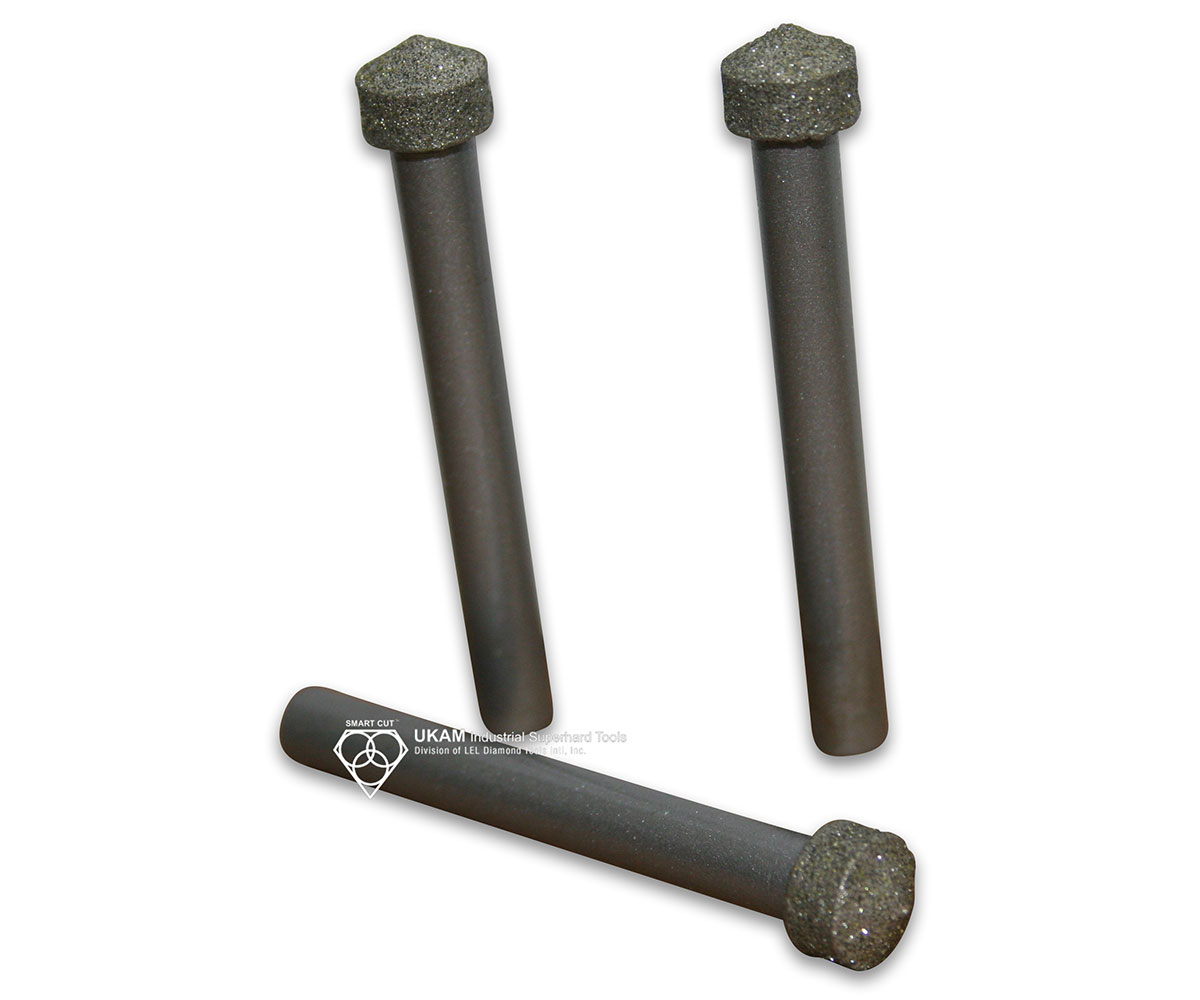
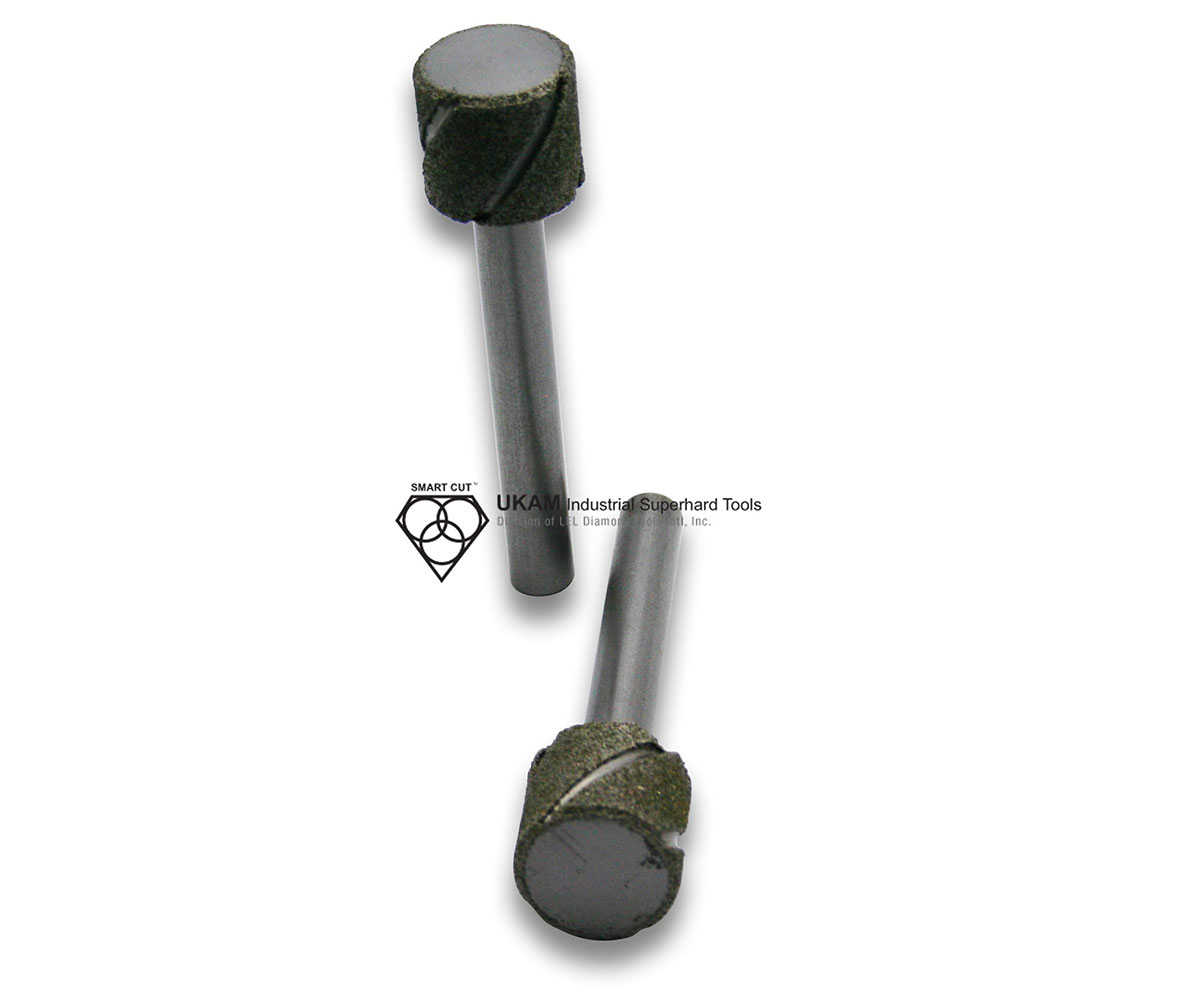
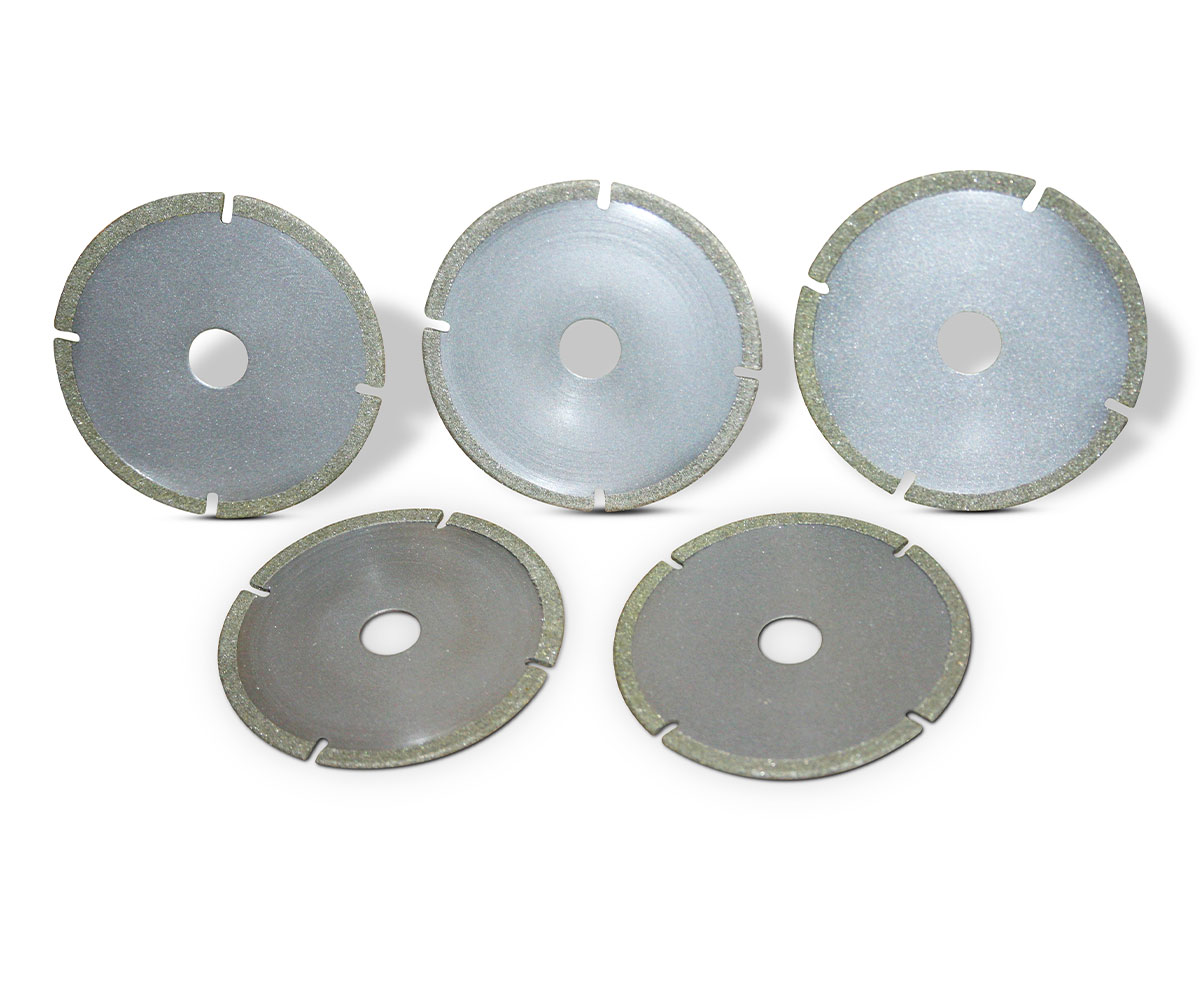
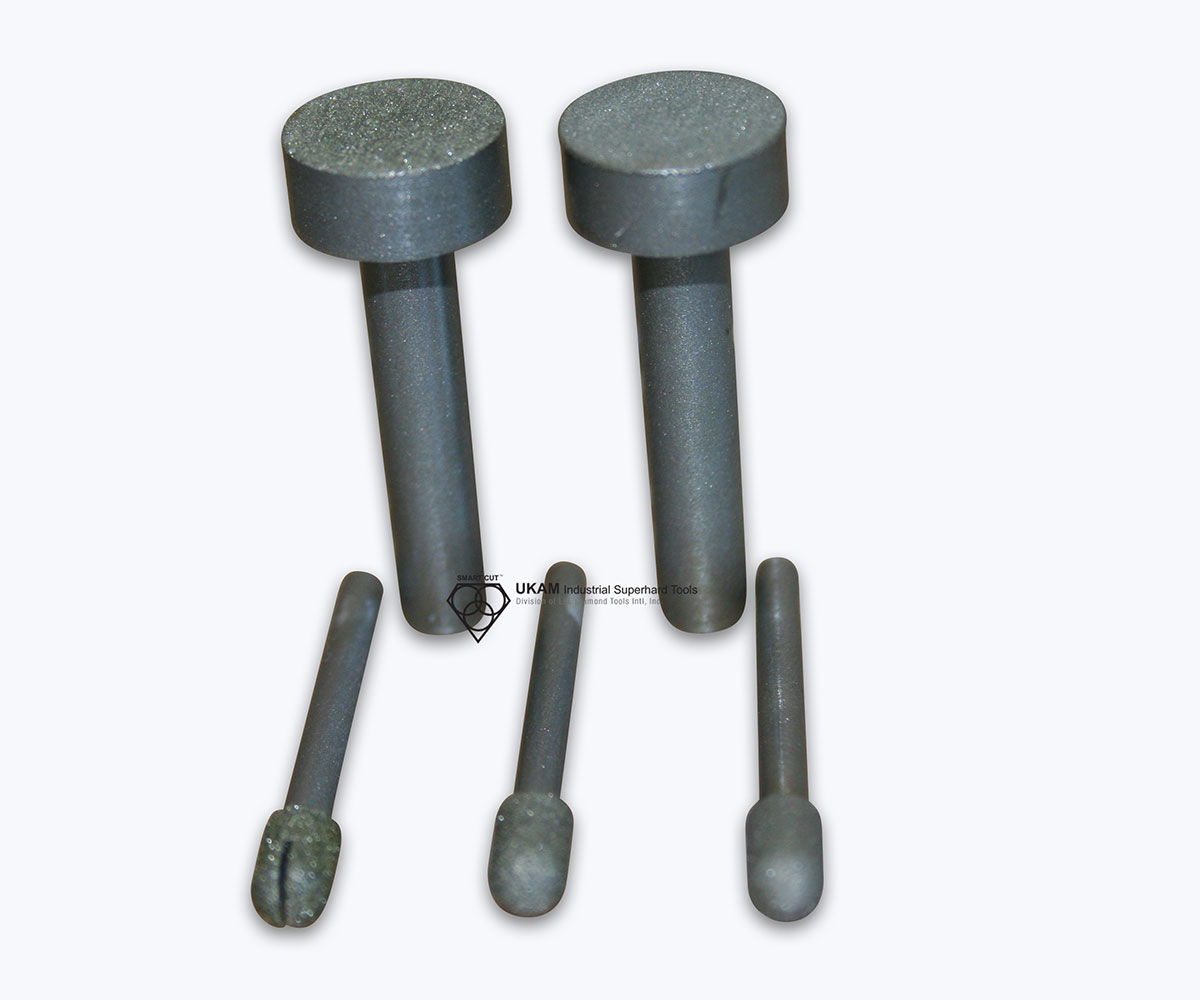
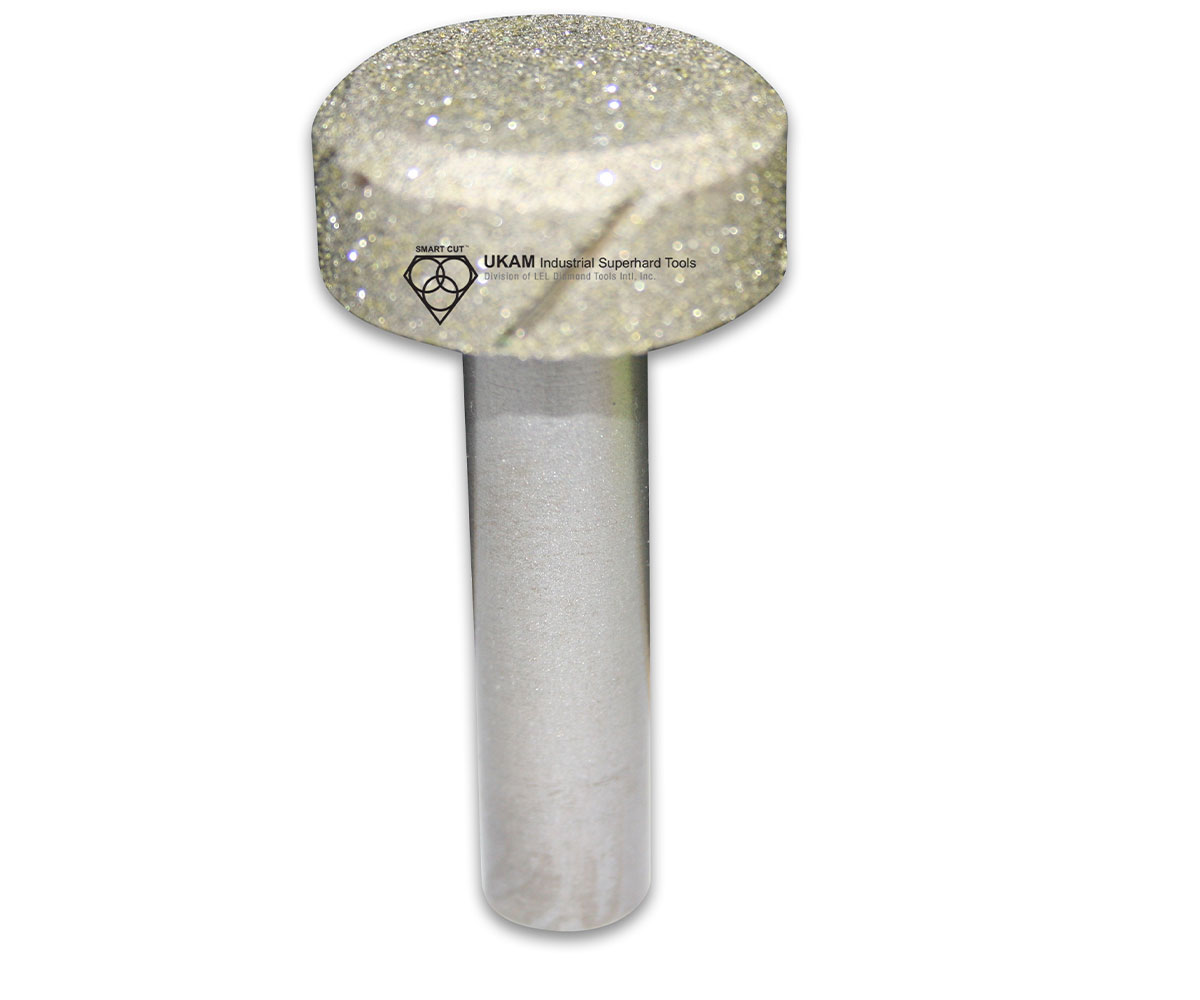
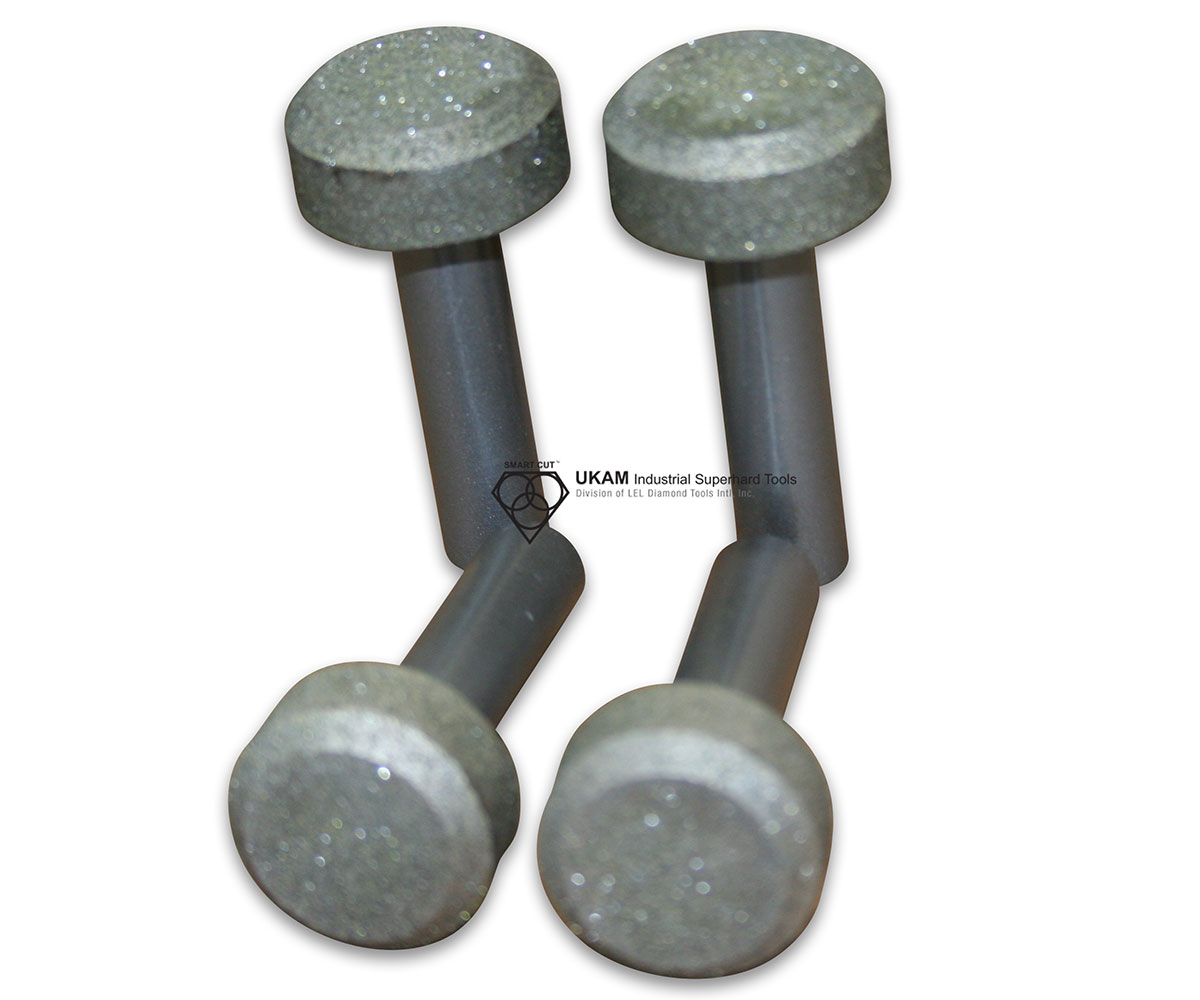
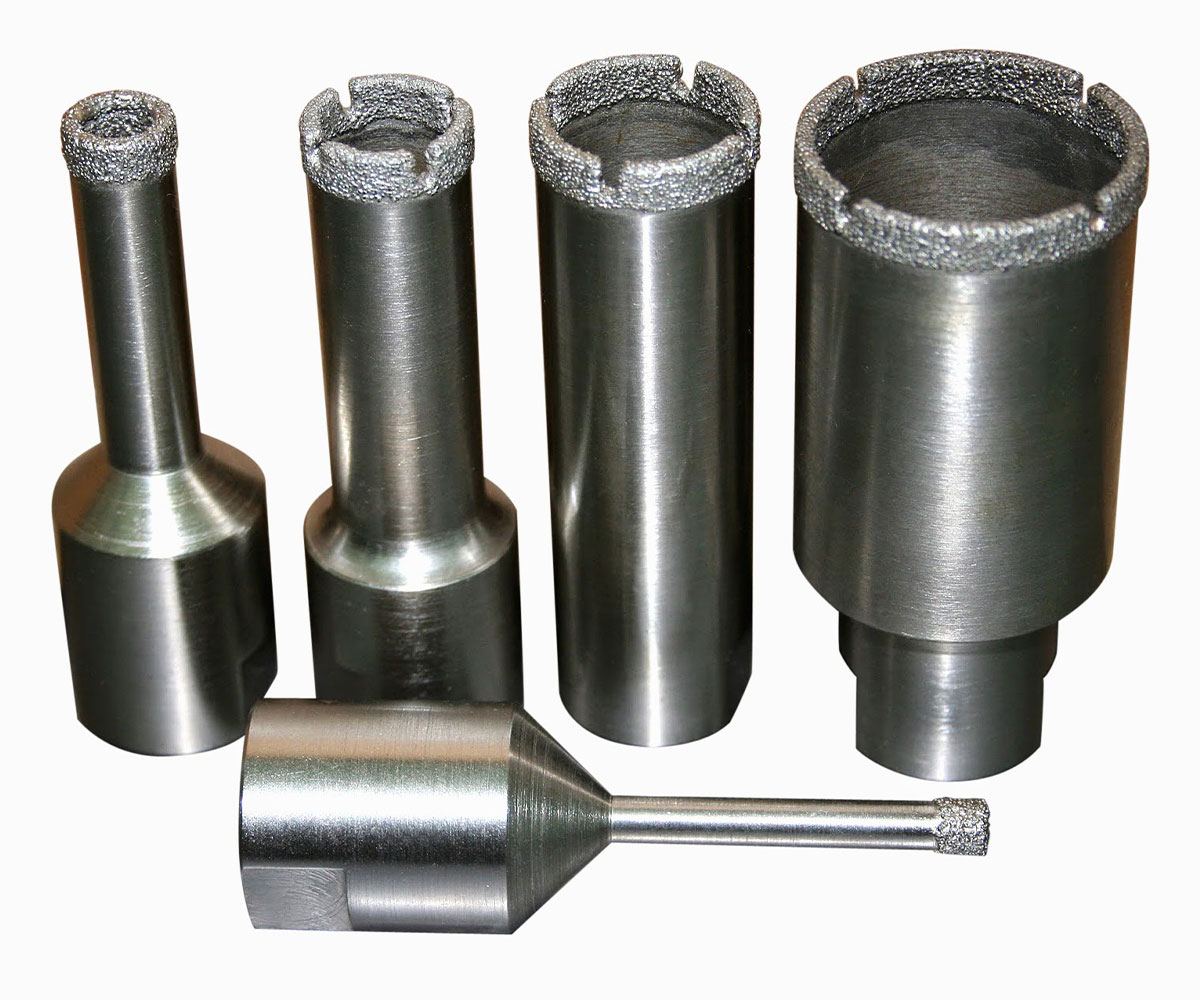
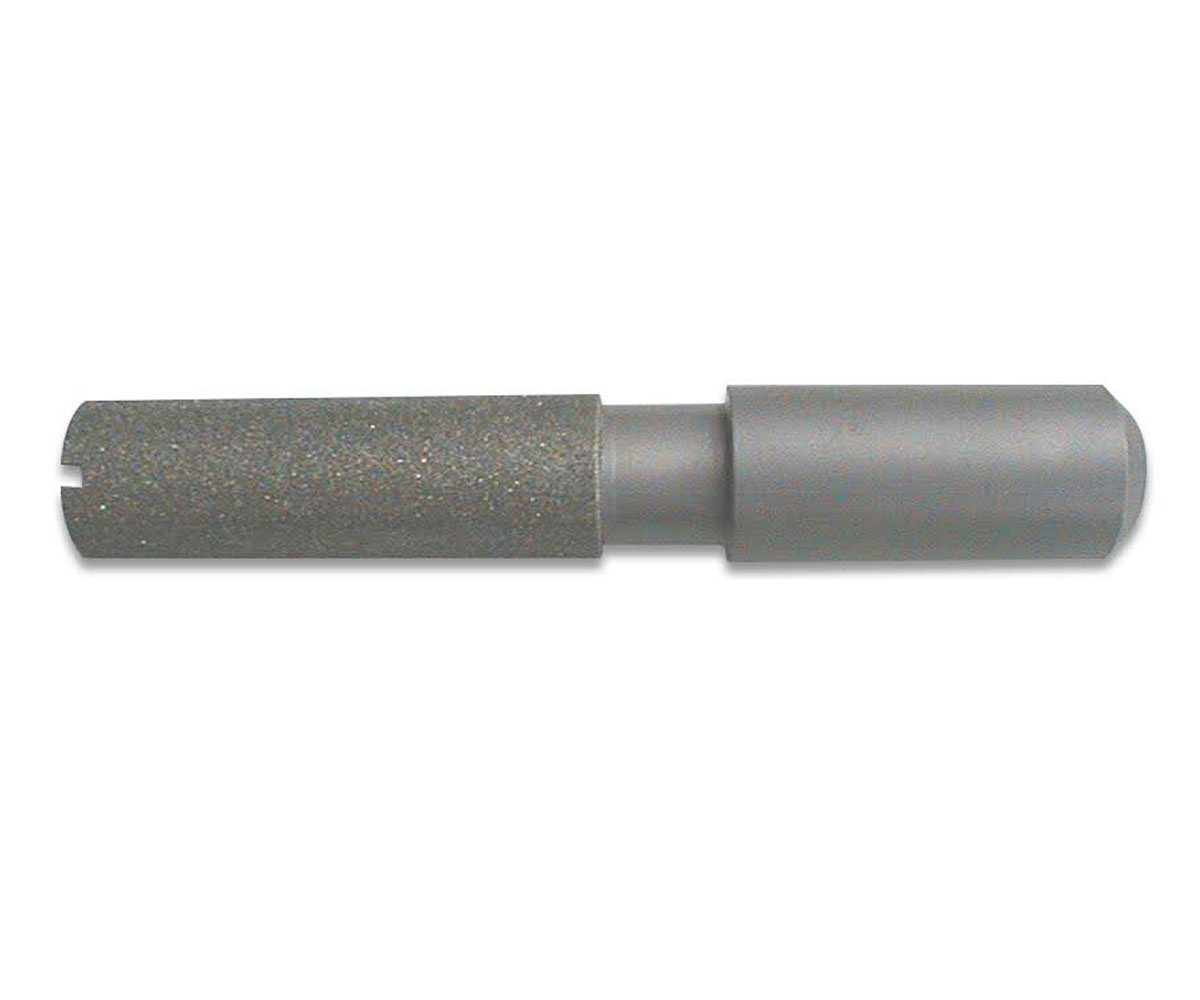
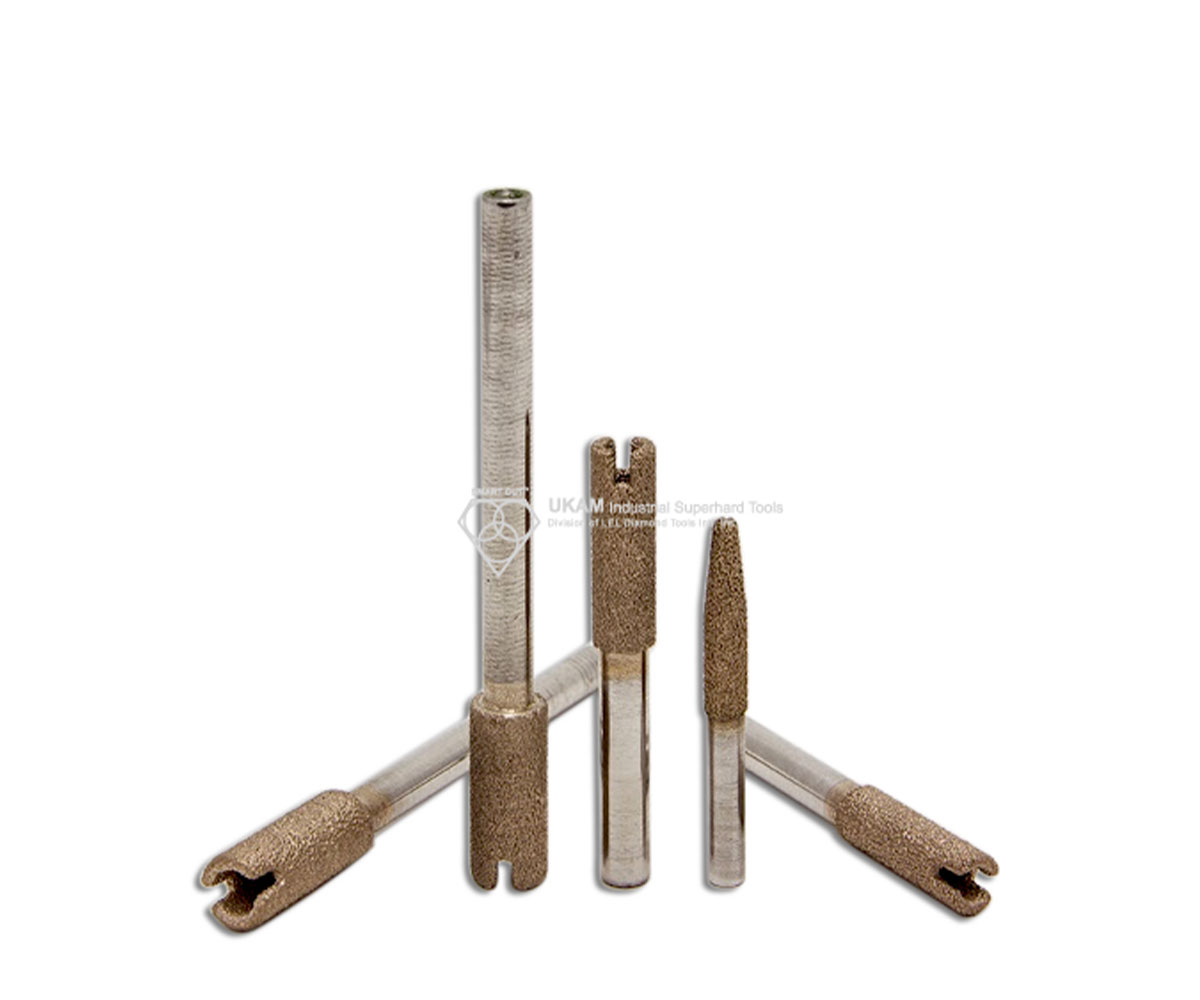
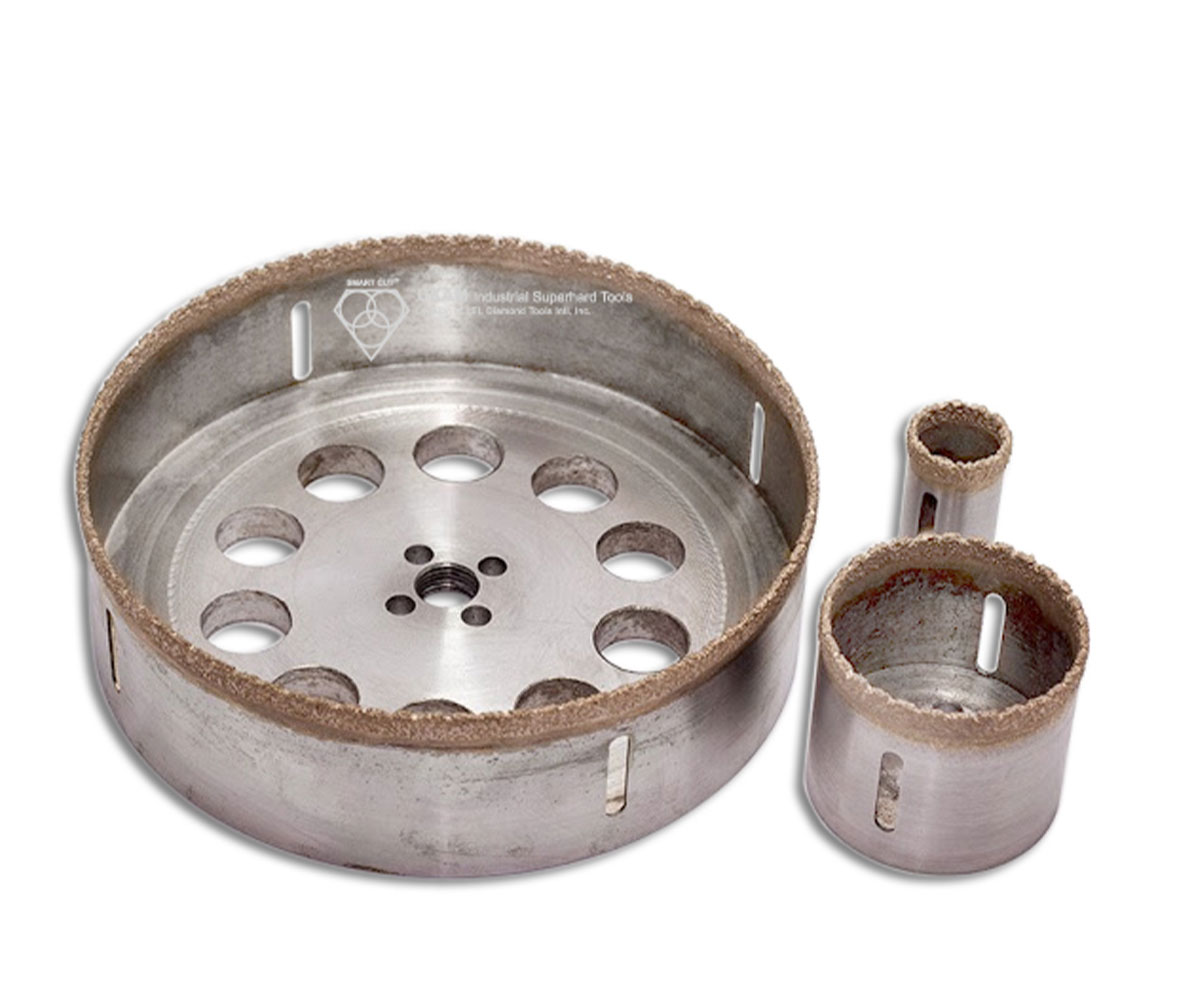
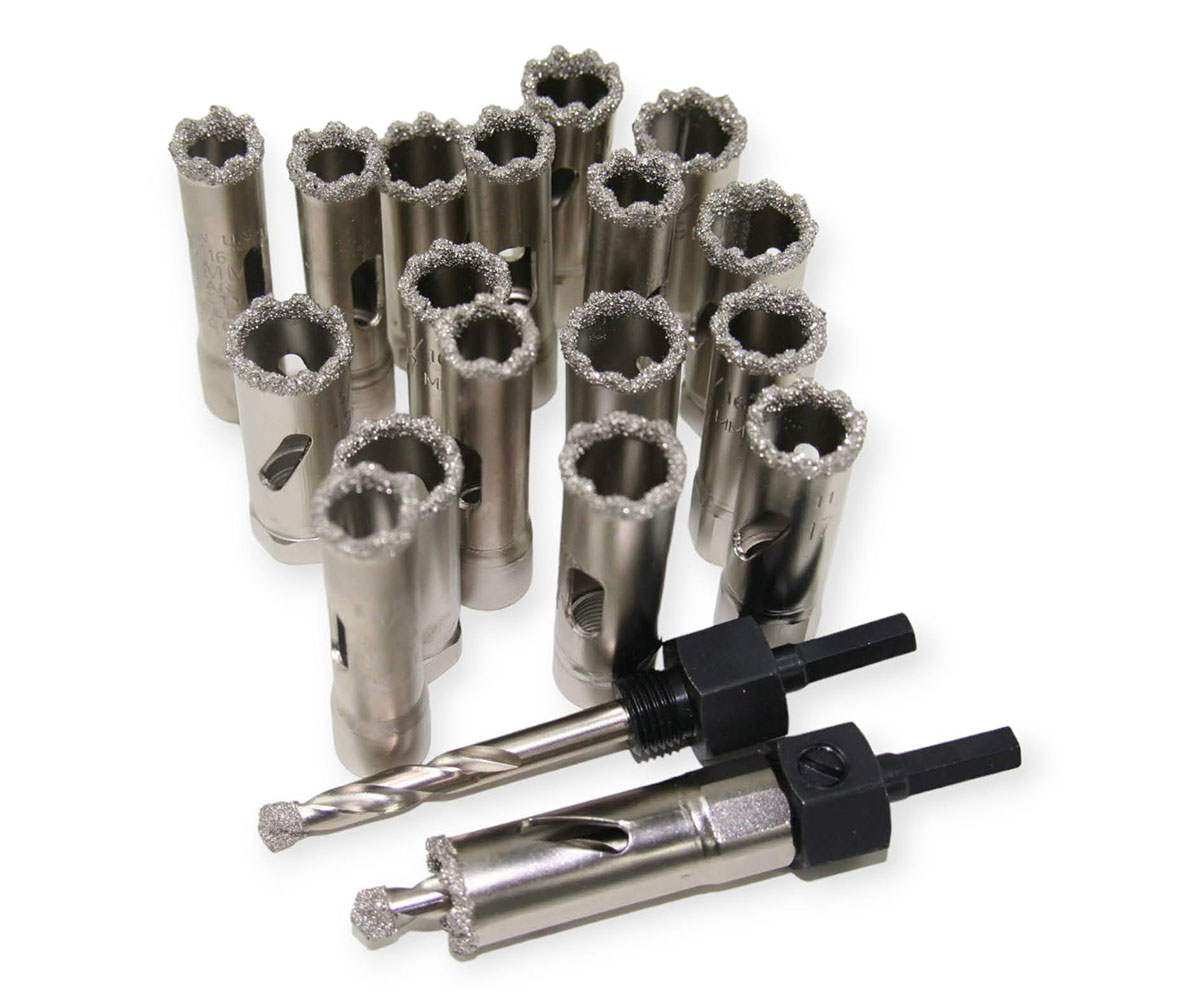
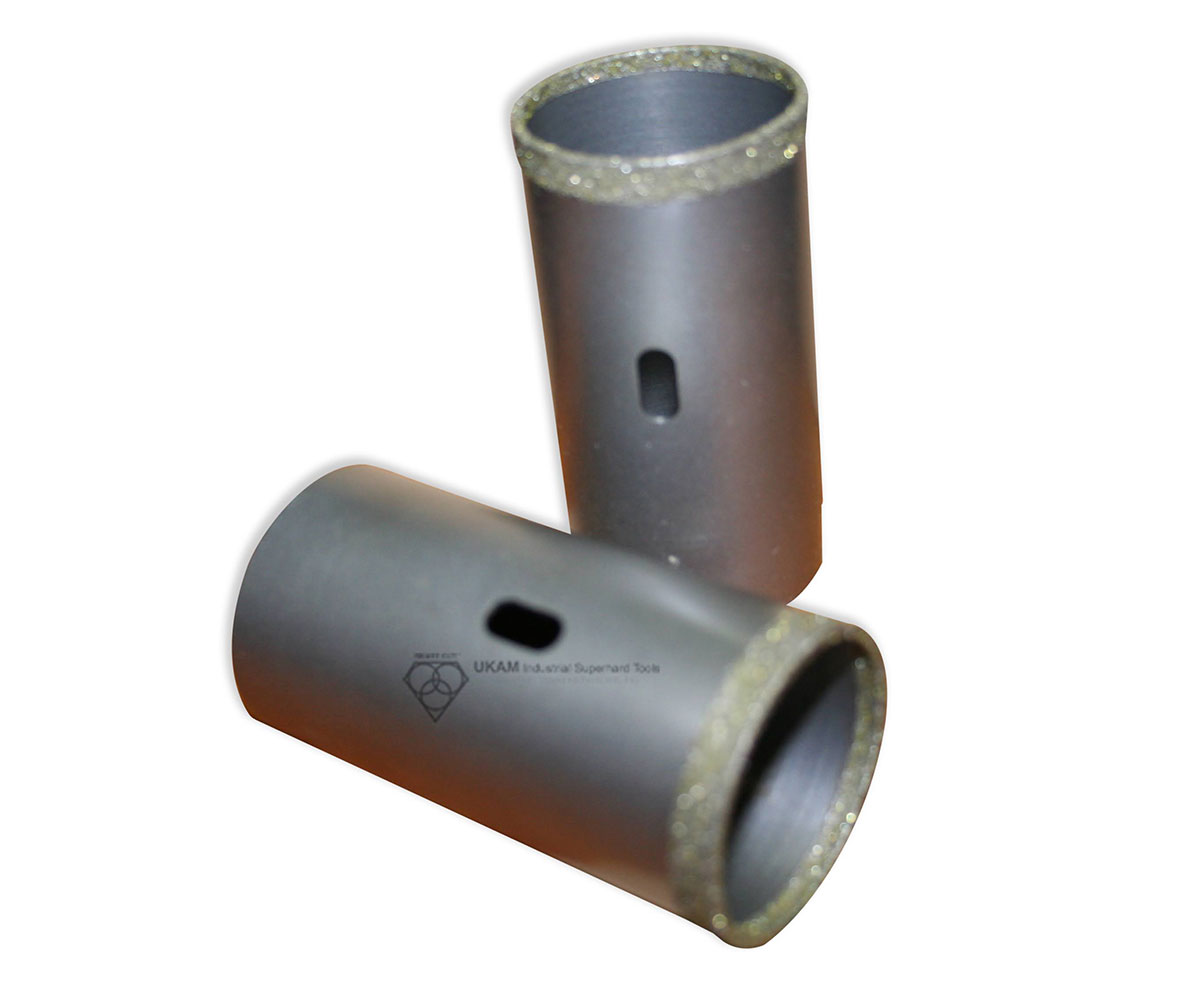
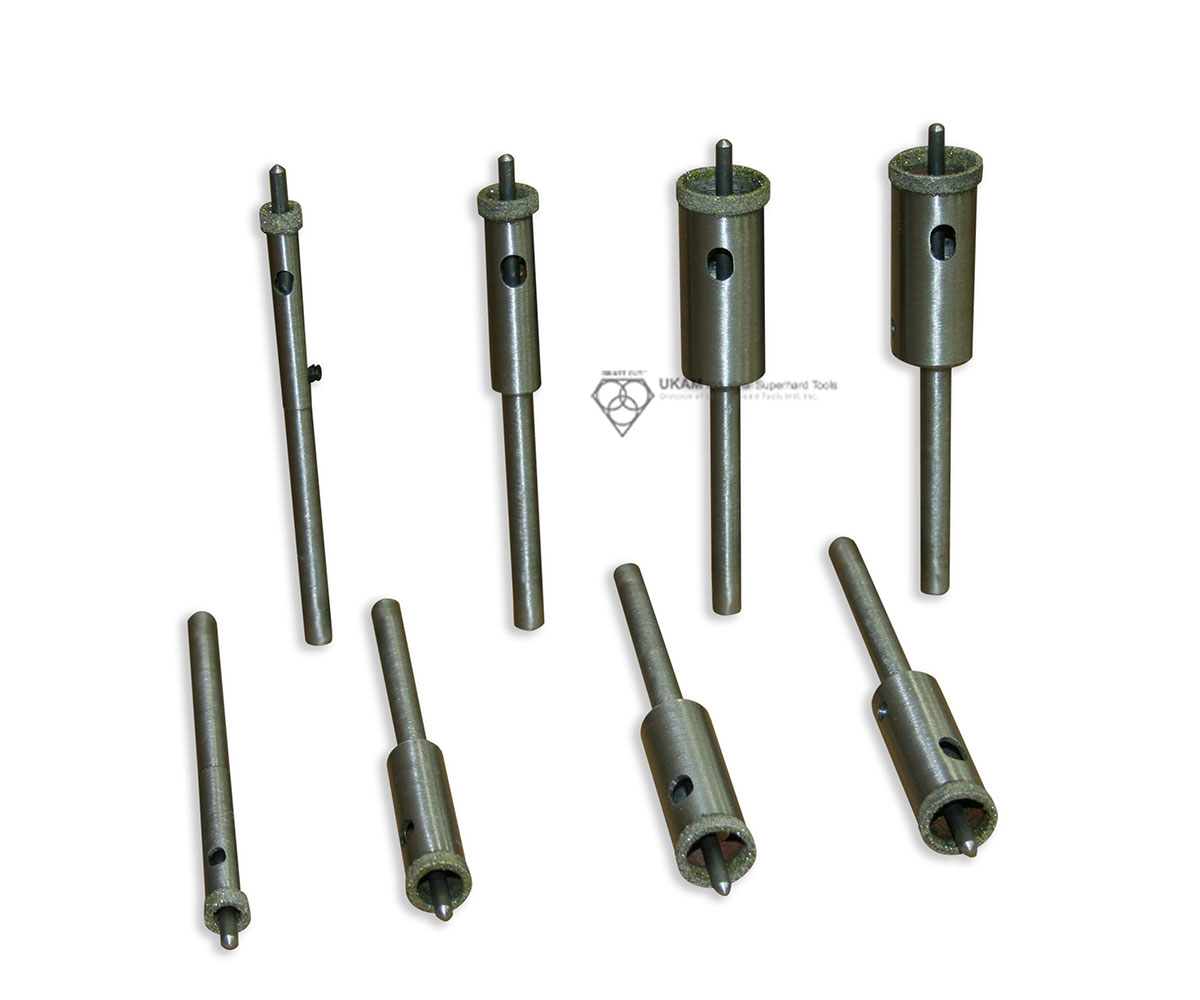
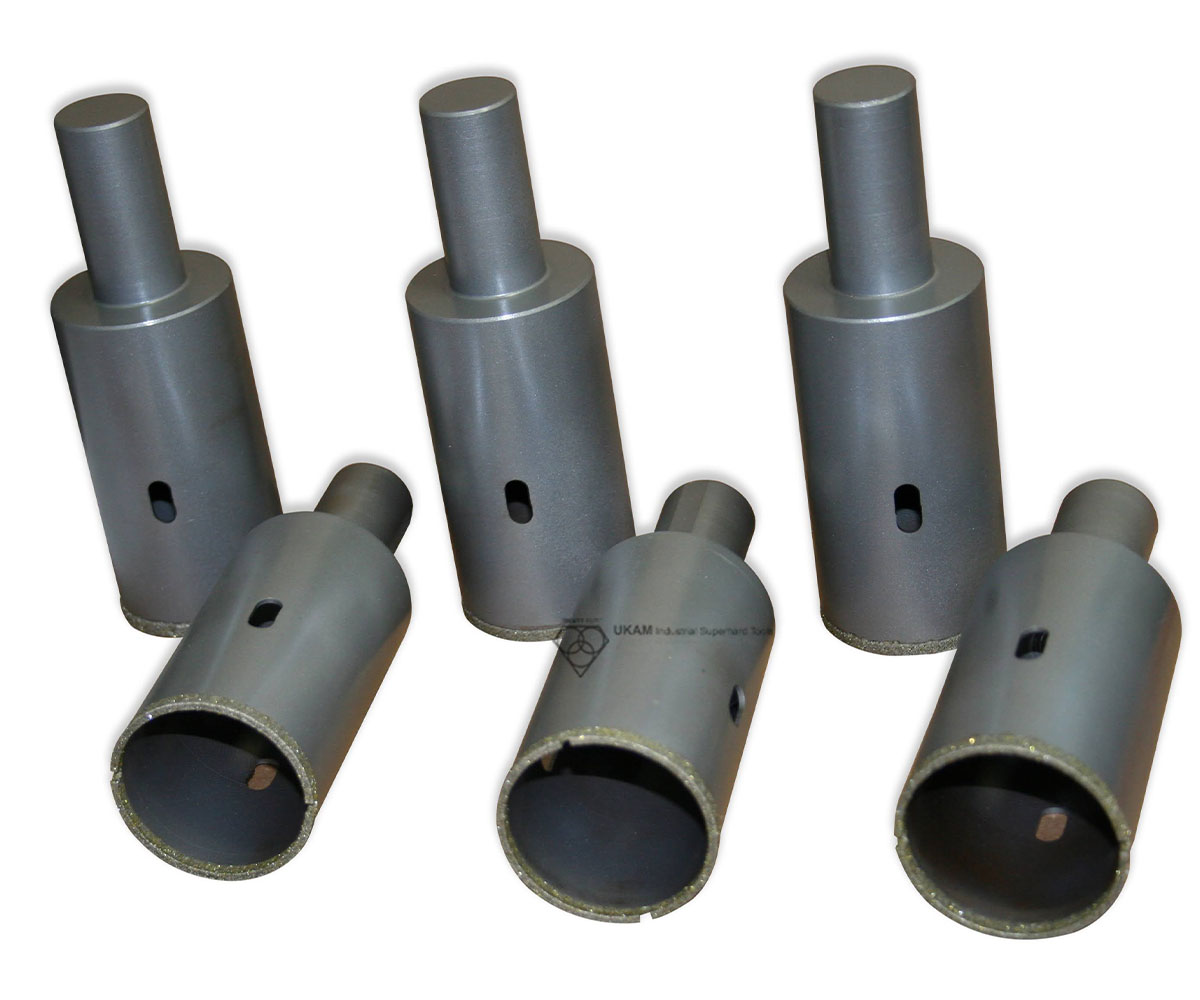
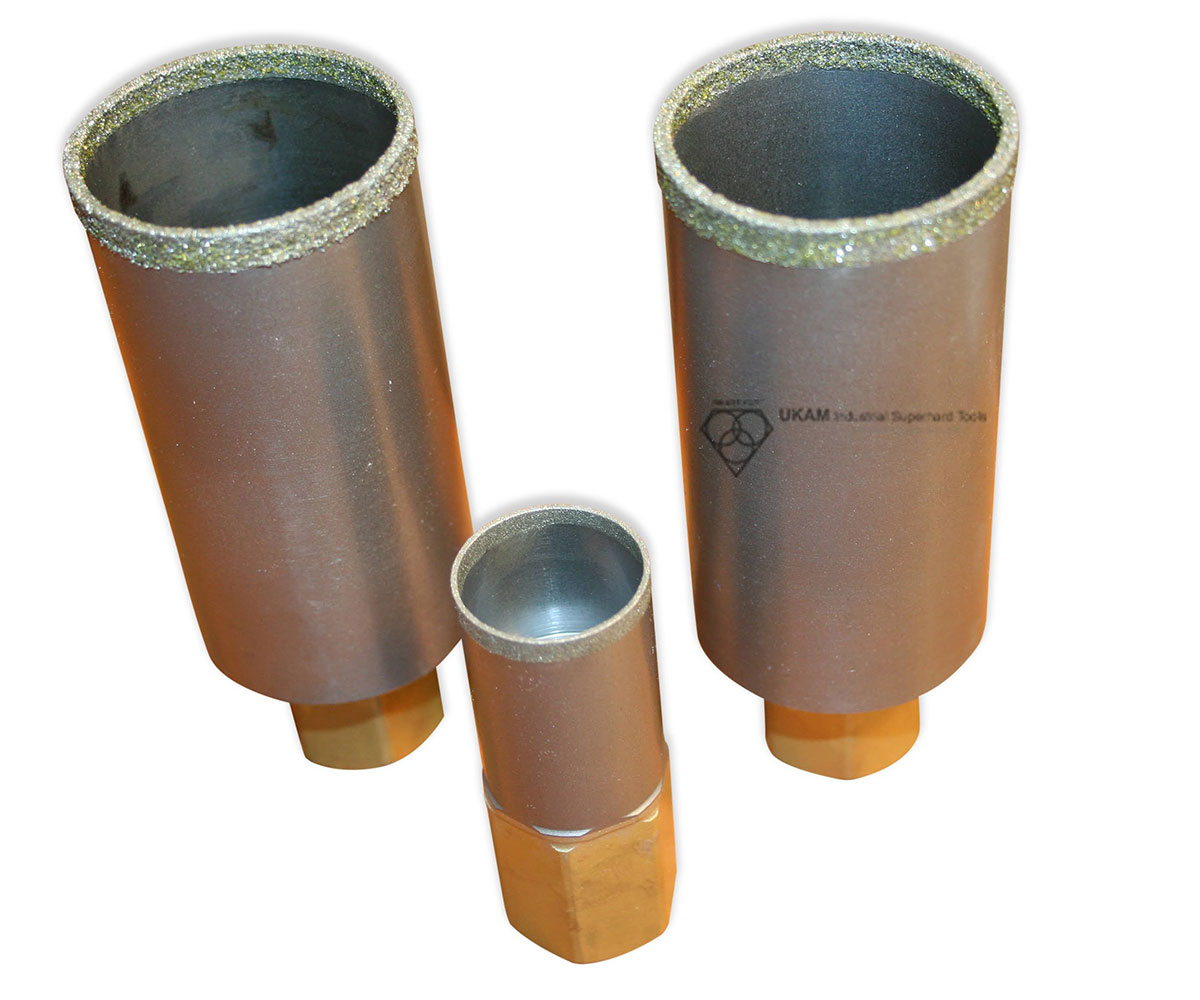
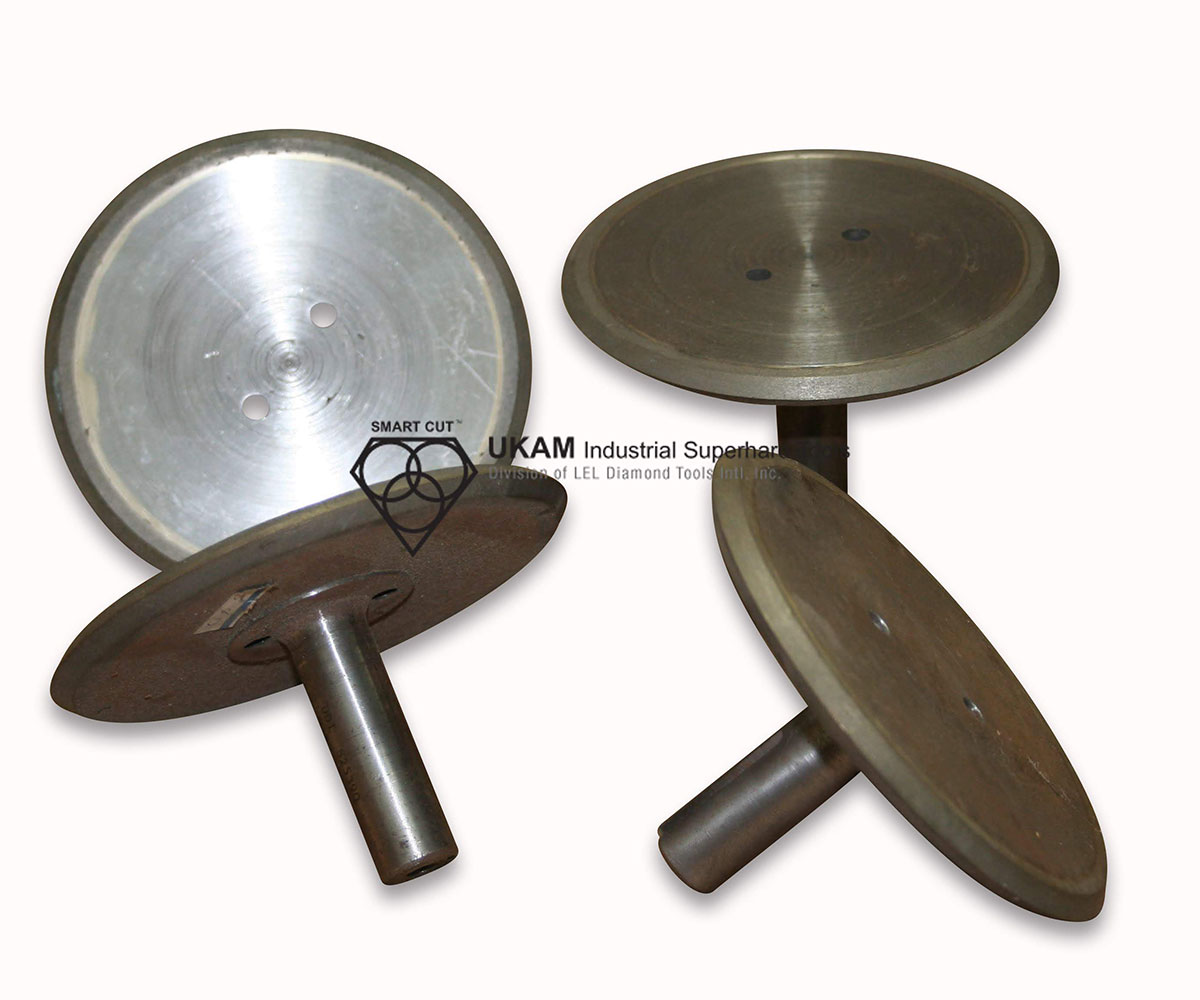













































About Nickel Bond (Electroplated) Tools
Electroplated (nickel bond) diamond products usually have a single layer of diamonds, held by a tough durable nickel alloy. Nickel is frequently used as a base for plating diamond. Because of its excellent strength, toughness and flexibility during the plating process. Electroplated diamond products are able to retain their original shape and dimensions thought their working life. Unlike sintered (meal bond) or resin bond diamond products, where diamond particles are buried in bond and held together by metal or resin binder deep inside.
Electroplating allows diamond particles to protrude from the bond matrix, providing a free, faster cutting action with minimum heat generation.
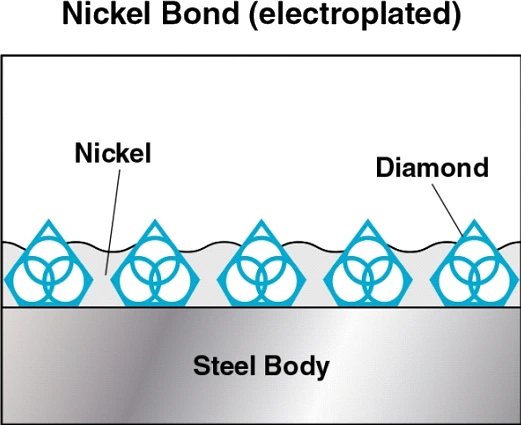
How SMART CUT ® Bond Works?
Step 1
Sharpest And Finest Quality Diamonds
Diamonds or CBN Crystals are activated only at the exposed layer. As Bond Matrix layer begin to wear out, diamonds in a new Bond Matrix layer are immediately activated, substituting the already used up diamond layer. The SMART CUT® Bond Diamond Bond makes sure every diamond is in the right place. and at the right time, working where you need it most.
Step 2
Diamonds or CBN Crystals
The newly exposed diamonds don’t effect diamonds already working on the material. Unlike many other diamond bonds, diamonds in a SMART CUT® remains sharp and grow sharper with each cut, prolonging product life and consistent performance.
Step 3
Advanced Formulated Open Diamond Bond Design
This advanced formulated open diamond bond design insures minimal chipping, fast
cut, constant speed of cut, minimal cutting noise, and most important of all, consistent performance.

Faster Cutting Action
Diamond & CBN tools made utilizing SMART CUT® technology are much more aggressive than your conventional tools. They can cut faster, while still leaving behind a smooth finish free of material deformation.

Longer Life
In most cases tools manufactured utilizing SMART CUT® technology, will outlast other conventional material (sintered), resin, and nickel bonded diamond & CBN tools. SMART CUT® diamond & CBN tools are more sturdy than tools manufactured with conventional technologies. They are capable to retain their form and bond configuration all the way through the tools life.

More Consistent Performance
SMART CUT Sintered (Metal Bond) Tools have diamonds crystals oriented and evenly positioned inside bond matrix. Unlike Many Other Tool Types, they wear evenly, and are known for their consistency. You will get consistent cutting speed, and overall consistent performance, with minimum amount of dressing even on the hardest to cut materials
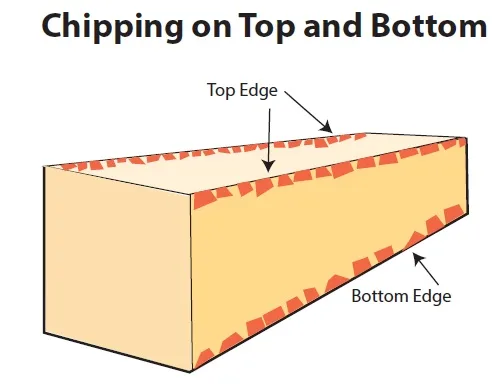
Minimize Chipping & Improve Surface Finish
SMART CUT® Sintered (Metal Bond) Tools have diamonds oriented and evenly distributed in a bond matrix. Providing faster, freer cutting action with minimum heat generation. This translates in improved surface finish and minimum chipping.

Best Performance & Value on the Market
SMART CUT® Sintered (Metal Bond) Diamond Tools are the best investment you can make! Although they may cost more than some Sintered (Metal Bond) Tools. They will more than pay for themselves in terms of overall performance and provide best Return on Investment.

Manufactured Using The Highest Quality Raw Materials
Only the highest quality synthetic diamonds and raw materials are used in the manufacturing process. The highest quality standards and product consistency is maintained, using sophisticated inspection and measurement equipment.

High Quality & Consistency
Electroplated (Nickel Bond) Tools
Our standard stock program and custom electroplated diamond tools are produced in a clean environment. Steel bodies are machined to very high precision tolerances from hardened steel on newest CNC machines. Only the highest quality raw materials are used in manufacturing process. Utilizing world class quality control, inspection, and measurement equipment. Highly Experienced Engineers and chemists constantly monitor and control all material input & output at all stages of manufacturing process. Insuring product consistency for use in demanding & sensitive applications
We have experience in working in fields challenging fields such: Nano Technology, MEMS, Materials Research, and etc. In last 25 years over 9 million plated tools/parts have been produced. Customers include some of the Leading Fortune 500 companies, Universities, Military, Space Flight Organizations, Laboratories, Advanced Material Fabricating Facilities to small machine shops.

Why Choose Us?
Optimize your application to ultimate level of efficiency
- Unmatched Selection For Many Applications
- Unmatched Technical Support & Expertise
- Superior Quality & Consistency
- Super Technology & innovation
- Immediate Worldwide Delivery
- American Based Manufacturer
-
Custom
Manufacturing - Better Value manufacturer Direct Price
Diamond & CBN Wheel
Selection Variables

Diamond Concentration
Diamond Concentration – Diamond Concentration is still a factor in determining the life and cutting speed of your Diamond Sectioning/Wafering Blade. Higher diamond concentration is recommended and usually used for cutting softer and more abrasive types of materials. However, the trade off is significantly slower cutting speed. Low diamond concentration is recommended and widely used for cutting ultra hard and brittle materials.
Low Diamond Concentration - typically low concentration wafering blades should be for cutting ultra hard and brittle materials such as ceramics and glass. In Low Concentration Wafering Blades, diamond works by fracture process. Pressure on each diamond crystal/particle is higher which provides enough stress to chip off small flakes in the cut.
High Diamond Concentration - High concentration diamond wafering blades are recommended for cutting metals, plastics and polymers. In this application, materials cut by a plowing mechanism. In this applications diamond plough through the material, work hardened strips of materials become brittle and break off. The greater number of diamond by volume, the quicker the cutting action will be. Increasing the number of diamond s also lowers the per unit force. For metals where it is possible to induce deep deformation layers, a lower per unit force is desirable to reduce the deformation during the cut.
Blade Thickness
Wafering blade thickness typically ranges from .006” to .040” (1mm). Thinner and thicker wafering blade are available, frequently from stock upon request. Kef thickness typically increases with blade diameter (in proportion to diameter of the blade). Kerf is the amount of material removed from the material/sample due to the thickness of blade passing though the material/sample. Blade thickness is important for users requiring most minimal amount of material loss during sectioning
For example if the user requires precision position of the cutting plane relative to the detail on the sample (IC circuit for example), a thinner and smaller diameter blade would be best for this application. Blades ranging from 3” to 5” (75mm to 125mm) in diameter and thickness .006” to .015” (0.2mm to 0.4mm) would be bet suited for this purpose. There are large variety of factors that will contribute to optimal blade thickness for your material/application Including your desired cutting speed, load/feed rate, material diameter, thickness, hardness, density, and shape. As well as skill & experience of the operator. Thicker wafering blades are more stiff and can whistand higher loads/feed rates. Another advantage of thicker kerf blades is they are more forgiving to operator error and abuse. Thicker kerf blade are recommended for use in environment where large number of individuals will be sharing and using same equipment. Perfect for less experienced and novice saw operators, such as in University laboratory.
.

Diamond Particle/Grit size
Diamond Mesh Size plays a major role in determining your cutting speed, cut quality/surface finish, level of chipping you will obtain, and material microstructure damage you will obtain. Diamond Mesh size does have considerable effect on cutting speed. Coarse Diamonds are larger than finer diamonds and will cut faster. However, the tradeoff is increase in material micro damage. If you are cutting fragile, more delicate materials then finer mesh size diamond wafering blades are recommended.
Bond Type
Metal bonding offers long life and durability, while resin bonding creates less heat, provides better surface finish and is well suited for cutting hard, delicate or brittle materials.
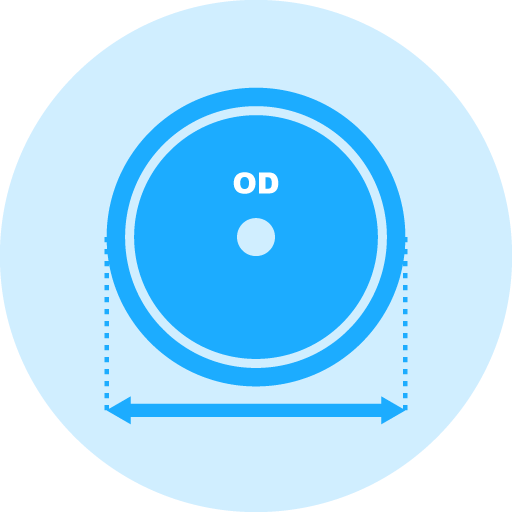
Blade Outside Diameter
typically wafering blade diameters range form 3” (75mm) to 8” (200mm). Wafering blade diameter should be selected based on material diameter and thickness being cut. Smaller diameter wafering blades are thinner than the larger diameter blades and are more prone to bending and warping. Although large diameter blades are thicker, they are typically used for cutting larger and heavier samples at higher loads and speeds than smaller blades

Feed Rates
load/feed rate applied to wafering blades typically vary from 10-1000 grams. Generally, harder specimens are cut at higher loads and speeds (e.g. ceramics and minerals) and more brittle specimens are cut at lower loads and speeds (e.g. electronic silicon substrates). The Speeds/RPM’s you are using, shape/geometry of the specimen, and how the specimen is being clamped/hold in place will affect the load that can be used for your application.
Bond Hardness
Ability of the bond matrix to hold diamonds. As the hardness of the bond is increased, its diamond retention capabilities increase as well. However the trade off is slower cutting speed. Life of the diamond blade is usually increased with hardness of its bond matrix. Bonds are designated on their scale of hardness from Soft, Medium, and Hard. There are dozens of variations and classification schemes based on bond degree of hardness or softness.
Using diamond blades with optimum bond hardness for your application is important to successful precision diamond sawing operation. Bond matrix that is too soft for the material being cut will release diamond particles faster than needed, resulting in faster wear and shorter diamond blade life. On other hand bond matrix that is too hard will result in much slower cutting speeds and require constant dressing to expose the next diamond layer. As rule of thumb, harder materials such as sapphire and alumina generally require a softer bond. Whereas softer and more brittle materials require a harder bond.

Blade Speeds/RPM’s
Most wafering blades are used between 50 to 6,000 RPM’s Typically harder and more denser materials such as Silicon Carbide, are cut at higher RPM’s/speeds Where more brittle materials such as silicon wafers and gallium arsenide are cutting at lower RPM’s. Low Speed saws RPM’s are typically limited from 0 to 600 RPM’s. Where high speed saws offer much large variety of cutting speeds from 0 to 6,000 RPM’s.
Diamond & Core Drill
Selection Variables

Diamond Concentration
Diamond concentration plays a critical role in determining the life and cutting speed of diamond core drills. Higher concentration offers longer tool life and faster cutting speeds, while lower concentration is typically used for softer materials that require a smoother finish.

Drilling Speed/RPMs
Diamond core drills generally operate at RPMs between 500 and 3,000, depending on the material being drilled. Softer materials allow for higher RPMs, while harder materials require slower speeds for improved cutting efficiency and to avoid damaging the tool or material. Always adjust RPM according to the specific characteristics of the material and drill size.

Diamond Particle/Grit size
The diamond grit size is crucial in determining the cutting speed, surface finish, and precision of diamond core drills. Finer grits provide a smoother surface finish, but may cut more slowly, while coarser grits offer faster cutting speeds but can leave a rougher surface. The choice of grit size depends on the material being drilled and the desired outcome.

Bond Type
The bond type used in diamond core drills influences the drill’s life, durability, and heat resistance. Common bond types for diamond core drills include: Sintered (Metal Bond): Provides a longer tool life and high resistance to wear and heat, making it ideal for drilling hard and abrasive materials. Electroplated: Offers a good combination of speed and precision, typically used for softer materials or applications where a smoother surface finish is needed. Braised Bond: Ideal for applications requiring higher strength, these bonds are used for tougher materials and applications where durability is key. PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond): Used for ultra-hard materials, PCD bond drills offer excellent wear resistance and are ideal for materials like ceramics and composite materials. CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Diamond: Offers exceptional cutting performance, often used in extremely hard materials like high-performance ceramics and advance.
Kerf (Wall) Thickness
The kerf, or wall thickness, of diamond core drills is a key variable in determining the overall performance of the drill. Standard core drills typically feature a kerf thickness ranging from 0.5mm to 3.0mm, with thicker kerfs providing longer tool life and greater stability during drilling. Thinner kerfs allow for faster cutting but may wear out quicker and require more frequent maintenance. The selection of kerf thickness depends on the material being drilled and the precision required.

Feed Rates
The load/feed rate applied to diamond core drills significantly impacts their performance and lifespan. For tougher materials, feed rates typically range between 5-50 mm/min, while softer materials may allow for higher feed rates. Proper feed rate adjustment ensures optimal tool life and drilling speed, while preventing overheating or excessive wear.
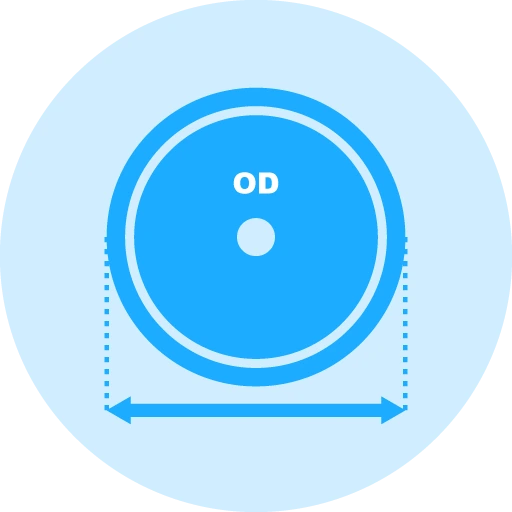
Core Drill Diameter
The diameter of the diamond core drill is directly related to the size of the hole you wish to create. Core drills typically range from small diameters (e.g., 3mm) up to large diameters (e.g., 200mm or more). Larger core drills offer greater drilling capacity, while smaller ones provide more precision for fine hole making.

Drilling depth
The depth of a diamond drill bit, often referred to as drilling depth, working length, or drilling length, is the maximum depth to which the drill can penetrate the workpiece. Drilling depth in diamond core drills depends on the material, drill size, and equipment. Softer materials allow for deeper holes with faster cutting, while harder materials require slower speeds and lower feed rates to prevent overheating. Larger drill diameters may reduce depth due to more material removal per rotation, often requiring multiple passes. Drilling equipment, including motor power and cooling systems, also plays a key role; more powerful motors and efficient cooling allow for deeper drilling.

Bond Hardness
For diamond core drills, the bond hardness plays a crucial role in the performance and longevity of the drill. The bond matrix's ability to retain diamonds directly impacts the drilling efficiency and the tool's lifespan. As the hardness of the bond increases, the retention of diamonds improves, but the trade-off is typically a slower cutting speed. A harder bond matrix provides greater tool life but may lead to reduced cutting efficiency.
There are generally three categories for bond hardness in diamond core drills: Soft, Medium, and Hard. The bond's hardness is selected based on the material being drilled. For example, harder materials such as ceramics or hard metals often require a softer bond to allow the diamonds to be released at a controlled rate, preventing excessive wear and improving cutting performance. Conversely, softer and more brittle materials like concrete or certain composites benefit from a harder bond, which maintains the diamond's retention and extends the drill's lifespan, though it may slow the cutting process.
Using the right bond hardness for the material you're drilling is key to optimizing both cutting speed and tool life. A bond that is too soft will cause diamonds to be released too quickly, resulting in faster wear and a shorter drill life. On the other hand, a bond that is too hard may cause the drill to cut slower and require more frequent dressing to expose new diamonds.

Mounting Type
The mounting type of a diamond core drill refers to how the drill is secured to the drilling machine or equipment. The mounting type plays a significant role in stability, precision, and overall drilling performance. Here are the typical mounting types for diamond core drills:
Unmounted diamond core drills:
Unmounted diamond core drills are specialized tools designed for precision drilling without being pre-mounted to any specific holding mechanism such as a male, female, or straight shank. These drills comprise a steel tube paired with a diamond-embedded segment, offering flexibility in setup and application.
Shaft Mounting:
In this type, the diamond core drill is mounted directly onto a shaft or spindle of the drilling machine. The shaft typically has a locking mechanism (like a set screw or collar) to securely hold the drill in place. This mounting method ensures a stable connection and allows for precise drilling. Shaft mounting is commonly used in machines where the drill operates at high speeds and requires excellent stability.
Threaded Mounting:
Some diamond core drills feature a threaded arbor or core bit holder, allowing the drill to be screwed directly onto the machine's spindle. This method is commonly found in portable core drilling systems or for specific applications like wet drilling, where easy removal and installation are essential.
Choosing the right mounting type for your diamond core drill depends on factors such as the size of the drill, the type of drilling machine, and the specific application requirements. Proper mounting ensures optimal performance, stability, and safety during the drilling process.

Tolerances on Outside or Inside Diameter
The tolerance range for the outside diameter of diamond core drills varies depending on several factors including the drill's diameter, wall thickness, bond type, and the intended application. These tolerances are crucial as they determine the drill's suitability for precision tasks and influence how the drill interacts with the material it cuts.
For small diamond core drills with diameters less than 10mm, the diameter tolerance typically ranges from ±0.02 to ±0.05 mm. This tight tolerance is necessary for applications that require high accuracy, such as in electronics or medical device manufacturing, where small, precise holes are crucial.
Medium-sized drills, ranging from 10mm to 50mm in diameter, usually have a tolerance of ±0.05 to ±0.15 mm. These are commonly used in mechanical applications and construction where slightly larger variances are acceptable.

Run Out
Runout is a critical specification for diamond drills as it directly impacts the quality of the holes drilled and the longevity of the tool itself. The term "runout" refers to the degree to which a tool or workpiece deviates from perfect rotation along its central axis. High runout can lead to uneven wear on the tool, compromised hole quality, and increased heat generation, which are particularly detrimental when drilling hard, brittle materials such as glass, ceramics, and certain stones where precision is critical.
Standard and Precision Diamond Drills - Standard diamond drills typically exhibit runout ranging from 0.0005 inches (0.013mm) to 0.002 inches (0.05mm), which is acceptable for general-purpose drilling where absolute precision is not necessary. However, "standard" runout may vary based on the drill's manufacturer and specific applications. Precision diamond drills, manufactured to higher standards with stricter tolerances, usually have runout less than 0.0002 inches (0.005mm), with ultra-precision drills potentially having even tighter runout specifications.
Related Products
Braised Bond Diamond Carving Points
SMART CUT® 135DB Braised Bond Diamond Core Drills & Non Core Formation Drills
Braised Bond Diamond Core Drills & Non Core Formation Drills
SMART CUT® 135DB Braised Bond Diamond Core Drills & Non Core Formation Drills with a 5/8-11" Female Thread – the ultimate solution for precision drilling in a wide range of materials. These high-quality core drills can be used both wet or dry and are designed to meet the demanding needs of professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike, offering exceptional performance and durability. SMART CUT® 135DB Braised Bond Diamond Core Drills & Non Core Formation Drills with a 5/8-11″ Female Thread. These diamond drills will drill large variety of materials faster and freer then any type of other diamond drills or other types of non diamond drills available.Recently Viewed Products

ARE YOU USING RIGHT DIAMOND HOLE SAWS
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET US
HELP YOU
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT DIAMOND HOLE SAWS?
Knowledge Center
02
Jun
Learn important diamond drill methodology. understand diamond drill specifications and their differences Selecting the right Diamond Drills/Bits for your application is key to obtaining desired diamond drilling results. Using the Right Diamond Drill will...
02
Jun
How to Properly Use Precision Diamond Drills
Step by step guide on how to properly use and care for your diamond drills. Selecting the right diamond drill/diamond drill bit parameters, often involves a trial and error process. Many which can be avoided...
02
Jun
Diamond Drills Guide
Diamond are used across large variety of industries and applications. This guide explores the wide range of diamond drill types, including hollow core drills designed for removing a cylindrical core, non-core formation drills that grind...
02
Jun
Optimizing your Diamond Drilling Operation
There are numerous factors that influence the performance of diamond drills. Understanding these factors helps users select the appropriate diamond drill specifications for their specific applications, optimizing drilling operations to achieve maximum efficiency....
02
Jun
Selecting Right Drilling Equipment for your Application. What you features & functionality you should look for?
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
There are hundreds or even thousands of different drilling equipment options. Selecting the right equipment for a specific application involves carefully considering several variables and attributes of the...
03
May
Diamond Core Drill & Drill Trouble Shooting Guide
Learn the most common problems most people have in using diamond drills. How to resolve them and avoid them in first place
https://ukam.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/diamond-drill-troublehsooting-guide.mp4
Troubleshooting Drilling Problems
Having issues with your diamond drilling operation? This Illustrated Guide...
09
Sep
Understanding & Calculating Return on Investment for Diamond Core Drills & Other Tools
The term "ROI" (Return On Investment) is widely used across industries, often interpreted differently depending on the context. However, few truly understand what ROI represents and its specific implications, particularly in the context of diamond...
09
Sep
Understanding Tradeoffs – Searching for Perfect Diamond Drill & Tool
Choosing the right diamond drill or tool can significantly impact efficiency, cost, and quality. However, this is not a simple and clear-cut process. Selecting the optimal drill or tool involves navigating a complex landscape of...
12
Sep
Drilling Composite Materials Using Diamond Drills & Hole Saws
Drilling composite materials presents a unique set of challenges due to their heterogeneous nature, which combines different materials with varying properties. To achieve precision and maintain the integrity of both the tool and the workpiece,...
12
Sep
Selecting Right Diamond Drills & Tools for Drilling Composites
Drilling composite materials, such as Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP), Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP), Kevlar, and hybrid laminates, presents unique challenges due to their abrasive nature, heterogeneous structure, and susceptibility to issues like delamination,...
20
Sep
Diamond Drill Terminology Guide – Key Terms Explained for Precision Drilling
How to fine tune each of these variables to improve and optimize your drilling operation in the success of your diamond drilling operation
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
DIAMOND DRILL...