Diamond Dressers: A Complete Guide to Types, Applications, and Best Practices in Grinding
-
Posted by
 Brian Farberov
Brian Farberov

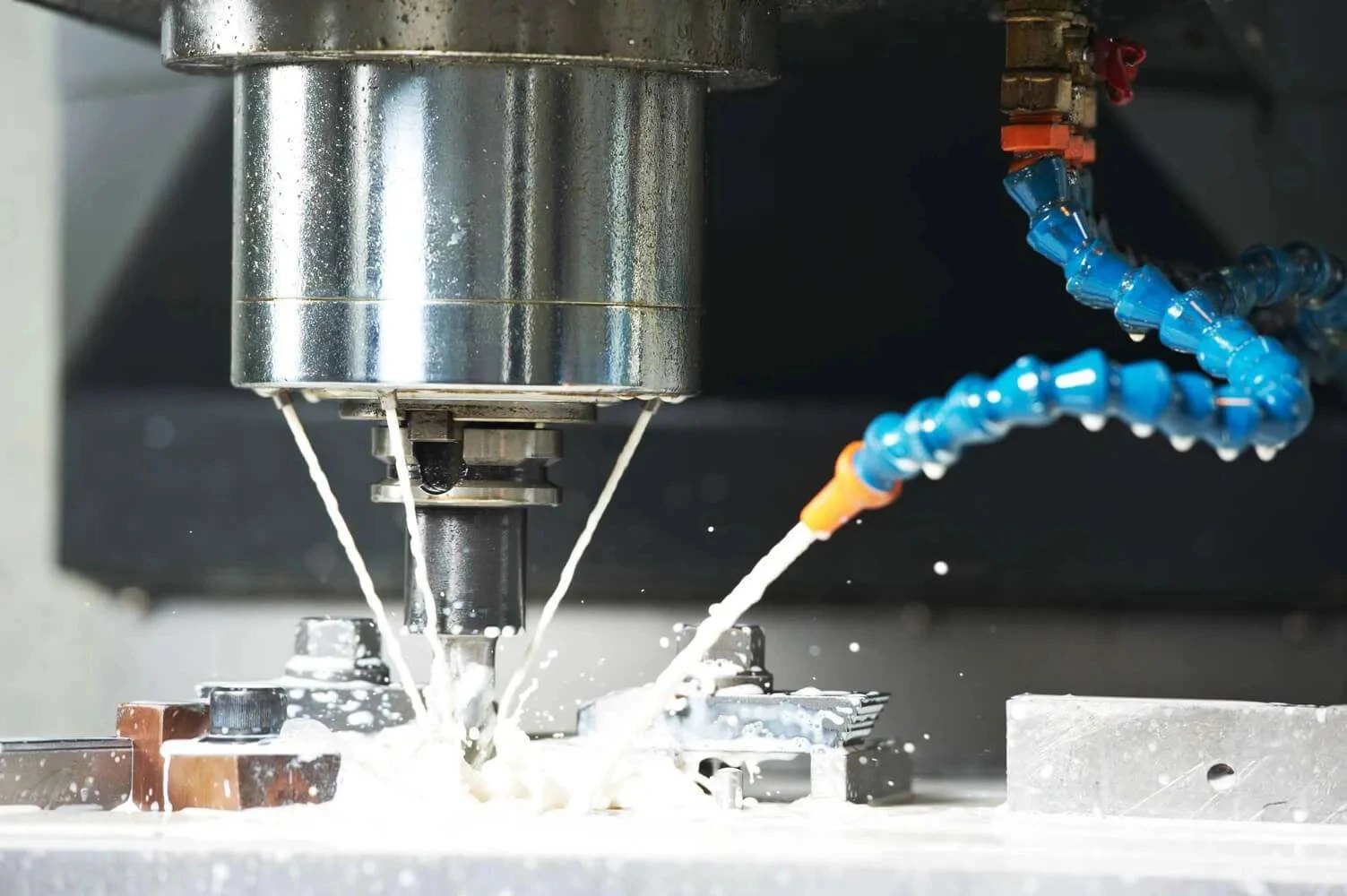
Grinding is an important finishing and material-removal stage on components in manufacturing processes, which are secondary to precision, surface finish, and form errors of the workpieces. But wheels tend to lose their effectiveness through natural wear, loading, and glazing. Diamond dressers are an integral tool for the maintenance and upkeep of grinding wheels.
Table of Contents
ToggleDiamond dressers are important for regaining the sharpness of grinding wheels, ensuring true wheel geometry, and extending the life of a wheel. As diamond is the hardest material, it can be used for dressing traditional abrasive grinding wheels extremely accurately and effectively.
From what diamond dressers are, how they work, the various types of diamond dressers available, and their uses in industry, all the basics, as well as best practices and tool selection tips, are included.
What Are Diamond Dressers?
Diamond dressers are a kind of diamond specially used for dressing or truing the surface of grinding wheels. Dressing cleans and removes worn abrasive grains, exposing fresh, sharp grains on the wheel’s surface, and truing does this by restoring a true wheel, thus resetting the concentricity.
Dressing removes worn grit and dull abrasive grains from the wheel’s face, while truing sharpens the wheel by removing material to produce a new face and restore its round shape.
Diamond dressers are primarily used on:
- Aluminum oxide grinding wheels
- Silicon carbide grinding wheels
They’re not for use on diamond or CBN wheels, because their own hardness can’t effectively cut equally hard materials.

Why Grinding Wheels Require Dressing
As time goes on, the abrasive grains will become dull due to grinding. Moreover, chips of the workpiece can obstructing pores of the wheel (so-called wheel loading). These issues result in:
- Reduced cutting efficiency
- Excessive heat generation
- Poor surface finish
- Increased grinding forces
- Risk of workpiece damage
Regular dressing with diamond dressers resolves these issues by exposing fresh, sharp abrasive grains and maintaining optimal wheel structure.
Functions of Diamond Dressers
Diamond dressers perform two primary functions:
1. Dressing
- Removes dull grains and debris
- Sharpens the grinding wheel
- Improves cutting action and surface finish
2. Truing
- Restores wheel roundness and profile
- Eliminates runout and vibration
- Ensures dimensional accuracy
Both functions are critical in precision grinding environments.

How Diamond Dressers Work
When a diamond dresser is brought into contact with a rotating grinding wheel, the diamond fractures and shears the abrasive grains on the wheel surface. This controlled micro-fracturing process:
- Removes worn abrasives
- Opens the wheel structure
- Improves chip clearance
- Restores wheel sharpness
The efficiency of this operation is influenced by dressing parameters like feed rate, depth of cut, and wheel speed as well as type and condition ofthe diamond dresser being used.
Types of Diamond Dressers
The type of diamond dresser chosen is critical to the grinding process. The following are the most commonly used diamond dresser types in industrial applications.
1. Single Point Diamond Dressers
Single-point diamond dressers consist of a single natural or synthetic diamond mounted in a steel or carbide shank.
Key advantages:
- High precision and accuracy
- Simple and economical design
- Easy to use and maintain
Typical applications:
- Surface grinding
- Cylindrical grinding
- Tool room and maintenance operations
To extend service life, the diamond should be periodically rotated to distribute wear evenly across the cutting edges.
2. Multi-Point Diamond Dressers
Multi-point diamond dressers contain multiple diamond particles embedded in the dressing surface.
Benefits:
- Longer life compared to single-point dressers
- Consistent dressing action
- Reduced risk of sudden failure
Applications:
- Production grinding
- Larger grinding wheels
- Heavy-duty operations
These dressers are well-suited for environments where consistent performance and durability are required.
3. Cluster Diamond Dressers
Cluster diamond dressers feature several diamond crystals grouped in a cluster configuration.
Key characteristics:
- Aggressive dressing capability
- High material removal rates
- Excellent for rough dressing
Common uses:
- Foundry applications
- Large surface grinders
- Rough grinding operations
Cluster dressers are typically used where wheel loading is severe and aggressive conditioning is needed.
4. Blade Type Diamond Dressers
Blade-type diamond dressers consist of diamonds brazed or bonded in a straight-line configuration.
Advantages:
- Uniform contact across the wheel surface
- Consistent wheel conditioning
- Suitable for wide wheels
Applications:
- Surface grinding machines
- Production grinding lines
- Precision dressing applications
These dressers are often used where uniformity and repeatability are critical.
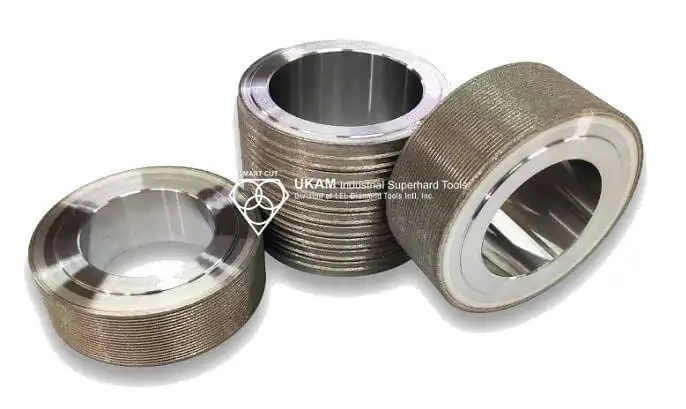
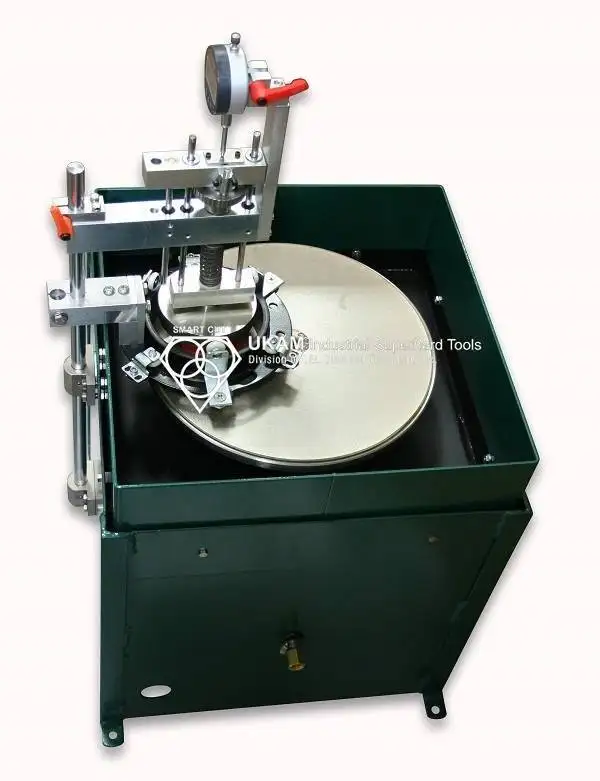
5. Rotary Diamond Dressers
Rotary diamond dressers use a rotating diamond roll or disc to dress the grinding wheel.
Key benefits:
- Extremely high profile accuracy
- Excellent repeatability
- Long service life in high-volume operations
Industries using rotary dressers:
- Automotive manufacturing
- Aerospace components
- Bearing and gear production
- CNC grinding operations
Rotary diamond dressers are ideal for complex wheel profiles and automated grinding systems.

Applications of Diamond Dressers
Diamond dressers are used across a wide range of industries that depend on precision grinding.
Common applications include:
- Dressing conventional grinding wheels
- Truing wheels for dimensional accuracy
- Profile dressing for complex geometries
- Improving surface finish quality
- Reducing grinding cycle times
Industries served:
- Aerospace and defense
- Automotive manufacturing
- Medical device production
- Tool and die making
- Electronics and semiconductor industries
Factors to Consider When Selecting Diamond Dressers
Choosing the right diamond dresser depends on multiple operational factors.
Grinding wheel specifications
- Abrasive type
- Bond type
- Wheel hardness and structure
Machine conditions
- Manual vs CNC grinding
- Dressing frequency
- Machine rigidity
Production requirements
- Volume of parts
- Surface finish requirements
- Cost-per-part optimization
Partnering with an experienced manufacturer ensures the diamond dresser is correctly matched to the application.
Best Practices for Using Diamond Dressers
To maximize performance and service life:
- Use correct dressing speed and feed
- Apply light, consistent pressure
- Use coolant to manage heat
- Rotate single-point diamonds regularly
- Avoid excessive dressing depth
Proper handling and storage of diamond dresser tools also help prevent premature damage.
Advantages of Using Diamond Dressers
- Improved grinding efficiency
- Better surface finishes
- Longer grinding wheel life
- Reduced machine wear
- Consistent and repeatable results
These benefits translate into lower operating costs and improved product quality.
Why Choose UKAM Diamond Dressers?
UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools offers a wide range of diamond dressers engineered for demanding industrial applications. With decades of expertise in superhard tooling, UKAM provides:
- High-quality industrial diamonds
- Precision manufacturing standards
- Application-specific solutions
- Reliable and consistent performance
UKAM diamond dresser tools are designed to meet the exacting requirements of modern grinding operations.
FAQs – Diamond Dressers
Diamond dressers are used to dress and true grinding wheels, restoring cutting efficiency and accuracy.
They are used on aluminum oxide and silicon carbide wheels, but not on diamond or CBN wheels.
Dressing frequency depends on wheel wear, application, and surface finish requirements.
Dressing sharpens the wheel, while truing restores its shape and geometry.
Multi-point and rotary diamond dressers are preferred for production environments.
Proper speeds, light pressure, coolant use, and regular rotation help extend service life.
Trusted by Tens of Thousands of Manufacturers, Laboratories,
Research Institutions Worldwide Since 1990

Established in 1990

Brian is an experienced professional in the field of precision cutting tools, with over 27 years of experience in technical support. Over the years, he has helped engineers, manufacturers, researchers, and contractors find the right solutions for working with advanced and hard-to-cut materials. He’s passionate about bridging technical knowledge with real-world applications to improve efficiency and accuracy.
As an author, Brian Farberov writes extensively on diamond tool design, application engineering, return on investment strategies, and process optimization, combining technical depth with a strong understanding of customer needs and market dynamics.