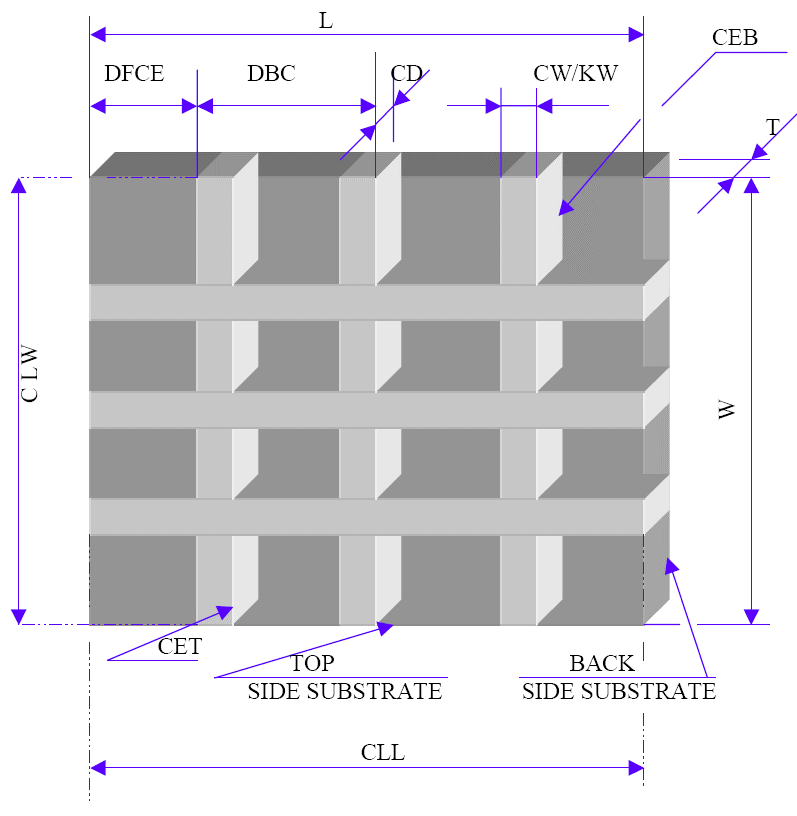
Dicing Blade Case Studies
-
Posted by
contactor6

02
Jun
DICING SOLUTIONS FOR PACKAGE SINGULATION
BGA (Ball-Grid Array)
Common Materials: FR4 and epoxy mold compound



Variations:
- LFBGA (Low-Profile Fine-Pitch)
- TFBGA (Thin & Fine-Pitch)
- W-BGA (Window-Type)
- FC-BGA (Flip Chip)
- VFBGA (Very Fine-Pitch)
- POP (Package-on-Package)
- SIP (System-in-Package)
- SD (Secure Digital)
- Micro SD Card
- CBGA (Ceramic)
- PBGA (Plastic)
- UFBG (Ultra-Fine)
- MBGA (Micro)
Typical Concerns:
- Cut quality
- chipping
- burrs
- slivers
- protrusions
- race shorts
- Blade life
Dicing Blade Recommendation:
- SMART CUT HYBRID BOND or sintered (metal bond) series
- Diamond size: 30 – 55 microns
- Blade Thickness: .008” – .014”
Dicing Process Recommendations:
- Feed rate: 50-250 mm/sec
- Spindle speed: 20-40 krpm depending on blade O.D.
- Multi panel mounting on UV tape
- Minimal dressing so as not to create a large radius on the blade edge
QFN (Quad Flat No Lead)
Common Materials - C194 and epoxy mold compound.



Variations:
- HVQFN (Heatsink Very-Thin)
- MLF (Micro Lead Frame)
- FUSION QUADR
- (VQFP: Very Thin Quad Flat Package)
- HQFN (High Power)
Typical Concerns:
- Chipping
- Burrs
- Lead smearing
- Melting
Dicing Blade Recommendation:
- SMART CUT HYBRID BOND or sintered (metal bond) series
- Diamond grit size: 45 – 88 microns
- Thickness: .008” – .020”
Dicing Process Recommendations:
- Feed rate: Half Etched substrates 30-75 mm/sec, Full Copper substrates 15-30 mm/sec
- Spindle speed: 22-35 krpm depending on blade O.D.
- Multi panel mounting on UV tape
- Override process over one substrate to reach final feed rate
LED (Light-Emitting Diode)
Common Materials - Copper, HTCC (High Temperature Co-fired Ceramics), LTCC (Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics).


Variations:
Chip LED, High Power LED.
Typical Concerns:
- Copper burrs
- End of blade life due to limited exposure
- Throughput (maximize UPH)
Dicing Blade Recommendation:
- SMART CUT HYBRID BOND or Nickel Bond series
- Diamond size: 10,13 & 17 microns
- Thickness: .003” – .008”
Dicing Process Recommendations:
- Feed rate: 80-150 mm/sec
- Spindle speed: 25-30 krpm
- Multi panel mounting on UV tape
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor)
Common Materials - Borosilicate Glass, HTCC (High Temperature Co-fired Ceramics).


Variations:
CIS (CMOS Image Sensor) Glass Lid, CIS (CMOS Image Sensor) Substrate.
Typical Concerns:
- Chip Damage and Breakage
- Cutting Precision and Kerf Control
- Heat Dissipation
- Surface Quality
- Blade Life & Consistency
Dicing Blade Recommendation:
- Bond Type: Resin Bond, Sintered (Metal Bond), Hybrid Bond, Nickel bond
- Diamond Size: 2 to 30 microns
- Kerf Thickness:10 to 30 microns
Dicing Process Recommendations:
- Feed rate: 80-150 mm/sec
- Spindle speed: 25-30 krpm
- Multi panel mounting on UV tape
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Mulitplexing) Filters
Common materials: Glass, Quartz.

Variations:
SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) Filter devices, Beam Splitters, Passive Components
Typical Concerns:
- Top-side and back-side chipping
- Cut perpendicularity
- Kerf side surface finish
Dicing Blade Recommendation:
- SMART CUT series Resin, HYBRID, & Sintered (metal bond) blades
- Diamond size: 30 – 45 microns (resin) and 7 – 15 microns (sintered)
- Thickness: .006″ – .012”
Dicing Process Recommendations:
- Feed rate: 4 – 20 mm/sec
- Spindle speed: 20 – 30 krpm (2″) 10 – 15 krpm (4″)
- Dicing synthetic water soluble coolants may reduce chipping and improve surface finish
HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
Common Material: AlTic (Aluminum Titanium Carbon), Ferrite Ceramic.


Typical Concerns:
- High Mechanical (internal) stress
- burrs
- large kerf width
- lack of accuracy
Dicing Blade Recommendation:
- Bond Type: Resin Bond, Sintered (Metal Bond)
- Diamond Size: 1 to 25 microns
- Kerf Thickness: 15 to 100 microns
Dicing Process Recommendations:
- Feed Rates: 1 mm/s to 5 mm/s
- RPM’s: 15,000 RPM to 30,000 RPM
- Mounting Type: Vacuum chucks or magnetic chucks
- Coolant Used: Water-soluble coolants
The MR head substrate is made of ferromagnetic ceramic material, which has an extremely hard wear resistance and excellent magnetic properties. a typical MR substrate is AlTiC. Substrate thickness typically ranges from 200 to 300 microns. Substrates for HDD read heads require machining after being sintered into bars or sheets. Than they have to be diced into very small unit with very high precision tolerances.
Semiconductor Wafer
Common Material: Silicon, LiNbO3 (Lithium Niobate).



Typical Concerns:
- Feed Rates: 1 mm/s to 5 mm/s
- RPM’s: 15,000 RPM to 30,000 RPM
- Mounting Type: Vacuum chucks or magnetic chucks
- Coolant Used: Water-soluble coolants
Dicing Blade Recommendation:
- SMART CUT Nickel Bond or HYBRID series
- Diamond size: 4 – 6 microns
- Thickness: .0008” – .0016”
Dicing Process Recommendations:
- Feed rate: 25 – 75 mm/sec
- Spindle speed: 30 – 50 krpm
- Mounting: Blue or UV tape
- Cooling type: DI water with and without additives
- Carbon dioxide bubbler is optional
Silicon & GaAs are the two most common materials used for semiconductor wafers. Wafers are typically available in sizes up to 12" in diameter, with 6" and 8" most popular. Typical thicknesses are between 100 - 650 microns.

ARE YOU USING RIGHT DICING BLADES
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET US
HELP YOU
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT DICING BLADES?
Knowledge Center
02
Jun
Select right Diamond Dicing Blade for your application
Selecting the right diamond dicing blade & parameters for your material/application can be a very time consuming, trial & error frustrating process. The guide below has been designed to help you better understand the most important...
02
Jun
Dicing Blade Operations Recommendations
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Selecting the right dicing blade parameters often involves a trial and error process, many aspects of which can be mitigated through experience and a deep understanding of how...
02
Jun
Optimizing Dicing Blade Performance
There are many variables that affect dicing blade performance. Each variable of the dicing process is only of the many components of a larger dicing system (equation). Changing one component or variable of...
02
Jun
Trouble Shooting Dicing Problems
Guide on most common dicing problems and how to resolve them
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
ARE YOU USING RIGHT TOOLS
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET USHELP YOU
CONTACT US
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT TOOLS?
Knowledge...
02
Jun
Application Recommendations
See what blade specifications we recommend to use for different applications, along with rpm's and feed rated
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
ARE YOU USING RIGHT TOOLS
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET USHELP...
02
Jun
Dicing Blade Case Studies
Common Materials - FR4 and epoxy mold compound.
Common Materials - Copper, HTCC (High Temperature Co-fired Ceramics), LTCC (Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics).
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
DICING SOLUTIONS FOR PACKAGE SINGULATION
BGA (Ball-Grid Array)
Common Materials: FR4...
02
Jun
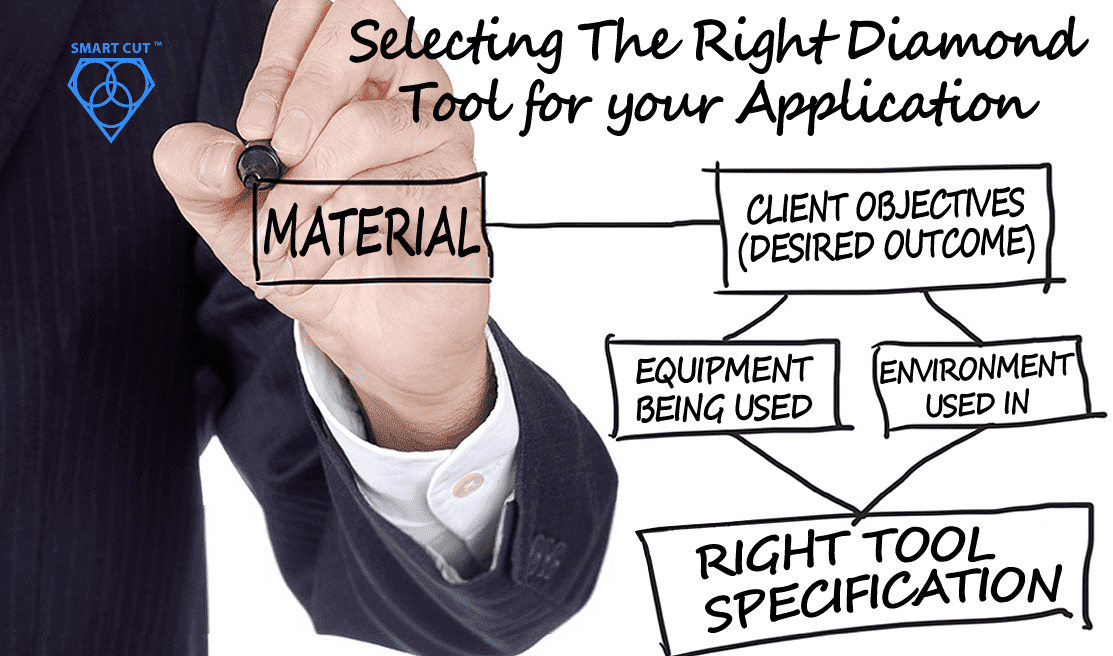
How to Selecting Right Diamond Tools for your application
Selecting the appropriate Diamond & CBN Tool specification is a crucial aspect of achieving your objectives. Opting for the ideal specification not only yields optimal results but also ensures the best return on investment. Conversely,...
02
Jun
How to properly use Diamond Tools
UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools manufactures precision diamond tools for a large variety of applications, materials, and industries.
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Metal Bonded Diamond Tools are “impregnated” with diamonds. This means that selected...
02
Jun
Why use diamond
Diamond is the hardest material known to man kind. When used on diamond/tools, diamond grinds away material on micro (nano) level. Due to its hardness Diamond will work all types of materials from...
02
Jun
What is Diamond Mesh Size and how to select best one for your application
Diamond grit size can be defined as the size of the diamond particles used in the bond matrix. The larger the diamond particles (grit size) the faster the tool will cut.
Share this Article with Friend or...
02
Jun
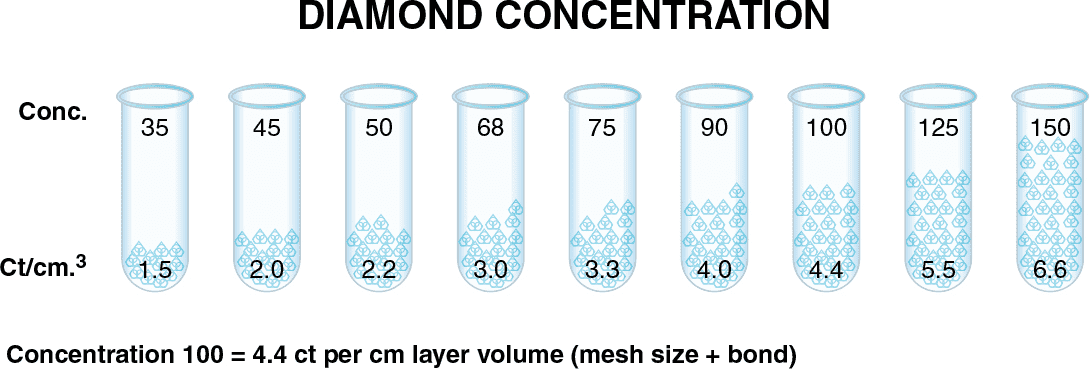
What is Diamond Concentration and which to use for your application
Diamond concentration is measured based on the volume of diamond within a section of the tool. It is typically defined as Concentration 100, which equates to 4.4 carats per cubic centimeter of the diamond layer...
02
Jun
Diamond Tool Coolants Why, How, When & Where to Use
Coolant is one of the most overlooked variables in the overall diamond or cbn tool machining process. Effective and proper use of coolant and recalculating coolant system will pay off in terms of improved surface...
02
Jun
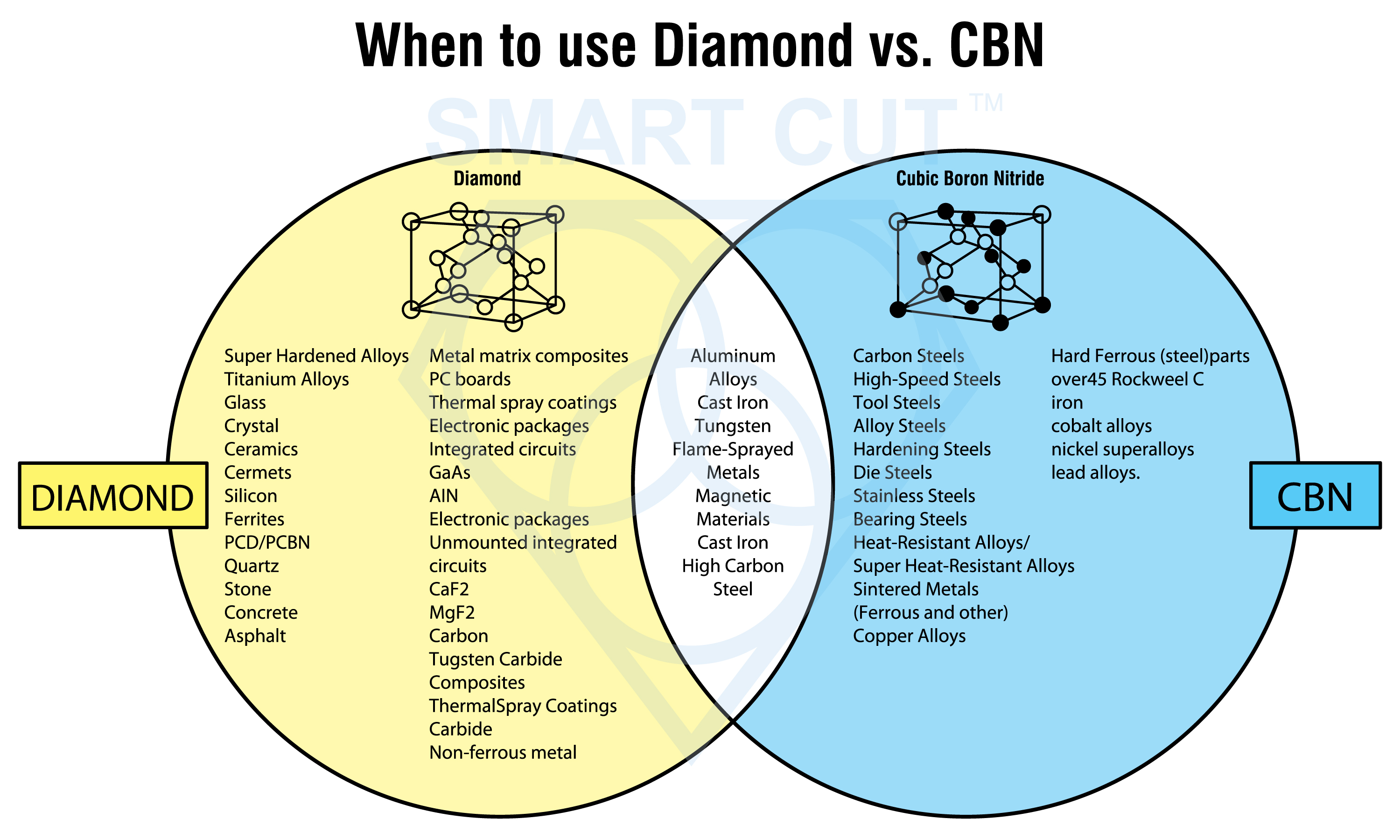
Diamond vs CBN (cubic boron nitride) Tools
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is a synthetic material that is renowned for its exceptional hardness and high thermal stability. It is composed of boron and nitrogen atoms arranged in a crystal lattice structure, similar to...
17
May
Get to Know the Diamond Tool Bond Types and Which to use for your application
Selecting the appropriate diamond bond type for specific applications is crucial for several reasons. Diamond bond type directly affects the tool's performance, efficiency, and longevity. Different bond types determine how well a tool can withstand...