-
0 items in quote
No products in the Quote Basket.
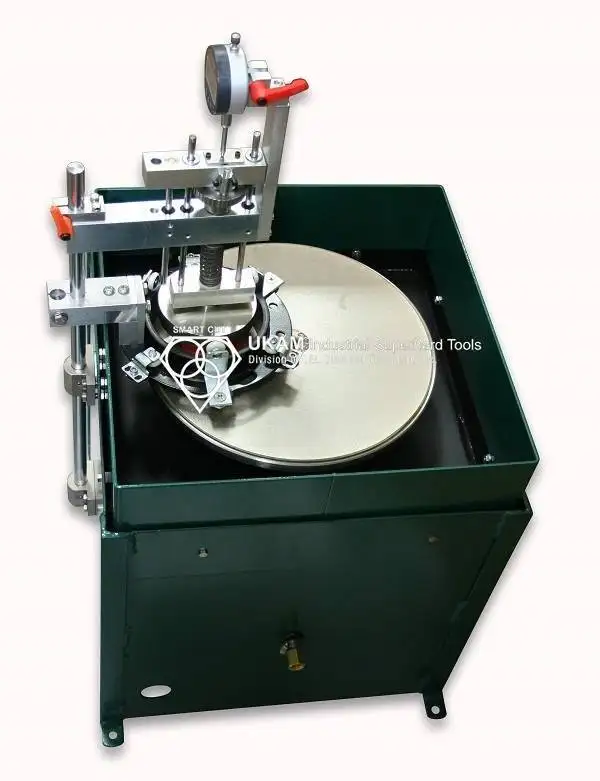
SMART CUT® 2010
Diamond, Nickel Bond Cut Off Blades for Laboratory & Abrasive Cut Off Saws
Nickel Bond Diamond Cut off blades Blades usually have a single layer of diamonds, held by a tough durable nickel alloy. diamond particles to protrude from the bond matrix, providing a free, faster cutting action with minimum heat generation.
Recommended for cutting softer and more gummy materials, where sintered (metal bond) diamond wafering blades load up or glaze over frequently. Unlike sintered (meal bond) cutting blades where diamond is impregnated inside metal binder matrix based on bronze, copper, nickel and other alloys.
DESCRIPTION
SPECIFICATIONS
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
INDUSTRIES USED IN
ACCESSORIES
USAGE RECOMMENDATION
DESCRIPTION
Nickle bond blades have diamond exposed right on surface of the blade. Hence they are able to provide more faster and freer cutting action than their sintered (metal bond) counterparts.
Nickel bond diamond wafering blades are particularly well suited for cutting thermosetting plastics, GRP, pre-sintered and pre-fired (green) materials, electro carbons, graphite, soft ferrites, farinaceous products, deep frozen fish, pones, pc boards, and etc.
SPECIFICATIONS
Tab Content
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Tab Content
INDUSTRIES USED IN
 INDUSTRIES USED IN:
INDUSTRIES USED IN:
-
Advanced Ceramics
-
Composites
-
Glass
-
Geology
-
Quartz
-
Materials Research
-
Medical Devices
-
Metallography
-
Photonics / Optics
-
Semiconductor
 FERROUS & NON-FERROUS METALS:
FERROUS & NON-FERROUS METALS:
-
Plain Carbon Steels
-
Electronic Packages
-
stainless Steels Plastics
-
Tool Steels Fasteners
-
Aluminum Refractories
-
Copper Base Alloys Integrated Circuits
-
Magnesium Thermal Spray Coatings
-
Titanium Metal Matrix Composites
-
Biomedical Wafers
- Petrographic
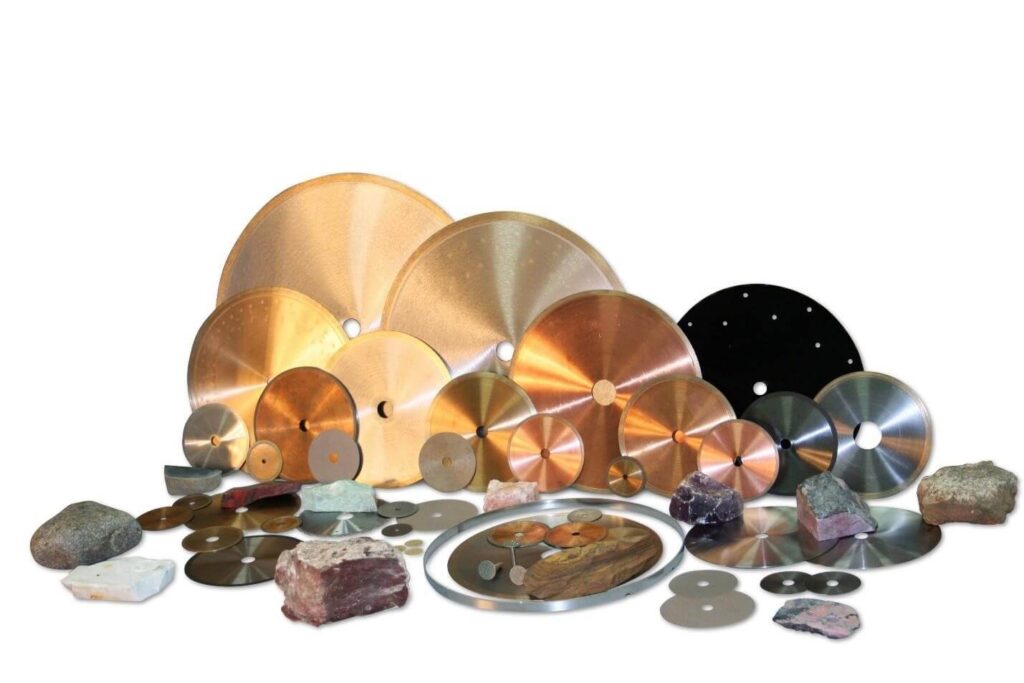
ACCESSORIES
Showing 1 – -1 of 13 results Showing all 13 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Price low to high
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
Image | Name | COMPATIBILITY WITH DRILL SERIES | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh… | $15.39 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills… | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
5/8″-11″ thread. Fits into drill press chuck. Shank adapter threads… | $22.46 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
5/8″-11″ thread. Fits into drill press chuck. Shank adapter threads… | $26.72 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $34.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh… | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills… | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $99.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
105DE, 135DB, 115DM, 125DM, 130DMN, 140DM (up to 1-5/8″ OD) | $154.87 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
105DE, 135DB, 115DM, 125DM, 130DMN, 140DM (up to 1-5/8″ OD) | $154.87 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
105DE, 135DB, 115DM, 125DM, 130DMN, 140DM (up to 1-5/8″ OD) | $235.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $317.41 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $1,745.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
USAGE RECOMMENDATION
Tab Content
Showing 1 – -1 of 7 results Showing all 7 results Showing the single result No results found
Sort by Price low to high
Filters Sort results
Reset Apply
Image | Outside Diameter | Kerf Thickness | Arbor Size / Inside Diamete | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
6" (154mm) | .040” (1.0mm) | ½” (12.7mm) | $145.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
6" (154mm) | .040” (1.0mm) | 5/8” (15.87mm) | $145.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
8” (204mm) | .040” (1.0mm) | ½” (12.7mm) | $175.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
8” (204mm) | .040” (1.0mm) | 5/8” (15.87mm) | $175.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
8” (204mm) | .050” (1.27mm) | 5/8” (15.87mm) | $185.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
10” (254mm) | .050” (1.27mm) | 5/8” (15.87mm) | $195.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||
10” (254mm) | .063” (1.6mm) | 5/8” (15.87mm) | $195.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
Advantages
- Freer cutting action
- Cut Faster
- More forgiving to operator errors
- Cut soft & gummy Materials
- May be used without coolant (for many applications)
Materials Used On
- PCB boards
- Microelectronic packages
- Fiber reinforced composites
- Plastics
- Green Ceramics
- Mounted Samples
- Fiberglass
- Epoxy
- Silicon
- Bones
- Softer alloy metals
How SMART CUT® Bond Works?
Step 1
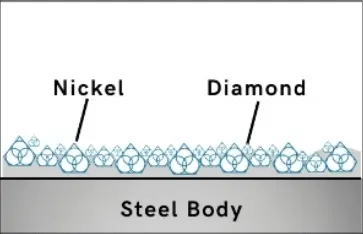
Sharpest And Finest Quality Diamonds
Diamonds or CBN Crystals are activated only at the exposed layer. As Bond Matrix layer begin to wear out, diamonds in a new Bond Matrix layer are immediately activated, substituting the already used up diamond layer. The SMART CUT® Bond Diamond Bond makes sure every diamond is in the right place. and at the right time, working where you need it most.
Step 2
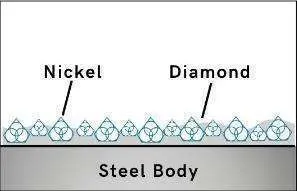
Diamonds or CBN Crystals
The newly exposed diamonds don’t effect diamonds already working on the material. Unlike many other diamond bonds, diamonds in a SMART CUT® remains sharp and grow sharper with each cut, prolonging product life and consistent performance.
Step 3
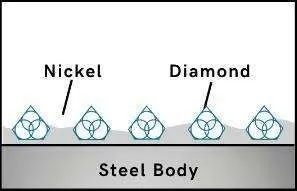
Advanced Formulated Open Diamond Bond Design
This advanced formulated open diamond bond design insures minimal chipping, fast
cut, constant speed of cut, minimal cutting noise, and most important of all, consistent performance.
About Nickel Bond (Electroplated) Tools
Electroplated (nickel bond) diamond products usually have a single layer of diamonds, held by a tough durable nickel alloy. Nickel is frequently used as a base for plating diamond. Because of its excellent strength, toughness and flexibility during the plating process. Electroplated diamond products are able to retain their original shape and dimensions thought their working life. Unlike sintered (meal bond) or resin bond diamond products, where diamond particles are buried in bond and held together by metal or resin binder deep inside.
Electroplating allows diamond particles to protrude from the bond matrix, providing a free, faster cutting action with minimum heat generation.


Faster & Freer Action
Diamond drills made utilizing SMART CUT technology are much more aggressive than your conventional Tools. They can cut faster, while still leaving behind a smooth finish free of material deformation.
Longer Life
In most cases tools manufactured utilizing SMART CUT technology, will outlast other conventional nickel bonded diamond CBN drills. SMART CUT diamond CBN tools are more sturdy than tools manufactured with conventional technologies. They are capable to retain their form and bond configuration all the way through the tools life.


More Consistent Performance
SMART CUT Multi Layered Electroplated diamond cutting blade three diamond layers impregnated inside the bond matrix. Unlike Many Other blade Types, they wear evenly, and are known for their consistency. You will get consistent cutting speed, and overall consistent performance, with minimum amount of dressing even on the hardest to cut materials
Manufactured Using The Highest Quality Raw Materials
Only the highest quality synthetic diamonds and raw materials are used in the manufacturing process. The highest quality standards and product consistency is maintained, using sophisticated inspection and measurement equipment.


Best Performance & Value on the Market
SMART CUT Multi Layered Electroplated Diamond Drills are the best investment you can make! Although they may cost more than electroplated (nickel bond), Diamond Drills. They will more than pay for themselves in terms of overall performance and provide best Return on Investment.
Diamond Wafering Blade
Selection Variables

Diamond Concentration
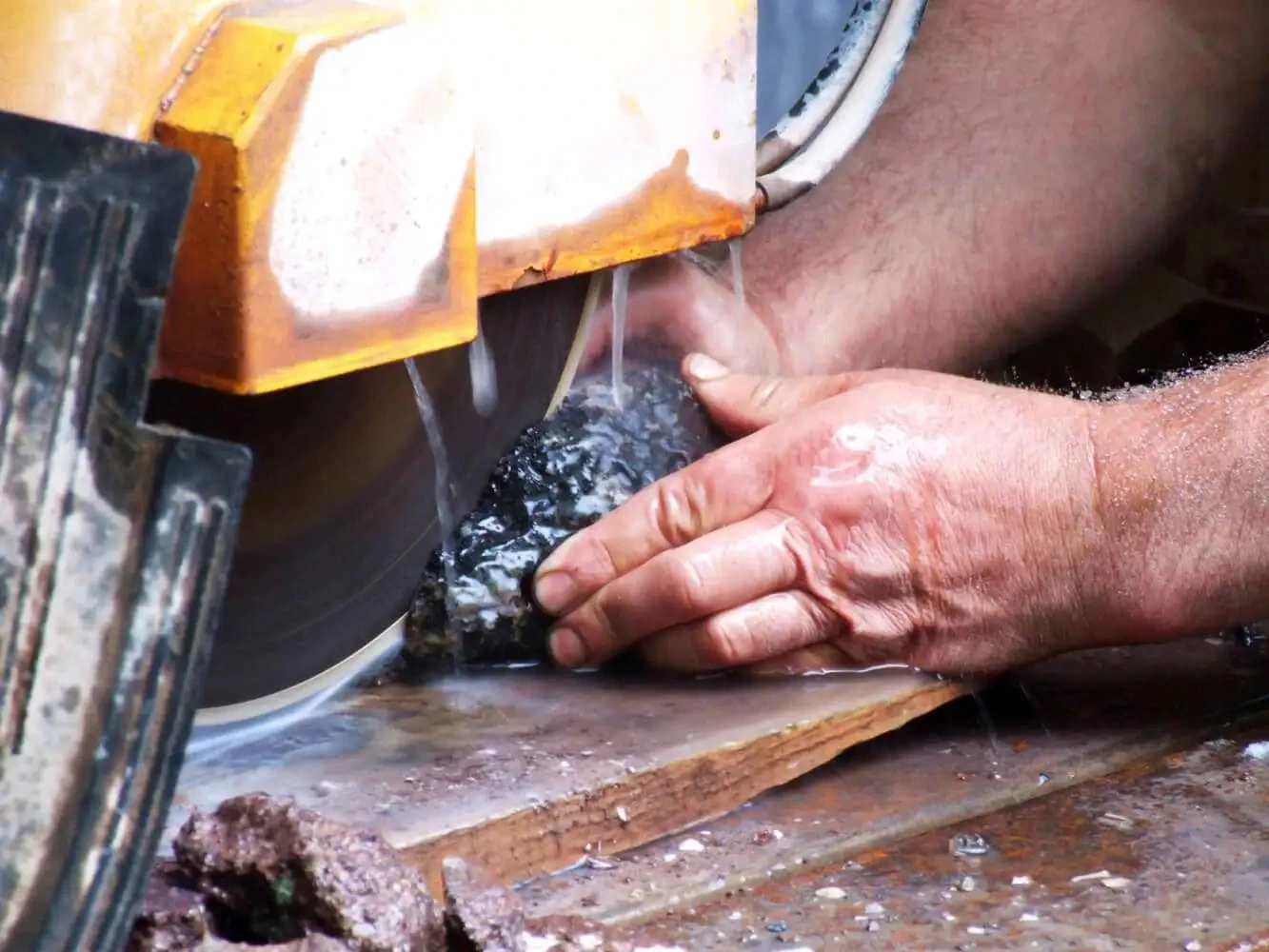
Diamond Concentration – Diamond Concentration is still a factor in determining the life and cutting speed of your Diamond Sectioning/Wafering Blade. Higher diamond concentration is recommended and usually used for cutting softer and more abrasive types of materials. However, the trade off is significantly slower cutting speed. Low diamond concentration is recommended and widely used for cutting ultra hard and brittle materials.
Low Diamond Concentration - typically low concentration wafering blades should be for cutting ultra hard and brittle materials such as ceramics and glass. In Low Concentration Wafering Blades, diamond works by fracture process. Pressure on each diamond crystal/particle is higher which provides enough stress to chip off small flakes in the cut.
High Diamond Concentration - High concentration diamond wafering blades are recommended for cutting metals, plastics and polymers. In this application, materials cut by a plowing mechanism. In this applications diamond plough through the material, work hardened strips of materials become brittle and break off. The greater number of diamond by volume, the quicker the cutting action will be. Increasing the number of diamond s also lowers the per unit force. For metals where it is possible to induce deep deformation layers, a lower per unit force is desirable to reduce the deformation during the cut.
Blade Thickness
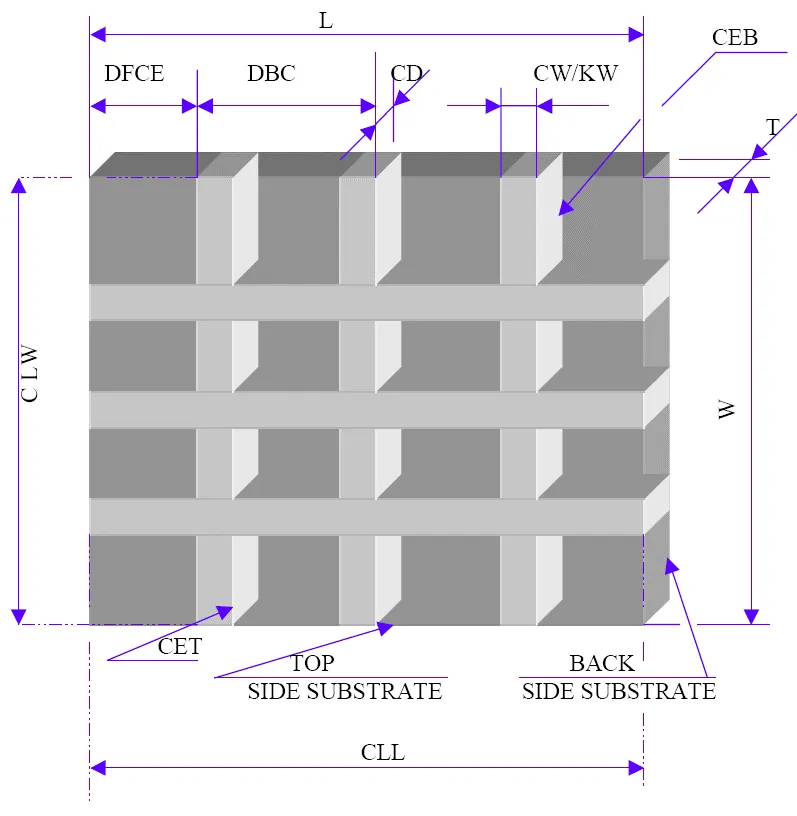
Wafering blade thickness typically ranges from .006” to .040” (1mm). Thinner and thicker wafering blade are available, frequently from stock upon request. Kef thickness typically increases with blade diameter (in proportion to diameter of the blade). Kerf is the amount of material removed from the material/sample due to the thickness of blade passing though the material/sample. Blade thickness is important for users requiring most minimal amount of material loss during sectioning
For example if the user requires precision position of the cutting plane relative to the detail on the sample (IC circuit for example), a thinner and smaller diameter blade would be best for this application. Blades ranging from 3” to 5” (75mm to 125mm) in diameter and thickness .006” to .015” (0.2mm to 0.4mm) would be bet suited for this purpose. There are large variety of factors that will contribute to optimal blade thickness for your material/application Including your desired cutting speed, load/feed rate, material diameter, thickness, hardness, density, and shape. As well as skill & experience of the operator. Thicker wafering blades are more stiff and can whistand higher loads/feed rates. Another advantage of thicker kerf blades is they are more forgiving to operator error and abuse. Thicker kerf blade are recommended for use in environment where large number of individuals will be sharing and using same equipment. Perfect for less experienced and novice saw operators, such as in University laboratory.
.

Diamond Particle/Grit size
Diamond Mesh Size plays a major role in determining your cutting speed, cut quality/surface finish, level of chipping you will obtain, and material microstructure damage you will obtain. Diamond Mesh size does have considerable effect on cutting speed. Coarse Diamonds are larger than finer diamonds and will cut faster. However, the tradeoff is increase in material micro damage. If you are cutting fragile, more delicate materials then finer mesh size diamond wafering blades are recommended.
Bond Type
Metal bonding offers long life and durability, while resin bonding creates less heat, provides better surface finish and is well suited for cutting hard, delicate or brittle materials.
Blade Outside Diameter
typically wafering blade diameters range form 3” (75mm) to 8” (200mm). Wafering blade diameter should be selected based on material diameter and thickness being cut. Smaller diameter wafering blades are thinner than the larger diameter blades and are more prone to bending and warping. Although large diameter blades are thicker, they are typically used for cutting larger and heavier samples at higher loads and speeds than smaller blades

Feed Rates
load/feed rate applied to wafering blades typically vary from 10-1000 grams. Generally, harder specimens are cut at higher loads and speeds (e.g. ceramics and minerals) and more brittle specimens are cut at lower loads and speeds (e.g. electronic silicon substrates). The Speeds/RPM’s you are using, shape/geometry of the specimen, and how the specimen is being clamped/hold in place will affect the load that can be used for your application.
Bond Hardness
Ability of the bond matrix to hold diamonds. As the hardness of the bond is increased, its diamond retention capabilities increase as well. However the trade off is slower cutting speed. Life of the diamond blade is usually increased with hardness of its bond matrix. Bonds are designated on their scale of hardness from Soft, Medium, and Hard. There are dozens of variations and classification schemes based on bond degree of hardness or softness.
Using diamond blades with optimum bond hardness for your application is important to successful precision diamond sawing operation. Bond matrix that is too soft for the material being cut will release diamond particles faster than needed, resulting in faster wear and shorter diamond blade life. On other hand bond matrix that is too hard will result in much slower cutting speeds and require constant dressing to expose the next diamond layer. As rule of thumb, harder materials such as sapphire and alumina generally require a softer bond. Whereas softer and more brittle materials require a harder bond.

Blade Speeds/RPM’s
Most wafering blades are used between 50 to 6,000 RPM’s Typically harder and more denser materials such as Silicon Carbide, are cut at higher RPM’s/speeds Where more brittle materials such as silicon wafers and gallium arsenide are cutting at lower RPM’s. Low Speed saws RPM’s are typically limited from 0 to 600 RPM’s. Where high speed saws offer much large variety of cutting speeds from 0 to 6,000 RPM’s.

Related Products
Petrographic Diamond Blades
SMART CUT® 2010
Diamond, Nickel Bond Cut Off Blades for Laboratory & Abrasive Cut Off Saws
Nickel Bond Diamond Cut off blades Blades usually have a single layer of diamonds, held by a tough durable nickel alloy. diamond particles to protrude from the bond matrix, providing a free, faster cutting action with minimum heat generation. Recommended for cutting softer and more gummy materials, where sintered (metal bond) diamond wafering blades load up or glaze over frequently. Unlike sintered (meal bond) cutting blades where diamond is impregnated inside metal binder matrix based on bronze, copper, nickel and other alloys.Abrasive Polishing Powders
Grinding & Polishing Powders Aluminum Oxide, & Silicon Carbide Powdered Abrasives
UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools offers a wide range of precision abrasives for grinding and polishing large variety of samples. Including petrographic specimens other metals, alloys, electronic devices, semiconductors, ceramics, ferrous metals and many others. Abrasive Powders are available in the following quantities: 1 lb, 5 lb, 10 lb containers Grit Sizes: 120 grit to 8 micronsDiamond, Nickel Bond Cut Off Blades for Laboratory & Other Saws
SMART CUT® 2020
Diamond, Nickel Bond Cut Off Blades for Laboratory & Abrasive Cut Off Saws
Nickel Bond Diamond Cut off blades Blades usually have a single layer of diamonds, held by a tough durable nickel alloy. diamond particles to protrude from the bond matrix, providing a free, faster cutting action with minimum heat generation. Recommended for cutting softer and more gummy materials, where sintered (metal bond) diamond wafering blades load up or glaze over frequently. Unlike sintered (meal bond) cutting blades where diamond is impregnated inside metal binder matrix based on bronze, copper, nickel and other alloys.SMART CUT® Fully Sintered (Metal Bond) Diamond & CBN, Wafering Blades
SMART CUT® Fully Sintered (Metal Bond) diamond wafering blades are fully sintered from OD to ID of the blade. Meaning they have diamonds completely impregnated through the blade. Unlike standard diamond & cbn wafering blades with steel core and diamond section. Instead of having a steel core and small diamond bond edge (usually 1/8"/3.2mm). The diamond edge is all the way through the blade, from its Outside Diameter to Inside Diameter of the blade. You can use until the entire Outside Diameter of the blade is consumed.
Recently Viewed Products
ARE YOU USING RIGHT TOOLS
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET US
HELP YOU
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT TOOLS?
Knowledge Center
02
Nov
Coolant is one of the most overlooked variables in the overall diamond or cbn tool machining process. Effective and proper use of coolant and recalculating coolant system will pay off in terms of improved surface...
29
Aug
Selecting the Right Coolant Method for your Diamond & CBN Tools
Coolant is one of the most important factors in CNC machining when using diamond and CBN tools. These tools are made to cut and grind very hard materials, which naturally produces high amounts of friction...
02
Jun
How to Selecting Right Diamond Tools for your application
Selecting the appropriate Diamond & CBN Tool specification is a crucial aspect of achieving your objectives. Opting for the ideal specification not only yields optimal results but also ensures the best return on investment. Conversely,...
02
Jun
How to properly use Diamond Tools
UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools manufactures precision diamond tools for a large variety of applications, materials, and industries.
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Metal Bonded Diamond Tools are “impregnated” with diamonds. This means that selected...
02
Jun
Why use diamond
Diamond is the hardest material known to man kind. When used on diamond/tools, diamond grinds away material on micro (nano) level. Due to its hardness Diamond will work all types of materials from...
02
Jun
Diamond vs CBN (cubic boron nitride) Tools
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is a synthetic material that is renowned for its exceptional hardness and high thermal stability. It is composed of boron and nitrogen atoms arranged in a crystal lattice structure, similar to...
02
Jun
What is Diamond Mesh Size and how to select best one for your application
Diamond grit size can be defined as the size of the diamond particles used in the bond matrix. The larger the diamond particles (grit size) the faster the tool will cut.
Share this Article with Friend or...
02
Jun
What is Diamond Concentration and which to use for your application
Diamond concentration is measured based on the volume of diamond within a section of the tool. It is typically defined as Concentration 100, which equates to 4.4 carats per cubic centimeter of the diamond layer...
17
May
Choosing The Correct Diamond Bond Type
Selecting the appropriate diamond bond type for specific applications is crucial for several reasons. Diamond bond type directly affects the tool's performance, efficiency, and longevity. Different bond types determine how well a tool can withstand...
03
Jan
How to Properly Use Diamond Tools: A Complete Guide to Performance, Safety, and Tool Life
The use of diamond tools in the manufacturing and precision machining industries, as well as in construction, research, etc., is essential. They are used for a wide range of materials, including sharpening, cutting, grinding, and polishing...