-
0 items in quote
No products in the Quote Basket.
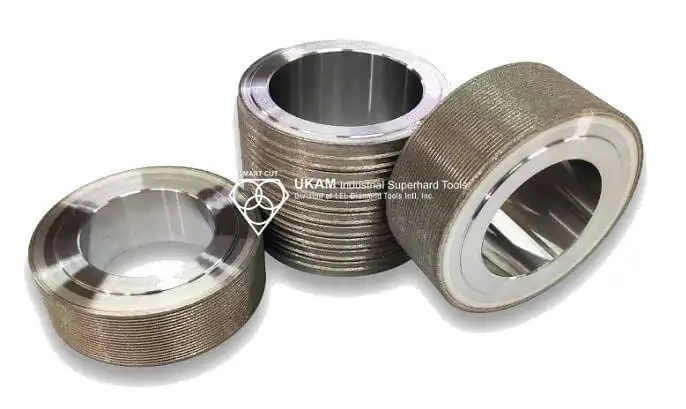
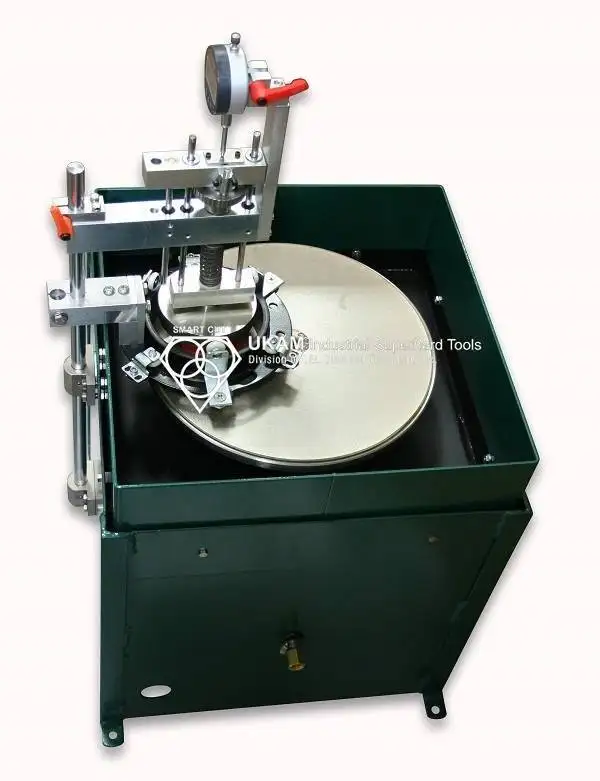
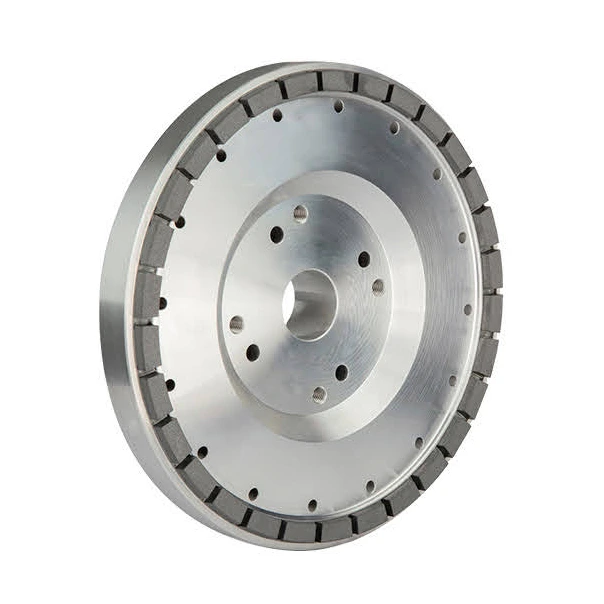
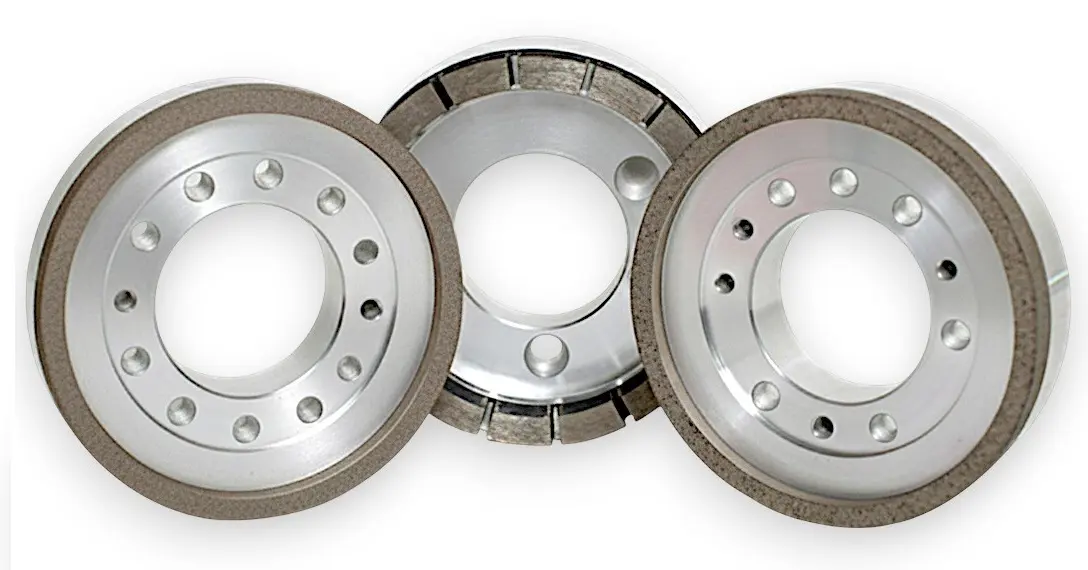
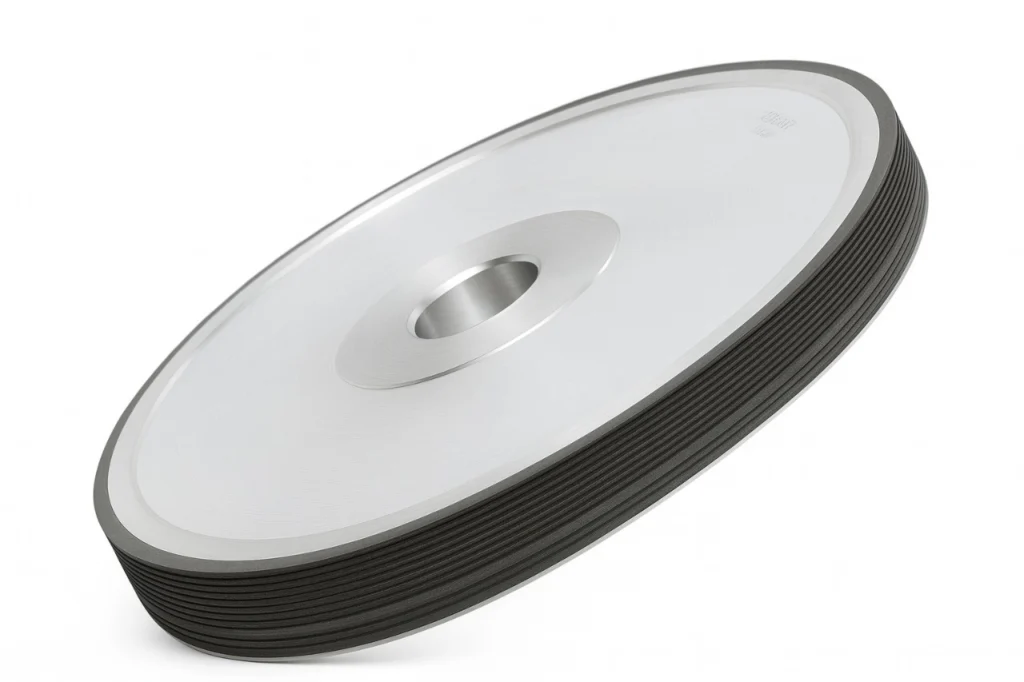
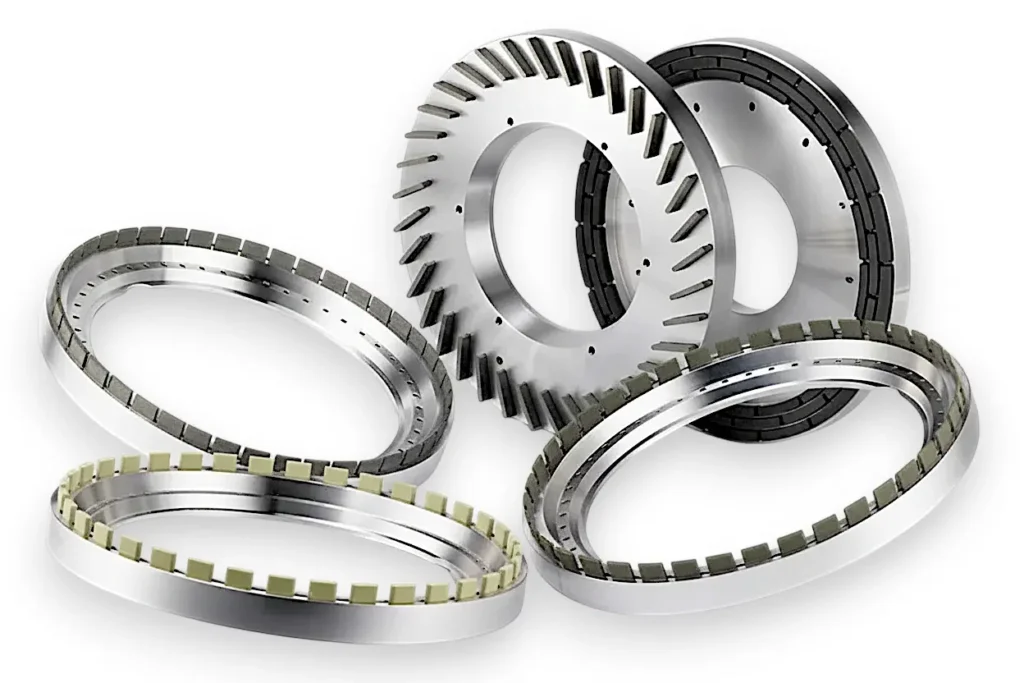
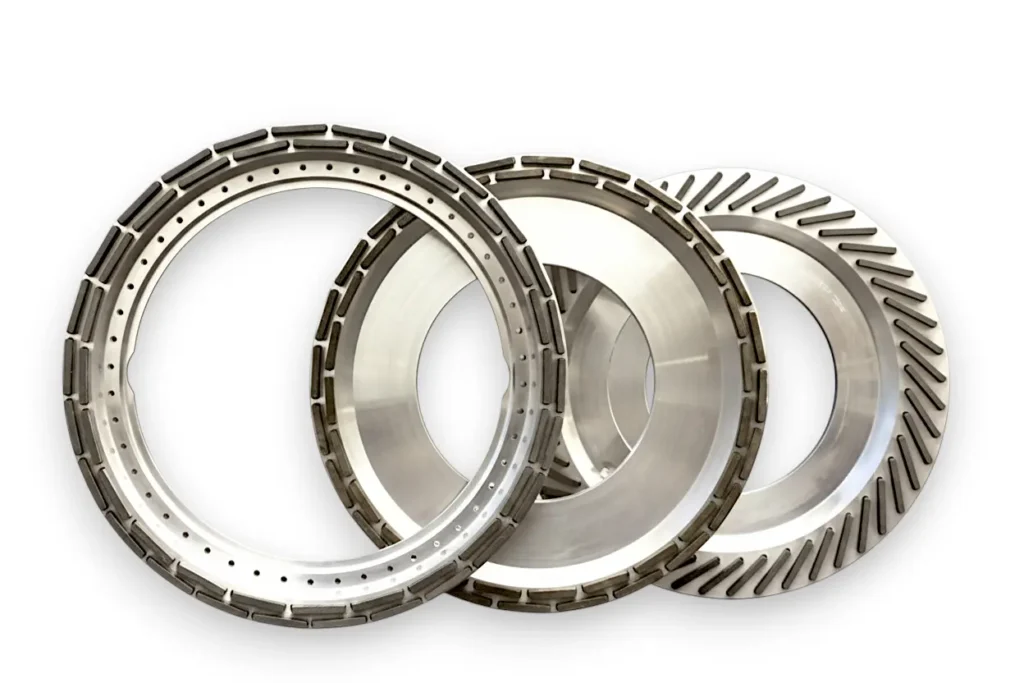
Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels
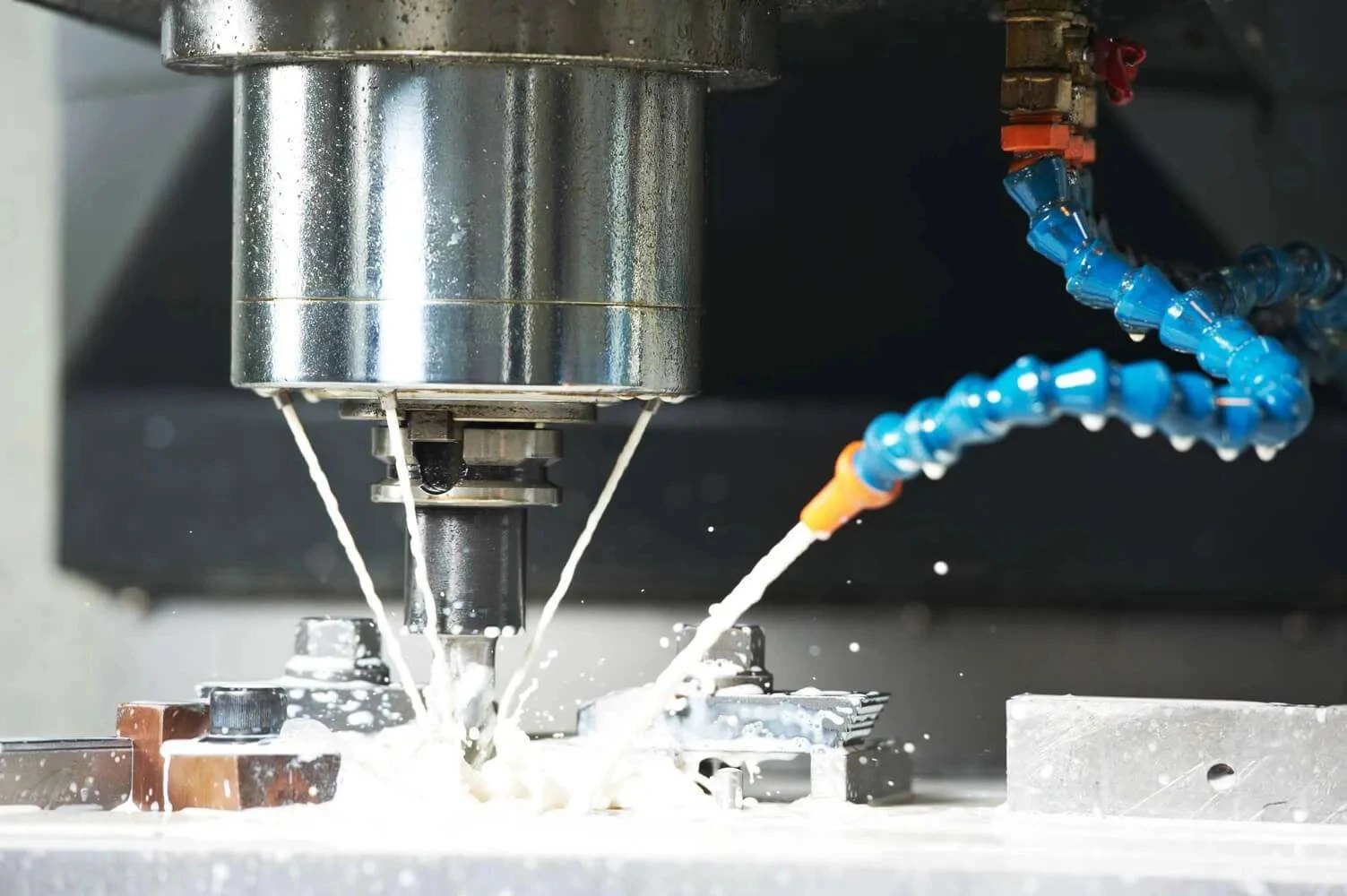
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are engineered for the precise peripheral grinding of silicon ingots, making them an ideal choice for industries such as semiconductors, electronics, automotive, and photovoltaics. These high-performance grinding wheels are designed to process the outer surfaces of silicon ingots, ensuring accurate orientation flats are created, which are essential for subsequent processing steps. The addition of the orientation flat, a marked edge indicating the crystallographic plane of the wafer, is crucial for the wafer’s alignment in future manufacturing processes.
During the post-slicing phase, wafers undergo shaping and smoothing through peripheral grinding.
DESCRIPTION
SPECIFICATIONS
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
INDUSTRIES USED IN
ACCESSORIES
USAGE RECOMMENDATION
DESCRIPTION
This stage involves grinding the outer edge of the wafer to exact specifications, ensuring it meets the precise dimensions required for further use. The SMART CUT ® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels excel in this process, offering exceptional accuracy and surface finish quality.
These grinding wheels are optimized for rapid material removal, enabling cost-effective operations while maintaining minimal impact on the crystalline structure of materials like silicon, sapphire, and gallium arsenide (GaAs). This ensures that the structural integrity of the material is preserved during grinding, making the wheels particularly suited for use in high-precision industries like semiconductor manufacturing.
SMART CUT ® wheels also feature a low grinding load, which ensures good grinding performance, long wear resistance, and a highly flat ingot surface. Their durable design minimizes the need for frequent dressing, further enhancing productivity and reducing maintenance downtime.
SMART CUT ® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are available in a variety of sizes and specifications to meet different grinding needs. These wheels are customizable to fit specific requirements, with diameters ranging from 100mm to 350mm, thicknesses from 28mm to 40mm, and multiple grit sizes ranging from 100 to 1000#. Whether used for rough or fine grinding, these wheels deliver consistent, high-quality results. They are also widely used for squaring, chamfering, and surface grinding of polycrystalline silicon, as well as surface grinding and cylindrical grinding of monocrystalline silicon. Their versatility and precision make them essential tools in industries such as semiconductor fabrication, photovoltaic production, and automotive manufacturing.
SPECIFICATIONS
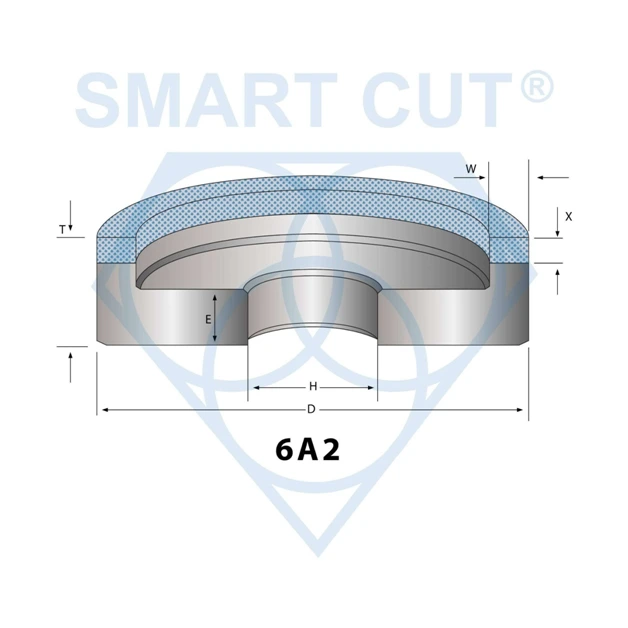
- Diameters (D): 100mm, 200mm, 300mm, 350mm
- Thicknesses (T): 28mm to 40mm
- Heights (H): 31.75mm to 127mm
- Wheel Widths (W): 3mm to 9mm
- Grit Sizes: 100 to 1000#
- Shapes Available: 6A2T, 6A2H, 11A2, 1A1, 6B9H/C, 6A2T/C
- Grinding Types: Rough and fine grinding
- Materials: Silicon, Sapphire, Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)
- Customization: Available in various sizes and specifications to meet customer requirements
- Common Applications: Squaring, chamfering, and surface grinding of polycrystalline silicon, as well as surface grinding and cylindrical grinding of monocrystalline silicon
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are designed for processing a variety of materials, including silicon, sapphire, and gallium arsenide (GaAs). These wheels are commonly used in the semiconductor, electronics, automotive, and photovoltaic industries.
These wheels are ideal for peripheral grinding, squaring, chamfering, and surface grinding of polycrystalline silicon, as well as surface grinding and cylindrical grinding of monocrystalline silicon.
The available shapes include 6A2T, 6A2H, 11A2, 1A1, 6B9H/C, and 6A2T/C. Custom shapes can also be produced according to customer specifications.
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are typically available in metal bond and resin bond types. The bond type is selected based on the application and material being processed.
The wheels are available in various sizes, including diameters ranging from 100mm to 350mm, thicknesses from 28mm to 40mm, and grit sizes from 100 to 1000#. Custom specifications can also be produced to meet specific requirements.
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are primarily used in industries such as semiconductors, electronics, automotive manufacturing, and photovoltaic production, due to their precision and high performance.
These grinding wheels are designed with low dressing frequency, thanks to their durable construction, which minimizes the need for frequent maintenance and increases productivity.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are suitable for both rough and fine grinding, offering flexibility for a variety of grinding applications.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels can be customized to meet specific customer requirements, including unique dimensions, bond types, and grit sizes.
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels offer several advantages, including rapid material removal, low grinding load, and high wear resistance. These features help reduce operational costs, improve grinding efficiency, and extend the lifespan of the wheels. Additionally, their ability to maintain minimal impact on crystalline structure ensures high-quality results without compromising the integrity of sensitive materials like silicon and sapphire.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels can be used for both dry and wet grinding applications. However, using coolant during wet grinding can help reduce heat generation and extend the life of the wheel, especially in high-speed operations.
The lifespan of the SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels depends on factors such as the material being ground, the specific application, and the grinding parameters. However, these wheels are designed for long-lasting performance with low wear, requiring fewer replacements and offering high efficiency over time.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are designed to perform consistently in high-volume production environments. Their durability, high material removal rates, and reduced need for maintenance make them ideal for continuous use in industrial applications.
The recommended RPM range varies depending on the wheel’s size, grit, and the material being ground. For optimal performance, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and adjust the RPM according to the specific grinding conditions.
To select the correct wheel, you need to consider the material type, grit size, bond type, and wheel dimensions suitable for your specific grinding application. If you are unsure, our team can help guide you to the right specifications based on your needs.
While these wheels are designed primarily for silicon, sapphire, and GaAs, they are versatile enough to be used for other materials as well, depending on the application and wheel specifications. For non-silicon materials, please consult with our technical team for recommendations on the most suitable wheel type.
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are compatible with most standard cylindrical grinding machines. However, depending on the specific application and wheel size, adjustments to the machine settings (such as RPM, feed rate, and coolant use) may be necessary for optimal performance.
To maintain the performance of your grinding wheels, it is important to regularly inspect them for wear, ensure proper coolant usage during grinding, and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for dressing intervals. Regular maintenance helps preserve the wheel’s performance and extends its lifespan.
Yes, safety precautions should always be followed when using diamond grinding wheels. Ensure that the grinding wheel is properly mounted on the machine, use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and ensure that the machine’s guards are in place. Always operate within the recommended RPM range and avoid overloading the wheel.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are suitable for both large-scale industrial applications and precision grinding in smaller, specialized operations. Their high precision and durable design make them versatile for a wide range of grinding tasks, from high-volume production to more intricate, small-scale work.
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are designed to produce a high-quality surface finish. Their low grinding load, combined with the appropriate grit size, ensures smooth, even surfaces with minimal surface defects, making them perfect for precision work in industries requiring tight tolerances and high surface quality.
The bond type plays a crucial role in the performance of the grinding wheel. Metal bonds are ideal for heavy-duty grinding applications, offering excellent wear resistance and longer tool life, while resin bonds are better for fine grinding and precision finishing, offering a sharper cutting edge and smoother surface finish. The bond type should be chosen based on the specific grinding task and material being processed.
The grit size of the grinding wheel is directly related to the desired finish and the material being ground. Finer grits (e.g., 1000#) are best suited for precision grinding and smooth finishes, while coarser grits (e.g., 100#) are more appropriate for rough grinding and faster material removal. Choose the grit size based on your requirements for surface quality, grinding speed, and the material hardness.
To optimize performance, ensure that the grinding wheel is matched with the correct grit size, bond type, and RPM settings for the material you are processing. Regularly monitor the grinding conditions (such as feed rate, coolant flow, and machine condition) and adjust as necessary. Proper machine setup and maintenance are key to maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of the grinding wheel.
Yes, these grinding wheels are versatile and can be used for both wet and dry grinding. Using coolant during wet grinding can help reduce heat buildup, enhance wheel life, and improve the finish quality. For dry grinding, ensure adequate cooling and airflow to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance.
The recommended feed rate depends on the specific application and the material being ground. For efficient grinding, the feed rate should be set according to the wheel’s grit size and the material’s hardness. Generally, a slower feed rate is used for fine grinding to achieve a higher-quality surface finish, while faster feed rates are suitable for rough grinding and faster material removal.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels should be stored in a dry and cool environment, away from direct sunlight or excessive heat. Avoid storing the wheels in areas with high humidity, which can affect the bond and performance of the wheel. Ensure that the wheels are stored in a secure location to prevent damage from impacts or vibrations.
While the primary applications for SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are silicon, sapphire, and GaAs, they can be used for grinding other hard materials as well, depending on the application. For best results, it’s important to select the appropriate wheel specifications based on the hardness and properties of the material being processed. If you’re uncertain, contact our technical team for guidance on selecting the optimal grinding wheel for your material.
When grinding polycrystalline silicon, it is important to use the correct grit size and bond type that provide a balance between material removal and surface finish quality. A coarser grit size is typically used for the initial grinding stages, while a finer grit may be employed for finishing. Additionally, using appropriate coolant and optimizing feed rates will help achieve the best results with minimal defects or damage to the material.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels can be used for ultra-thin materials such as thin wafers or microelectronics components. The wheels are designed to provide precise cuts with minimal impact on the material, making them ideal for delicate and thin materials in semiconductor and electronics applications. For ultra-thin materials, it’s important to adjust the grinding parameters to prevent warping or cracking during processing.
Rough grinding is typically used for the initial stages of material processing, where fast material removal is the priority. Coarser grit sizes (e.g., 100-400#) are used for this type of grinding to quickly shape the material. In contrast, fine grinding involves using finer grit sizes (e.g., 600-1000#) to achieve high-precision finishes and smoother surfaces. SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are designed to handle both types of grinding with superior results depending on the application.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are suitable for grinding parts with irregular shapes, especially when combined with the right grinding machine. Their high precision and versatility make them ideal for parts that require custom grinding profiles, such as in semiconductor and electronics applications where precise edge finishes or flatness is required.
The ideal RPM depends on the size of the wheel and the material being ground. For silicon wafers, it’s important to maintain an appropriate RPM range to avoid excessive heat buildup that can affect the material’s integrity. Typically, an RPM range of 1,500 to 5,000 RPM is used, but this can vary based on the specific wheel and application. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for RPM settings for optimal results.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are specially designed to handle extremely hard materials such as sapphire and gallium arsenide (GaAs). The diamond abrasive particles in the wheels provide excellent hardness and wear resistance, enabling them to perform effectively in grinding these tough materials without compromising the wheel’s integrity.
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels should be dressed periodically based on their wear and the surface finish. If you notice a decrease in performance, such as slower material removal rates or poor surface finish quality, it may be time to dress the wheel. In cases where the wheel shows visible damage, cracks, or significant wear, it should be replaced to maintain optimal grinding efficiency.
Yes, these grinding wheels are compatible with both manual and automated grinding machines. Whether used in a highly automated production line or a more manual operation, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels offer the same high-performance results, making them a versatile solution for various grinding processes.
When using SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels, always ensure that you are following proper safety protocols. This includes wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection. Ensure that the wheel is mounted securely on the machine and that the grinding machine is in proper working condition. Always check the RPM limits and feed rates to prevent excessive wear or damage, and ensure adequate cooling during the grinding process.
Using the wrong bond type or grit size can lead to suboptimal results, such as increased wear on the wheel, poor surface finishes, or excessive heat generation. For instance, a too-coarse grit will leave rough surfaces, while a too-fine grit may slow down material removal. Similarly, using the incorrect bond type can lead to premature wheel degradation. To ensure the best results, it’s important to choose the correct bond and grit size for the material and type of grinding you’re performing.
Yes, these grinding wheels are designed to perform in both wet and dry grinding applications. However, wet grinding with the use of coolant is often recommended for silicon materials, as it helps dissipate heat, reduces wheel wear, and improves the surface finish. For dry grinding, it’s essential to monitor the grinding parameters carefully to prevent overheating, as dry grinding can lead to thermal damage to sensitive materials like silicon.
After each use, it’s essential to clean the grinding wheel to remove any debris or material buildup that may affect performance. Use a soft brush or a compressed air blower to clean the wheel. If the wheel requires dressing, follow the manufacturer’s recommended dressing procedures to maintain optimal cutting ability. Regular cleaning helps ensure consistent grinding results and prolongs the life of the wheel.
As SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels wear, their ability to remove material efficiently decreases, which can affect the surface quality and overall productivity. Excessive wear can result in uneven grinding or a rougher surface finish. Dressing or replacing the wheel when wear becomes noticeable ensures that the grinding process continues to be effective, and the final results meet required specifications.
⦁ SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are compatible with most cylindrical grinding machines, including both manual and CNC-controlled machines. The performance of the wheels will depend on the machine’s specifications, such as the ability to maintain constant RPM and feed rates, as well as proper coolant flow. If you have a specific machine in mind, consult with the manufacturer or our technical support team to ensure compatibility.
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are designed with high-precision in mind, offering minimal impact on material structure, consistent surface finish, and the ability to create highly flat surfaces. These attributes make them ideal for semiconductor fabrication, photovoltaic production, and automotive component manufacturing, where exact tolerances and surface quality are crucial. Their low grinding load and high wear resistance further ensure consistent performance across high-precision tasks.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are designed to be flexible and efficient for both large-scale production and smaller, specialized operations. Their high performance, durability, and precision make them a great choice for continuous industrial production as well as more controlled, low-volume, high-precision tasks.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels can be used for grinding materials with complex geometries, such as those found in semiconductor components and optical materials. Their high precision and ability to be customized to specific shapes make them suitable for applications requiring detailed, intricate grinding tasks. When grinding complex parts, it’s important to adjust the grinding parameters accordingly to maintain consistent performance.
To optimize the cooling system, it’s important to use the correct amount and type of coolant, ensuring it flows efficiently over the grinding surface to keep both the wheel and the workpiece cool. This is especially important for wet grinding, as it helps reduce heat buildup, prolongs wheel life, and prevents thermal damage to sensitive materials. Regular maintenance of the coolant system, such as cleaning filters and ensuring proper coolant pressure, will help maintain the performance of the grinding wheel.
For high-precision grinding of thin and fragile wafers, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are well-suited due to their ability to provide minimal impact on the material. The wheels should be used with a gentle feed rate and appropriate RPM settings to avoid stress or cracking in delicate materials. Additionally, careful monitoring of the grinding process ensures that the wafer thickness and flatness are maintained without compromising the material’s integrity.
For grinding brittle materials such as sapphire and gallium arsenide (GaAs), it’s recommended to use medium to fine grit sizes such as 400# to 1000#. Finer grit sizes are ideal for producing smooth finishes and reducing the risk of cracking or damaging the material. However, for initial material removal, coarser grits may be used, followed by finer grits for finishing to achieve the desired surface quality.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are designed to withstand high-speed grinding while maintaining consistent performance. The advanced design and durable materials used in these wheels ensure they can operate efficiently at high RPMs, making them suitable for fast material removal and high-volume production. It’s important to follow the recommended operating guidelines for RPM and feed rates to avoid overheating and ensure optimal results.
Some common problems include wheel glazing, excessive wear, and surface defects. These issues can typically be avoided by using the correct grit size and bond type for your application, maintaining the proper coolant flow, and ensuring that the RPM and feed rates are adjusted to match the material and the grinding wheel. Regular wheel dressing and proper machine maintenance are also essential for preventing these problems.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are compatible with automated grinding systems and are well-suited for continuous production environments. Their durability, high material removal rate, and ability to maintain consistent results make them ideal for automated operations, where efficiency and repeatability are critical. Automated systems can help maximize the productivity and precision of the grinding process, particularly in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing and photovoltaic production.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are ideal for fine grinding of both flat and cylindrical surfaces. Whether you are working on wafers, semiconductor components, or cylindrical parts, these wheels offer precise results with a smooth finish. Their low grinding load and high wear resistance ensure they can handle fine grinding tasks efficiently without compromising the material’s integrity.
The bond type plays a key role in the grinding wheel’s ability to maintain a sharp cutting edge. Resin bonds are designed to break down more easily, exposing fresh diamond particles that help maintain a sharp cutting edge, making them ideal for precision grinding and fine finishes. In contrast, metal bonds are more durable and resistant to wear, making them better suited for heavy-duty applications where long-lasting performance and high material removal rates are required.
Yes, SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels can be used for both rough and fine grinding in a single operation by changing the grit size and adjusting the machine settings. For rough grinding, a coarser grit size is used for rapid material removal, followed by a finer grit for finish grinding to achieve a smooth and precise surface. This makes the wheels versatile for a range of applications and provides flexibility for different processing needs.
To ensure consistency in the surface finish, it’s important to maintain steady grinding parameters, including the feed rate, coolant flow, and RPM settings. Regular monitoring of the grinding process, along with using the correct grit size and bond type, will help achieve a consistent surface finish. Dressing the wheel at the appropriate intervals also ensures that the cutting edges remain sharp, maintaining the desired finish quality throughout the grinding process.
Coolant plays a critical role in maintaining optimal grinding conditions. It helps reduce heat buildup, which can cause thermal damage to both the grinding wheel and the workpiece, especially when grinding hard materials. Coolant also assists in lubricating the grinding process, reducing friction, and improving surface finish. Using the right type of coolant, along with consistent flow and pressure, will extend wheel life and improve overall grinding efficiency.
While SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels are primarily designed for grinding applications, they can be used in polishing applications depending on the bond and grit size selected. Finer grit wheels and specialized bond types are better suited for polishing operations, providing smooth, high-gloss finishes on materials like silicon and sapphire. Adjusting parameters such as feed rate and coolant flow can help achieve the desired surface finish during polishing.
INDUSTRIES USED IN
Tab Content
ACCESSORIES
Tab Content
USAGE RECOMMENDATION
Tab Content
Features:
- Efficient Material Removal for cost-effective operations and faster processing times
- Minimal Impact on Crystalline Structure, preserving the integrity of materials like silicon, sapphire, and gallium arsenide (GaAs)
- Low Grinding Load, ensuring consistent performance with less strain on the equipment
- Good Grinding Performance with excellent wear resistance for longer tool life
- Highly Flat Surface Finish, delivering precise and uniform results on ingot surfaces
- Low Dressing Frequency, reducing maintenance downtime and improving productivity
- Customizable Specifications, including various diameters (100mm to 350mm), thicknesses (28mm to 40mm), and grit sizes (100 to 1000#)
- Ideal for rough and fine grinding applications
- Durable Design for high performance in semiconductor, photovoltaic, and automotive industries
Advantages:
- Increased Productivity: SMART CUT® wheels provide fast material removal, reducing overall processing time and enabling higher throughput in grinding operations.
- Cost-Effective: Efficient material removal and long tool life result in lower operational costs, making these wheels an economical choice for large-scale production.
- High Precision: The ability to create precise orientation flats and achieve a highly flat surface finish ensures accurate and consistent results, crucial for industries like semiconductor manufacturing and photovoltaics.
- Minimal Crystalline Disruption: The wheels preserve the integrity of the crystalline structure of sensitive materials such as silicon, sapphire, and gallium arsenide (GaAs), maintaining material quality during the grinding process.
- Low Maintenance: The durable design minimizes the need for frequent dressing, leading to reduced maintenance time and increased uptime for grinding equipment.
- Long Tool Life: SMART CUT® wheels feature excellent wear resistance, ensuring that they last longer and require fewer replacements, contributing to overall cost savings.
- Customizable Options: A wide range of sizes and grit options allows for tailored solutions, making these wheels versatile for a variety of grinding applications in different industries.
- Versatility: Ideal for both rough and fine grinding, these wheels offer flexible solutions for various materials and grinding requirements.
- High Performance in Critical Industries: The wheels are specifically designed to meet the demanding needs of industries such as semiconductor fabrication, solar energy, and automotive manufacturing.
- Minimal Environmental Impact: Efficient grinding processes and low dressing frequency contribute to a reduced environmental footprint by lowering waste and energy consumption.
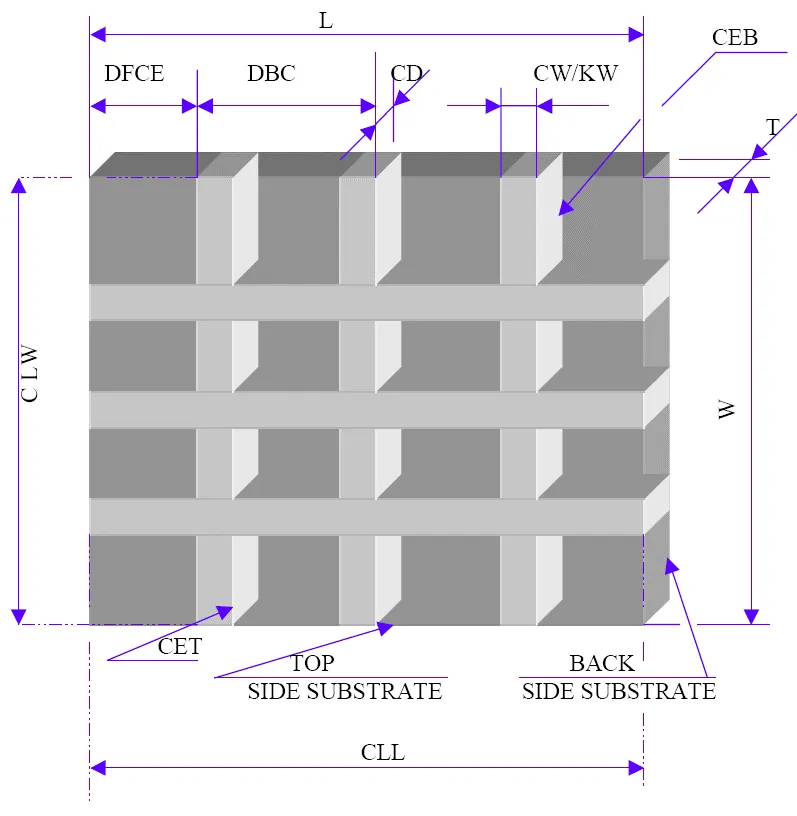
SMART CUT® Diamond Cylindrical Grinding Wheels Available
|
Wheel Shape |
Diameter (D) |
Thickness (T) |
Hole Diameter (H) |
X(W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
6A2T |
220 |
65 |
130 |
5 |
|
6A2T |
200 |
35 |
76 |
5 |
|
6A2H |
200 |
60 |
80 |
5 |
|
11A2 |
100 |
28 |
40 |
31.75, 20 |
|
1A1 |
300 |
35 |
127 |
5, 7, 10 |
|
6B9H/C |
300 |
50 |
48 |
10, 20 |
|
6A2T/C |
250 |
60 |
38.1 |
10, 15 |
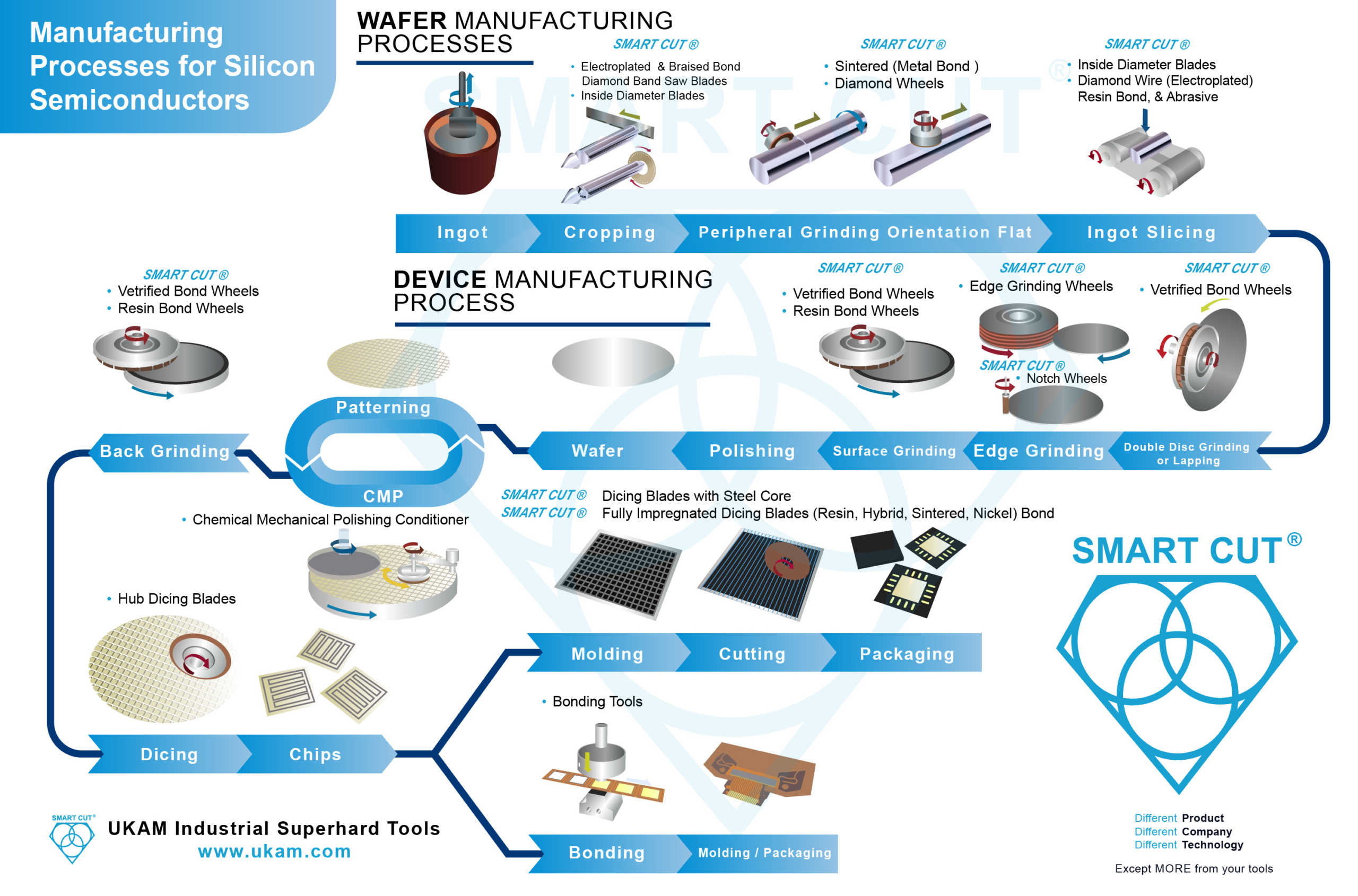
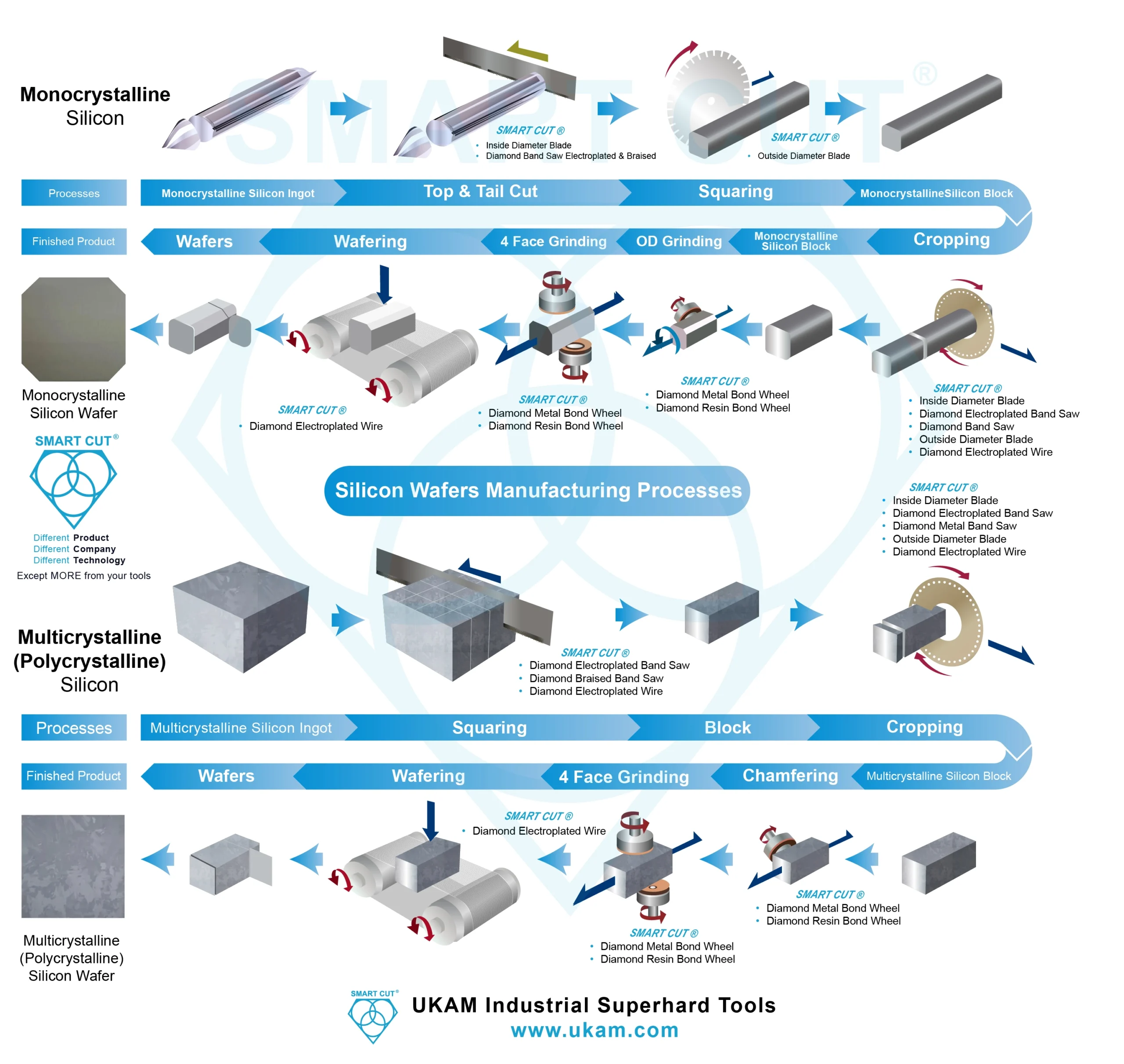
About Peripheral and Orientation Flat Grinding
After the delicate process of slicing silicon ingots into thin wafers, the next critical step in semiconductor manufacturing is peripheral grinding. This procedure is essential for refining the shape and dimensions of the wafers, ensuring they meet stringent industry standards for subsequent processing steps.
Peripheral grinding focuses on the outer edge of the silicon wafer, serving multiple crucial purposes:
-
 1. Dimensional Accuracy: Ensures that the wafer's diameter and roundness adhere to precise specifications. This accuracy is vital for the wafers to fit correctly in the equipment used in later stages of semiconductor fabrication.
1. Dimensional Accuracy: Ensures that the wafer's diameter and roundness adhere to precise specifications. This accuracy is vital for the wafers to fit correctly in the equipment used in later stages of semiconductor fabrication.
-
 2. Edge Quality: Improves the mechanical strength of the wafer by removing any microcracks and surface imperfections that could lead to breakage during processing. A smooth edge is less susceptible to chipping.
2. Edge Quality: Improves the mechanical strength of the wafer by removing any microcracks and surface imperfections that could lead to breakage during processing. A smooth edge is less susceptible to chipping.
-
 3. Surface Preparation: Prepares the wafer for subsequent processing steps, such as layer deposition and photolithography, by ensuring a uniformly smooth edge that can influence the overall flatness and evenness of the wafer surface.
3. Surface Preparation: Prepares the wafer for subsequent processing steps, such as layer deposition and photolithography, by ensuring a uniformly smooth edge that can influence the overall flatness and evenness of the wafer surface.
Peripheral grinding is performed using specialized grinding machines that are capable of achieving the necessary precision. These machines typically employ a rotating grinding wheel coated with an abrasive material such as diamond or silicon carbide. Key considerations in this process include:
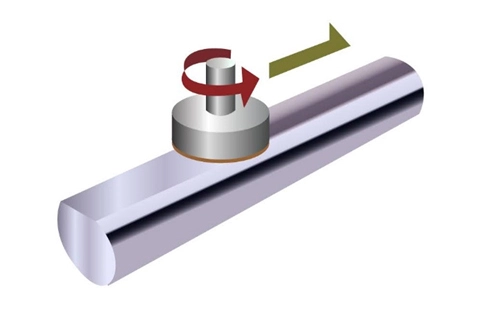
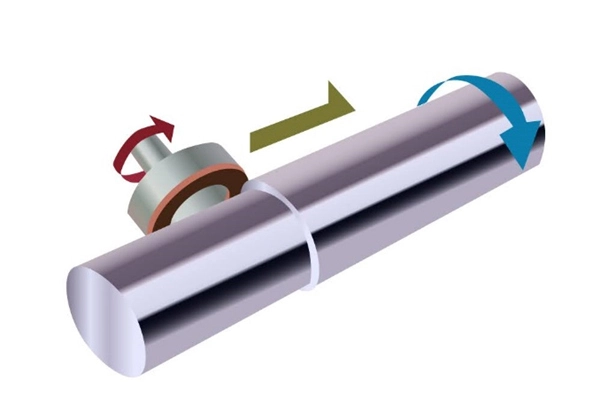
-
 1. Grinding Wheel Speed: Must be carefully controlled to avoid excessive heat generation, which can damage the wafer.
1. Grinding Wheel Speed: Must be carefully controlled to avoid excessive heat generation, which can damage the wafer.
-
 2. Feed Rate: The rate at which the wafer is fed into the grinding wheel affects both the finish quality and the rate of material removal.
2. Feed Rate: The rate at which the wafer is fed into the grinding wheel affects both the finish quality and the rate of material removal.
-
 3. Coolant Application: Coolants are essential not only for temperature control but also for removing debris from the grinding area, thus preventing contamination and ensuring a clean cut.
3. Coolant Application: Coolants are essential not only for temperature control but also for removing debris from the grinding area, thus preventing contamination and ensuring a clean cut.
Orientation Flat
An integral part of the wafer processing that occurs during the peripheral grinding stage is the creation of an orientation flat. This flat is a precisely ground edge on the wafer that serves several vital functions:
-
 1. Indicating Crystallographic Plane: The orientation flat marks the wafer's crystallographic plane, which is crucial for aligning the wafer correctly in subsequent processing equipment. Accurate alignment is essential for the photolithography steps, where patterns must be precisely positioned on the wafer.
1. Indicating Crystallographic Plane: The orientation flat marks the wafer's crystallographic plane, which is crucial for aligning the wafer correctly in subsequent processing equipment. Accurate alignment is essential for the photolithography steps, where patterns must be precisely positioned on the wafer.
-
 2. Handling and Identification: It also aids in the handling of wafers and helps operators and automated systems quickly identify the orientation and type of wafer, facilitating efficient and error-free processing.
2. Handling and Identification: It also aids in the handling of wafers and helps operators and automated systems quickly identify the orientation and type of wafer, facilitating efficient and error-free processing.
-
 3. Standardization: The location and size of the orientation flat are standardized depending on the wafer diameter and type of silicon crystal (e.g., n-type or p-type), making it a universal marker used across the semiconductor industry.
3. Standardization: The location and size of the orientation flat are standardized depending on the wafer diameter and type of silicon crystal (e.g., n-type or p-type), making it a universal marker used across the semiconductor industry.
The precision achieved during the peripheral grinding and the addition of an orientation flat are critical for the integrity and functionality of the final semiconductor devices. Any deviations in this stage can lead to alignment issues in layer deposition and patterning, which can ultimately affect the electrical properties and performance of the integrated circuits. Thus, maintaining high standards in this step is imperative for the production of reliable and efficient semiconductor devices.
Recommended Coolant for peripheral grinding & orientations flat grinding
Coolants play an essential role in peripheral grinding & orientations flat grinding, minimizing thermal stress and flushing away silicon particles from the grinding interface. This prevents overheating and reduces the risk of surface contamination and damage. An excellent coolant for this application.
SMART CUT® HD-2 is a synthetic coolant specifically designed for the cutting of semiconductor materials, including sapphire, silicon, germanium, single-crystal SiC, and II-VI crystals. This coolant offers excellent cut rates and imparts outstanding surface finishes with reduced warp and total thickness variation (TTV). It is ideal for diamond abrasive cropping, squaring, and wafering of silicon ingots and wafers.
Case Studies - SMART CUT® vs Competitors Wheels
These case studies compare the surface speed (m/min) between SMART CUT and the Competitor's wheel across three different grinding stages: Rough Grinding, Semi-Finish Grinding, and Finish Grinding. The goal was to assess and compare the performance of both products in terms of efficiency in material removal.
Workpiece: 156mm Silicon Blocks
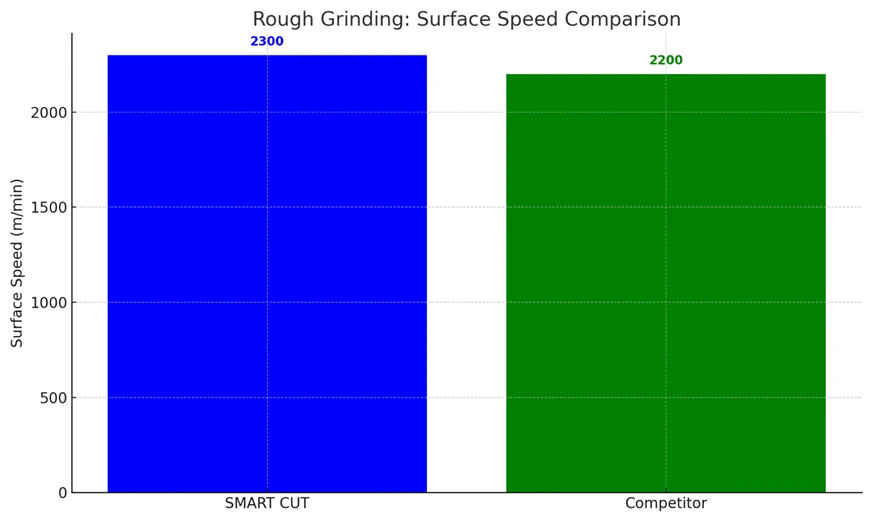
|
Parameter |
SMART CUT® Diamond Wheel |
Competitor's Wheel |
|---|---|---|
|
Surface Speed |
2,300 m/min |
2,200 m/min |
|
Stock Removal |
1.0 mm |
0.9 mm |
|
Table Feed |
450 mm/min |
420 mm/min |
|
Surface Roughness |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Case Study 2: Semi-Finish Grinding
Workpiece: 156mm Silicon Blocks
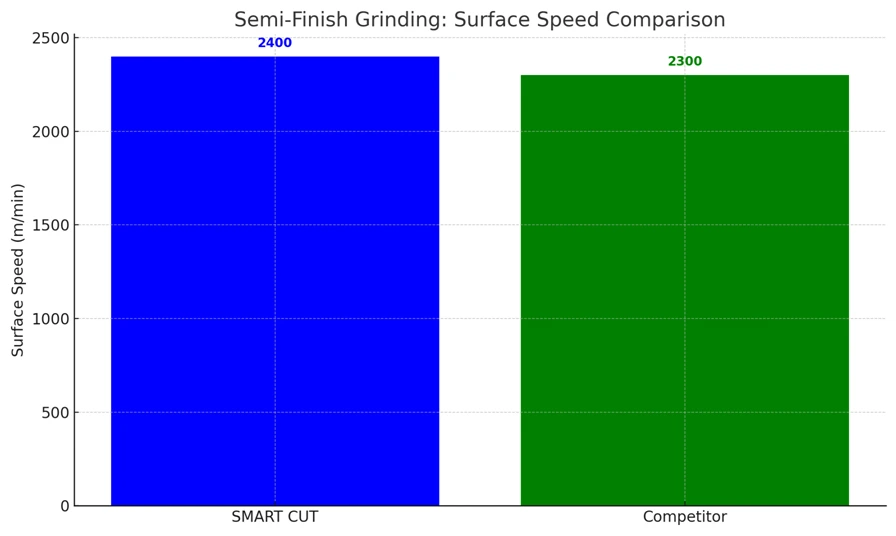
|
Parameter |
SMART CUT® Diamond Wheel |
Competitor's Wheel |
|---|---|---|
|
Surface Speed |
2,400 m/min |
2,300 m/min |
|
Stock Removal |
0.07 mm |
0.06 mm |
|
Table Feed |
420 mm/min |
410 mm/min |
|
Surface Roughness |
Ra 0.1 μm |
Ra 0.15 μm |
Case Study 3: Finish Grinding
Workpiece: 156mm Silicon Blocks
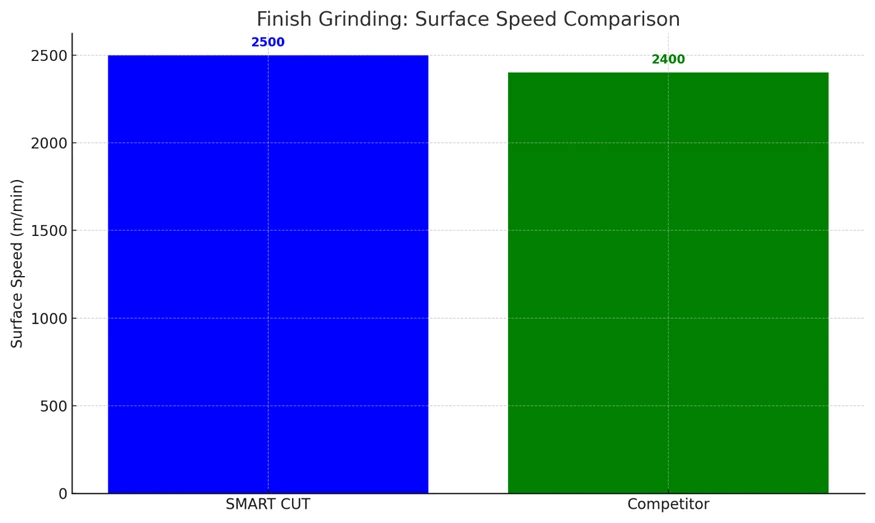
|
Parameter |
SMART CUT® Diamond Wheel |
Competitor's Wheel |
|---|---|---|
|
Surface Speed |
2,500 m/min |
2,400 m/min |
|
Stock Removal |
0.05 mm |
0.04 mm |
|
Table Feed |
400 mm/min |
380 mm/min |
|
Surface Roughness |
Ra 0.03 μm or less |
Ra 0.05 μm |
Conclusion for Each Grinding Stage:
- Rough Grinding: SMART CUT Diamond Wheel offers superior surface speed, better stock removal, and faster table feed, leading to a more efficient grinding process.
- Semi-Finish Grinding: SMART CUT Diamond Wheel maintains better stock removal, slightly higher surface speed, and feed rates, resulting in a finer finish and better overall efficiency.
- Finish Grinding: SMART CUT Diamond Wheel improves surface speed, stock removal, and surface roughness control, delivering faster processing and higher-quality results.
Related Products
SMART CUT® Diamond Notch
SMART CUT® Diamond Notch Grinding Wheels in Single & Multi Layered electroplated nickel bond & sintered (metal bond) are construction are developed for high precision notch formation on semiconductor wafers. These wheels support performance requirements for Silicon, Silicon Carbide, Gallium Arsenide, and Sapphire. The electroplated structure holds diamond particles firmly on the surface, producing accurate geometry, clean edges, and stable performance during continuous wafer processing. You receive predictable grinding behavior, long wheel life, and consistent notch dimensions under demanding production conditions.
SMART CUT® Diamond Edge Grinding Wheels (Electroplated)
SMART CUT® Diamond Edge Grinding Wheels are engineered to deliver exceptional performance for precision grinding applications, providing superior results in both rough and fine grinding. These wheels are ideal for use in industries that require highly accurate EDM processing and consistent wafer-to-wafer results. Manufactured with synthetic diamond grit, SMART CUT® wheels offer improved surface roughness and extended tool life due to their tightly controlled diamond distribution and uniform bond structure.
Electroplated (Nickel Bond) Diamond Band Saw Blades
SMART CUT® Braised Bond Diamond Band Saw Blades
ID blades
Diamond Wire
SMART CUT Diamond wire produces minimum kerf loss, less sub-surface damage, and contamination free coolant. Used for precision cutting of various types of artificial crystal, ceramic, quartz glass, monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, sapphire and special metal materials. Diamond Wire cutting is an environmentally friendly cutting process as it eliminates slurry recycling and disposal issues.
It is widely used for slicing artificial crystals, ceramics, quartz glass, monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon, sapphire, and specialty metals. The design provides high dimensional accuracy and smooth surfaces, often eliminating the need for extensive secondary processing.
SMART CUT® HD Synthetic Low IFT Coolant/Lubricant For Diamond Wire Sawing Silicon
SMART CUT® is a synthetic coolant specifically designed for the cutting of semiconductor materials, including sapphire, silicon, germanium, single-crystal SiC, and II-VI crystals. This coolant offers excellent cut rates and imparts outstanding surface finishes with reduced warp and total thickness variation (TTV). It is ideal for diamond abrasive cropping, squaring, and wafering of silicon ingots using ID, band, and wire saws. SMART CUT® HD-2B can also be used as a non-re-circulating edge grinding coolant or lubricant for silicon wafers and ingots.
DIAMOND BACKGRINDING WHEELS
SMART CUT® Diamond Backgrinding Wheels are designed for precision thinning and flattening of silicon wafers, glass, and ceramic substrates. These high-performance wheels are used on backgrinding machines, including models from Disco, Okamoto, Strasbaugh, and other leading manufacturers. Available in sizes ranging from 8” to 14” O.D., they are engineered to handle a wide range of materials and applications, from semiconductor wafers to microelectronic packages.
Recently Viewed Products
ARE YOU USING RIGHT ID CUTTING BLADES
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET US
HELP YOU
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT ID CUTTING BLADES?
Knowledge Center
02
Jun
Cutting silicon wafers is a critical process in the manufacturing of semiconductor devices, where precision and control are paramount to the success of the final products. Silicon, a semi-metallic or metalloid, is the base material...
08
Jul
Manufacturing Processes for Silicon Semiconductors From Ingot to Integrated Circuit
Trusted by Tens of Thousands of Manufacturers, Laboratories,
Research Institutions Worldwide
Since 1990
American Based Manufacturer
Established in 1990
Expert technical support
Custom manufacturing
Thousands of Stock Products
Same day shipping
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
1. Ingot Production
The journey begins...
08
Jul
The Comprehensive Guide to the Processes of Silicon Wafers Production
The production of silicon wafers, an essential component in semiconductor manufacturing, involves several intricate steps to ensure precision and quality. This article explores the detailed processes depicted in the provided illustration, covering both monocrystalline and...