-
0 items in quote
No products in the Quote Basket.
Blade Troubleshooting
Diamond & CBN Blade
Trouble Shooting Guide
Our illustrated troubleshooting guide was designed to help you optimize your cutting operations. It assists in diagnosing most possible issues that may arise when using precision and ultra-thin diamond & CBN cutting blades. This guide highlights the signs to watch out for, their potential causes, their impact on cutting performance, and recommended solutions for resolving these issues and preventing them in the first place. Additionally, please be sure to explore our KNOWLEDGE CENTER articles. You can also contact our technical support for further assistance.
Diamond Section Glazed Over
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Surface of diamond section is smooth with no visible signs of diamond protruding from bond matrix.
Diamond crystal are too friable
Blade slow down and eventually stops cutting
Make sure the RPM's Recommended for that specific diamond blade you are using.
Bond Matrix is too hard
Blade & material overheats
Use a dressing stick mode from aluminum code or silicon carbide to dress the blade ( sharpen diamonds / expose diamond layer )
Cutting speed is too high
Possible Material Deformation
Cut into dressing stock 10 to 20 times. or as much as necessary. until blade starts near same speed as when it was new.
Cutting speed is too low
Possible Material burning, chipping, cracking
Increase RPM ( speed )
Insufficient coolant flow to cutting zone ( reaching this cutting area }
Possible diamond section breakage
improper blade specification. Diamond concentration, mesh size, and bond hardness in inappropriate for material being out. Use different blade with right bond type, hardness, concentration and gift size for material being cut. contact us for recommendation.
Inappropriate blade specification for the application
Possible Loss of blade
Over Exposed Diamond Crystals
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Bond Matrix wears away before the diamond crystals. There is insufficient amount of bond matrix to support the over exposed diamond crystals on the cutting edge face. Hence the diamond crystals are released from the bond matrix prematurely resulting in low blade life. There is visible amount of diamond crystal pullout at cutting edge.
Diamond Bond is too Soft for the Application
Blade Cuts very bad
Reduce Feed Rate or Reduce RPM's
Inappropiate Blade Specification
Super bad blade wear
Change Blade Specification
Diamond Crystal Type, shape, coating inappropi- ate for the material being cut
Very Short Blade Life
User Harder Bond Matrix
Feed Rate / Lead is too high for the RPM's used
Inconsistent Cutting Performance
Excessive Premature Diamond Loss
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Diamond section show signs of high amount of lost diamond crystal from the bond matrix.
Diamond type, grade, shape, hardness, coating in inappropiate for the Blade Specification
Blade Cuts very fast
Use different blade with right bond type, hardness, concentration and grit size for material being cut. Contact us for recommendation
Feed rate is too high for the application
Fast Blade wear
Reduce Feed Rate or Reduce RPM's
Excessive amount of Horse Power of the cutting machine is used
Short Blade Life
Change Blade Specification
Bond Hardness too soft for the application
Inconsistent Cutting Performance
Use Harder Bond Matrix
Incorrect RPM's [too high or too low for the application]
Possible Material Scratches
Possible Material Deformation
Slow Cutting Speeds
Power Inefficiency
Crushed Diamond Crystals
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Diamond crystals in bond show signs of high amount of fracture. Diamond crushed at the matrix level. There is no protrusion, diamond crystal has lost its cutting properties.
Diamond type is too Friable
Blade Cuts very fast
Use Correct RPM's [not too high and not too low]
Diamond Particles are too large or blocky
Fast Blade wear
Use Correct Blade Specification
Excessive blade pound- ing or vibration
Short Blade Life
Reduce Feed Rate
Inappropiate blade mounting
Inconsistent Cutting Performance
Optimize Coolant Flow & Application
Flanges wear, unclear flanges, or material particles providing uneven mounting of blade
Slow cutting speeds
Worn out arbor or bearings
Chipping
Incorrect Material Fixturing / Holding Method
Host generation & stress to material
Inappropriate Bond Hardness or Blade Specification
Possible material deformation
Loss of output & Effciency
Diamond Crystal Premature Loss Of Sharp Point
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Diamond crystal premature glazing (loss of sharp point) and poor exposure from the bond matrix.
Diamond Crystal too high. Impact resistance
Inconsistent cutting speed
Use Finer (smaller) Diamond Grit Size
Diamond Crystal too large. for the application
Inconsistent cutting performane
Use lower Diamond Concentration Blade
Diamond Concentration is too high for the application
Blade & Material overheating
Dress the Blade when needed and periodically to maintain optimum diamond crystal exposure
RPM's are too low or too high
Possible material chipping & burning
Use the Right Cutting Equipment that has sufficient HP motor
Cutting machine has insufficient Horse Power for diamond crystal to have enough force to grind into the material
Possible diamond section breakage
Use Correct RPM's (not too high and not too low)
Insufficient amount of coolant is reaching the cutting
Possible loss of blade tension & flatness
Optimize Coolant:
Check to see if sufficient amount of coolant in reaching the cutting zone.
- Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned, positioned, and enough coolant velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
- Make sure you are Using Optimum Coolant for the Application [check mix ratio, and condition of the coolant to make sure it is properly being filtered and change when and if needed]
Inappropiate Coolant Used for the Application
Blade is not periodically Dressed when needed or incorrectly dressed
Inappropriate Blade Specification for the Application
Excessive amount of Material [Swarf Particles in Coolant]
Blade Wobble
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Blade flexing while cutting (not cutting straight).
Flange diameter too small for the blade diameter and thickness
Excessive Chipping
Make sure the size of flanges on your cutting machine are appropiate for use which blade diameter and thickness you are using.
Too much blade exposure for size and dimension of material you are cutting
Irregular kerf width
Make sure the exposure of blade is appropiate for size and dimension of material you are cutting.
Insufficient coolant supply to cutting zone
Possible Blade Breakage
Increase size of your saw flanges by using diamond wheel stiffeners.
Cutting Saw is missaligned or blade not properly installed
Possible damage to holding fixture
If blade is dished send to us to flatten or purchase new diamond wheel.
Possibly the blade was mishandled prior to mounting
Check condition of your saw to make sure it is not out of order or parts need replacement.
Excessive Feed Rate and / or RPM's
Make sure the RPM's and feed rate is appropriate for the application.
Not Appropiate Blade Specification selected for Application
Make sure the blade specification is appropiate for the application.
Material not properly secured / fixtured
Make sure the material is properly secured in appropiate material holding fixture and does not move.
Blade Lost Its Tension/Flatness
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Blade not completely flat while placed against flat surface.
Not sufficient coolant amount
Blade can no longer be used
Minimize Blade Exposure
Blade not properly mounted
Chipping
Use a thicker blade if possible
Inappropiate blade Specification
Not Straight Cut
Optimize the mounting to minimize vibration and blade loading
Inappropiate RPM's of Feed Rate
Wider Kerf Width
Optimize the coolant flow & application
Material not properly secured
Possible Material Deformation
Optimize the cutting parameters to minimize loads
Not following recommended dressing process
Possible Blade Breakage
Check the RPM's to make sure they are not too high or too low
Too High Blade Exposure
Process Inconsistency
Make sure the material to properly secured / fixtured and doesnot move while cutting
Bond Hardness too High
Loss of Productivity
Reduce Feed Rate
Diamond Crystal Size too Small
Higher Cutting Cost
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Broken Diamond Section
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Diamond Section Breaks and flies off while cutting.
Improper blade dressing
Possible damage to material
Use a mechanical dressing fixture
Insufficient clamping of specimen
Possible injury to operator or surrounding environment
Secure specimen with a rubber pad
Too high on initial load / feed rate
Process Inconsistency
Reduce initial loading to not cutting kerf
Material Not Properly Secured and shifting/ moving while cutting
Higher process cost
Distribute Coolant Evenly
Too high Blade Exposure
Check the flange condition
Incorrect Blade Specification
Minimize Blade Exposure
Blade Incorrectly Mounted
Check the saw axis movement x & y if applicable
Burn on Flanges
Try a lower Diamond cone to minimize loads
Incorrect RPM's for the Application
Use a thicker blade if possible
Coolant not effectively or insufficiency reaching the cutting zone
Optimize the mounting to minimize vibration and blade loading
Cutting Saw Out of Condition / Not well Maintained
Optimize the coolant flow & application
Optimize the cutting parameters to minimize loads
Dress the Blade When Needed
Check the RPM's to make sure they are not too high or too low
Make sure the material is properly secured / fixtured and does not move while cutting
Check condition of machine and spindle to make sure it is not out of alignment or have excessive run out / vibration while cutting
Crack In Dimond Section
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Visible Crack in Diamond Section, or changed in cutting sound/ or sharp change in cutting performance.
Incorrect RPM's (too high or too low)
Blade diamond section Breakage
Check the RPM's to make sure they are not too high or too low
Too High Feed Rate
Possible damage to material
Reduce Feed Rate
Coolant not effectively or insufficiency reaching the cutting zone
Possibly injury to operator or surrounding environment
Optimize Coolant:
Check to see if sufficient amount of coolant in reaching the cutting zone.
- Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned, positioned, and enough coolant velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
- Make sure you are Using Optimum Coolant for the Application [check mix ratio, and condition of the coolant to make sure it is properly being filtered and change when and if needed]
Process Inconsistency
Loss of Productivity
Higher Cutting Cost
Nick Of Diamond Section Chipped Out
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Piece of Diamond Section visibly chipped out for the blade kerf.
Material Not Correctly Clamped / Fixtured in vice / chuck
Blade will not be safe to use (and should be discarded)
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Incorrect Matenal Holding Fixture
Check Condition of Spindle and its Runout
Material Moving while Cutting
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Incorrect RPM'S
Optimized the coolant :
- Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
- Optimize the cooling flow
Too Rah Feed Rate
Make Sure Blade Is Properly Mounted
Coolant not reaching cutting zone
Check the Condition of Cutting Machine
Minimize Vibrationte
Check to make sure the blade Is properly mounted and spindle is aligned and does not vibrate
Over Heated Blade
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Diamond Section Discoloration tension and possible of blade core.
RPM's too fast for Inn application
Possible Chipping
Check the RPM's to make sure they are not too high or too low
RPM's too low for the application
Possible materiel deformation
Reduce Feed Rate
Feed rate too high for the application
Process Inconsistency & Insufficiency
Use Optimum Blade Specification Optimize Coolant:
Insufficient coolant amount reaching cutting zone
Premature blade failure
Optimized the coolant :
- Check to see it sufficient amount of coolant is reaching the cutting zone
- Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned. positioned, and enough cadent velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
Inappropiate blade specification
Lost money in using more blades that needed for operation
Excessive Blade Wear
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Diamond Section Wearing in a very short period of time.
Inappropiate blade specification for the application
Loss of time in having to stop operations and change blades
Optimized the coolant:
Use different blade with right bond type. hardness, concentration and grit size for material being cat. Contact us for recommendation.
- Try Larger (Coarser) Diamond Size
- Try Harder Bond Matrix
- Try Higher Diamond Concentration
- Optimize the Diamond Type or Coating
- If possible, try thicker blade
- If possible, try a mounted or side grooved blade
- Try Different Bond Type
Insufficient amount of coolant is reaching the cutting zone
Process inconsistency & Inefficiency
Optimize Coolant:
Check to see if sufficient amount of coolant in reaching the cutting zone.
- Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned, positioned, and enough coolant velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
- Make sure you are Using Optimum Coolant for the Application [check mix ratio, and condition of the coolant to make sure it is properly being filtered and change when and if needed]
Inappropiate blade diameter and / or thickness for size and dimensions of material you are cutting
Lost Money in high blade cost
Optimize the Blade RPM's 8 Feed Rate:
- Higher RPM's acts like a harder blade matrix
- Higher feed rate increases loading and wear
Bond hardness too soft tot the application
Proper Maintenance For Blade 8 Equipment :
- Make sure the blade is dressed when needed (recommended pre set process and also as needed)
- Cutting equipment is properly and maintained (along with spindle and flanges)
Diamond concentration, Mesh size is inappropiate for material being cut
Incorrect RPM's and / or Feed Rate
Not Using Correct Coolant or Coolant Not Adequately Reach-ing Cutting Zone
Not Dessing Blade When Needed and / or Poor Equipment Maintenance
One Sided Chipping
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Chipping on only one side of the Kerf.
Coolant nozzles are not possIttoned property
Poor Cut Quality! Surface Finish
Check Alignment and runout of the saw spindle
Saw spindle is misaligned
Secondary Finishing Operatioans may be required to remove the damage caused
Check Positioning of the material and make sure it Is evenly hold down and secure
Material / wafer is not parallel to the spindle axis
Process Inconsistency
Check Condition of the saw flanges (clean and repair if necessary)
The flanges need cleaning
Loss of Productivity
Make Sure to Dress the Blade when and if necessary
Flanges require lapping
Higher Cutting Costs
Align Coolant Nozzles to make sure optimum amount of coolant is reaching cutting zone at best angle possible.
Use of hubless blades
Scrap Parts
Use synthetic water soluble coolant to reduce surface denslon, provide additional lubrication, reduce heat generation
Consistency Spaced Chipping
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Consistency Spaced Chipping on edge of the cut.
lnproper blade dressing
Poor Cut Quality! Surface Finish
Make Sure to Dress the Blade when and if necessary
Insufficient or Improper blade dressing
Secondary Finishing Operatioans may be required to remove the damage caused
Make Sure there is sufficient Blade Exposure just to cut the desired material thickness
Insufficient blade exposure
Process Inconsistency
Make Sure the RPMS and Feed Rate is optimized for the Application
Insufficient amount of coolant is reaching the cuffing zone
Loss of Productivity
Align Coolant Nozzles to make sure optimum amount of coolant is reaching cutting zone at best angle possible
Loss of Productivity
Use synthetic water soluble coolant to reduce surface dension. provide additional lubrication, reduce heat generation
Higher Cutting Costs
Scrap Parts
Excessive Backside Chipping
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Excessive & Visible Backside Chipping on back side of Material.
Substrate or wafer was incorrectly mounted on tape
Poor Cut Quality! Surface Finish
Use substrate and bond to wax to support material
Excessive air bubble between tape and material
Secondary Finishing Operatioans may be required to remove the damage caused
Optimize the feed rate / spindle RPM
Blade is cutting too deep Into the mounting media
Process Inconsistency
Dress the blade to minimize loading
Incorrect diamond size was selected
Loss of Productivity
Use Finer Size Diamond Crystal
Feed rate is too high
Higher Cutting Costs
Reduce Blade Exposure
Blade is worn and requires replacing
Scrap Parts
Use Optimum Malarial Holding Method
Coolant injections are misaligned
Align Coolant Nozzles to make sure optimum amount of coolant is reaching cutting zone at best angle possible
Blade exposure is too great
Use synthetic water soluble coolant to reduce surface tension, provide additional lubrication, reduce heat generation
Insufficient vacuum
If using vacuum chuck, make sure its optimum condition and enough force is used to keep the thin material [wafer or substrade in place]
Vacuum chuck requires resurfacing
Make sure the matedal Is properly mounted and there are no air gaps between material and substrate its mounted
Incorrect mounting media was selected
Blade was not properly dressed
Bottom Side Chipping
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Stress at bottom surface of material caused by the diamond fracture when exiting the cut can cause bottom chipping.
Higher temperature in bottom due insufficient amount Of coolant reaching the cueing zone
Poor Cut Quality! Surface Finish
Use Substrate and bond to was to support material
Material is not mounted ideally flat in holding lecture or by holding method
Secondary Finishing Operatioans may be required to remove the damage caused
Optimize the feed rate / spindle RPM
Possible air gaps between material and holding fixture
Process Inconsistency
Dress the blade to minimize loading
Unsupported fragile Material when mounted
Loss of Productivity
Add additives to the coolant to lower the surface tension of the coolant
Not Cutting into the mounted supporting material
Higher Cutting Costs
Optimize the diamond concentration to minimize the blade edge radius
Not Reducing the Feed Rate / Load when easing the cut
Scrap Parts
Use a higher wear bond to minimize loading
Use the thinnest blade possible to Minimize the radius on the blade edge
Adjust the cooling noozle and minimize the flow to reduce blade vibrations
Top Side Chipping
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Cracks similar in size with some slightly larger chipping along the edges.
Diamond crystals too coarse for the application
Poor Cut Quality! Surface Finish
Use smaller size diamond crystal
Feed rate too high
Secondary Finishing Operatioans may be required to remove the damage caused
Use different type of diamond crystal (such as uncoated)
Insufficient amount of coolant reaching the cutting zone
Process Inconsistency
Optimize the diamond concentration
Vibration of spindle or machine
Loss of Productivity
Try Softer Bond Matrix
Inapproppiate material mounting that causes material to move while cutting
Higher Cutting Costs
Try More Softer Bond Type
Excessive blade exposure
Scrap Parts
Minimize vibration
Insufficient blade exposure
Check to make sure the blade is properly mounted and spindle is aligned and does not vibrate
Incorrect diamond mesh size
Use optimum blade RPM'S
Blade is worn out
Make sure the material is mounted correctly. supported and does not move while cutting
Excessive feed rate
Minimize Blade Exposure
Material Is not parallel to spindle
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle now
Flanges need cleaning
Viewing optics are realigned with saw spindle
Material Micro Cracks
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution
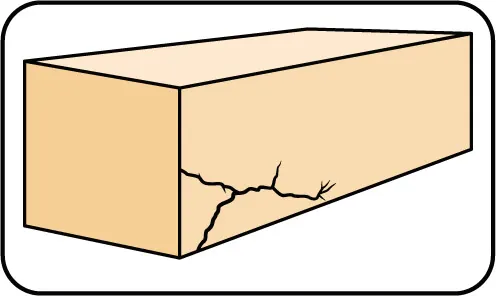
Signs: Fracture in brittle materials & materials with different phases. Usually results when energy used to cut material is more than can be assorted by material.
Inappropriate blade specification used
Possible Material Breakage
Optimized the coolant :
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle flow
- Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned. positioned, and enough coolant velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
- Make sure you are Using Optimum Coolant for the Application [check mix ratio, and condition of the coolant to make sure it is properly being filtered and change when and d needed)
Feed rate too high
Possible Material Deformation
Minimize Blade Exposure
Insufficient or incorrect clamping / fixtuting of the material
Possible Material I Part Hidden Detect
Use Different Blade Specification
Insufficient amount of coolant reaching cutting zone
Material Losses its Strength I Integrity
Use Optimum Blade RPM'S
RPM's too low or too high for the application
Use Optimum Feed Rate
Incorrect Blade Exposure
Too High Cut depth In Constation to Blade Thickness
Too High Cutting Speed
Material Not Correctly Supported
Material Pull Out
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Cavities in material that are left after the grains or particle of material are torn out of the material during cutting. This mainly applies for hard or brittle material only.
Excessive heat and stress caused by inaPProninle cutting methods
Possible Material Deformation
Use Correct Blade Specification
Inappropriate blade specification used
Possible Material Breakage
Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned. positioned, and enough coolant velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
RPM's too low or too high for the application
Possible Material / Part Hidden Detect
Use Optimum Blade RPM's
Insufficient support of material in the clamping / fixturing process
Material Losses its Strength/ Integrity
Use Optimum Feed Rate
Insufficient amount of coolant reaching cutting zone
Material Smearing
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Instead of material being cut it is pushed and moved across the surface.
Insufficient amount of coolant reaching cutting zone
Possible Maternal Deformation
Use Correct Blade Specification
Inappropiate blade specification used [diamond grit sae typically is too fine]
Possible Material / Pan Hidden Detect
Use Optimum Blade RPM'S
RPM's too low or to high for the application
Secondary Finishing Operations may be required to remove the damage caused
Use Optimum Feed Rate
Bond Hardness to Hard
Use Softer Bond Matrix Blade
Feed Rate too High
Try Different Bond Type
Incorrect Bond Type
Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned, positioned, and enough coolant velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
Material Scratches
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

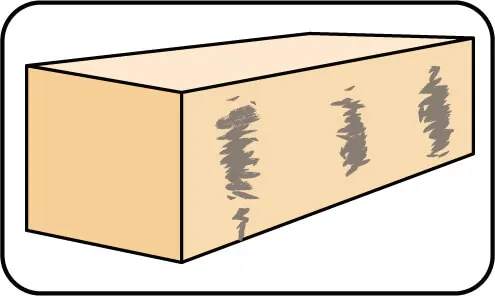
Signs: Grooves on the surface of the material typically produced by diamond crystals or material swarf abrasive particles.
Material swan abrasive particles trapped on surface of material that are not flushed away by coolant
Possible Material Deformation
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle flow
Polluted coolant, possible time to change the coolant
Possible Material / Part Hidden Detect
Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned, positioned, and enough coolant velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
Insufficient amount of coolaant reaching cutting zone
Secondary Finishing Operations may be required to remove the damage caused
Make sure you are Using Optimum Coolant for the Application [check mix ratio, and condition of the coolant to make sure it is propedy being filtered and change when and if needed]
Inappropriate blade specification
Use Coned Blade Specification
Material Burning
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

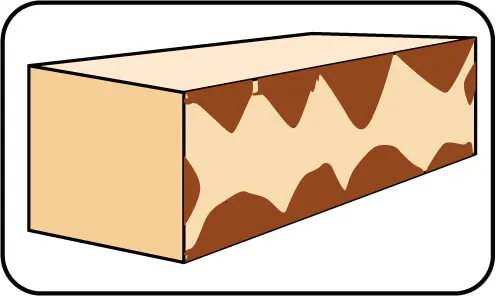
Signs: Small pieces of material debris at edges of cut kerf caused from the stress of the diamond micro fracture process.
Incorrect blade specification / diamond size
Poor Cut Quality / Surface Finish
Optimize Blade Specification :
Use different blade with right bond type. hardness, concentration and grit size for material being cut. Contact us for recommendation.
Incorrect RPM's
Secondary Finishing Operations may be required to remove the damage caused
Check the RPM's to Make sure they are not too high or too low
Incurred feed rate
Process Inconsistency
Reduce Feed Rate
Incorrect material mounting
Loss of Productivity
Optimize Coolant :
Check to see if sufficient amount of coolant in reaching the cutting zone
- Make sure coolant nozzle are properly aligned. positioned. and enough coolant velocity to provide optimum flow of coolant into cutting zone
- Make sure you are Using Optimum Coolant for the Application [check mix ratio, and condition of the coolant to make sure it is properly being filtered and change when and it needed]
Insufficient amount of coolant reaching cutting zone
Higher Cutting Costs
Scrap Parts
Possible Material Deformation
Possible Material / Pan Hidden Detect
Shell Type Chipping
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Mainly occurs in brittle materials, material breaks off in a shell shape. Usually these chips are large and similar to shell shape.
Diamond crystals too coarse for the application
Poor Cut Quality Surface Finish
Use smaller size diamond crystal
Feed rate too high
Secondary Finishing Operations may be required to remove the damage caused
Use different type of diamond crystal (such as uncoated)
Insufficient amount of coolant reaching the cutting zone
Process Inconsistency
Optimize the diamond concentration
Vibration of spindle or machine
Loss of Productivity
Try Softer Bond Matrix
Inappropriate material mounting that causes a 'needle! to move while cutting
Higher Cutting Costs
Try More Softer Bond Type
Excessive blade exposure
Scrap Parts
Minimize vibration
Insufficient blade exposure
Possible Material Deformation
Check to make sure the blade is property mounted and spindle Is aligned and does not vibrate
Incorrect diamond mesh size
Use optimum blade RPM'S
Blade is worn out
Make sure the material is mounted correctly, supported and does not move while cutting
Excessive feed rate
Minimize Blade Exposure
Insufficient supply of coolant in cutting zone
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle flow
Incorrect mounting
Incorrect speed ( RPM's )
Spindle is missaligned
Blade requires dressing
Material is not parallel to spindle
Flanges need lapping
Flanges need cleaning
Viewing optics are misaligned with saw spindle
Slanted Cut At The Kerf
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Uneven Kerf.
Excessive blade exposure
Not Straight Cut
Minimize Blade Exposure
Not Proper Blade Diameter
Blade Losses In Tension Flatness
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle low
Blade too Thin for the Cutting Depth
Possible Blade Breakage
Try Using Larger Blade Diameter
Feed Rate too High
Blade Stops Cutting
Try Using Thicker Kerf Blade
Incorrect RPM's [too high or too low for the application
Process Inconsistency
Use correct RPM's
Excessive Coolant Velocity 8 Incorrect Nozzle Positioning
Loss of Productivity
Reduce Feed Rate
Incorrect Blade Specification
Higher Cutting Costs
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Check Condition of Spindle and its Runout
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Wider Cut At The Top
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Wider Kerf thickness at cut entrance.
Blade Lost its Kerf Edge Forrn
Not Straight Cut
Use Optimum Blade specification
Uneven Blade Wear
Process Inconsistency
Change Bond Matrix Hardness
Incorrect Blade Specification
Loss of Productivity
Change Bond Type
Bond Hardness too Hard
Higher Cutting Costs
Too High Diamond Concentration
Wider Cut At Top On One Side Or Both Sides
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Blade Lost its Kerf Edge Forrn
Larger Cut Width
Minimize Blade Exposure
Uneven Blade Wear
Process Inconsistency
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle flow
Incorrect Blade Specification
Loss of Productivity
Try Using Larger Blade Diameter
Bond Hardness too Hard
Higher Cutting Costs
Try Using Thicker Kerf Blade
Too High Diamond Concentration
Scarp Parts
Use Correct RPM's
Possible Material Deformation
Reduce Feed Rate
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Check Condition of Spindle and its Runout
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Lip Effect At Bottom Side
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Blade not cutting all the way through the material and supporting substrate
Larger Cut Width
Minimize Blade Exposure
Blade Lost ils Ken Edge Form
Process Inconsistency
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle flow
Uneven Blade Wear
Loss of Productivity
Try Using Larger Blade Diameter
Incorrect Blade Specification
Higher Cutting Costs
Try Using Thicker Kerf Blade
Bond Hardness too Hard
Scarp Parts
Use Correct RPM's
Too High Diamond Concentration
Possible Material Deformation
Reduce Feed Rate
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Check Condition of Spindle and its Runout
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Asymmetric Chamfer On One Or Both Sides
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Blade Lost ds Ken Edge Form
Larger Cut Width
Minimize Blade Exposure
Uneven Blade Wear
Process Inconsistency
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle flow
Incorrect Blade Specification
Loss of Productivity
Try Using Larger Blade Diameter
Bond Hardness too Hard
Higher Cutting Costs
Try Using Thicker Kerf Blade
Too High Diamond Concentration
Use Correct RPM's
Reduce Feed Rate
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Check Condition of Spindle and its Runout
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Wavy Cut
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution
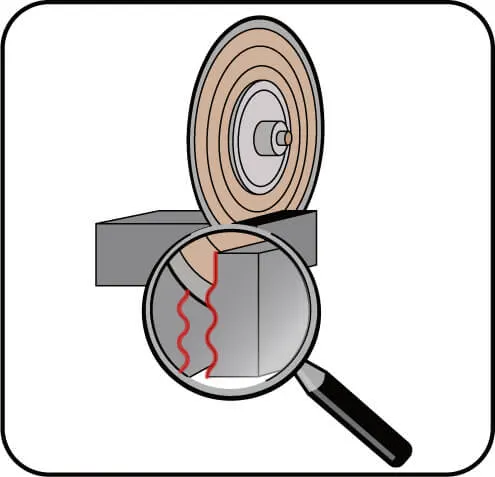

Signs: Uneven, wavy kerf (not starlight cut).
Excessive blade exposure
Possible Chipping
Minimize Blade Exposure
Blade Lost Tension
Larger Cut Width
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle flow
Spindle Vibration
Not Straight Cut
Try Using Larger Blade Diameter
Incorrect Blade Specification
Process Inconsistency
Try Using Thicker Kerf Blade
Feed Rate too High
Loss of Productivity
Use Correct RPM's
Incorrect RPM's Roo high or too low for the application]
Higher Cutting Costs
Reduce Feed Rate
Insufficient Amount of Coolant Reaching Cutting Zone
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Excessive Coolant Veloclt) & Incorrect Nozzle Positioning
Check Condition of Spindle and Its Runout
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Try Using Coarser (larger) size diamond crystal
Wider Cut At The Entrance Or Exit Of Cut
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Signs: Wider kerf at entrance and exit of the cut.
Incorrect feed rate (in and out)
Possible Chipping
User proper feed rate for the application
Spindle vibration
Larger Cut Width
Check condition of spindle and its runout
Not Straight Cut
Process Inconsistency
Loss of Productivity
Higher Cutting Costs
Flange Overtightning
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Overnighting the flange cause deflection of the flange, which in turn causes blade wobbing.
Operator overnight in monitoring the cutting operation
Blade cuts off track(wanders)
User proper torque in not to poor or under tighten the flange
Wide Kerf
Process Inconsistency
Possible flange damage
Possible Chipping
Possible material Deformation
Nick On Flange Edge
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Scratch on nick on flange causes improper blade mounting.
Piece of Material Swart! Debris left on inside surface of the flange
Cuts off track (blade wanders)
Check to make sure flanges are flat
Dropping or hitting the Flange while mounting or during use
Wide Kerf
Check to make sure flanges are clean
Failure to periodically clean and maintain the flange
Process Inconsistency
Make sure proper torque not to over or undertighten flanges
Operator overnight In monitoring the cutting operation
Possible blade shattering and breakage
Replace flanges that may damage or worn out
Slanted cuts
More Chipping
Loss On Kerf Edge / Geometry
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Loss of Blade Radius.
Incorrect Blade Mounting
Possible Chipping
Check condition of Mounting Flanges
Spindle Run Out
Larger Cut Width
Check condition of spindle and its Runout
Worn Out Spindle
Not Straight Cut
Make sure blade is properly Mounted
Worn Out or Damaged Flanges
Process Inconsistency
Defect on Back Side of Flange
Loss of Productivity
Material Not Correctly Clamped! Fixtured in Vice / Chuck
Higher Cutting Costs
Possible Blade Breakage
Excessive Blade Exposure
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Excessive Blade Vibration, not straight cut loss of blade tension and possible blade breakage.
Flange Size to small for the material being cut
Possible Chipping
Adjust the cooling nozzle & the coolant flow
Too High Feed Rate
Possible Blade Breakage
Check me option of using a thicker blade
Incorrect Blade Mounting
Larger Cut Width
Reduce feed rate and f or increase the RPM
Spindle Run Out
Not Straight Cut
Use specialized water soluble coolant
Worn Out Spindle
Short Blade Life
Optimize the blade to minimize loads
Worn Out or Damaged Flanges
Poor Cut Quality / Surface Finish
Use a Lower diamond concentration
Defect on Back Side of Flange
Optimize the diamond size
Material Not Correctly Clamped / Fixtured
Use seraled blades to minimize the loading
Material Moving white Cutting
Improve the mounting method
Incorrect Blade Specification
Slow down the feed rate to minimize the load
Add coolant additives to minimize the load
Material Overheating
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

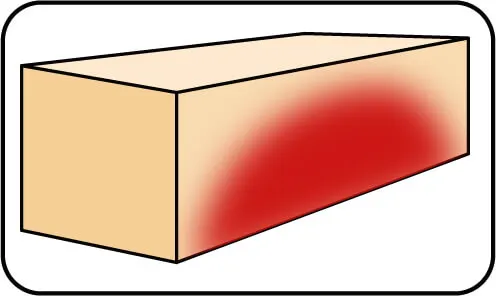
Signs: Discoloration of the cut surface.
Incorrect Coolant or Mix Ratio Used
Possible Chipping
Optimized the coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the coding flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant d possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Inadequate amount of coolant reaching cutting zone
Possible Material Micro Cracking
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Incorrect RPM'S for the Application
Possible Material Deformation
Use Correct RPM's
Too High Feed Rate
Possible Material Change Properties I Structure
Reduce Feed Rate
Incorrect Blade Specification
Material Saw / Vibration
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Spindle or Blade Vibration.
Small flange diameter is the largest cause of blade vibration
Possible Chipping
Change Blade tension
Larger Cut Width
Slow Down Feed Rate
Not Straigh Cut
Check Saw Shaft. It may be worn out
Process Inconsistency
Check Flange 'lightness, lack of tightness causes vibration
Loss of productivity
Make sure your saw does not vibrate
Higher Cutting costs
Make sure your material is securely held in place
Make sure your material is securely held in place
When blade speed slows down. proceed to dress
Improper Blade Fixturing /Material Holding
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Chipping, Material Breakage & Process Inconsistency.
Incorrect Material Mounting
Possible Chipping
Make sure your material is securely held in place
Not Supporting Material Underneath
Larger Cut Width
Support Material by bond to Sacrifficial substrate made from glass. ceramic, or graphite
Possible Air Gap from Wax Mounting
Not Straigh Cut
Make Sure there are no air gaps undemeath
Material Moving while Cutting
Process Inconsistency
Use beet material holding method for the material type, shape, and dimensions
Loss of productivity
Higher Cutting costs
Possible Blade Breakage
Blade Gummed Up
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Material Swarf Particles Smeared Over Diamond Section of the blade Causing Slower Cutting Speeds, Inconsistent Performance & large variety of possible issues.
Blade not being dressed properly or when needed
Blade Stops Cut-tong
Use Proper Blade Specification
Blade not being dressed properly or when needed
Blade Stops Cutting
Optimized the coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the coding flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant d possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Cutting near soft materials such as plastic
Material Burning
Use Higher RPM's
Insufficient amount of coolant maching cutting zone or cutting dry
Slow Cutting Rates
Use Coarser (Larger) Size Diamond Crystals
Inappropiate blade specification [diamond size too line, incorrect bond type]
Material Chipping and 1 or Overheating
Use Different Blade Bond Type
RPM's usually too low
Inconsistent Results
Dress the Blade to remove material swart
Possible Chipping
Possible Smearing
Possible Material Deformation
Possible Blade 8 Material Overheating
Blade Stops Cutting
Loss of Productivity
Higher Cutting Cost
Sparks Coming From Material Or Blade
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Diamond Crystal Too Fine (Small for the application)
Blade slows down and inventoally stops cutting
Make sure the RPM's recommended for the specific diamond blade you are using.
Bond Matrix is too Hard
Blade 8 Material overheats
Use a dressing stick made from alumina oxide or silicon carbide to dress the blade [sharpen diamonds / expose diamond layer].
Inappropiate Blade specification for the application
Possible Material Deformation
Cut into dressing stick 10 to 20 times. Or as much as necessary, until blade starts to out near same speed as when it was new.
Cutting Speed is too High
Possible Material burning, chipping. cracking
Indease RPM [speed].
Cutting Speed is too Low
Possible Diamond Section Breakage
Improper blade specification. Diamond Concentration, Mesh Size, and Bond Hardness is inappropiate for material being cut. Use different blade with right bond type, hardness, concentration and grit size for material being cut. Contact us for recommendation.
Insufficient Coolant Flow to cutting zone [reaching the cutting area)
Material Edges Cracking
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution


Insufficient coolant reaching cutting zone
Possible material Micro cracking
Machine Maintenance
Spindle Vibration
Possible Material Deformation
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Incorrect Blade Specification
Possible Material change properties/Structure
Check Condition of Spindle and its Roma
Material incorrectly mounted
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Blade lost its tension r flatness
Minimize Blade Exposure
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Slanted Cut Due To High Water Pressure
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Not Starlight Cuts and blade Flexing or lost Blade Tension.
Excessive Coolant Pressure
Possible Chipping
Adjust the cooling nozzle & the coolant flow
Incorrect Coolant Nozzle Positioning
Possible Blade Breakage
Check the option of using a thicker blade
Incorrect Blade Exposure
Larger Cut Width
Use Thicker Blade Kerf Thickness
Incorrect Blade Specification
Not Straight Cut
Optimize the blade to minimize loads
Short Blade Life
Use serated blades to minimize the loading
Poor Cut Quality/Surface Finish
Improve the mounting method
Slow down the feed rate to minimize the load
Uneven Diamond Section Wear
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Part of diamond section wears faster than the other causing an uneven radius on face of the blades diamond section.
Loose Blade ID
Not Straight cut
Check condition of mounting flanges
Incorrect Blade Mounting
Check condition of spindle and its runout
Spindle Run Out
Make sure blade is properly mounted
Worn Out Spindle
Worn Out of Damaged Flanges
Defect on Back Side of Flange
Broken Blade
Incorrect RPM's
Incorrect Material Holding Fixture
Material Not Correctly Clamped/ Fixtured in Vice / Chuck
Material Moving While Cutting
Undercutting Steel Core
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Steel core wears faster than diamond section caused by highly abrasive particles from material being cut grinding against blade during cutting.
Blade not being dressed properly or when needed
Blade Stops Cut-tong
Use Proper Blade Specification
Blade not being dressed properly or when needed
Blade Stops Cutting
Optimized the coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the coding flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant d possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Cutting near soft materials such as plastic
Material Burning
Use Higher RPM's
Insufficient amount of coolant maching cutting zone or cutting dry
Slow Cutting Rates
Use Coarser (Larger) Size Diamond Crystals
Inappropiate blade specification [diamond size too line, incorrect bond type]
Material Chipping and 1 or Overheating
Use Different Blade Bond Type
RPM's usually too low
Inconsistent Results
Dress the Blade to remove material swart
Possible Chipping
Possible Smearing
Possible Material Deformation
Possible Blade 8 Material Overheating
Blade Stops Cutting
Loss of Productivity
Higher Cutting Cost
Kerf Wider Than Blade Thickness
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Cutting kerf wider than the blade.
Incorrect RPM's for the application
Higher Cutting Costs
Use Correct RPM's
Too High Feed Rate
Loss of Productivity
Adjust Feed Rate
Incorrect Coolant Used
Scrap Parts
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Coolant not adequately reaching the cutting zone
Optimize the Coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the cooling flow
Blade Incorrectly Mounted
Blade & Flanges Excessive Vibration
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Blade & Flanges not running true and / or excessive noise.
Loose Blade ID
Higher Cutting Costs
Use Correct RPM's
Incorrect Blade Mounting
Loss of Productivity
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Spindle Run Out
Scrap Parts
Check Condition of Spindle and its Runout
Worn Out Spindle
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Worn Out of Damaged Flanges
Defect on Back Side of Flange
Broken Blade
Incorrect RPM's
Slow Cutting Rates
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Blade Cutting very slow (compared to normal)
Incorrect Blade Specification
Higher Cutting Costs
Optimize Blade Specification:
- Use a Larger [Coarser] Diamond Crystal
- Use a Harder Bond Matrix
- Use a Higher Diamond Concentration
- Optimize the Diamond Crystal Type
- If possible, use a Thicker Blade
- If possible, try a Serrated/ Slotted Blade
Incorrect RPM's Used
Loss of productivity
Optimize the spindle RPM & the feed rate :
- Try Higher RPM's
- Try Dressing [as short term solution to correct the issue]
Coolant no adequately reaching the cutting zone
Process Inconsistency
Optimize the Coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the cooling flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant if possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Incorrect Usage Process
Excessive Heat Generation
Incorrect Blade Exposure
Possible Chipping, Burning, Smearing
Incorrect Feed Rate
Short Blade Life
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Blades worn out in a very short period of time (compared to normal life span)
Incorrect Blade Specification
Higher Cutting Costs
Optimize Blade Specification:
- Use a Larger [Coarser] Diamond Crystal
- Use a Harder Bond Matrix
- Use a Higher Diamond Concentration
- Optimize the Diamond Crystal Type
- If possible, use a Thicker Blade
- If possible, try a Serrated/ Slotted Blade
Coolant no adequately reaching the cutting zone
Loss of productivity by having to more frequently change blade and setup
Optimize the spindle RPM & the feed rate :
- Try Higher RPM's
- Try Dressing [as short term solution to correct the issue]
Incorrect Blade Exposure
Optimize the Coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the cooling flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant if possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Incorrect Feed Rate
Incorrect RPM's Used
Incorrect Usage Process
Poor Process Consistency
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: Large variation in cutting results.
Operator Skill & Experience
Higher Cutting Costs
Optimize the Coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the cooling flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant if possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Set Up Process
Loss of Productivity
Use Correct RPM's
Condition of Equipment & Maintenance
Process Inconsistency
Reduce Feed Rate
Condition of Coolant
Excessive Heat Generation
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Coolant Flow Rate
Possible Chipping, Burning, Smearing
Check Condition of Spindle and its Runout
How Frequently Coolant is Monitored & Changed
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Dressing Frequency
Check the Condition of Cutting Machine
Material Mounting Process
Minimize Vibration
Variation in Material Specification
Check to make sure the blade is properly mounted and spindle is aligned and does not vibrate
Variation in Blade Specification or Quality
High Blade Cost (Higher Cost Per Cut)
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Signs: High Blade cost compared to normal.
Incorrect blade specification
Higher Consumables & process cost
Optimize the Coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the cooling flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant if possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Not optimum RPM's
Use optimum blade specification
Not optimum Feed rate
Use correct RPM's
Incorrect coolant used
Reduce feed rate
Process not optimized for the application
Use different type of diamond crystal ( such as uncoated )
Condition of coolant
Optimized the diamond concentration
Coolant flow rate
Try softer bond matrix
Try more softer bond type
Material Deformation
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Diamond Crystal too Coarse or Fine for the Application
Possible Chipping
Optimize the Coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the cooling flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant if possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Cutting Speed is too High
Possible Material Micro Cracking
Use optimum blade specification
Cutting Speed is too Low
Possible Material Change Properties / Structure
Use correct RPM's
Insufficient Coolant Flow to Cutting Zone (Reaching the Cutting Area)
Process Inconsistency
Reduce feed rate
Inappropriate Blade Specification for the Application
Loss of Productivity
Use different type of diamond crystal ( such as uncoated )
Higher Cutting Costs
Optimized the diamond concentration
Try softer bond matrix
Try more softer bond type
Rough Surface Finish
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Diamond Crystal too Coarse or Fine for the Application
Scrap Parts
Use smaller size diamond crystal
Cutting Speed is too High
Possible Material Change Properties / Structure
Use different type of diamond crystal [such as uncoated]
Cutting Speed is too Low
Process Inconsistency
Optimize the diamond concentration
Insufficient Coolant Flow to Cutting Zone (Reaching the Cutting Area)
Loss of Productivity
Try Softer Bond Matrix
Inappropriate Blade specification for Application
Higher Cutting Costs
Try More Softer Bond Type
Use optimum blade RPM's
Make sure the material is mounted correctly, supported and does not move while cutting
Minimize Blade Exposure
Adjust the coolant pressure and align the nozzle flow
Loss Of Productivity
Possible Cause
Affect On Cutting Performance
Solution

Diamond Crystal too Coarse or Fine for the Application
Possible Chipping, Burning, Smearing
Optimize the Coolant :
- Align the cooling noozle
- Optimize the cooling flow
- Use specialized water soluble coolant if possible
- On deep cuts try a high cooling flange
Cutting Speed is too High
Larger Cut Width
Use Optimum Blade Specification
Cutting Speed is too Low
Not Straight Cut
Use Correct RPM's
Insufficient Coolant Flow to Cutting Zone (Reaching the Cutting Area)
Process Inconsistency
Reduce Feed Rate
Inappropriate Blade specification for Application
Loss of Productivity
Use different type of diamond crystal [such as uncoated]
Operator Oversight in monitoring the cutting operation
Higher Cutting Cost
Optimize the diamond concentration
Failure to Maintain Equipment, Spindle, and Flanges
High Blade Load
Try Softer Bond Matrix
Spindle Vibration
Possible Blade Breakage
Try More Softer Bond Type
Incorrect Coolant or Mix Ration Used
Scrap Parts
Check Condition of Mounting Flanges
Excessive Host Generation
Check Condition of Spindle and its Runout
Possible Chipping, Burning, Smearing
Make Sure Blade is Properly Mounted
Check the Condition of Cutting Machine
Minimize vibration
Check to make sure the blade is properly mounted and spindle is aligned and does not vibrate

ARE YOU USING RIGHT DIAMOND & CBN BLADES
FOR YOUR APPLICATION?
LET US
HELP YOU
HAVING ISSUES WITH
YOUR CURRENT DIAMOND & CBN BLADES?
02
Jun
Selecting the right parameters for your Precision & Ultra Thin Diamond Blade can be a very time consuming, trial & error frustrating process. The guide below has been designed to help you better understand...
02
Jun
How to Properly Use Precision Diamond & CBN Blades
The diamond blade itself is only a small factor in your cutting operation. Successful diamond sawing is both an art & science. Requiring proper use and understanding of the right: RPM's, Coolants, Equipment, Dressing Devices, Accessories...
02
Jun
Precision & Ultra Thin Diamond Blade Guide
Diamond and CBN blades are available in an extensive array of varieties, each differing in bond types, manufacturing methods, and design specifics. Ultra Thin & High Precision Diamond Blades are particularly versatile, applicable...
02
Jun
How to Improve & Optimize Your Diamond Sawing Operation
There are numerous variables that affect the performance of diamond and CBN cutting blades. Understanding these variables will help end users select the right diamond blade specifications for their applications and optimize their...
02
Jun
Evaluating & Comparing Diamond Blades
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Proper testing procedures and methodologies must be set up and used to obtain accurate as well as repeatable testing results. This article will discuss several simple procedures which...
31
Jul
Top 5 Diamond & CBN Cutting Blade Performance Metrics
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
When evaluating diamond and cubic boron nitride (CBN) cutting blades, it's crucial to consider key performance metrics and criteria. Different applications have varying goals, making it...
01
Aug
Diamond & CBN Cutting Blade Performance Metrics that you Should Know
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
When evaluating diamond and cubic boron nitride (CBN) cutting blades, it's crucial to consider key performance metrics and criteria. Different applications have varying goals, making it important to...
02
Aug
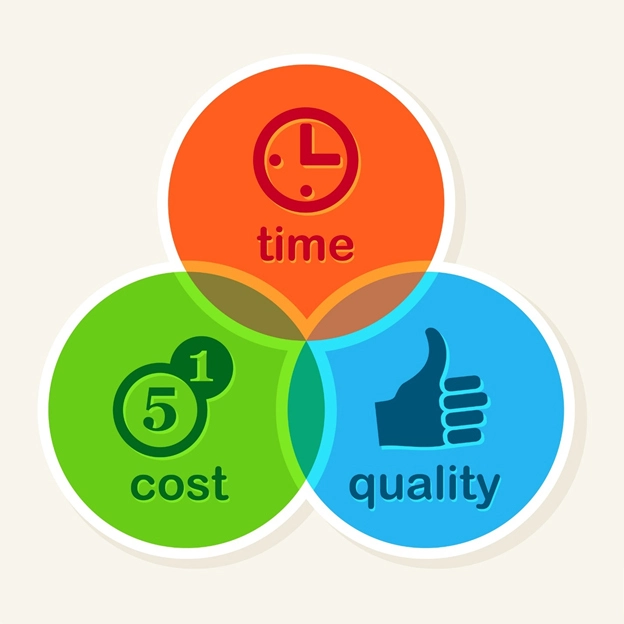
Total Cost of Ownership & Why its Important
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Diamond and CBN cutting blades are available in a myriad of specifications, with virtually limitless options. The industry is saturated with numerous manufacturers, each professing to offer the...
05
Aug
Understanding Tradeoffs- Searching for Perfect Diamond & CBN Blade
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
Choosing the right blade diamond or cbn blade can significantly impact efficiency, cost, and quality. However, this is not simple and clear cut process. Selecting the optimal blade...