Menu
No products in the Quote Basket.
9 am to 6 pm PST time
No products in the Quote Basket.
The 1A1 wheel shape is one of the most common and straightforward wheel shapes used in grinding and cutting applications.The 1A1 diamond wheel shape is a flat, straight-edged wheel with a concentric circle design, where the abrasive diamond particles are embedded in the perimeter of the wheel.
APPLICATION FOR 1A1 DIAMOND & CBN WHEELS
Applications: Flute Grinding, Surface Grinding, OD Grinding, Knife Grinding, Profile Grinding, Centerless Grinding, Sharpening & Finishing Carbide Tools, Machining Conical, Cylindrical & Flat Surfaces & Conical Apertures
Bond Availability: Resin Bond, Sintered (Metal Bond), Hybrid Bond, Nickel Bond (Plated), Braised Bond, Vitrified Bond
Available in: Diamond, CBN
Core Materials: Aluminum, Steel, composite, sintered, abrasive
Size Availability: 1″ (25.4mm) – 27″ (685mm)Diamond Sizes:
Diamond Grit Sizes: 25 mesh to 3 microns
Diamond Concentration: low, medium & high (from 10 con to 150 con)
Tolerances:
Standard Lead Times: 4 to 5 weeks.
Expedited lead time of 1to 2 weeks is also available at additional cost
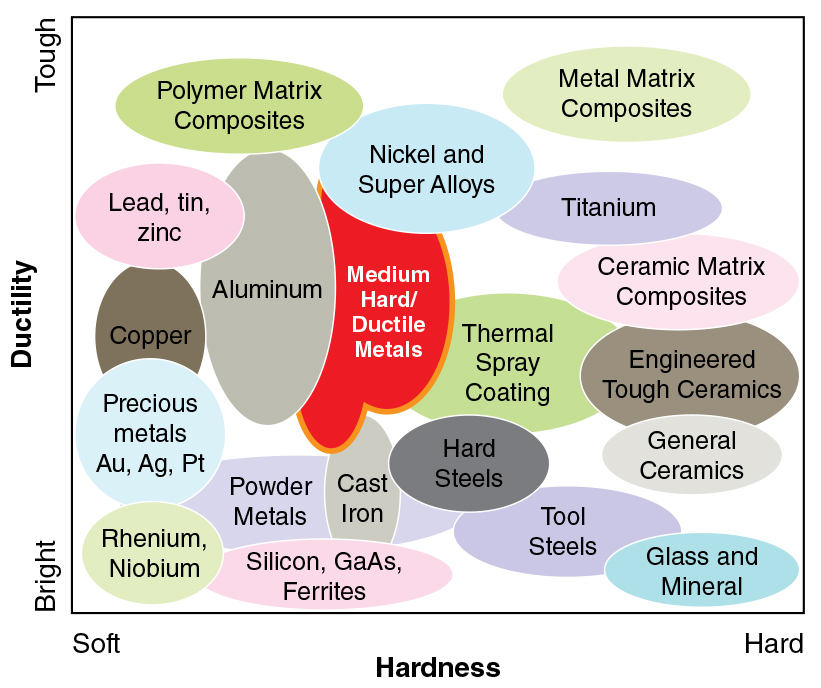

INDUSTRIES USED IN:

Ferrous & Non-Ferrous Metals:
1A1 diamond wheel is a type of grinding wheel with a flat, straight-edged shape and abrasive diamond particles embedded in the perimeter.
1A1 diamond wheel is suitable for grinding hard materials such as carbide, glass, ceramics, and other hard-to-grind materials.
Common applications include surface grinding, tool and cutter grinding, carbide grinding, glass and ceramic grinding, and sharpening.
Typical tolerances include diameter tolerance of ±0.005 to ±0.02 inches, thickness tolerance of ±0.005 to ±0.02 inches, and bore diameter tolerance of ±0.0005 to ±0.002 inches.
Yes, the grit size, bond type, and concentration of diamond particles can be customized to meet specific requirements.
Regular dressing of the wheel is essential to maintain its shape and ensure consistent grinding results. The wheel should also be stored properly to prevent damage.
Yes, 1A1 diamond wheels are compatible with various types of coolants, which can help to reduce heat generation during grinding.
Common industries include aerospace, automotive, toolmaking, electronics, medical, glass and ceramics, optics, and more.
Always follow safety guidelines, including wearing appropriate protective gear, ensuring proper installation of the wheel, and operating the grinding machine at the correct speed.
While some applications may allow for dry grinding, using coolant is generally recommended to prevent overheating and ensure a higher-quality finish.
Synthetic diamond is man-made and typically more consistent in size and shape compared to natural diamond, which is mined from the earth. Both types can be used in 1A1 wheels, depending on the specific application.
The bond type affects the wheel’s wear rate, grinding performance, and heat resistance. Common bond types include resin, metal, vitrified, and electroplated.
1A1 diamond wheels offer higher precision, longer lifespan, and the ability to grind hard materials that might be difficult or impossible with other types of wheels such as abrasives
Yes, 1A1 diamond wheels can be used on CNC machines and are often preferred for high-precision applications.
The grit size should be selected based on the desired finish and material being ground. Coarser grits are used for rapid material removal, while finer grits are used for a smoother finish.
Yes, 1A1 diamond wheels can be re-dressed to restore their grinding capabilities. The process should be done by trained professionals.
When stored properly, 1A1 diamond wheels do not have a specific shelf life. However, it is essential to inspect the wheel for any signs of damage or deterioration before use.
The concentration of diamond affects the cutting action and lifespan of the wheel. Higher concentrations provide a more aggressive cutting action and longer lifespan.
1A1 diamond wheels should be stored in a dry, cool place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. They should be kept in their original packaging to prevent damage.
Yes, 1A1 diamond wheels can be used on handheld grinders, provided the grinder is suitable for the wheel’s diameter and speed requirements.
Always follow safety guidelines, including wearing safety glasses, gloves, and other protective gear. Ensure the wheel is correctly mounted and balanced before use.
Common mistakes include using the wrong grit size, incorrect wheel speed, and not using coolant when required.
Coolant helps to reduce heat generation, improve surface finish, and prolong the wheel’s lifespan.
Yes, 1A1 diamond wheels are well-suited for precision grinding due to their flat, straight-edged shape.
The hardness of the bond affects the wheel’s wear rate and grinding performance. Harder bonds generally have a longer lifespan but may not provide as aggressive of a cutting action as softer bonds.
The maximum RPM depends on the wheel’s diameter and thickness.
The feed rate should be selected based on the material being ground, desired finish, and other application-specific factors. Consult the manufacturer or supplier for guidance.
Yes, 1A1 diamond wheels are suitable for grinding non-ferrous materials such as carbide, ceramics, and glass.
4 to 5 weeks. Expedited lead time of 1 to 2 weeks is also available at additional charge.
1A1 diamond wheels should be stored in a dry, cool place, away from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and any potential sources of damage.
Check the machine’s specifications and compare them to the wheel’s specifications. Ensure the wheel’s diameter, thickness, and bore size are compatible with the machine.
While 1A1 diamond wheels can be used for dry grinding in some cases, wet grinding is often recommended to reduce heat and improve the lifespan of the wheel.
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe operation, including proper mounting, balancing, and speed settings. Regularly inspect the wheel for any signs of damage or wear.
The workpiece should be properly secured and supported to prevent any movement during the grinding process.
The thickness of the wheel affects its rigidity and cutting action. Thicker wheels are generally more rigid and suitable for heavier grinding applications.
While 1A1 diamond wheels are primarily designed for surface grinding, some profile grinding applications may be possible depending on the specific requirements.
Use a suitable dressing tool and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for dressing the wheel. Dressing helps to restore the wheel’s cutting action and ensure a consistent finish.
While 1A1 diamond wheels are primarily designed for grinding, some cutting applications may be possible depending on the specific requirements.
Consider the material being ground, desired finish, wheel speed, and other application-specific factors. Consult the manufacturer or supplier for guidance.
The diamond particle size affects the cutting action and finish. Coarser particles are used for rapid material removal, while finer particles are used for a smoother finish.
Image | Item No. | Description | Price | Quantity | Add to cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 Gallon Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $99.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1 Quart Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $34.81 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
5 Gallons Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $317.41 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
55 Gallons Blue SMART CUT® General Materials Formula Synthetic Water Soluble Coolant | $1,745.00 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1/2″ x 1/2″ x 6.0″ White Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $8.65 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ White Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1/2″ x 1/2″ x 6.0″ White For use on diamond tools 150 to 220 Grit Size. | $8.65 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh size) or finer. | $15.39 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0″ x 2.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for use in Diamond Tools 150 Grit Size (mesh size) or finer. | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
1.0″ x 1.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $15.99 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | |||
2.0″ x 2.0″ x 6.0″ Black Recommended for coarser grits found in segment wheels, core drills, or Blanchard grinding. Excellent performance on 120 grit tools. | $39.47 | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 |
we manufacture custom tools to fit your specific requirements and specifications. We have the capability to manufacture over 30,000+ different types of custom diamond & cbn tools and consumables to better fit your particular material, application, specifications, and requirements
Not all requirements are the same. We manufacture tools to fit your particular equipment, tolerances, surface finish, life span, and overall see the difference tools optimized for your application can make?
We will work with you to determine your needs, and develop the right bond formulation, concentration, and grit sizes. Our tools are designed and specially selected to provide maximum possible tool life, for your desired cut quality and speed.
The following process describes custom tool manufacturing process form initial first inquiry to final delivery.

We discuss your specific requirement in detail to determine the best solution for your needs.

We provide you with recommend options for your application based on your requirements along with quotation and lead time.

When you are ready to order, we send you confirmation of the tool specification always in writting. Your order is placed in que to be produced within the quoted lead time.

The finished products go through quality control process and also inspected for conformance to specification agreed upon. The order is packaged and shipped to you using your requested shipping method. Certificate of conformance or any other documentation can be provided upon request.

We follow up with you to receive feedback on the tool performance. We also provide usage recommendatios and technical support if needed.
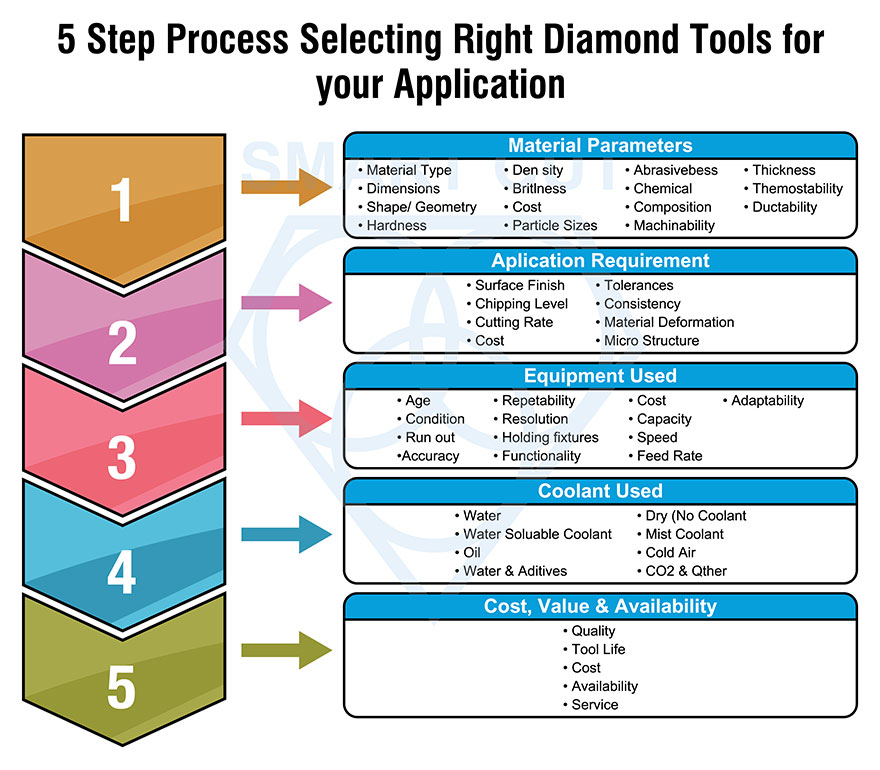
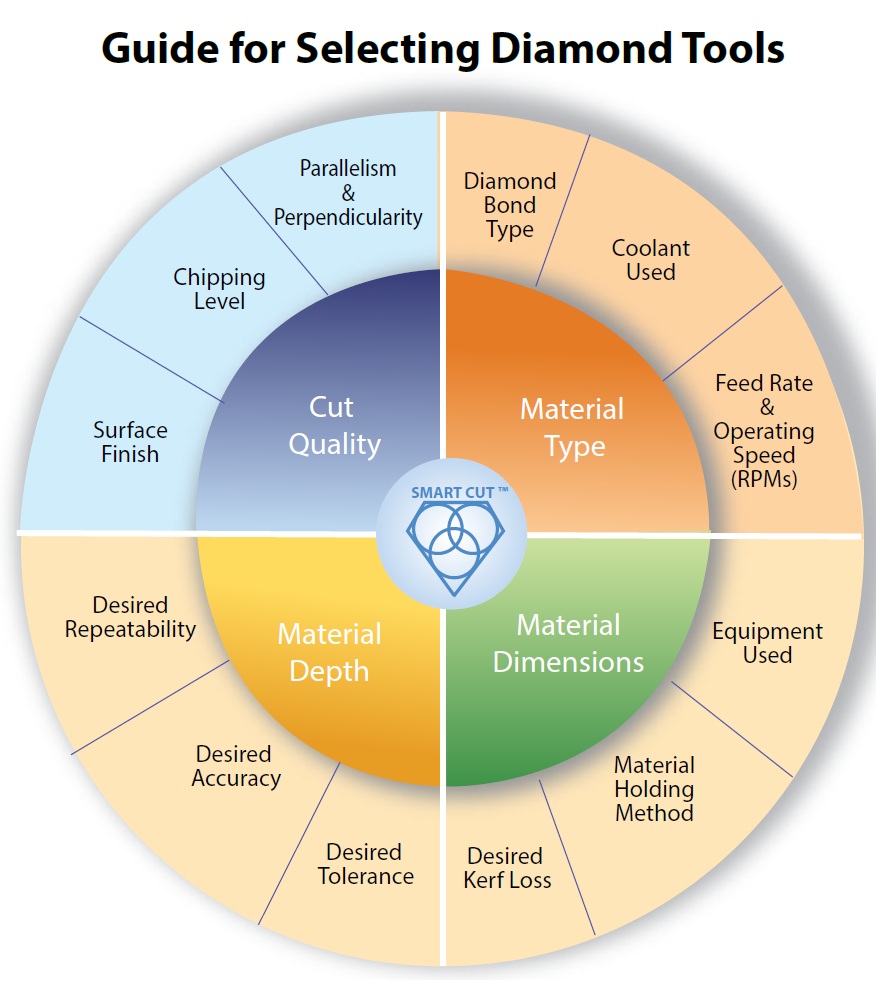
To place an order, you can contact our customer service team via phone, email, or our website. You will need to provide specific details about your grinding application, including material to be ground, required wheel dimensions, and desired grit size.
Yes, we are happy to help. We will send you a question are asking many questions about your requirements, how the tool will be used and the usage environment. This information is very important for helping us understand your unique specifications and requirements. The more information you can provide the more accurate recommendation and solutions we can provide.
Usually there is no minimum order for custom tools, with few acceptations. We encourage you to try small quantity to make sure you are happy with the tool performance first. As additional fine tuning and improvements can be made based on your feedback.
Lead time varies depending on tool specification and current schedule. Usually the lead time range can be from 1 to 5 weeks. expedited lead time of 1 to 2 weeks is usually available at additional cost if needed
Prices are based on tool specification, tolerances, quantity and lead time. Our prices are pretty competitive for world market. We regularly export our products to dozens of different countries across all continents. Usually custom products in small quantity the pricing is usually higher then standard of the shelf products which are mass produced in large quantities.
Over many decades we have made and sold thousands of different types of unique and one of a kind tools for almost every application. we maintain records of bond formulations and specifications used over many years we have also acquired the “know how” of several other US tool manufacturers that have produced custom tools over many decades, some going far back as to 1960’s. we also have our own R & D research program and we regularly work with different research originations and outside consultants. Most of the time we produce the right tool formulation first time, but sometimes we can make additional improvements second and third time around. Our goal is to make you happy
We ask lot of detailed question about tool specification and your usage process. Sometimes it may be worthwhile for you to send us your used tool so we can inspect it.
Yes we can provide basic recommendations and recommended usage information. If you need specific hands on approach such as “process development” this can be done on case by case based for a fee. If we are not able to help we can often recommend independent outside consultant or organization that can assist.
For a custom wheel order, you should provide the following information:
• Type of wheel (Diamond or CBN)
• Wheel dimensions (diameter, thickness, and arbor hole size)
• Grit size
• Material to be ground
• Grinding machine details
• Desired surface finish
Yes, you can request a specific bond type based on your grinding application. Common bond types include resin, vitrified, metal, and electroplated.
The lead time for custom wheels varies depending on the complexity of the wheel and our current production schedule. Typical leads times range from 4 to 5 weeks. Expedited lead time of 1 to 2 weeks is also available at additional cost if needed. Our customer service team will provide an estimated delivery date when you place your order.
Due to the custom nature of these wheels, they are typically non-returnable. However, if the wheel does not meet the specified requirements or is defective, we will work with you to resolve the issue.
Yes, you can order a sample wheel to test on your application before placing a bulk order. We highly encourage that you test the wheel for your particular application in your environment. Please contact our customer service team for more information.
Yes, we offer discounts for bulk orders. Please contact our sales team for more information.
Proper care and maintenance are essential to ensure the longevity and performance of your wheel. You should regularly clean the wheel, check for any damage, and use it at the recommended speed. Additionally, it’s important to use the correct coolant and dressing tools.
Yes, we can customize the wheel profile to meet your specific requirements. Please provide detailed drawings or specifications of the profile you need when placing your order.
Diamond wheels are suitable for grinding non-ferrous and non-metallic materials such as glass, ceramics, and tungsten carbide. CBN wheels are ideal for grinding ferrous materials such as steel, cast iron, and nickel-based alloys.
Yes, we have a team of experienced engineers and technicians who can provide technical support and advice for your specific grinding application.
Yes, you can request specific tolerances for your custom wheel. Please provide the required tolerances when placing your order, and we will do our best to meet your specifications.
Once your order has been placed, you will receive an order confirmation with a tracking number. You can use this number to track the status of your order on our website or contact our customer service team for updates.
We will do our best to accommodate any changes to your order, but please note that changes may not be possible once the production process has started.
We accept various payment methods, including credit card, PayPal, and bank transfer. Please contact our sales team for more information.
Cancellations are handled on a case-by-case basis. If the production process has not started, we may be able to cancel your order. However, once production has begun, cancellations are generally not accepted.
A balanced wheel is essential for optimal performance and safety. If you notice any vibrations or irregularities during operation, your wheel may be out of balance. Please contact our technical support team for assistance with balancing your wheel.
Yes, we offer a warranty on our custom wheels. The length and terms of the warranty will depend on the specific wheel and application. Please contact our sales team for more information.
The grit size should be selected based on the material to be ground and the desired surface finish. A coarser grit is generally used for rapid material removal, while a finer grit is used for a smoother finish. Our technical support team can help you choose the right grit size for your application.
Yes, we can manufacture custom wheels to fit specific brands and models of grinding machines. Please provide the make and model of your machine when placing your order.
Yes, we ship custom wheels internationally. Please contact our sales team for more information on shipping options and costs.
Resin bonds are flexible and suitable for grinding materials that are prone to heat damage. Vitrified bonds are rigid and offer high precision grinding. Metal bonds are durable and suitable for grinding hard materials. Electroplated bonds have a single layer of abrasive and are used for precision grinding.
A custom wheel may be necessary if your application requires specific dimensions, grit sizes, bond types, or shapes that are not available in standard wheels. Our technical support team can help you determine if a custom wheel is necessary for your application.
Diamond is the hardest known material and is suitable for grinding non-ferrous and non-metallic materials. CBN is the second-hardest known material and is suitable for grinding ferrous materials.
Yes, you can request a specific concentration of Diamond or CBN in your custom wheel. The concentration will affect the wheel’s performance and life.
Please refer to local regulations and guidelines for disposing of grinding wheels. In general, worn-out wheels should be treated as industrial waste and disposed of accordingly.
Yes, we can manufacture custom wheels with specific colors or logos. Please provide your requirements when placing your order.
Yes, we can manufacture a custom wheel with different abrasive grains to suit specific grinding applications.
Always wear safety goggles, gloves, and other appropriate personal protective equipment when using any grinding wheel. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and safety instructions for your specific grinding machine.
The performance of a custom wheel can be measured in terms of material removal rate, wheel wear rate, surface finish quality, and overall efficiency.
The wheel speed will depend on the specific grinding application, material to be ground, and the wheel’s dimensions. Our technical support team can help you determine the optimal wheel speed for your application.
Yes, you can specify the hardness level for your custom wheel, which will affect its grinding performance.
Our custom wheels comply with industry standards and regulations, including ANSI, ISO, and OSHA. Specific certifications may vary depending on the wheel and application.
Yes, you can request a custom wheel with specific porosity to achieve desired grinding performance and coolant flow.
You can conduct a trial run with the custom wheel on your grinding machine, following all safety guidelines. Observe the wheel’s performance in terms of material removal rate, surface finish quality, and overall efficiency. Our technical support team can assist you in evaluating the wheel’s performance.
Factors that affect the life of a custom wheel include the type of material being ground, the grit size, bond type, wheel speed, and coolant usage.
Yes, you can specify whether the custom wheel is intended for wet or dry grinding, and we will manufacture the wheel accordingly.
The bond type should be selected based on the material to be ground, desired surface finish, and grinding machine characteristics. Our technical support team can help you choose the right bond type for your application.
The minimum order quantity for a custom wheel depends on the specific requirements and dimensions of the wheel. For most wheels there is no minimum order quantities. Please contact our sales team for more information.
Yes, you can specify the face width or thickness for your custom wheel, and we will manufacture the wheel accordingly.
The wheel bond plays a crucial role in holding the abrasive grains together. The bond type affects the wheel’s wear rate, grinding performance, and the finish quality of the workpiece.
If you’re not satisfied with the performance of your custom wheel, please contact our customer service team immediately. We will work with you to address any issues and find a suitable solution.
The abrasive concentration in a wheel is typically measured as a percentage of the volume of abrasive grains to the total volume of the wheel. A higher concentration means more abrasive grains and typically results in a longer wheel life and better performance.
The wheel’s hardness affects its ability to resist wear and maintain its shape during grinding. A harder wheel typically lasts longer but may produce a rougher surface finish.
Yes, we can manufacture custom wheels with specific arbor hole sizes to fit your grinding machine.
Yes, we can manufacture custom wheels with specific grinding face geometries to meet your unique requirements. Please provide detailed drawings or specifications when placing your order.
Factors to consider when choosing the grit size include the material to be ground, desired surface finish, and grinding operation type. A finer grit is typically used for finishing operations, while a coarser grit is used for roughing operations.
Yes, we can manufacture custom wheels designed specifically for grinding materials such as glass or ceramics.
Wheel balance is critical for achieving optimal grinding performance and preventing vibration and machine wear.
Yes, you can specify the bond hardness for your custom wheel, which will affect its grinding performance.
The wheel diameter affects the peripheral speed of the wheel, which in turn influences the grinding performance and resulting surface finish.
The type of abrasive grain (e.g., Diamond, CBN, aluminum oxide) affects the wheel’s hardness, sharpness, and heat resistance, which in turn influences the grinding performance.
Yes, we can manufacture custom wheels with specific profiles for gear grinding applications. Please provide detailed specifications or drawings when placing your order.
Factors to consider when choosing the bond type include the material to be ground, grinding operation type, wheel speed, and desired surface finish.
Wheel speed affects the material removal rate, heat generation, and resulting surface finish of the workpiece.
Yes, we can manufacture custom wheels with specific porosity levels to meet specific grinding requirements.

The newly exposed diamonds don’t effect diamonds already working on the material. Unlike many other diamond bonds, diamonds in a SMART CUT ® Bond remains sharp and grow sharper with each cut, prolonging product life and consistent performance.

Diamonds or CBN Crystals are activated only at the exposed layer. As Bond Matrix layer begin to wear out, diamonds in a new Bond Matrix layer are immediately activated, substituting the already used up diamond layer. The SMART CUT Diamond Hybrid Bond makes sure every diamond is in the right place and at the right time, working where you need it most.

This advanced formulated open diamond bond design insures minimal chipping, fast cut, constant speed of cut, minimal cutting noise, and most important of all, consistent performance.
Diamond & CBN tools with SMART CUT technology make any work much faster & easier, Thousands of sharp and high quality diamond or CBN particles oriented and evenly distributed on both matrix, allow most jobs to be completed by applying little or only moderate amount of pressure even on the most toughest and challenging materials. Freeing the user from constantly having to dress and renew the diamond layer.


Diamond & CBN tools with SMART CUT® technology require minimum dressing, the bond renews itself.

Diamond & CBN Wheels are produced using only the highest quality raw materials are used in manufacturing process. Utilizing world class quality control, inspection, and measurement equipment. Highly Experienced Engineers constantly monitor and control all material input & output at all stages of manufacturing process. Insuring product consistency for use in demanding & sensitive applications SMART CUT® DIAMOND & CBN wear evenly, and are known for their consistency. You will get consistent cutting speed, and overall consistent performance, with minimum amount of dressing.

Diamond & CBN tools made utilizing SMART CUT® technology are much more aggressive than your conventional tools. They can cut faster, while still leaving behind a smooth finish free of material deformation.

In most cases tools manufactured utilizing SMART CUT® technology, will outlast other conventional material (sintered), resin, and nickel bonded diamond & CBN tools. SMART CUT® diamond & CBN tools are more sturdy than tools manufactured with conventional technologies. They are capable to retain their form and bond configuration all the way through the tools life.

SMART CUT® Diamond & CBN Wheels are the best investment you can make! Although we may not always be the lowest cost solution provider. Our Diamond & CBN wheels can provide the best ROI. Designed for users that understand and appreciate quality. They will more than pay for themselves in terms of overall performance and provide best Return on Investment.

Only the highest quality synthetic diamonds and raw materials are used in the manufacturing process. The highest quality standards and product consistency is maintained, using sophisticated inspection and measurement equipment.
Optimize your application to ultimate level of efficiency

The concentration of diamond or cubic boron nitride (CBN) in grinding wheels significantly influences both the wheel's lifespan and its effectiveness in grinding. Typically, a higher concentration of these abrasives is recommended for softer, more abrasive materials to enhance the durability of the wheel by spreading the wear across more abrasive particles. This setup, however, may reduce the grinding speed due to the increased friction from the many cutting points involved.
Wheels with a lower concentration of diamonds or CBN are best suited for grinding ultra-hard and brittle materials, such as ceramics and glass. With fewer abrasive particles, each one exerts more force, leading to a precise material removal process through micro-fractures. This approach helps to minimize wheel wear while efficiently grinding hard materials.
Conversely, for grinding softer or less brittle materials like metals, plastics, and polymers, wheels with a high concentration of diamonds or CBN are preferred. These wheels operate by plowing through the material with a dense array of abrasive particles, causing work-hardened strips to become brittle and break away. The large number of abrasives not only speeds up the grinding process but also reduces the force each particle exerts, helping to prevent deep deformation in metals.
Selecting the right concentration of diamond or CBN in grinding wheels depends on the material properties and specific grinding requirements. High concentrations generally yield faster material removal on softer materials, whereas lower concentrations are crucial for detailed and precise grinding of hard and brittle materials.
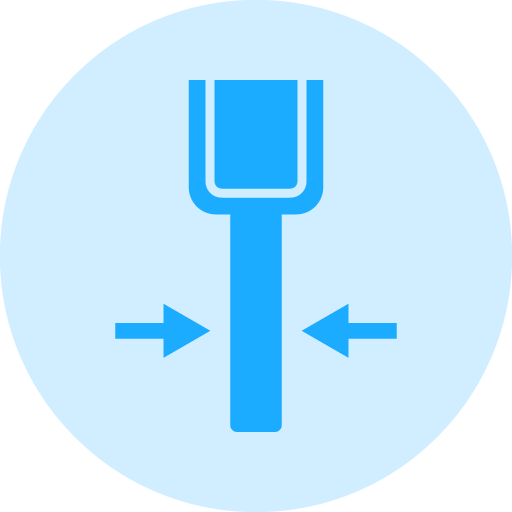
The thickness of diamond and CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) grinding wheels varies widely to suit different applications and material processing needs. For precision grinding tasks, wheels are typically thinner, ranging from about 0.5 mm to 10 mm, allowing for meticulous and detailed material removal. Cut-off wheels, used primarily for slicing through materials, tend to be even thinner, with thicknesses from 0.1 mm to 3 mm to facilitate precise cuts. Conversely, surface and tool grinding wheels, which are used for more extensive surface grinding, generally have thicknesses from 3 mm to 40 mm. For heavy-duty grinding operations involving large workpieces or substantial material removal, wheel thickness can be significantly greater, often from 10 mm up to 100 mm or more.
The thickness of a diamond or CBN grinding wheel directly impacts its grinding performance. Thicker wheels facilitate higher material removal rates, making them suitable for heavy-duty grinding tasks but tend to generate more heat and require more power. Thinner wheels excel in precision grinding tasks due to their ability to produce finer finishes and more detailed work. They also dissipate heat more effectively, minimizing thermal damage to both the wheel and the workpiece.
Stability increases with wheel thickness; thicker wheels resist bending under pressure, thereby enhancing their lifespan and ensuring consistent performance. However, they may require multiple dressings over their lifespan to maintain effectiveness. Thinner wheels, while more flexible for precision work, wear out quicker as they contain less material for dressing.
.

Feed rates in diamond and CBN grinding wheels are essential for achieving optimal grinding performance, balancing material removal, surface finish, and wheel life. The rate at which the workpiece is fed into the wheel depends on factors such as material hardness, wheel type, depth of cut, and the desired surface finish. Harder materials require slower feed rates to prevent damage and excessive wheel wear, while softer materials can tolerate higher feed rates. Deeper cuts also necessitate slower feed rates to avoid overloading the wheel.
Faster feed rates increase productivity but may sacrifice surface finish and reduce wheel life, while slower feed rates provide better control, finer finishes, and longer wheel life. Properly balancing the feed rate based on the material and grinding conditions ensures efficient grinding, quality results, and longer-lasting wheels. Adjusting the feed rate to match the needs of the specific task is key to optimizing performance and prolonging the life of diamond and CBN grinding wheels.

The RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) of diamond and CBN grinding wheels plays a key role in determining grinding performance. Harder materials like ceramics and hardened steel typically require lower RPMs to prevent overheating and excessive wear, while softer materials can be ground at higher RPMs. Larger wheels, due to their size, should run at lower speeds compared to smaller wheels, which can handle higher RPMs.
For fine precision and smooth surface finishes, lower RPMs are ideal, providing better control and reducing the risk of surface damage. Higher RPMs can be used for faster material removal but require careful attention to heat generation and wheel wear. Excessive RPMs can cause overheating, damaging both the wheel and the workpiece, particularly with heat-sensitive materials.
In general, diamond and CBN wheels operate effectively within a range of 3,000 to 6,000 RPM, depending on the material and wheel size. Adhering to optimal RPMs ensures efficient grinding, longer wheel life, and better overall results.

In diamond and CBN grinding wheels, the particle or grit size profoundly influences several aspects of the wheel's performance. Coarser grits enable faster material removal rates due to their aggressive cutting action, which is beneficial for increasing productivity in scenarios where high grinding speeds are necessary. Conversely, finer grit sizes produce a smoother finish, as the smaller particles make less aggressive cuts, reducing surface roughness. This is crucial for applications that demand a high-quality finish.
The amount of chipping during grinding is also impacted by the grit size. Finer grits typically result in less chipping, making them suitable for grinding brittle materials or when precise, clean edges are essential. However, coarser grits might cause more significant damage to the material’s microstructure because of their aggressive nature, which could be problematic in precision engineering applications where the integrity of the material is critical.
Selecting the appropriate grit size is vital for optimizing both the material removal rates and the quality of the finished surfaces. Coarse grits are preferred for rapid material removal when finish quality is less critical, while finer grits are ideal for achieving high-quality finishes and minimizing damage, particularly in delicate or precise grinding tasks.
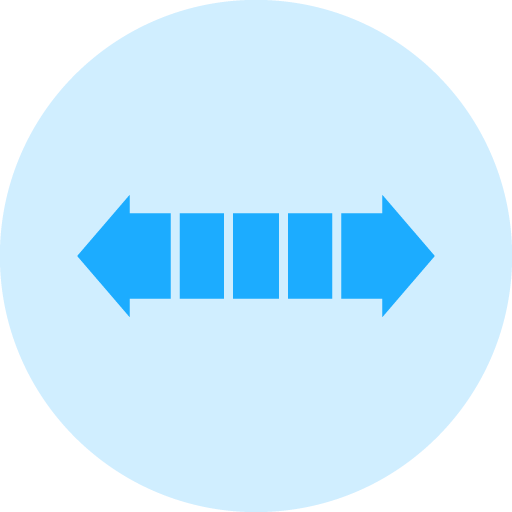
For diamond and CBN grinding wheels, the hardness of the bond matrix is crucial in determining how effectively the diamonds or CBN particles are held in place. As the hardness of the bond increases, so does its capability to retain these abrasive particles, which can extend the life of the grinding wheel. However, a harder bond typically results in a slower grinding speed.
Grinding wheels are categorized based on the hardness of their bonds, ranging from Soft, Medium, to Hard, with numerous variations and classifications within these categories to suit different materials and applications..
Selecting the optimal bond hardness for your specific application is essential for achieving efficient and precise grinding results. A bond that is too soft for the material being ground tends to release the abrasive particles too quickly. This premature release can lead to faster wear and a reduced lifespan of the grinding wheel. Conversely, a bond that is too hard can impede the grinding speed, .
necessitating frequent dressing of the wheel to expose new layers of abrasive particles.
As a general guideline, harder materials such as sapphire and alumina benefit from grinding wheels with softer bonds, which allow for more aggressive material removal without compromising the integrity of the wheel. Softer or more brittle materials, on the other hand, are better matched with harder bonds, which help prevent excessive wear and maintain the wheel's effectiveness over time.
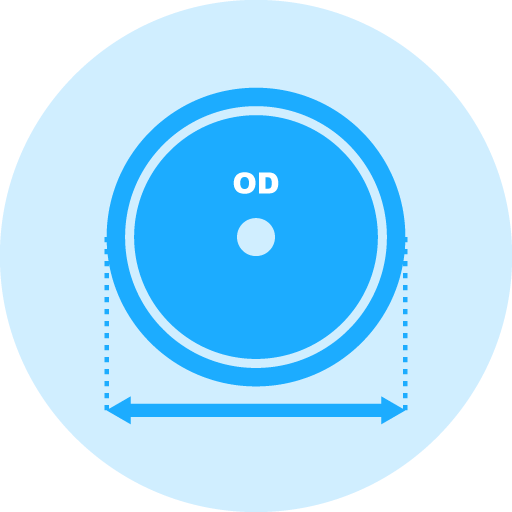
These diameters are carefully chosen based on the specific needs of the application, the properties of the material being cut, and the capabilities of the cutting machine. Resin diamond cut off blades & cutoff wheels, which are available in sizes ranging from 1 inch to 20 inches in diameter, offer varied capabilities based on their size. The diameter of the blade should be chosen with consideration to the diameter and thickness of the material being cut. Smaller diameter blades, which tend to be thinner, are more susceptible to bending and warping during use. On the other hand, larger diameter blades, being thicker, provide greater stability and are typically employed for cutting larger and heavier materials. These larger blades can handle higher loads and speeds, making them suitable for more demanding cutting tasks.
Diamond and CBN grinding wheels are available with various bond types, each suited for specific grinding applications.
Resin Bond wheels are popular for tool, cutter, and precision grinding due to their self-sharpening properties and fast cutting speeds. They offer a balance between material removal, wheel life, and finish.
Metal Bond wheels provide durability and long life, excelling in high-precision applications like grinding hard materials (e.g., ceramics, glass, hardened steels). Though slower cutting, they are highly wear-resistant.
Vitrified Bond wheels are rigid and heat-resistant, ideal for high-speed grinding. Their porous structure aids in chip clearance and cooler operation, making them perfect for precision grinding.
Electroplated Bond wheels feature a single layer of abrasives bonded with nickel, maintaining excellent form stability. They are used for precise profile grinding but have a shorter lifespan.
Hybrid Bonds combine resin, metal, or vitrified components to balance cutting efficiency, finish, and wheel life, making them suitable for demanding grinding tasks.
Selecting the appropriate bond type ensures optimal performance, finish quality, and wheel longevity for specific materials and grinding operations.
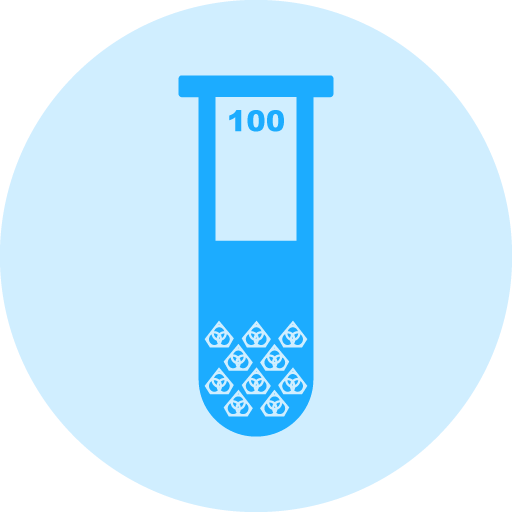

Diamond Concentration – Diamond Concentration is still a factor in determining the life and cutting speed of your Diamond Sectioning/Wafering Blade. Higher diamond concentration is recommended and usually used for cutting softer and more abrasive types of materials. However, the trade off is significantly slower cutting speed. Low diamond concentration is recommended and widely used for cutting ultra hard and brittle materials.
Low Diamond Concentration - typically low concentration wafering blades should be for cutting ultra hard and brittle materials such as ceramics and glass. In Low Concentration Wafering Blades, diamond works by fracture process. Pressure on each diamond crystal/particle is higher which provides enough stress to chip off small flakes in the cut.
High Diamond Concentration - High concentration diamond wafering blades are recommended for cutting metals, plastics and polymers. In this application, materials cut by a plowing mechanism. In this applications diamond plough through the material, work hardened strips of materials become brittle and break off. The greater number of diamond by volume, the quicker the cutting action will be. Increasing the number of diamond s also lowers the per unit force. For metals where it is possible to induce deep deformation layers, a lower per unit force is desirable to reduce the deformation during the cut.
Wafering blade thickness typically ranges from .006” to .040” (1mm). Thinner and thicker wafering blade are available, frequently from stock upon request. Kef thickness typically increases with blade diameter (in proportion to diameter of the blade). Kerf is the amount of material removed from the material/sample due to the thickness of blade passing though the material/sample. Blade thickness is important for users requiring most minimal amount of material loss during sectioning
For example if the user requires precision position of the cutting plane relative to the detail on the sample (IC circuit for example), a thinner and smaller diameter blade would be best for this application. Blades ranging from 3” to 5” (75mm to 125mm) in diameter and thickness .006” to .015” (0.2mm to 0.4mm) would be bet suited for this purpose. There are large variety of factors that will contribute to optimal blade thickness for your material/application Including your desired cutting speed, load/feed rate, material diameter, thickness, hardness, density, and shape. As well as skill & experience of the operator. Thicker wafering blades are more stiff and can whistand higher loads/feed rates. Another advantage of thicker kerf blades is they are more forgiving to operator error and abuse. Thicker kerf blade are recommended for use in environment where large number of individuals will be sharing and using same equipment. Perfect for less experienced and novice saw operators, such as in University laboratory.
.

Diamond Mesh Size plays a major role in determining your cutting speed, cut quality/surface finish, level of chipping you will obtain, and material microstructure damage you will obtain. Diamond Mesh size does have considerable effect on cutting speed. Coarse Diamonds are larger than finer diamonds and will cut faster. However, the tradeoff is increase in material micro damage. If you are cutting fragile, more delicate materials then finer mesh size diamond wafering blades are recommended.
Metal bonding offers long life and durability, while resin bonding creates less heat, provides better surface finish and is well suited for cutting hard, delicate or brittle materials.
typically wafering blade diameters range form 3” (75mm) to 8” (200mm). Wafering blade diameter should be selected based on material diameter and thickness being cut. Smaller diameter wafering blades are thinner than the larger diameter blades and are more prone to bending and warping. Although large diameter blades are thicker, they are typically used for cutting larger and heavier samples at higher loads and speeds than smaller blades

load/feed rate applied to wafering blades typically vary from 10-1000 grams. Generally, harder specimens are cut at higher loads and speeds (e.g. ceramics and minerals) and more brittle specimens are cut at lower loads and speeds (e.g. electronic silicon substrates). The Speeds/RPM’s you are using, shape/geometry of the specimen, and how the specimen is being clamped/hold in place will affect the load that can be used for your application.
Ability of the bond matrix to hold diamonds. As the hardness of the bond is increased, its diamond retention capabilities increase as well. However the trade off is slower cutting speed. Life of the diamond blade is usually increased with hardness of its bond matrix. Bonds are designated on their scale of hardness from Soft, Medium, and Hard. There are dozens of variations and classification schemes based on bond degree of hardness or softness.
Using diamond blades with optimum bond hardness for your application is important to successful precision diamond sawing operation. Bond matrix that is too soft for the material being cut will release diamond particles faster than needed, resulting in faster wear and shorter diamond blade life. On other hand bond matrix that is too hard will result in much slower cutting speeds and require constant dressing to expose the next diamond layer. As rule of thumb, harder materials such as sapphire and alumina generally require a softer bond. Whereas softer and more brittle materials require a harder bond.

Most wafering blades are used between 50 to 6,000 RPM’s Typically harder and more denser materials such as Silicon Carbide, are cut at higher RPM’s/speeds Where more brittle materials such as silicon wafers and gallium arsenide are cutting at lower RPM’s. Low Speed saws RPM’s are typically limited from 0 to 600 RPM’s. Where high speed saws offer much large variety of cutting speeds from 0 to 6,000 RPM’s.




Signup for email offers, updates, and more

UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools is a U.S. High Technology, Specialty Diamond Tool & Equipment manufacturer. We specialize in producing ultra thin & high precision cutting blades and precision cutting machines diamond drills, diamond micro tools, standard & custom advanced industrial diamond tools and consumables.
Shipping Methods

Safe & Secure Payments

© Copyright 1990-2024. UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools – Terms of Use
No products in the Quote Basket.
No account yet?
Create an AccountSign up to receive exclusive usage recommendations, Illustrated Trouble Shooting Guides & Sales