Menu
No products in the Quote Basket.
9 am to 6 pm PST time
No products in the Quote Basket.
SMART CUT® Miniature sintered turbo type diamond wheels mounted on a mandrel are used for cutting, engraving, and carving of large variety of materials. Available from 15mm to 85mm Diameter, with various kerf thicknesses, and shank/mandrel diameters.
These are specialized tools used for precise cutting, engraving, and carving on hard materials like granite, marble, and concrete. They consist of diamond wheels mounted on a mandrel, available in diameters from 15mm to 85mm, with varying kerf thicknesses and shank diameters.
They are ideal for industries like construction, masonry, and artistic sculpture. They can be attached to rotary hand pieces, drills, CNC machines, and more.
The Turbo Type design allows for faster material removal rates, which leads to quicker processing and efficiency when working with hard materials.
Yes, their small size and precise design make them perfect for detailed and intricate work, such as in artistic stone carving or precision engineering tasks.
SMART CUT Diamond Wheels offer several advantages over non-diamond abrasive wheels:
While primarily designed for hard materials like granite, marble, concrete, and sandstone, they may be suitable for other materials. However, it’s essential to check the compatibility of the material with the wheel specifications.
Yes, the wheels are designed for easy installation and replacement. They can be quickly mounted on or detached from the mandrel, fitting various types of equipment.
Safety is crucial when using these wheels. Always wear protective gear, including eye protection, gloves, and a dust mask. Ensure that the tool is securely mounted and operated within the recommended speed limits.
The lifespan varies depending on usage, material hardness, and frequency of use. However, due to their sintered diamond construction, they generally last longer than standard abrasive wheels.
Yes, using water or coolants can help reduce dust and heat buildup, which is especially beneficial when working with heat-sensitive materials.
The shank diameter (6.4mm or 1/4″) is a common size that fits many types of equipment, making these wheels versatile for different setups.
While specialized training is not always required, a basic understanding of the equipment and safety procedures is essential. Users with experience in handling similar cutting, engraving, or carving tools will find it easier to adapt.
The variety of kerf thicknesses available allows users to select the appropriate wheel for their specific cutting needs, whether they require a fine, precise cut or a wider groove for more substantial material removal.
While extremely versatile, the effectiveness of these wheels can vary depending on the material hardness and the complexity of the cut. Extremely intricate designs may require additional tools or specialized wheels.
Yes, these wheels are typically suitable for both wet and dry cutting. Wet cutting is preferable for reducing dust and extending the wheel’s life.
The turbo type edge design enhances the cutting efficiency by providing a better balance between speed and precision, which is particularly useful for tough materials like granite and concrete.
The sintered (metal bond) type holds the diamond particles strongly, providing a balance between wear rate and sharpness. This bond type is known for its durability and longevity, especially when cutting harder materials.
Choosing the right wheel depends on the material being worked on and the desired outcome. Larger diameters and thicker kerfs are typically used for more significant, less detailed work, while smaller diameters and thinner kerfs are for finer, more detailed work.
The choice of shank diameter (6.4mm or 1/4″ in this case) should match the collet size of the equipment being used. A correct match ensures stable and safe operation, as well as optimal performance of the wheel.
Typically, diamond wheels come in various grit sizes, catering to different levels of finish and material removal rates. The choice of grit size will depend on the specific application and desired outcome.
It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for optimal speed settings. Using the wheel at a correct speed ensures safety, efficiency, and prolongs the life of the wheel.
Yes, these wheels are compatible with CNC machines, provided they fit the machine’s specifications, particularly the shank diameter.
A thinner kerf typically allows for more precise cuts but may reduce cutting speed and be less suitable for thicker materials. A thicker kerf increases material removal rate but might reduce precision.
Balancing speed and finish quality involves selecting the right wheel type and grit size, adjusting the cutting speed, and sometimes using a combination of rough and fine wheels for initial cutting and finishing.
To extend their life, use the wheels within recommended speed and pressure limits, avoid overheating, use appropriate coolants, and store them correctly when not in use.
Water is the most common coolant, but other coolants designed for stone or hard material cutting can also be used. The choice of coolant may depend on the material being cut and the specific requirements of the process.
Customization of the wheel specifications is possible, there may be a small minimum order quantity Special orders can typically be made for specific diameters, kerf thicknesses, and bond types.
Wheel wear can affect the precision and efficiency of the cuts. Signs of significant wear or damage indicate it’s time to replace the wheel. Regular inspections are recommended to assess wear.
While primarily designed for use with powered equipment, in some cases, they can be used manually. However, this requires great care and might not provide the same level of precision or efficiency.
The hardness and abrasiveness of the material dictate the choice of wheel. Harder materials require wheels with stronger bonds and possibly coarser grit, while softer materials can be cut with finer grit wheels.
First-time users should start with basic projects, follow all safety guidelines, and familiarize themselves with the tool’s operation and handling. Practicing on scrap material before moving on to actual projects is also advisable.
Under continuous use, these wheels maintain performance but may require more frequent checks for heat buildup and wear. Adequate cooling and proper operating speeds are important in such conditions.
Common mistakes include using the wrong wheel type for the material, operating at incorrect speeds, applying excessive pressure, and neglecting safety precautions.
The skill level can significantly impact the precision and quality of the work. Experienced users can achieve better results and are more adept at handling complex tasks.
These wheels are widely used in industries like masonry, construction, and sculpting. Beginners should be aware of the specific demands and standards of these industries to ensure appropriate use of the wheels.
The angle at which the wheel contacts the material can significantly affect the quality of the cut. The correct angle ensures efficient cutting and minimizes the risk of chipping or damage to the material or the wheel.
While primarily designed for cutting and shaping, with the right specifications (like grit size and wheel type), they can be used for both roughing and finishing works. However, finer finishes might require additional tools or processes.
Generally, compatibility is determined by the shank diameter and the equipment’s collet size. As long as these match, there should be no brand-specific compatibility issues.
Larger diameters generally allow for cutting larger areas or deeper cuts, while smaller diameters are better for detailed or intricate work. The choice of diameter should match the scale and detail of the project.
The procedure involves safely removing the worn-out wheel from the mandrel and replacing it with a new one, ensuring it’s securely fastened. Always follow the equipment’s manual for specific instructions.
Quality diamond wheels typically produce less noise and vibration compared to conventional abrasive wheels. However, this can also depend on the equipment used and the material being worked on.
The right pressure depends on the material’s hardness and the wheel’s specifications. Generally, it’s advisable to start with lighter pressure and increase as needed, avoiding excessive force that can damage the wheel or the material.
Operating speed can greatly influence the cutting efficiency and the lifespan of the wheel. Using the manufacturer-recommended speed ensures optimal performance and safety.
The thickness of the wheel determines the maximum depth of cut that can be achieved. Thicker wheels can make deeper cuts and can be used for grinding, but they might reduce the level of detail and precision.
To prevent overheating, users should use appropriate coolants, take regular breaks during prolonged use, and avoid excessive pressure and speed that can generate excessive heat.
This can be done by cutting into a dressing stone several times to wear away metal layer to expose the diamond and sharpen the diamond crystals
The wheel’s speed rating should always match or exceed the maximum RPM of the equipment it’s used on. Using a wheel at speeds higher than its rating can be dangerous and lead to wheel failure.
These wheels are primarily designed for hard, non-metallic materials like granite and marble. Cutting metals requires different types of diamond wheels specifically designed for metalworking.
Dispose of worn-out diamond wheels according to local regulations and guidelines. They should not be thrown in regular waste due to the metal and diamond content.
A common misconception is that diamond wheels can cut any material. While they are extremely hard and versatile, they are primarily designed for specific types of materials and applications.
Sintered bond, involving the fusion of diamond particles with a metal matrix, provides a strong bond that holds up well against the rigors of cutting hard materials. This results in a longer-lasting wheel compared to other bonds like resin or electroplated bonds, especially under heavy use.
Uneven wear can indicate issues with the equipment or improper use. Users should check the equipment’s alignment and ensure that the wheel is being used at the correct angle and pressure. If the issue persists, consulting a professional is advisable.
Yes, these wheels can be used at different angles to achieve various cutting depths and profiles. However, users must ensure that the wheel and the equipment can safely handle the desired angle.
The diameter of the wheel influences the types of equipment it can be used with. Larger diameters are typically used with more powerful equipment, while smaller diameters are suited for handheld or precision tools.
These wheels are particularly advantageous in industries where precision cutting of hard materials is crucial, such as in stone masonry, monument building, sculpture, and in certain types of construction and renovation work.
Extreme temperatures can affect the metal bond and the overall integrity of the wheel. It’s advisable to use these wheels within a moderate temperature range and avoid exposing them to extreme heat or cold.
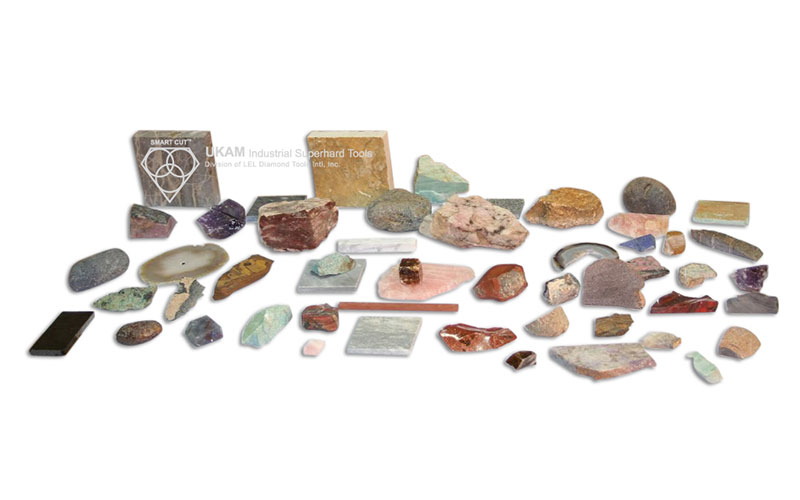



| Outside Diameters Available: | Shank Diameter |
| 15mm, 25mm, 30mm, 40mm, 50mm, 60mm, 70mm, 85mm | 6.4mm (1/4″) |
*other specifications are available upon request
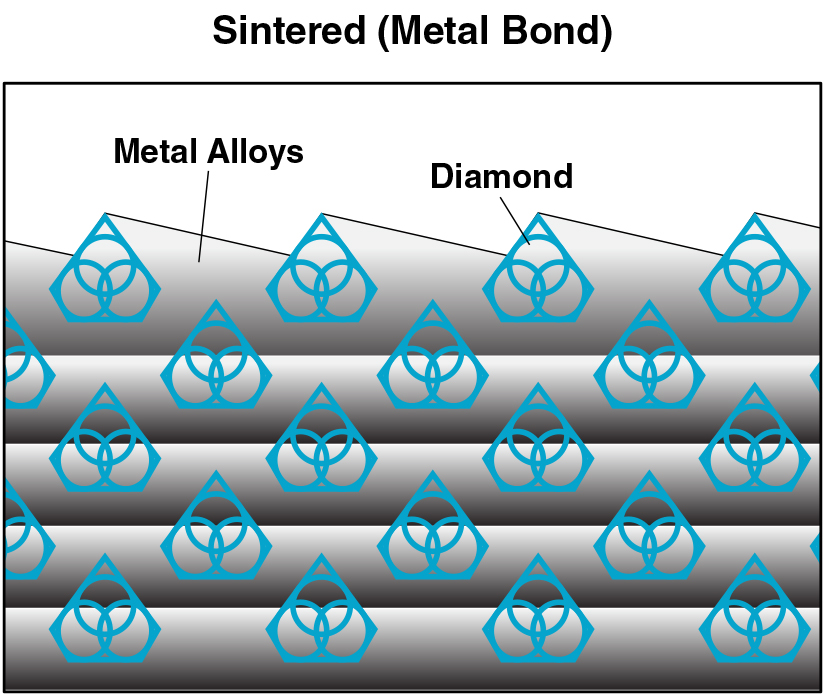
Sintered (Metal Bond) diamond tools have multiple layers of diamonds impregnated inside the metal matrix. Diamonds are furnaces sintered in a matrix made of iron, cobalt, nickel, bronze, copper, tungsten, alloys of these powders or other metals in various combinations. Metal bonded diamond tools are “impregnated” with diamonds. This means that selected diamonds are mixed and sintered with specific metal alloys to achieve the best cutting performance possible on any materials such as sapphire, advanced ceramics, optics, glass, granite, tile and etc. The metal bond surrounding the diamonds must wear away to continuously keep re-exposing the diamonds for the diamond tool to continue cutting. Sintered (metal bonded) diamond tools are recommended for machining hard materials from 45 to 75 on rockwell scale (5 to 9.5 on mohe’s scale of hardness).

Diamonds or CBN Crystals are activated only at the exposed layer. As Bond Matrix layer begin to wear out, diamonds in a new Bond Matrix layer are immediately activated, substituting the already used up diamond layer. The SMART CUT Diamond Hybrid Bond makes sure every diamond is in the right place and at the right time, working where you need it most.

The newly exposed diamonds don’t effect diamonds already working on the material. Unlike many other diamond bonds, diamonds in a SMART CUT ® Bond remains sharp and grow sharper with each cut, prolonging product life and consistent performance.

This advanced formulated open diamond bond design insures minimal chipping, fast cut, constant speed of cut, minimal cutting noise, and most important of all, consistent performance.

Diamond drills made utilizing SMART CUT technology are much more aggressive than your conventional drills. They can drill faster, while still leaving behind a smooth finish free of material deformation.
In most cases tools manufactured utilizing SMART CUT technology, will outlast other conventional Diamond Core Bits SMART CUT diamond & CBN tools are more sturdy than tools manufactured with conventional technologies. They are capable to retain their form and bond configuration all the way through the tools life.


SMART CUT Diamond Core Bits are produced using advanced technology Unlike Many Other Core Bits they wear evenly, and are known for their consistency. You will get consistent cutting speed, and overall consistent performance, with minimum amount of dressing even on the hardest to cut materials
Only the highest quality synthetic diamonds and raw materials are used in the manufacturing process. The highest quality standards and product consistency is maintained, using sophisticated inspection and measurement equipment.


SMART CUT® Dry Diamond Core Bits are the best investment you can make! Although they may cost more than Dry Diamond Core Bits They will more than pay for themselves in terms of overall performance and provide best Return on Investment.



Signup for email offers, updates, and more

UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools is a U.S. High Technology, Specialty Diamond Tool & Equipment manufacturer. We specialize in producing ultra thin & high precision cutting blades and precision cutting machines diamond drills, diamond micro tools, standard & custom advanced industrial diamond tools and consumables.
Shipping Methods

Safe & Secure Payments

© Copyright 1990-2024. UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools – Terms of Use
No products in the Quote Basket.
No account yet?
Create an AccountSign up to receive exclusive usage recommendations, Illustrated Trouble Shooting Guides & Sales