Diamond Drill Terminology
-
Posted by
contactor6

How to fine tune each of these variables to improve and optimize your drilling operation in the success of your diamond drilling operation
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague
DIAMOND DRILL / DIAMOND DRILL BIT - TERMINOLOGY
Accuracy - The exactness of a measurement produced compared to the desired result.
American national standard institute (ANSI) - A US private, non-profit organization that administers and coordinates voluntary standards and systems. This organization is responsible for setting standards for various industries and applications.
Bottoming tool – tool with flat bottom tip diamond. Used to grind away material center core.
Bond hardness – ability of bond matrix to hold diamonds in place. Life of diamond drill is usually increased with bond hardness
Bond - The composition or material that holds diamond particles/diamond crystals together in a diamond drill matrix. Bonds for diamond drills may be sintered (metal), electroplated, or braised.
Break in time – amount of time it takes for diamond drill to start producing fast, consistent and chip free drilling performance.
Coarse diamond mesh (grit) size – large diamond particles designed for fast drilling, produces coarser surface finish.
Coolant - A substance, usually liquid, used to reduce or maintain the temperature of a part being ground.
Coolant volume – amount of coolant and pressure applied at drilling zone.
Concentricity - The degree to which a given dimension resembles a perfectly round circle or cylinder.
Chipping - A small particle of material that is removed during grinding, cutting, or abrasive processes.
Collet – holding device to hold tool/drill in drilling machine. forms a collar around the object to be held and exerts a strong clamping force on the object when it is tightened via a tapered outer collar.
Carving – process in which material such as stone, glass, ceramic or other materials is shaped into intricate shape, geometry, or form. Using various shape and pointed diamond carving points.
core sample is a cylindrical section of a naturally occurring medium consistent enough to hold a layered structure. Core sample is obtained by drilling into material with diamond core drill. Core is than extracted from diamond core drill tube and analysis is done on martial structure.
Counterboring - A hole that has been slightly widened from one end to a particular depth. A counterbored hole typically provides space for a recessed bolt or screw head.
Diamond - The hardest known substance. Made from carbon, diamond is both a naturally occurring and manufactured abrasive.
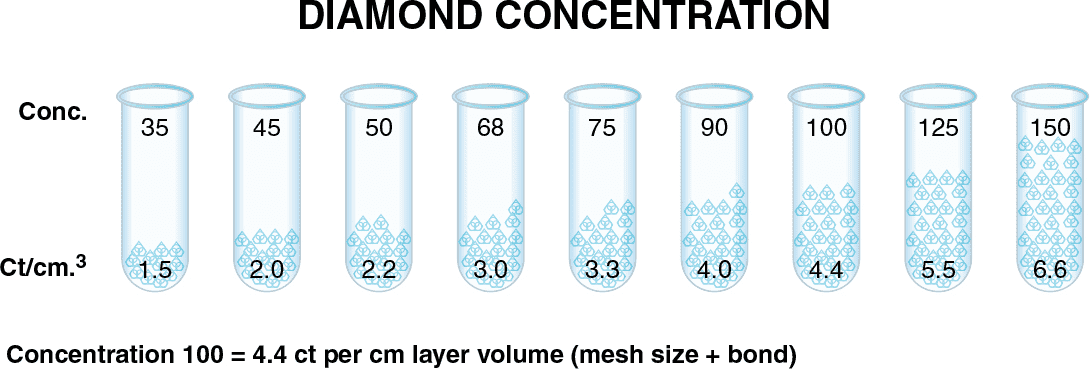
Diamond concentration – amount of diamond particles obtain in diamond drill bond matrix. Typical diamond concentrations include low, medium, and high. Diamond concentration will influence the drilling speed.
Diamond mesh size – size of diamond crystals in diamond drill matrix. Plays major role in determining surface finish quality, drilling speed, chipping level, and material micro structure you will obtain. Hence diamond size is selected depending on surface finish and drilling seed you wish to obtain.
Drilling accuracy – how close drill produces desired hole to point (location) desired.
Drilling depth – thickness of material drilling through
drill chuck - specialized three-jaw chuck, usually fits up to ½” (12.7mm) shank diameter diamond drills.
Drill depth – maximum thickness of material a specific diamond drill can drill through.
Diamond drill failure - The point at which a diamond drill is no longer useful for drilling or stops working. Lack of coolant reaching drilling zone, using in appropriate RPM’s, drilling at an angle, or having material core stuck inside the diamond core drill eventually lead to diamond drill failure.
Diamond drill wear - The rate at which the diamond cutting edge of a drill wears away during drilling.
Dial indicator - A device that measures the angles at the drill point to assure the drill point is symmetrical and on center
Diamond Drill Life – typically calculated in number of parts, holes, or cores a diamond drill will drill through before its diamond section completely wears away.
Diamond depth (height) – height of diamond crown (diamond core drill section). Portion that contains either embedded diamonds or diamond coating. Diamond drill will stop working when this is worn away.
Diamond section - diamond drill tip that contains diamond particles. This is the portion of the drill bit that actually does the drilling
Drilling - The process of using a diamond drill to penetrate the surface of a workpiece and make a round hole.
Diamond mesh size – size of diamond particles (diamond crystal) inside diamond drill bond matrix.
Diameter - The distance from edge to edge of the widest point of a circle.
Dimension - A measurement of space, especially length, width and height.
Drilling zone - The area of contact between the diamond drill and material being drill.
Dressing – process of re-exposing (re-sharpening) diamond particles on surface and inside diamond drill. This process removes swarf, dull diamond particles, and bonding material from diamond drill. Hence rexposes the next diamond layer to start working
Drilling template – drilling accessory used to help start drilling, keeps diamond drill in place and prevents it from wobbling. Frequently used when drilling horizontal surface.
Drill press - A drill press is composed of a base that supports a column, the column in turn supports a table. Work can be supported on the table with a vise or hold down clamps, or the table can be swiveled out of the way to allow tall work to be supported directly on the base. Height of the table can be adjusted with a table lift crank than locked in place with a table lock. The column also supports a head containing a motor. The motor turns the spindle at a speed controlled by a variable speed control dial. The spindle holds a drill chuck to hold the cutting tools such as diamond drills. A drill press is preferable to a hand drill when the location and orientation of the hole must be controlled accurately.
Extension – extends useable drilling depth of diamond drill. Extensions are available in different lengths and diameters. Extension diameter must be same or smaller than diameter of diamond drill being used.
Electroplated diamond bond – An industrial diamond (superabrasive) bond accomplished by immersing a diamond drill in an electrically charged chemical bath that contains metal particles. Only one layer or few layers of diamond stay on surface of the diamond drill tip. Nickel is the binder that actually keeps diamond in place
Flat bottom drill – also known as non core formation diamond drill. Grinds away core in material being drilled. Typically used when drilling only partially through material.
Feed rate - velocity (speed) at which the diamond drill is forced against material being drilled. Usually measured by how fast diamond drill tip can penetrate given material per specific time unit (time frame). For example some diamond drills can drill 2.0” of material per minute. Where other type of diamond drills can only drill .010” thickness of material per minute.
Fine diamond mesh (grit) size – small diamond particles, produce smooth surface finish quality. Will drill slower than medium size or coarse diamond particles.
Fracture - The breaking apart of diamond particles in diamond drill during drilling. It is part of the wheel's self-sharpening process.
Frequency of dressing – number of times required to drill into dressing stick to sharpen and rexpose diamond particles inside diamond drill. This will depend on material being drilled, RPM’s used, and performance of the diamond drill itself.
Glazing - The unwanted formation of a smooth surface on a diamond drill. Glazing occurs when the heat from drilling process reacts with a diamond drill.
High speed air spindle – operate using air pressure. Use for drilling micro holes where high degree of precision and accuracy is needed.
Hardness - The ability of a metal to resist scratching and penetration. usually measured the Moh's scale or Knoop.
Heavy wall diamond core drill – sintered (metal bond) diamond core drill typically with 2.0mm to 3.00mm crown wall thickness
High diamond concentration – large number of diamond particles in diamond bond. To increase life of the tool.
Horsepower – unit of measurement used to describe maximum power output of drilling machine.
ID diamond drill – diamond core drill made with focus on Inside diameter. In order to obtain specific core diameter
Low diamond concentration – fewer diamond particles present in tool bond. Produces softer and freer cutting bond.
Lubricant - A substance, often a liquid, used to reduce or prevent friction, resistance, heat, and wear during grinding.
Loading - A build up of swarf in a diamond drill diamond section that clogs the spaces between diamond particles in diamond drill bond
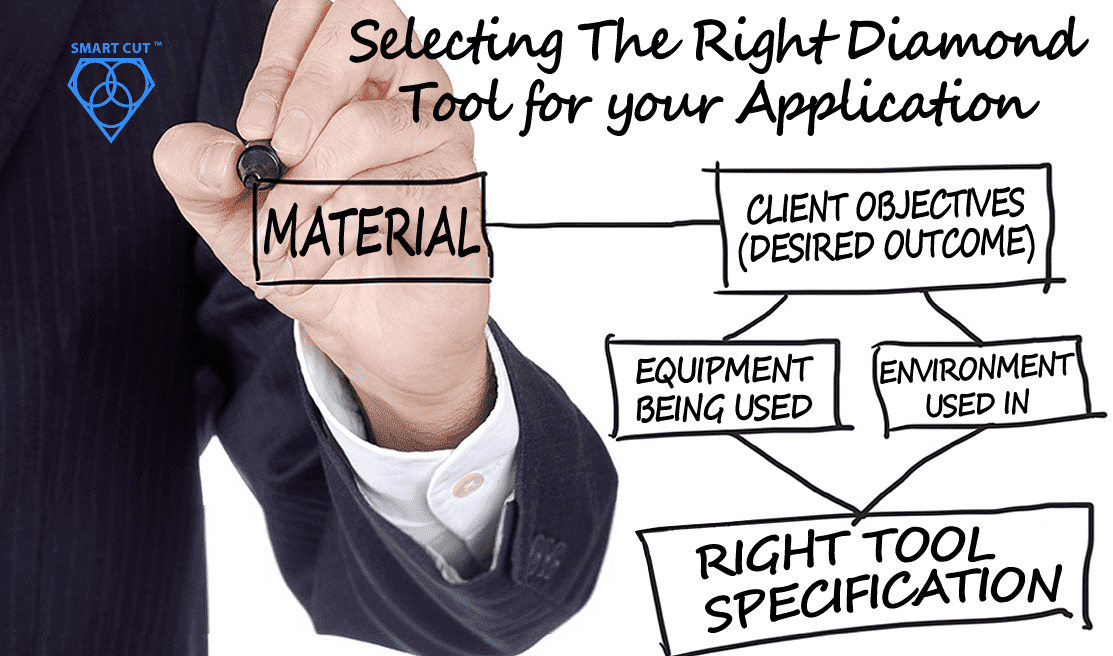
Material Geometry – shape and configuration of material being drilled. Can be flat piece of material, tube, rod, or irregularly shaped material.
Material Density – amount of mass contained by cubic volume
Mohe’s scale of hardness – scale used to measure material hardness. Uses minerals of various harnesses by applying harder material to scratch a softer material. diamond is at the top of the scale. The hardness of a material is measured against the scale by finding the hardest material that the given material can scratch, and/or the softest material that can scratch the given material.
Material density - The relative compactness of a material. Density is the mass of a material per unit volume.
Material hardness - The ability of a material to resist penetration, indentation, or scratching.
Mount – method of placing diamond drill into drilling machine. Typically made from steel or brass with female or male thread on to water swivel adapter / drill head assembly
Morse tapper – allows diamond drill to be mounted directly into drilling machine spindle. Most frequently used with milling machines. Morse Tapers come in eight sizes identified by number between 0 and 7. Such as morse taper # 1, # 2, # 3 (most popular) for use with diamond drills.
Micron - A measurement equal to one twenty-fifth of a thousandth of an inch (0.00004 inch).
Milling - The use of a machine to remove material from the surface of a workpiece with a rotating solid cylindrical tool.
OD diamond drill – diamond core drill manufactured specially to drill precision holes of a specific diameter
Offcentric Diamond Drill: Designed with what is commonly called Half Moon shaped ID, allowing the core drill to move material and coolant at the same time as it drills the hole. ID (Inside Diameter) of the Diamond Drills/Bit is made larger (off center). OD (outside diameter) is made smaller to accomplish this purpose.
Pecking cycle – interrupted drilling process. Typically used on cnc machines where predetermined amount of pressure is used at consistent time intervals to achieve desired hole depth. The user is able to control the depth of material the diamond drill drills through at each pass (point of contact with material).
PSI – pressure per square inch. In diamond drilling application this is typically referred to pressure of coolant running through center of spindle.
Non Coring / DISINTEGRATING ID Diamond Drill: Inside diameter of this diamond drill is offset. It is still considered a diamond core drill because it has a slot on side for coolant to pass through center of the diamond drill. This type of diamond drill leaves no core behind (destroys core when drilling), because its ID (inside diameter) is Offset.
Shank – part of the diamond drill that goes into drilling machine chuck or collet. Most shank types used for diamond drills are a straight stem with or without hole in center. Most frequently used shank diameters for diamond drills are ¼”, 3/8”, and ½”.
SDS shank – most frequently found on precoussonary drilling equipment, such as hammer drills. Fits into simple spring-loaded chuck, so that diamond core bit can be chucked with a simple and quick hand action. The diamond drill is not held solidly in the chuck, but can slide back and forth like a piston.
Shank diameter – outside diameter of straight stem to be placed into drilling machine chuck
Shank length – length of diamond drill stem portion that goes into drilling machine.
Shank hole diameter – inside hole diameter of stem
Standard wall diamond core drill – sintered (metal bond) diamond core drills typically with 1.2mm to 2.0mm diamond crown wall thickness
Segmented diamond core drill - sintered (metal bond) diamond core drill with individual segments braised or laser welded on to core drill tube steel body.
Segment spacing – distance between diamond segments on surface of diamond core drill.
Surface Feet per Minute (SFM)- unit of velocity used in machining to identify the machinability ratings of a material.
Swarf - The gritty combination of chips, abrasive grains, and worn bonding material that is produced during drilling.
Shank adapter – adapter with one end with male thread and other end with cylindrical stem. This is used to allow the operator to convert diamond drill with female or male thread to into straight stem tool to place into drilling machine chuck.
Submerged pressure – drilling technique in which diamond drill is fed into material into evenly timed up and down cycles (movements). Drilling down for 30 seconds, than lifting diamond drill up for 30 seconds, letting coolant penetrate deeper into material being drilled and diamond drill cool in air.
Surface finish quality – amount of chipping generated on face of material. Surface finish consists of three components: form, waiveness, and roughness. There are many different ways to measure surface finish quality.
Speed - The rate at which the cutting edge of the tool moves past the workpiece surface at the point of contact. For turning, speed describes the rotation of the workpiece. For milling and drilling, speed describes the rotation of the cutting tool.
Tolerance – defined a maximum allowable deviation from required size range on hole or core diameter produced by diamond drill. Tolerance is usually specified for either diamond drill outside or Inside diameter. If close tolerance is desired for hole diameter, tolerance called out on OD of diamond drill for example: + / - .001”, + / - .005”, and etc. same thing applied for diamond core drill inside diameter.
Thin wall diamond core drill -sintered (metal bond) diamond core drill typically with 0.5mm to 1mm diamond crown wall thickness
Truing - The dressing of a diamond drill in order to return the diamond drill to its original shape.
Radius - The distance from the center to the edge of a circle.
Vice – workholding mechanical device with one fixed jaw and one movable jaw. Vices are used for holding or clamping martial or object being drilled in place, in order to prevent it from moving. There is a wide varity and types of vices available to accommodate just about any material type, shape and geometry.
Wall thickness – thickness of diamond core drill diamond section. Usually available from 0.5mm to 3mm thickness. Proper diamond drill wall thickness selection is influenced by material being drilled, drilling depth, drilling equipment being used, and customer requirements.
Share this Article with Friend or Colleague